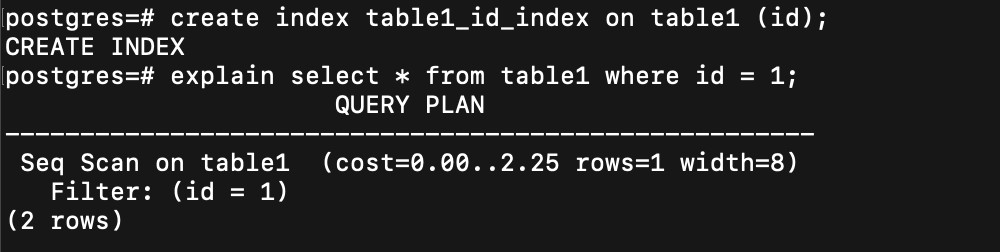
用 EXPLAIN 來檢查 SQL 查詢計劃
微介紹
seq scan, index scan & bitmap index scan
SQL Query
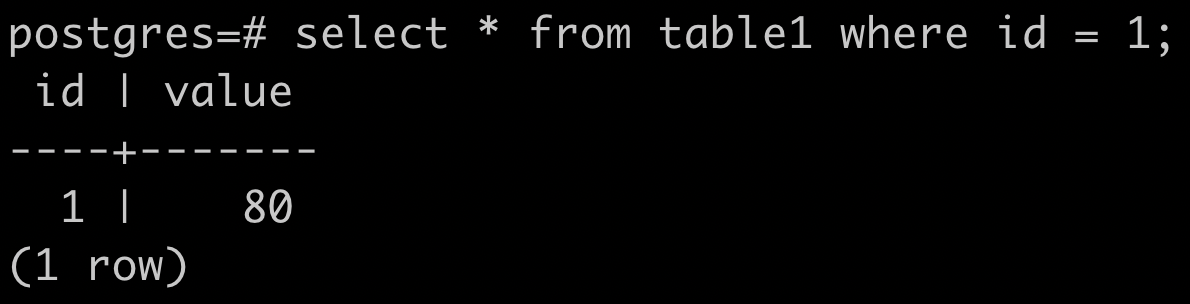
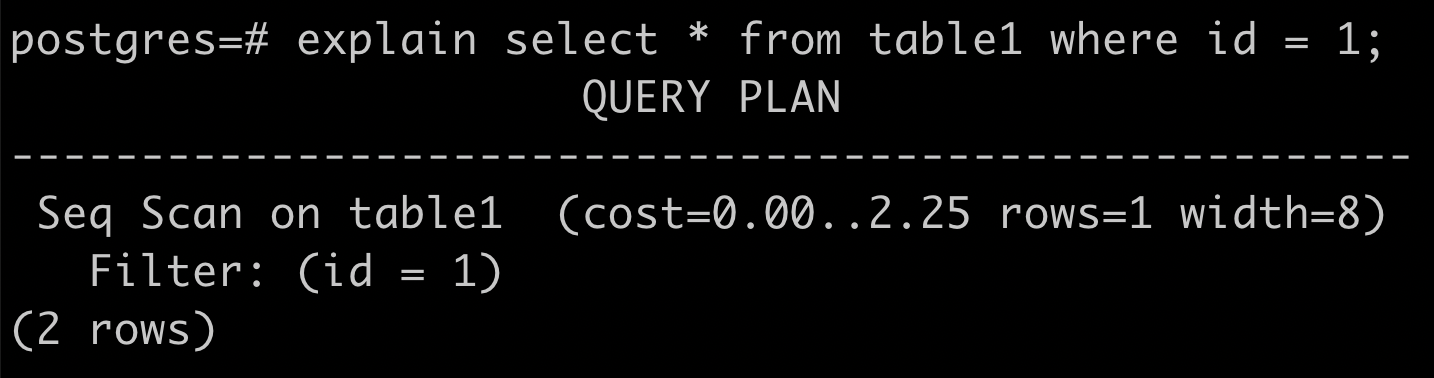
seq scan 是什麼
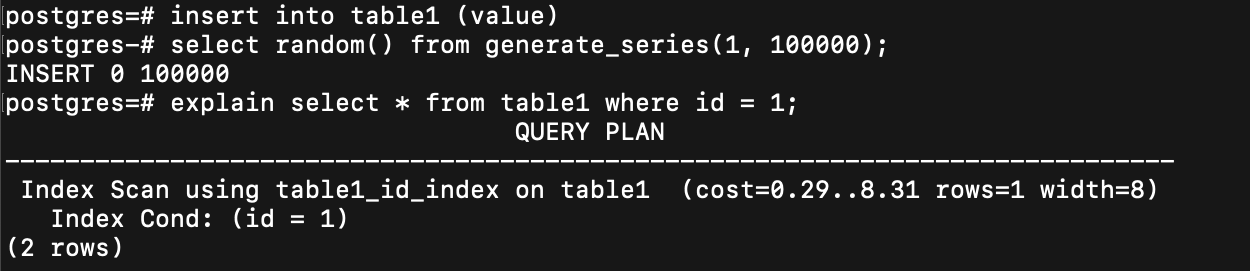
還有 index scan
index only scan
bitmap index scan
bitmap heap scan
sort
nested loop
merge join
hash join
...
有幾十種
前情提要
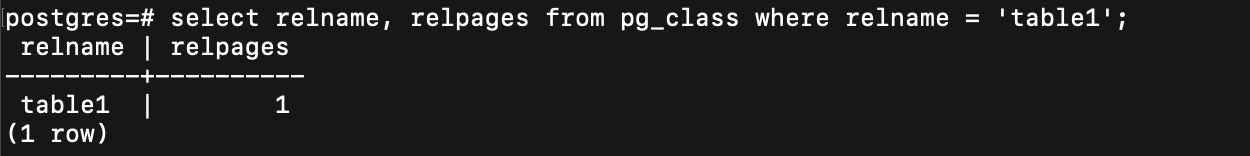
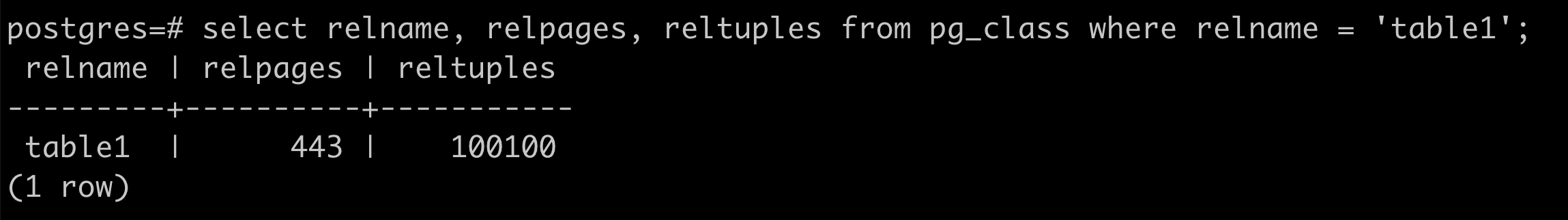
資料是存在 disk
每個資料檔案會再被細分為固定大小一塊一塊 (block, page)
資料的存取以 page (block) 為基本單位

前情提要2
disk 讀寫的速度滿慢的
比 memory 的讀寫速度慢很多
所以會盡量減少 disk 的讀寫
比較耗時的 query
大多都是因為多次讀寫 disk
基本上可以用 disk 的讀寫次數
來估算做法的好壞
舉個例

seq scan (sequential scan)
就是從第 0 個 page 開始一個個拿出來找
如果要找的資料不多
卻每個 page 都讀出來再過濾
可能會多花很多時間
不太划算
這時 index 就可以來幫忙
關於 index
有很多種
關聯式資料庫最基本最常見的是 b+ tree 的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
3
5
9
11
7
- 表示 tuple id (block number & index)
例子
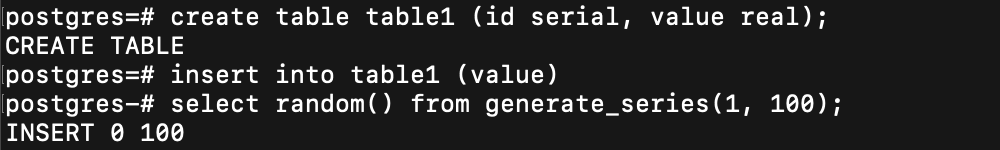
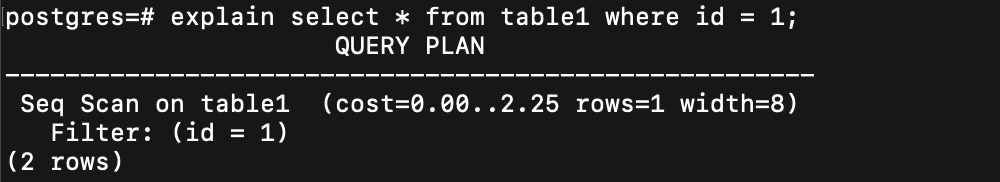
例子

???
例子
前面說
主要會考量 disk 讀取多少次
不過好像
用 index 也不能保證
抓 table 資料的時候
可以不用抓太多個 page
如果要抓的資料超多
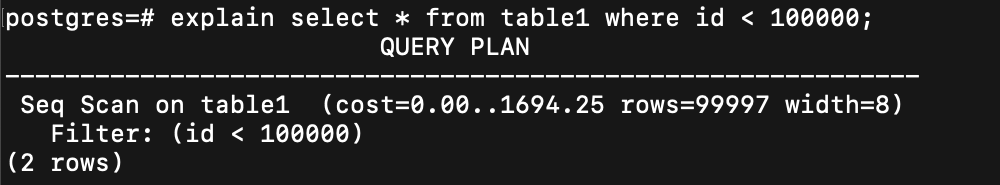
就還是用 sequential scan
再舉一個極端例子
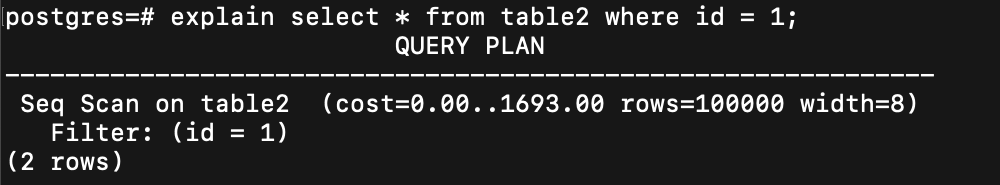

postgreSQL 會自己估計 selectivity
大概 select 了多少比例
第一個是用 most common value
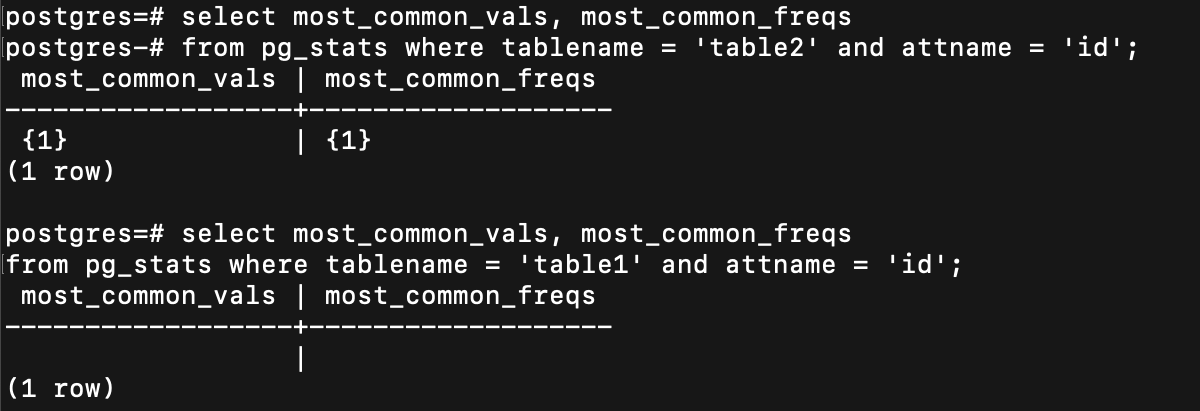
most common value 不好用的話
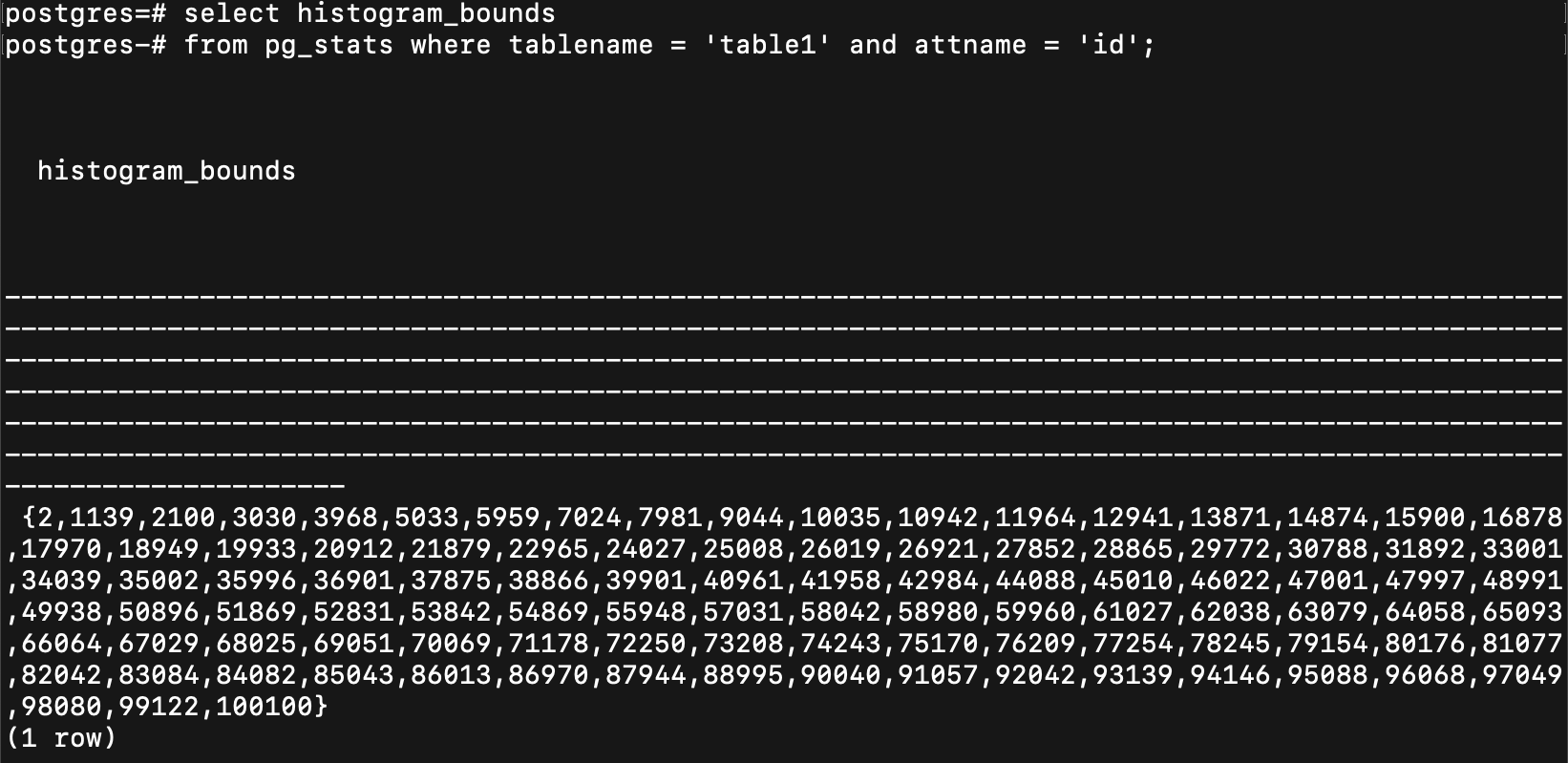
就大概切一下
default 分 100 個 bucket
每一個 bucket 內的資料筆數會差不多



有了 selectivity 還不夠
有沒有可能只選取 10 %
可是卻還是需要撈很多 pages
其實用 index 省不到太多?
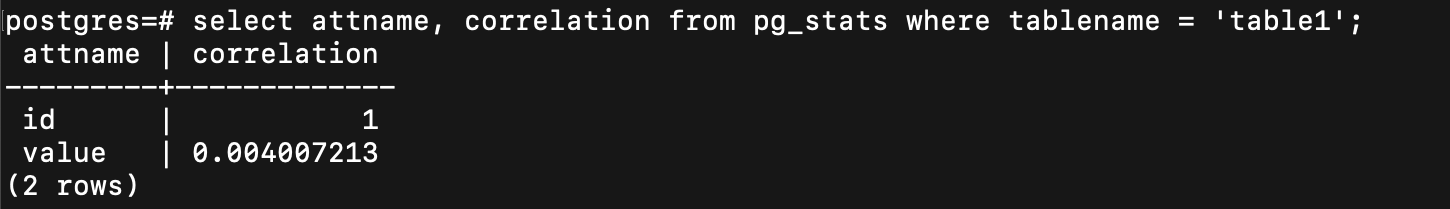
correlation

postgreSQL 也有算~
postgreSQL 對可能的方案分別計算 cost
total cost = start-up cost + run cost
start-up cost: 去拿第一筆 tuple 之前的 cost
run cost: 拿 tuples 的 cost
白話:
index 部分的 cost 是 start-up cost
heap 部分的 cost 是 run cost

start-up
total
seq scan 的 cost 估算公式
start-up cost = 0
run cost = cpu run cost + disk run cost
= (cpu_tuple_cost + cpu_operator_cost) x + seq_page_cost x
0.01
0.0025
1
可以在 postgresql.conf 更改數值
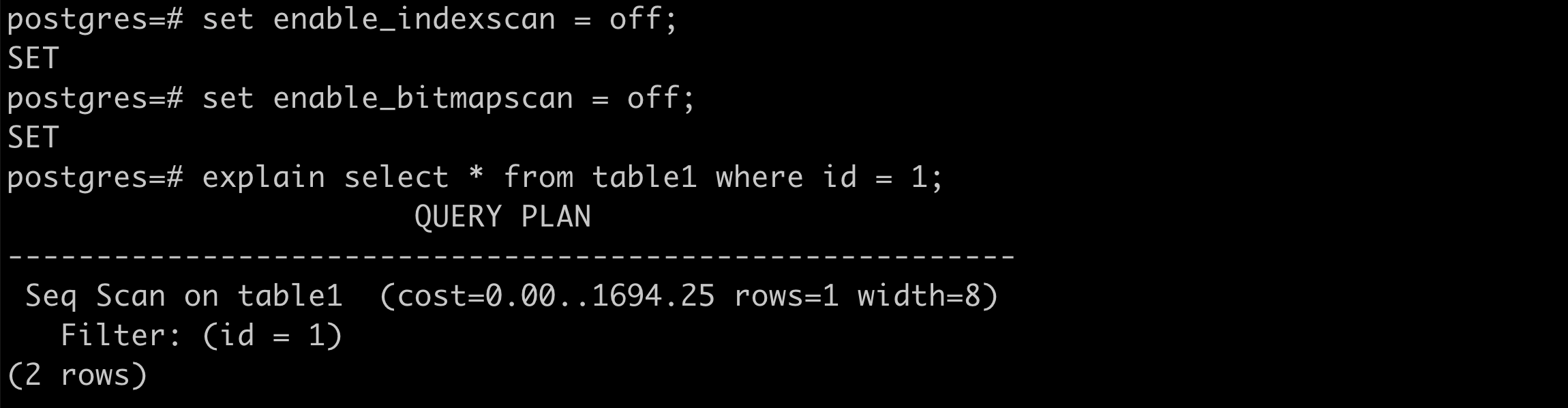
seq scan
total cost = 0.0125 x + 1 x
total cost = 0.0125 x 100100 + 1 x 443 = 1694.25
index scan 的 cost 估算公式
start-up cost = cpu_operator_cost
index scan 的 cost 估算公式
run cost = index cpu cost + table cpu cost + index IO cost + table IO cost
index cpu cost = selectivity × × (cpu_index_tuple_cost + qual_op_cost)
table cpu cost = selectivity × × cpu_tuple_cost
index IO cost = ceil(selectivity × ) × random_page_cost
table IO cost = max_IO_cost + indexCorrelation × (min_IO_cost − max_IO_cost)
worst case
best case
seq scan vs index scan?
感覺上
選取範圍小 -> index scan
選取範圍大 -> seq scan
不太確定的時候 -> bitmap scan ??
想要用 index,但
⋮
⋮
bit array
⋮
⋮
1
1
1
0
bit array
bitmap index scan
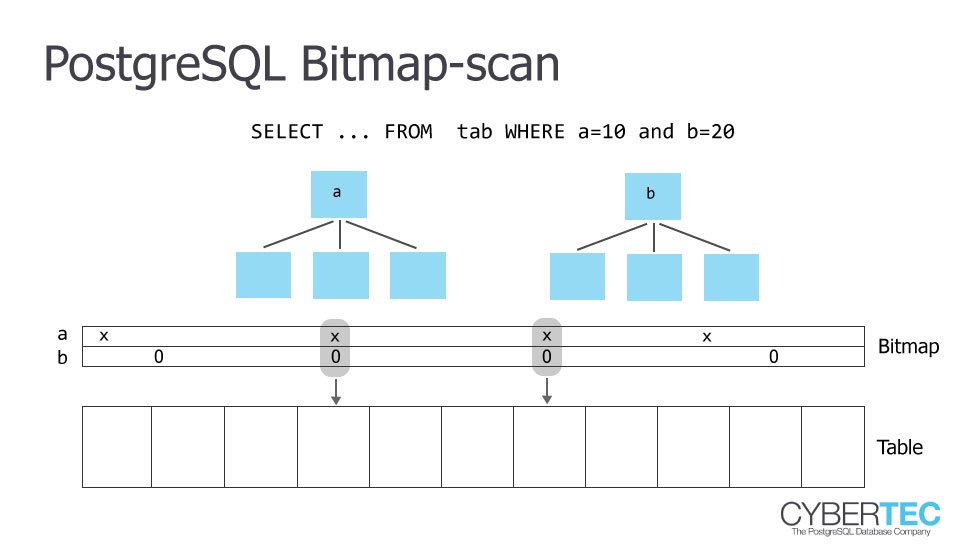
同時多個條件判斷可能很好用
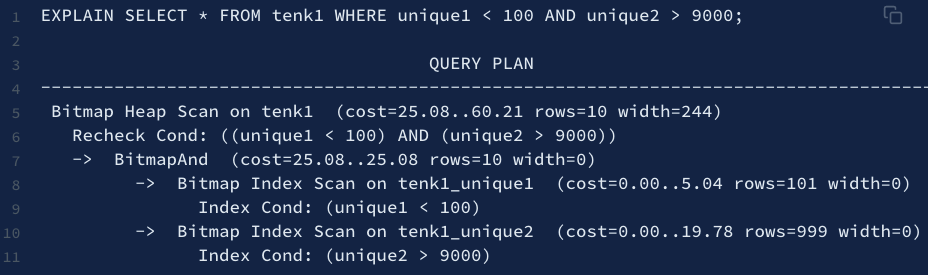
顯示更多訊息
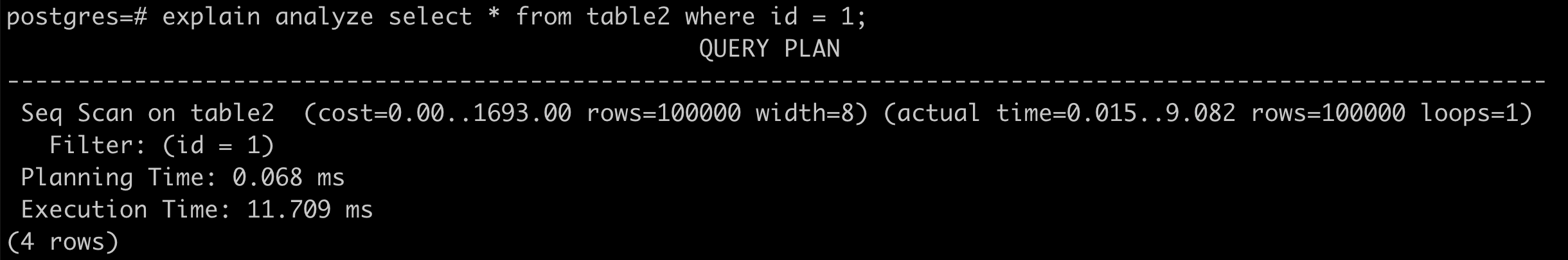
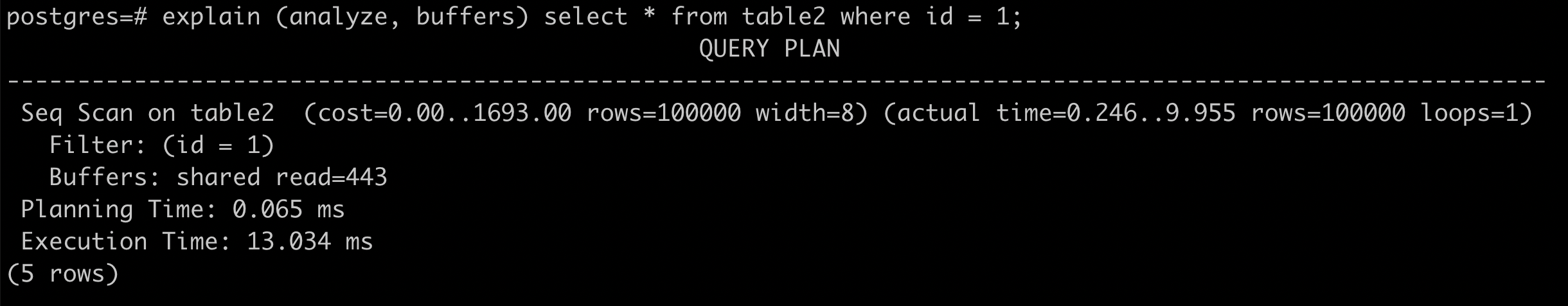
參考資料
EXPLAIN
By luyunghsien
EXPLAIN
- 595



