Sustainable Land Use Planning
October 20, 2015
Overview
*Sprawl - What is it & Why?
*Consequences
*Understanding Density
Sprawl
Coming to a neighborhood near you.


Source: http://www.digitaltrends.com/photography/how-one-dslr-pioneer-shoots-for-the-big-screen-with-a-little-cam/
Source: http://www.fastcodesign.com/3028661/slicker-city/urban-sprawl-get-fat-stay-poor-and-die-in-car-crashes

"Sprawl is like pornography- hard to define but you know it when you see it."
- David Rusk*, Urban Sprawl: a Comprehensive Reference Guide
*Rusk's method: The ration of growth of urbanized population to the growth of urbanized land.
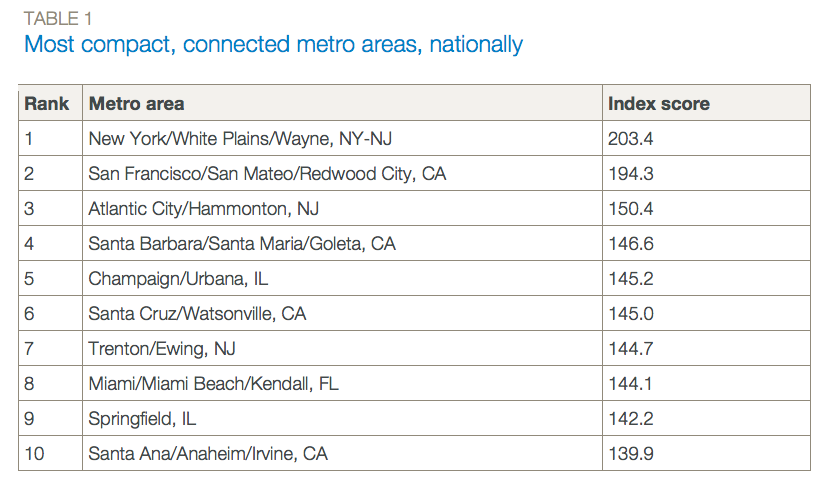
Source: http://www.smartgrowthamerica.org/documents/measuring-sprawl-2014.pdf
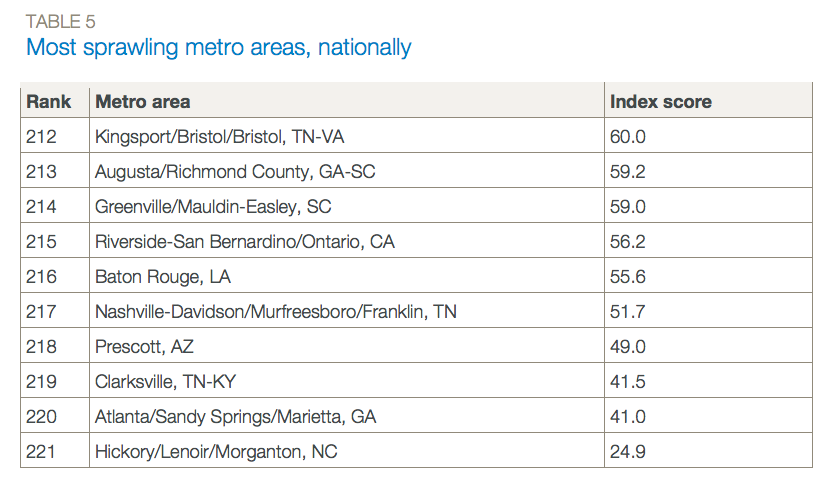
Source: http://www.smartgrowthamerica.org/documents/measuring-sprawl-2014.pdf
How did they measure sprawl?
- Development Density
- Land Use Mix
- Activity Centering
- Street Accessibility
Each of the four points includes multiple sub-indicators.
Eight Dimensions of Sprawl
- Density
- Continuity
- Concentration
- Clustering
- Centrality
- Nuclearity
- Mixed Uses
- Proximity
Source: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/10511482.2001.9521426
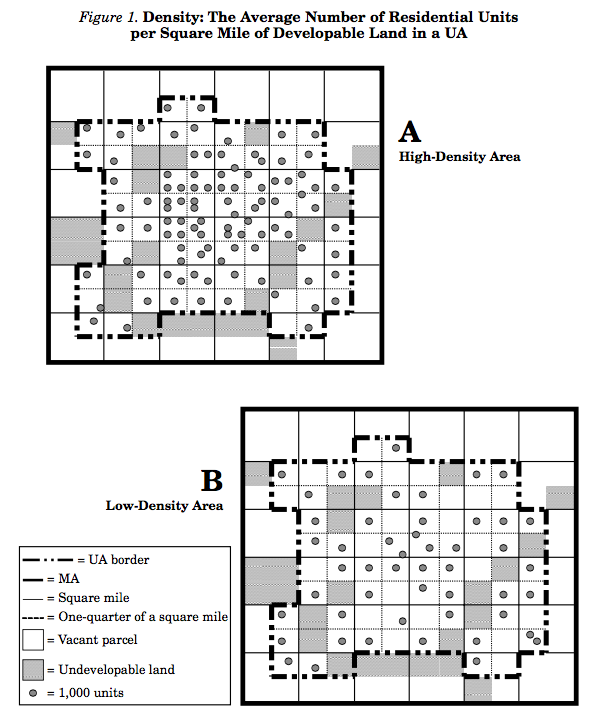
Density
Density is the average number of residential units per square mile of developable land in an urban area.
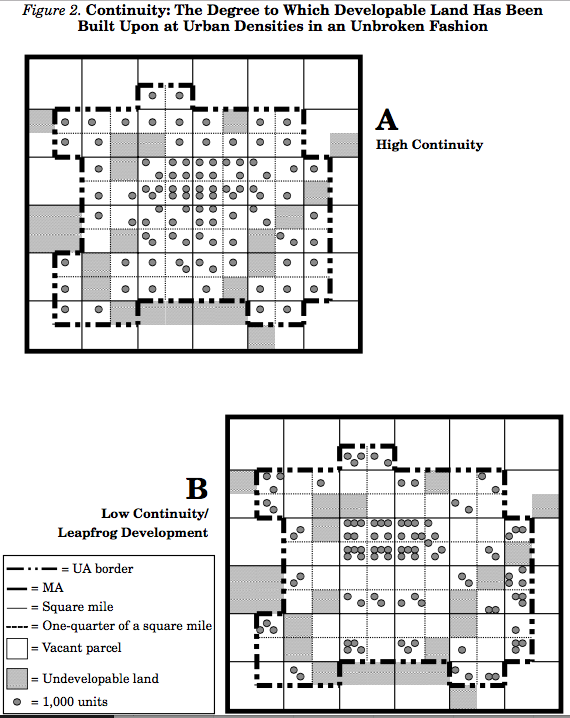
Continuity
Continuinty is the degree to which developable land has been built upon at urban densities in an unbroken fashion.
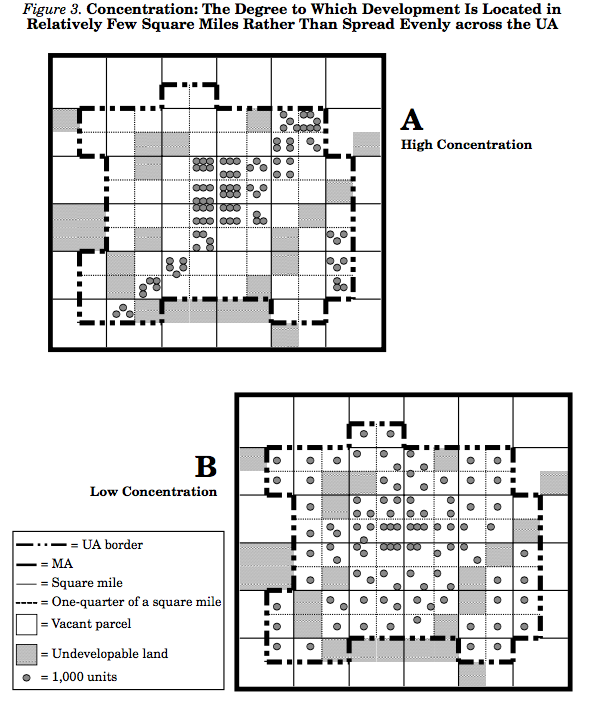
Concentration
Concentration is the degree to which development is located disproportionately in relatively few square miles of the total UA rather than spread evenly throughout.
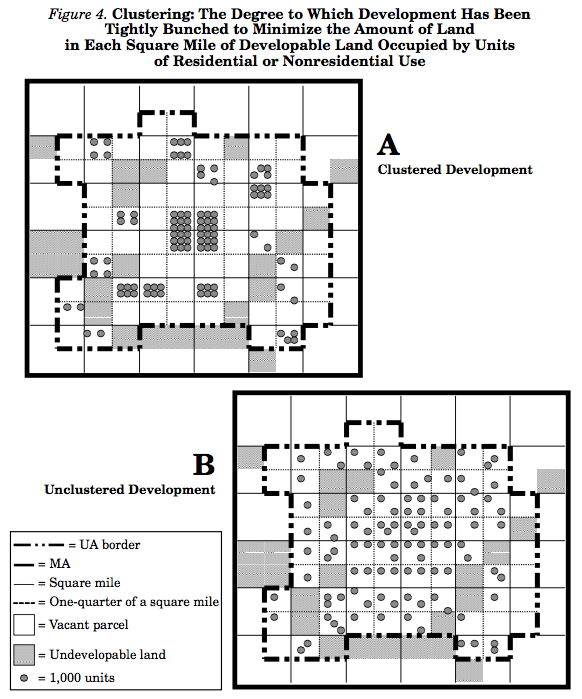
Clustering
Clustering is the degree to which development has been tightly bunched to minimize the amount of land in each square mile of developable land occupied by residential or nonresidential uses.
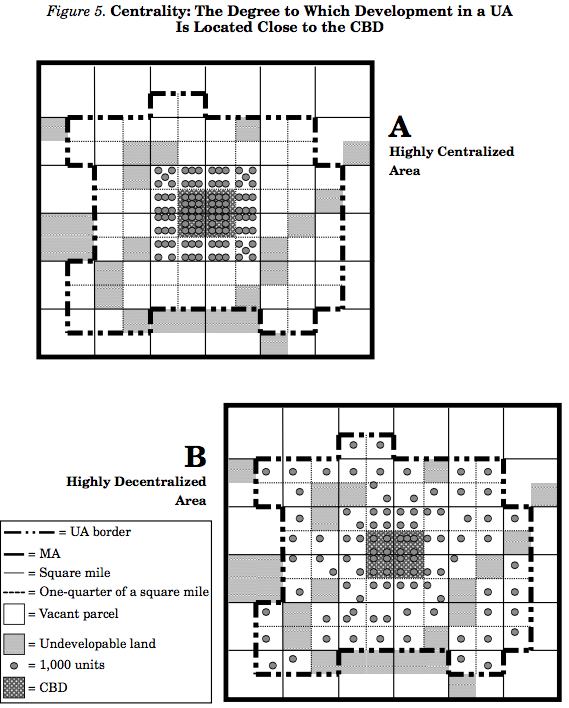
Centrality
Centrality is the degree to which residential or nonresidential development (or both) is located close to the central business district (CBD) of an urban area
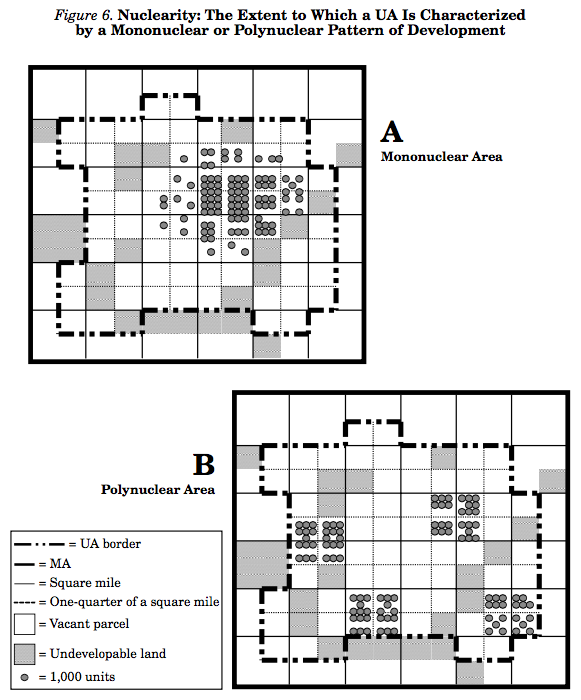
Nuclearity
Nuclearity is the extent to which an urban area is characterized by a mononuclear (as opposed to polynuclear) pattern of development.
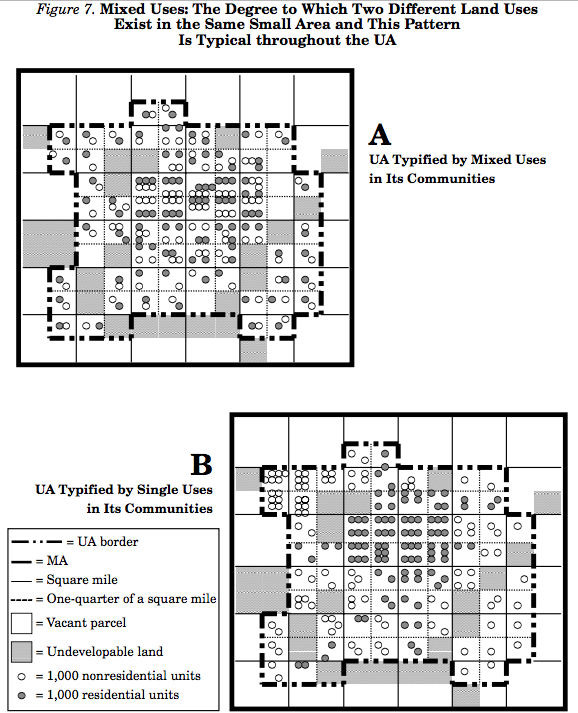
Mixed Uses
Mixed uses means the degree to which two different land uses commonly exist within the same small area, and this is common across the UA.
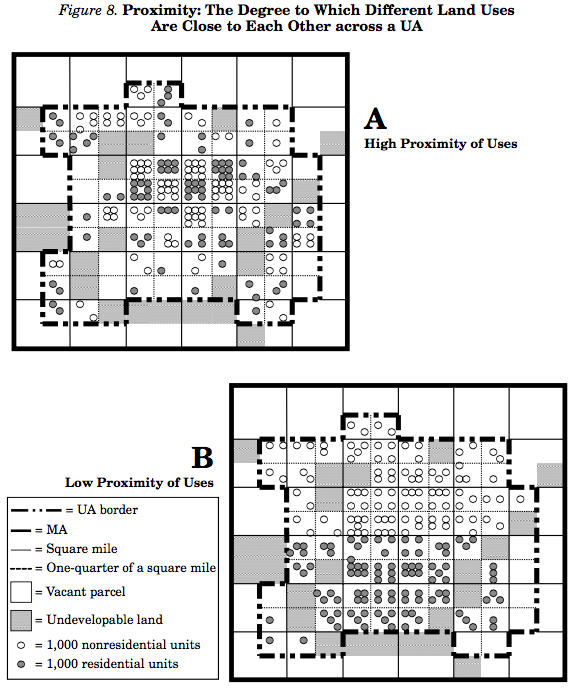
Proximity
Proximity is the degree to which different land uses are close to each other across a UA.
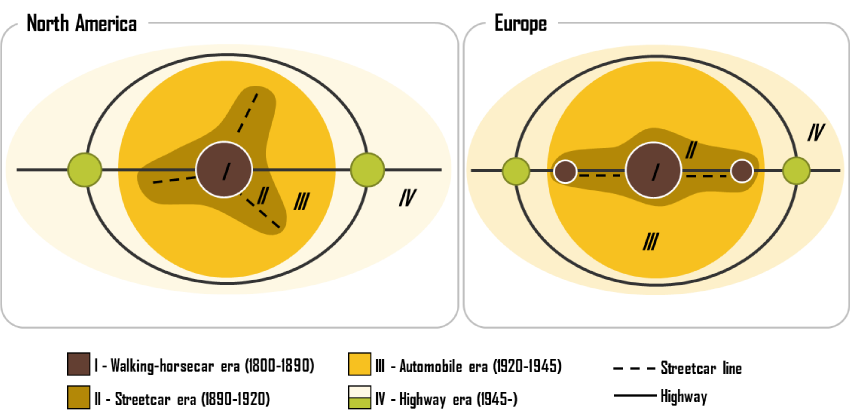
How did we get here?
Historically, transportation and housing policy have had big impact on urban form.
The Times They Are A Changin', Especially Post-WWII
- Population growth spurred by baby boom and post-war immigration
- Federal highway construction (National Interstate and Highways Defense Act)
- Urban renewal building replaces dense neighborhoods with large scale road and highway projects
- Federal housing administration and VA subsidize mortgages for single family homes
- Local zoning laws begin to segregate uses by use type
Sprawl has consequences.
Our challenge today is to manage tradeoffs between today's needs and tomorrow's capacity.
More GHG Emissions
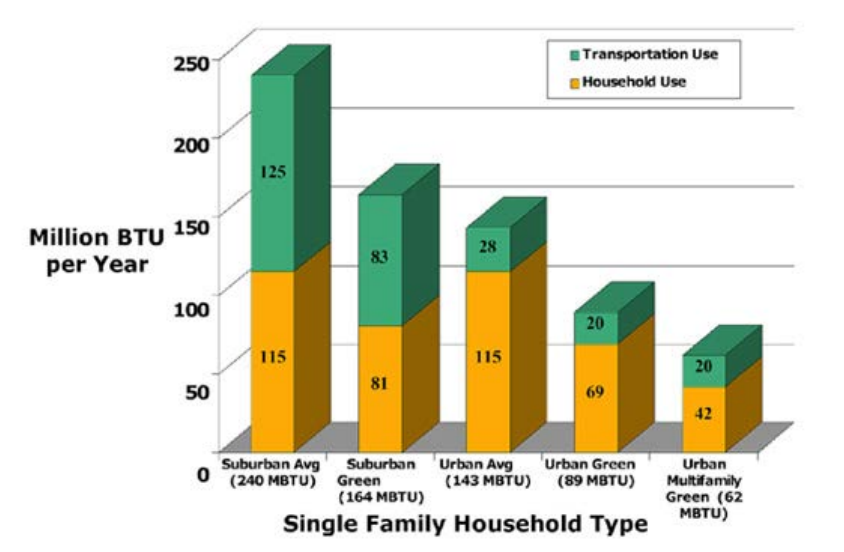
Less Return on Investment
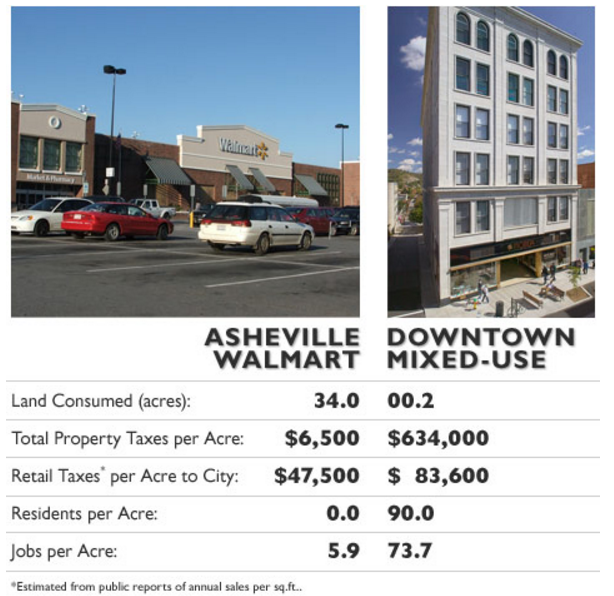
Source: http://www.planetizen.com/node/53922
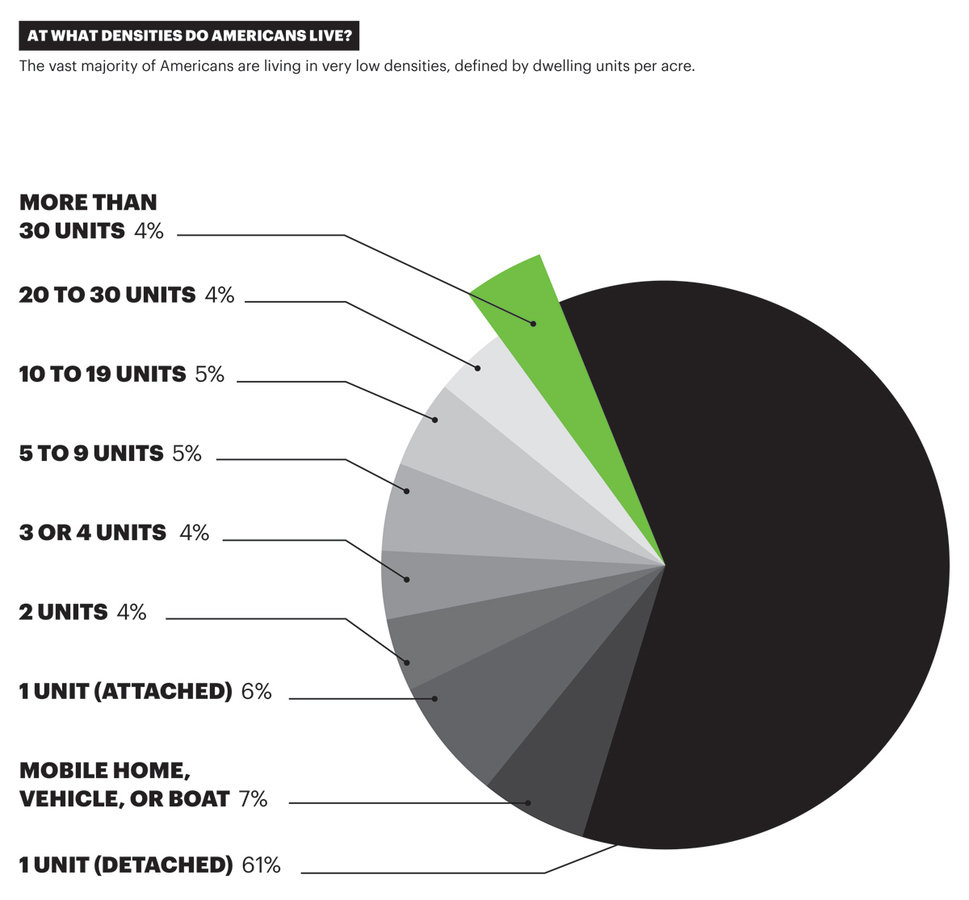
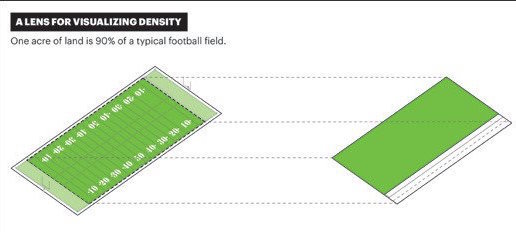
So what does sustainable density look like?
http://persquaremile.com/2012/08/08/if-the-worlds-population-lived-like/
Source: https://placesjournal.org/article/building-hyperdensity-and-civic-delight/
Source: https://placesjournal.org/article/building-hyperdensity-and-civic-delight/
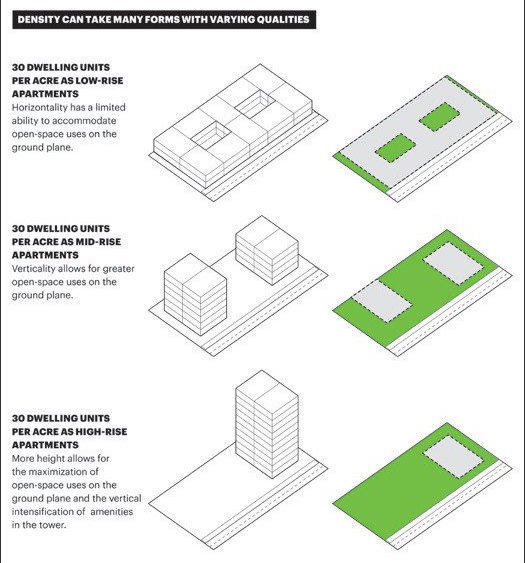
Source: https://placesjournal.org/article/building-hyperdensity-and-civic-delight/
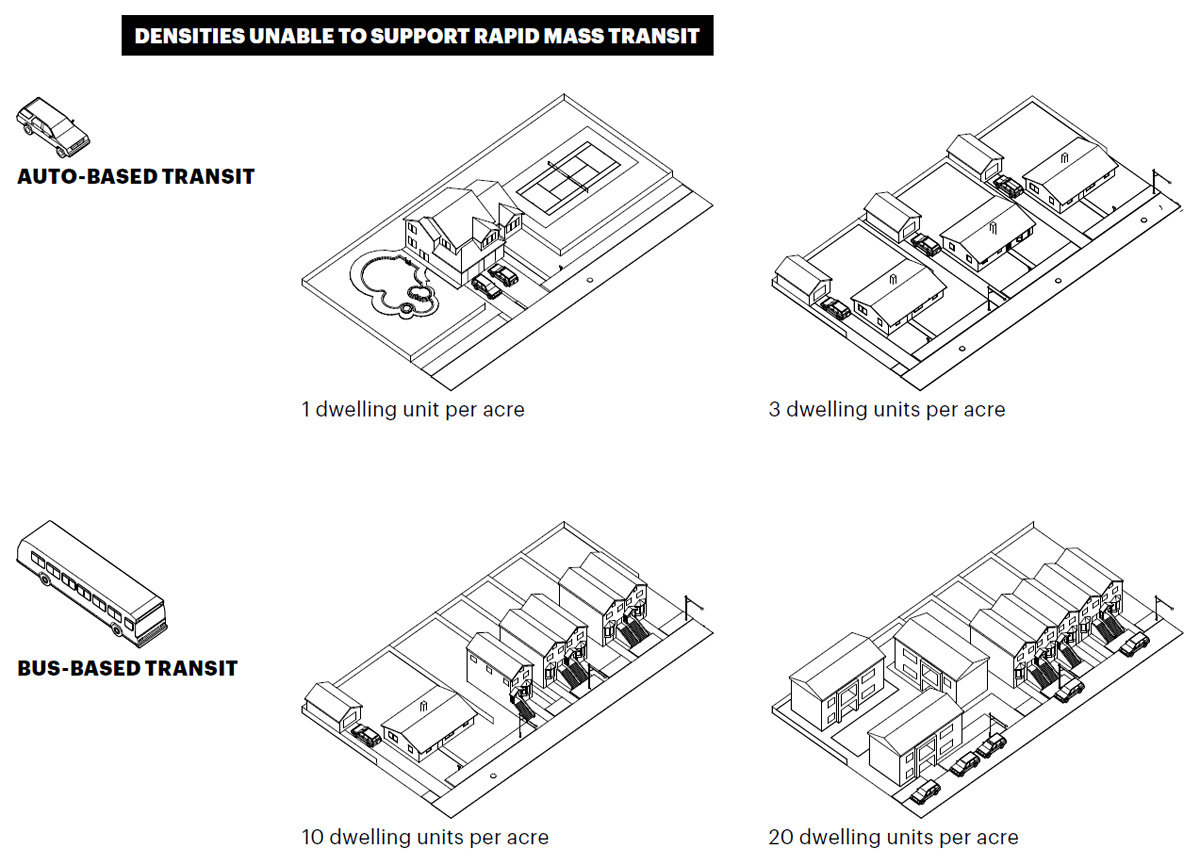
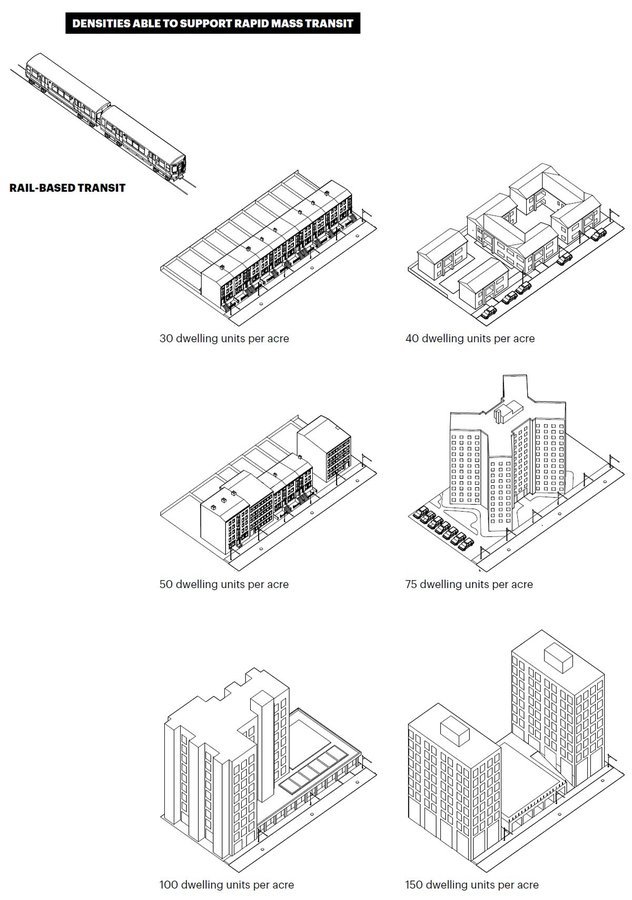
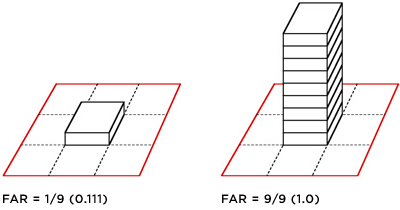
Floor-Area Ratio (FAR)
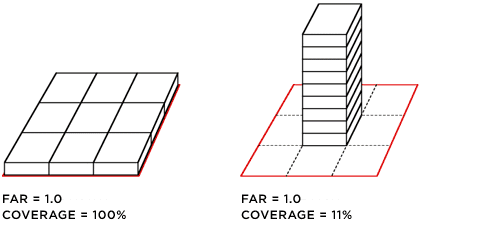
FAR alone is not enough to understand density
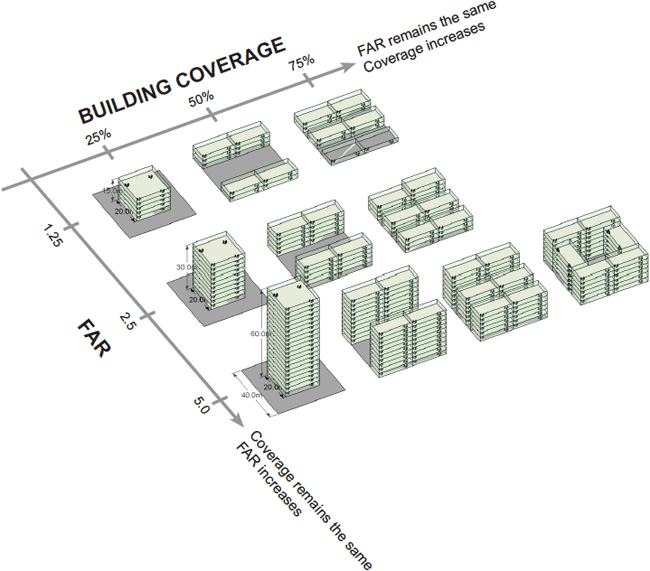
Source: http://densityatlas.org/measuring/metrics.shtml
So what planning tools exist to manage for sustainable densities?
- Comprehensive Planning
- Flexible & Form-Based Zoning
- Land Conservation to Constrain Growth
- Incentives for density, mixed use, and walkability
- Smart allocation of capital infrastructure funds
Environmental Land Use Planning
By Lucas Lindsey
Environmental Land Use Planning
- 1,706



