關聯式資料庫
Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC)
實作方式微介紹
上次說到 transaction 的 ACID
- Atomicity 原子性
- Consistency 一致性
- Isolation 隔離性
- Durability 持久性
Isolation
| Write: A = A - 100 Write: B = B + 100 |
Read: A Read: B |
T1 T2
轉帳
算 A、B 總和
Isolation level
- Serializable
- Repeatable Read
- Read Committed
- Read Uncommitted
Serializable
| Write(A) Write(B) |
Read(A) Read(B) |
T1 T2
| Write(A) Write(B) |
Read(A) Read(B) |
T1 T2
serializable
not serializable
conflict
conflict
Multi-Version
| Write(A) Write(B) |
Read(A) Read(B) |
T1 T2
Serializable
Repeatable Read
Read Committed
Read Uncommitted
根據 isolation level 決定看到哪個版本
Multi-Version
| Write(A) Write(B) |
Read(A) Read(B) |
T1 T2
| Write(A_1) Write(B_1) |
Read(A_0) Read(B_0) |
T1 T2
如果 T2 讀的是
T1 寫入之前的版本
|
Write(A_1) Write(B_1) |
Read(A_0) Read(B_0) |
T1 T2
Multi-Version
| Begin Read(A) Read(A) Commit |
Begin Write(A) Commit |
T1 T2
Serializable
Repeatable Read
Read Committed
Read Uncommitted
根據 isolation level 決定看到哪個版本
Multi-Version
| Begin Read(A) Read(A) Commit |
Begin Write(A) Commit |
T1 T2
如果 T1
Repeatable Read
| Begin Read(A_0) Read(A_0) Commit |
Begin Write(A_1) Commit |
T1 T2
| Begin Read(A_0) Read(A_0) Commit |
Begin Write(A_1) Commit |
T1 T2
data rows
| id | value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 123 |
| 2 | 124 |
| 3 | 125 |
row1
row2
row3
⋮
基本作法
| id | value | begin | end |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | 3 | - |
| 2 | 124 | 11 | - |
| 3 | 125 | 22 | - |
begin/end 放 create/delete 的
transaction 的 id 或 timestamp
| id | value | begin | end |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | 3 | |
| 2 | 124 | 11 | |
| 3 | 125 | 22 | |
| Begin Read(A) |
Begin Write(A) |
txn_id = 33 txn_id = 34
以 postgresql 的 update 為例
Serializable
Repeatable Read
Read Committed
Read Uncommitted
根據 isolation level 決定看到哪個版本
| transaction | status |
|---|---|
| 33 | active |
| 34 | active |
34
1
999
34
| id | value | begin | end |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | 3 | 34 |
| 2 | 124 | 11 | - |
| 3 | 125 | 22 | - |
| 1 | 999 | 34 | - |
visibility
| txn_id | status |
|---|---|
| 3 | commit |
| 11 | commit |
| 22 | abort/rollback |
| 33 | active |
| 34 | active |
Serializable -> 可能會 block 住,或沒 block 住
Repeatable Read -> ??
Read Committed -> ??
Read Unmmitted -> ??
請問 transaction_id 為 33 的,可以看到哪些呢
| id | value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 123 |
| 2 | 124 |
| 3 | 125 |
| 1 | 999 |
不同版本的資料如何存放
main table space
放一起
| id | value | pointer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 999 | |
| 2 | 124 | |
| 3 | 125 | |
main table space
分開放
| id | value | pointer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | |
別的地方
version chain
微前情提要:index
rowA
rowB
rowC
rowD
rowE
rowF
rowG
rowH
rowI
rowJ
rowK
rowL
rowM
⋮
⋮
main table space
index
⋮
valueH
valueI
valueJ
valueK
valueL
valueM
valueN
valueO
valueP
valueA
valueB
valueC
valueD
valueE
valueF
valueD
valueE
valueF
valueG
⋮
可以為某些 columns 建立 index,它 (大部分) 是樹狀結構,可以加快尋找速度
微前情提要:index
main table space
id 的 index 的 leaf nodes
| id | pointer |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 6 |
| id | column1 | column2 | column3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | aa | 34 |
| 2 | 124 | bb | 23 |
| 3 | 125 | cc | 234 |
| 6 | 126 | dd | 234 |
| 4 | 127 | ee | 43 |
經過一番值的比較然後
走到 leaf
index
root
如果 index 的 leaf nodes 同時也是 main table space
index 的 leaf nodes + main table space
資料直接放在同一個地方
這種 index 叫做 clustered index
(剛剛那種叫 secondary index)
index
root
經過一番值的比較然後
走到 leaf
| id | column1 | column2 | column3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | aa | 34 |
| 2 | 124 | bb | 23 |
| 3 | 125 | cc | 234 |
| 6 | 126 | dd | 234 |
| 4 | 127 | ee | 43 |
MySQL 每個 table 一定會有一個 clustered index,即使沒有指定 primary key
PostgreSQL 每個 index 都是 secondary index,即使是 primary key 的 index 也一樣
一個 table 最多只能有一個 clustered index
為什麼要提 index
因為資料位置有變化的話
也會需要更新 index 所指的位置
main table space
id 的 index 的 leaf nodes
| id | pointer |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| id | value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 123 |
| 2 | 124 |
| 3 | 125 |
| 1 | 999 |
?
?

不同版本的資料如何存放
衆多作法之一:不改動舊資料,在同樣的空間新增一筆
main table space
| id | value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 123 |
| 2 | 124 |
| 3 | 125 |
| 1 | 999 |
| id | pointer |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 |
如果有別的 index
也新增一個
PostgreSQL 的做法比較類似這樣
update 不移資料 (immutable) rollback 的話什麼都不用動 (但大多應該不會 rollback)
不同版本的資料如何存放
衆多作法之二:原地改 data,舊的資料拿去放別的地方
main table space
別的地方
| id | value | pointer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 999 | |
| 2 | 124 | |
| 3 | 125 | |
| id | value | pointer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | |
version chain
MySQL 的做法比較類似這樣 而且只紀錄有更動的欄位 那個地方叫 rollback segment
update 要先移資料 rollback 的話再移回來
如果有別的 index
| key | pointer |
|---|---|
| x | |
| y | |
| z | |
比較一下
| id | value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 123 |
| 2 | 124 |
| 3 | 125 |
| 1 | 999 |
main table space
作法一
| id | value | pointer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 999 | |
| 2 | 124 | |
| 3 | 125 | |
main table space
作法二
| id | value | pointer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | |
別的地方
可以討論儲存空間使用的效率、過時資料清除/空間回收、相關 index 的更新等等
延伸出的議題很多
index 的更新是一個重點
讀/寫 disk 次數多的話 效能可能較差
尤其是寫
除了底層鎖定可能會影響其他讀取之外
只要有更動資料都要先寫 log 到 disk 以保證 atomicity
如果還要同步到別台機器 像 PostgreSQL 用 log 來同步
影響就更多
Uber 抱怨 PostgreSQL 這件事情很有名
他們把這個也叫做 "Write Amplification"
作法一 可能改一點點東西就也必須更新多個 index
其實 PostgreSQL 還有一些減緩 "write amplification" 的做法
HOT Update
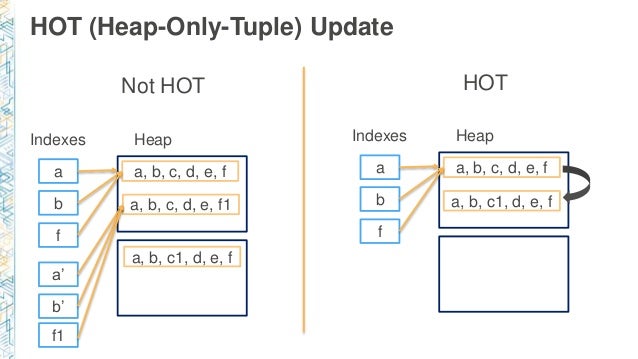
條件 1: 同一個 page/block 內還有空間
條件 2: 沒改有 index 的 column
其實 PostgreSQL 還有一些減緩 "write amplification" 的做法
Indirect indexes??
Indirect indexes are similar to regular indexes, except that instead of carrying a heap TID as payload, they carry the value of the table's primary key.
參考資料
MVCC
By luyunghsien
MVCC
- 583



