Nuclear
Unit 2
Isotopes

Neutrons
Each atom's nucleus is made of protons and neutrons stuck together.
Isotope
Isotopes are elements that have different numbers of neutrons.
For example, lithium normally has 3 protons and 3 neutrons. There is a kind of lithium though, that has 4 neutrons; one extra neutron!
Isotopes



Get this!
Neutrons are like the atom's glue
Stable
When the number of protons and neutrons is equal, there is enough glue (neutrons) to hold everything together, and nothing breaks down.
unstable
When atoms get really large (like Uranium), they need more glue to hold them together. If they are big enough, they can't hold on to everything and pieces fly off. They're unstable
Isotopes
In other words, you need enough glue (neutrons) to hold it all together!
Magnets
What happens when you put the (+) sides of two magnets together?
unstable
All of the protons really want to get away from each other! If there is enough of them working together, they can overcome the neutron glue and the nucleus will decay (break down)
But...WHy?

Writing it out
= 6
6
SYmbolic notation
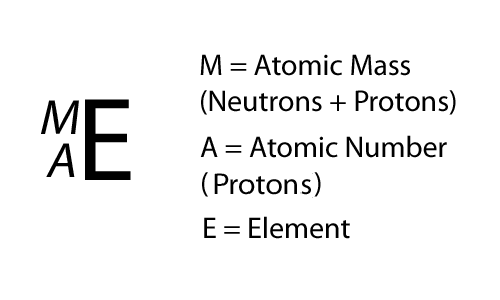


Which is the isotope?
6-protons
6-neutrons
12 -
= 8
6
14 -
6-protons
8-neutrons
Remember, the isotope is the one with different amounts of protons and neutrons
you've reached the bottom
head back to the top
Types
of
Radiation
Color...
Is just light waves hitting your eyes at different frequencies

Color
The difference between orange and red light, is just that red light has a greater frequency.
Electromagnetic Radiation

...but what happens if you increase the frequency even more?
...or make the frequency shorter than than violet?
Visible light is only a small part of all the different things light can do!
Electromagnetic Radiation

...and it's all called electromagnetic radiation





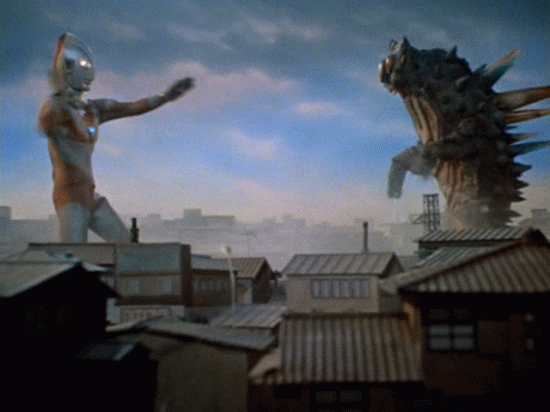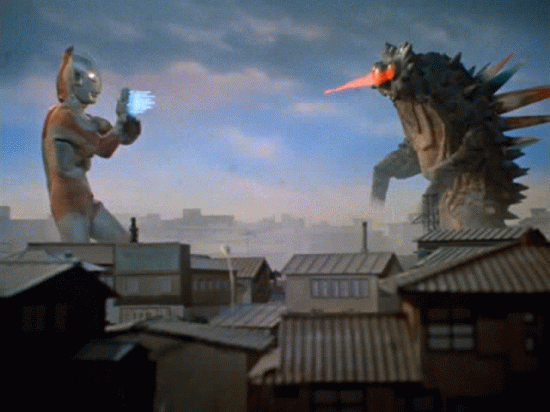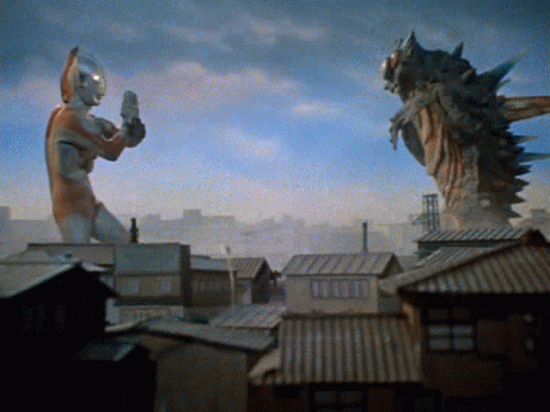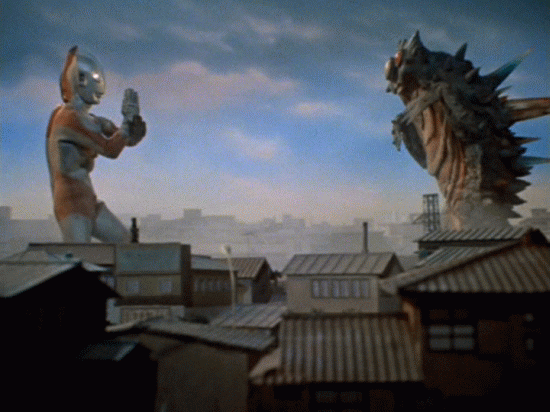
Nuclear Radiation
Comes in 3 flavors.
Nuclear decay

We can't detect alpha, beta, or gamma radiation with our senses. To detect them, we need special tools
Alpha Decay
A nucleus gives off two protons and two neutrons
Nuclear Radiation
As a result, the original atom hops down the periodic table by 2 (because it has lost two of its protons) and is now more stable

example...
An atom of Uranium goes through alpha decay, and we are left with Thorium

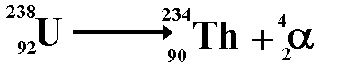
beta Decay
A neutron decays into a proton and an electron
Nuclear Radiation
As a result, the original atom hops up the periodic table by one (it has one more proton) and is now more stable.
example...
An atom of carbon goes through beta decay so that one of its neutrons turns into a proton and electron. The mass stays the same, but it now has an atomic number of 7, making it nitrogen!


The electron flies off to live its own life...We call it a beta particle
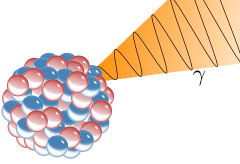
Gamma Decay
A nucleus emits pure energy.
This energy comes in the form of a high frequency photon
Nuclear Radiation
Nuclei can be too energetic as a result other interactions... and it just needs let the energy out.
Go back up a few slides and find gamma rays on the spectrum!
Alpha decay
Symbolic notation can help us keep track of what happens to the atomic number, and mass of an atom after decay.
Symbolic Notation
beta decay
gamma decay
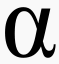



Alpha decay
Alpha particles are so fat and slow, they can be stopped by paper!
How to protect yourself
beta decay
gamma decay
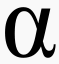


Beta particles are fast little electrons that take a few sheets of aluminum foil to stop
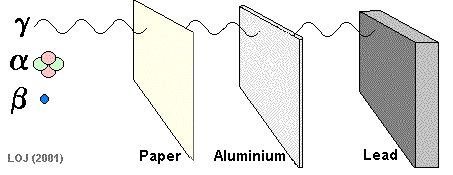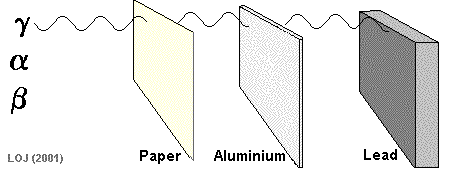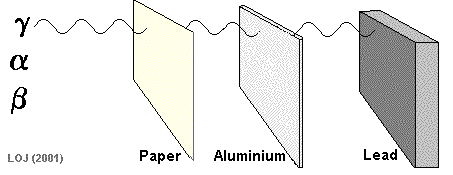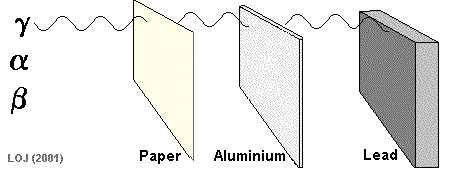
Gamma rays are very high energy, and can go through most materials. A thick sheet of lead can protect you from these dangerous rays
you've reached the bottom
head back to the top
Half-lives

Time
Unstable atoms decay over time. Some decay quickly, some take billions of years.
A half-life is how long it takes for half of the material to decay into another material.
example
Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 years. This means that you can start with any size sample (ex. 50g), and after 5730 years go by, you will have only half of your carbon-14 remaining (ex. 25g).
Half-life

graphing
In graphs, half life is the same. The time it takes (x-axis) to go from a full sample to half sample is called the half-life of that element.
Half-life

neat!
Each atom of carbon-14 has a 50% chance of beta-decay every 5730 years.

uses
When was the Earth formed? When were the Dead Sea Scrolls written? When did Wooly Mammoths live?
We can use what we know about nuclear decay to answer these questions with a technique called radiometric dating.
Half-life



How?
When a rock is formed, or an animal dies, it dies with an amount of unstable atoms in it, and the clock, essentially, starts ticking.
Half-life


you've reached the bottom
head back to the top
Fission
Splitting
When a big atom splits into smaller parts, it is called fission
Uranium
Fission happens to big fat atoms like uranium.
When uranium splits into smaller parts, it also releases energy and extra neutrons
Fission


Missing mass?
Imagine this...
... you are in your lab and you have a uranium nucleus in a sealed container. You make the uranium nucleus fission by firing a neutron at it. Then you weigh the results.
You should get:
uranium nucleus+neutron=mass
Mysterious!
Energy
...But you don't.
You actually get a smaller number!
It's like saying 10 + 1 = 9

Enter Lise Meitner & albert einstein

What happens to the missing mass?
Lise Meitner used Einstein's equation to solve this riddle.
The missing mass was converted to ENERGY via
amounts
Even though only a tiny amount of mass goes missing, it gets converted to a HUGE amount of energy.
Missing mass

chain reaction
Splitting a nucleus into smaller parts also releases extra neutrons
Those extra neutrons split other atoms, which release neutrons that split other atoms, which release neutrons that split other.... okay, you get it.
nuclear Power



slow it down!
Nuclear power plants use the same fission chain reaction, but they don't normally explode.
nuclear Power

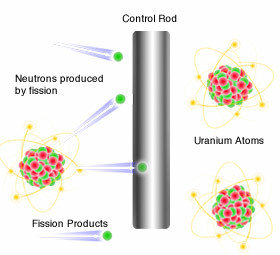
Nuclear power plants have control rods which absorbs some of the extra neutrons to keep them from hitting other atoms.
Fusion
Fusing elements
Fusion is a process that combines 2 smaller nuclei into 1 larger nucleus.
To get this to happen, the small nuclei have to hit each other really hard! (Otherwise, they wont fuse)
energy
When fusion does happen, it releases HUGE amounts of energy (more than fission even!).
fusion

Fusing elements
Fusion creates new, larger elements.
In fact, all of the elements in the universe larger than helium were created by stars!
Why is it bright outside?
The sun is constantly fusing hydrogen into helium and releasing that energy as light radiation!
fusion

Your teeth, your brain, your skin; most of the atoms inside you were created in a star in the distant past.
you've reached the bottom
head back to the top
Practice
makes
perfect

Isotopes
What is the difference between Carbon-12 and Carbon-14?
Different numbers of neutrons
Which isotope is stable, Neon-20, Sodium-23, or Phosphorus-34?
Neon-20 (10 protons and 10 neutrons)
How can an unstable atom become more stable?
Nuclear Decay (changes the numbers of protons and neutrons)
nuclear decay
What happens in beta-decay?
A neutron turns into a proton and electron. The proton stays put, the electron flies off on its own (called a beta particle).
What is the least amount of material needed to stop an alpha particle?
Big fat alpha particles can be stopped by a piece of paper. (or a little bit of smoke!)
Complete the equation
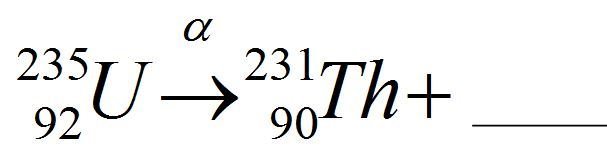
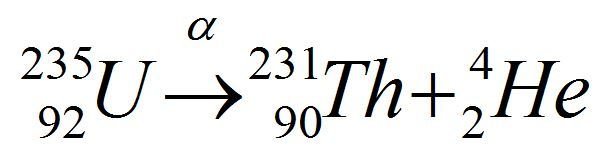
fission fusion
What process is used in nuclear power plants?
A fission chain reaction
What can tell us about the mass that seems to go missing in fission?
That missing mass actually gets converted into a huge amount of energy!
You are a star with a bunch of hydrogen. What can you do to make new helium atoms?
Stars create new heavier elements (and release energy!) by fusing smaller elements like hydrogen
half lives
A sample of Francium decays to 1/16 of its original mass after 80 minutes. What is the half-life of Francium?
1/16 --> 4 half lives
80/4=20 minutes per half life
Use the graph to find the half-life of Mercury-203
It takes approximately 48 years for half of the sample to decay into the new product.

half lives
Carbon-14 has a half life of 5730 years. How much of a 264g sample will remain after 17,190 years?
17,190/5730=3 half lives
264g -->132g --> 66g --> 33g
What happens to the carbon-14 that decays?
Decay is a process that changes the amounts of protons and neutrons. Carbon-14 happens to go through beta-decay, which means when it decays, it decays into nitrogen-14
you've reached the bottom
head back to the top
Nuclear
By Luke Gliddon
Nuclear
All you need to know for Unit 2
- 1,545



