React & Redux
Modern UI libraries
Madhan Ganesh
Agenda
Component
Rendering Logic
Multiplatform
Redux
Meet React
A Javascript library for building user interfaces
Meet React
Renders your UI and responds to
events
Meet React
AKA: The V in MVC
Meet React
Can work with plain JavaScript models
Meet React
React enables Component
based UI
Meet React
Plays nicely with your stack,
whatever it maybe
Meet React Component

JSX
A syntax extension to JavaScript
JSX
A syntax extension to JavaScript

React Component
A highly cohesive building block UIs loosely coupled with other components
class TodoApp extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
this.handleSubmit = this.handleSubmit.bind(this);
this.state = {items: [], text: ''};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>TODO</h3>
<TodoList items={this.state.items} />
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<input onChange={this.handleChange} value={this.state.text} />
<button>{'Add #' + (this.state.items.length + 1)}</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}
handleChange(e) {
this.setState({text: e.target.value});
}
handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
var newItem = {
text: this.state.text,
id: Date.now()
};
this.setState((prevState) => ({
items: prevState.items.concat(newItem),
text: ''
}));
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<TodoApp />, mountNode);class TodoList extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.items.map(item => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.text}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
}Abstraction
Composition
Expressive
Components are reusable
Components are composable
Components are unit testable
Components are small
Components has only display logic
const React = require('react');
class ActionButton implements React.Component {
render() {
return (
<button class="ActionButton" onClick={this.props.onAction}>
<span>{this.props.text}</span>
</button>
)
}
}Props & Actions
<ActionButton text="Book flight" onAction={someFunc} />State
class Timer extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {secondsElapsed: 0};
}
tick() {
this.setState((prevState) => ({
secondsElapsed: prevState.secondsElapsed + 1
}));
}
componentDidMount() {
this.interval = setInterval(() => this.tick(), 1000);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.interval);
}
render() {
return (
<div>Seconds Elapsed: {this.state.secondsElapsed}</div>
);
}
}<Timer />State used in render
Initial State
State Updated
Component Props & States
React Component
Properties
Actions
State
render()
Breaking the monolith
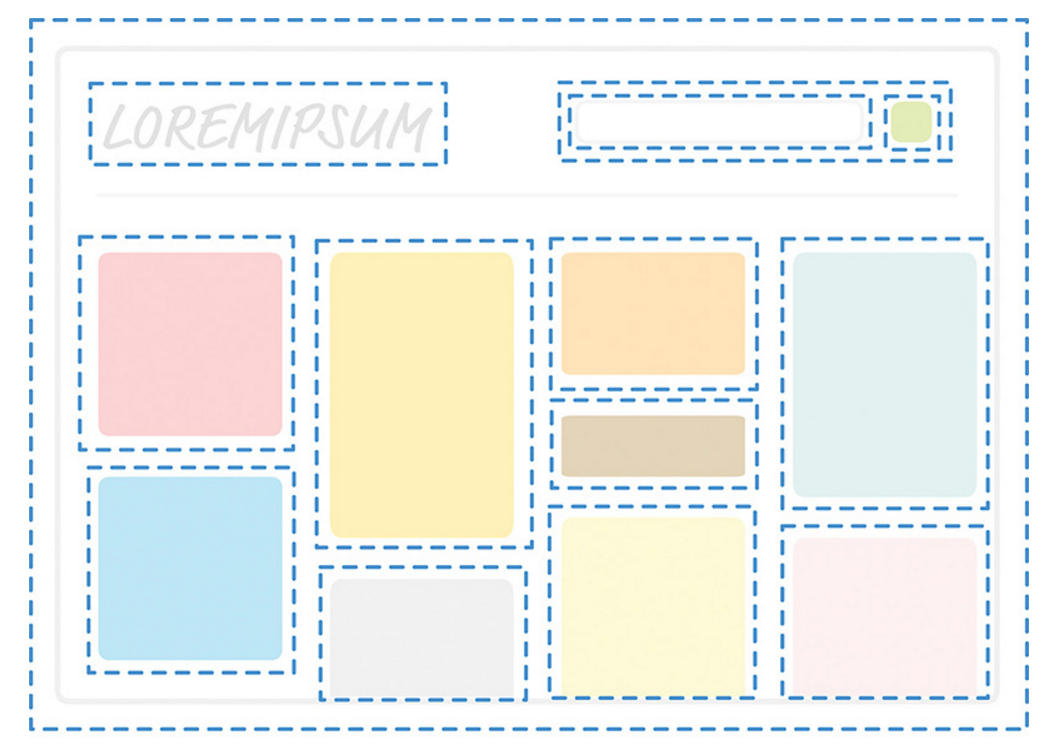
React Styling
class Card extends Component {
render() {
const style = {
height: '200',
width: '150'
};
return (
<div style={style}>
</div>
);
}
}
Rendering Logic
Re-render the whole app on every update
The key design decision that makes React awesome
Building UIs is hard because there is so much state
Process vs State
Following processes is difficult programming model
vs
Programming snap-shot of state
DOM
The main problem is that DOM was never optimized for creating dynamic UI.
When.
When the data is changed and needed to be updated. But how do we know that the data is changed?
Dirty Checking
poll the data at a regular interval and check all of the values in the data structure recursively.
Observable
observe for the state change. If nothing has changed, we do nothing. If it changed, we know exactly what to update.
Virtual DOM
The Virtual DOM is an abstraction of the HTML DOM. It is lightweight and detached from the browser-specific implementation details.
Knockout
Angular
React



Observable
Dirty Checking
Virtual DOM

Virtual DOM
Benchmarks
https://auth0.com/blog/more-benchmarks-virtual-dom-vs-angular-12-vs-mithril-js-vs-the-rest/

Demo
https://jsfiddle.net/madhanganesh/bujwyv18/
https://jsfiddle.net/madhanganesh/92edcx4p/
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor() {
this.state = { blue: false, green: false }
}
onBlueClick() {
this.setState({ blue: !this.state.blue });
}
onGreenClick() {
this.setState({ green: !this.state.green });
}
render() {
var blue = this.state.blue ? 'BLUE ON' : 'BLUE OFF';
var green = this.state.green ? 'GREEN ON' : 'GREEN OFF';
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.onBlueClick}>Blue</button>
<br/><br/>
<button onClick={this.onGreenClick}>Green</button>
<h4>{blue}</h4>
<h4>{green}</h4>
</div>
)
}
}function MyController($scope) {
$scope.showBlue = false;
$scope.showGreen = false;
$scope.onBlueClick = function() {
$scope.showBlue = !$scope.showBlue;
}
$scope.onGreenClick = function() {
$scope.showGreen = !$scope.showGreen;
}
}<div ng-app>
<div ng-controller="MyController">
<button ng-click="onBlueClick()">Blue</button>
<br /><br />
<button ng-click="onGreenClick()">Green</button>
<div ng-show="showBlue">
<h4>BLUE ON</h4>
</div>
<div ng-hide="showBlue">
<h4>BLUE OFF</h4>
</div>
<div ng-show="showGreen">
<h4>GREEN ON</h4>
</div>
<div ng-hide="showGreen">
<h4>GREEN OFF</h4>
</div>
</div>
</div>Dirty Checking (Angular)
Virtual DOM (React)
Multiplatform
Learn once; write anywhere
Multiplatform
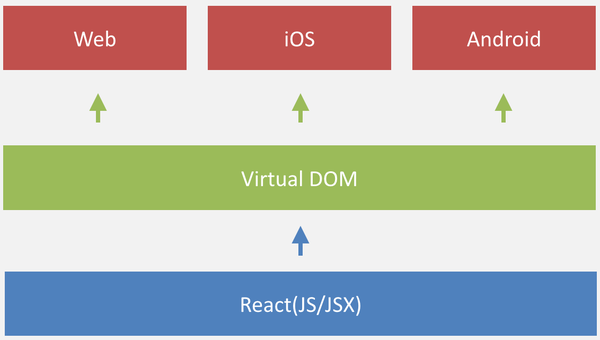
React Native (ios)
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, Text } from 'react-native';
class HelloWorldApp extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Text>Hello world!</Text>
);
}
}
AppRegistry.registerComponent('HelloWorldApp', () => HelloWorldApp);React is for UI and not webapps
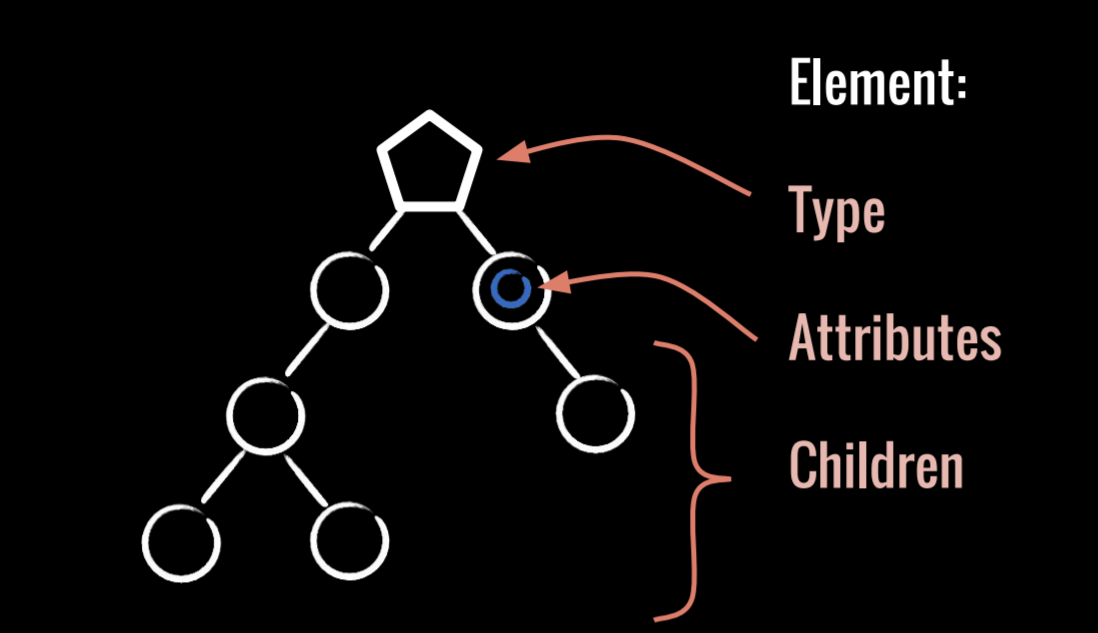
Component
(Data) => Element
UI Element
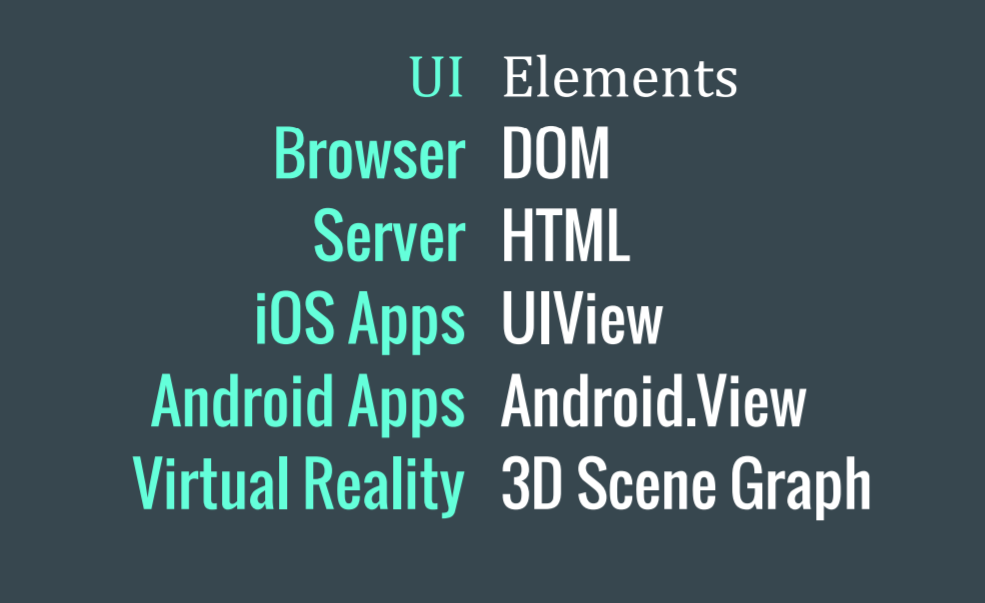
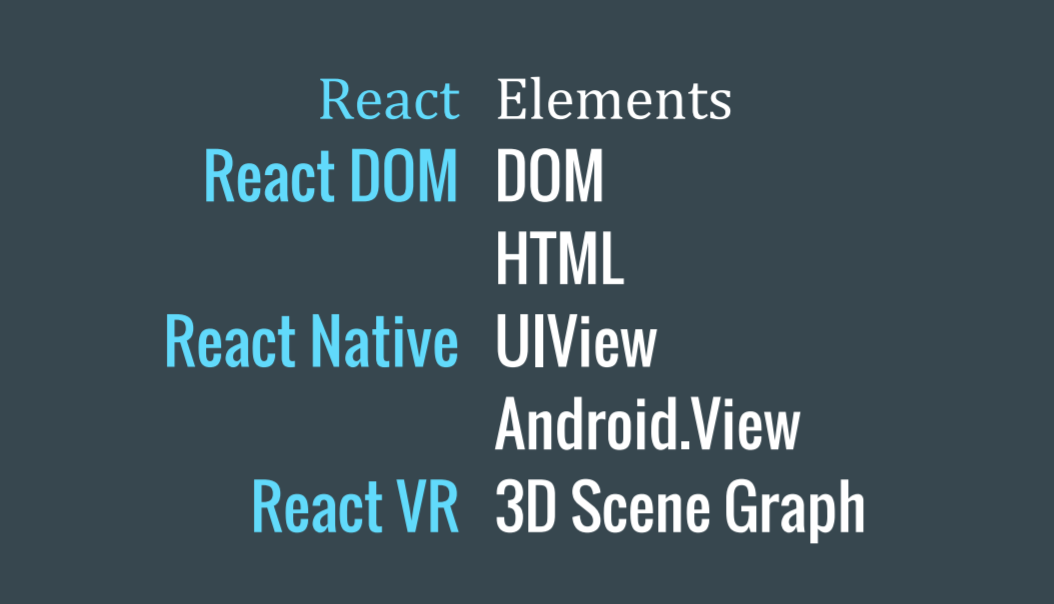
Redux
Architecture Pattern for
uni-directinal data flow
Uni-directional data flow
Initial Data
Realtime Updates
User Input
Dispatcher
Store
View
Traditional MVC
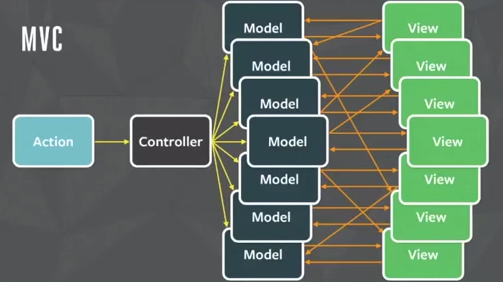
Redux
Datastore
var appState = {
user: {
name: 'madhan'
},
taskData: {
filter: 'pending',
tasks: [
'task A',
'task B'
]
}
};Read State
Action(s)
var action = {
ACTION: 'SHOW_PENDING'
};var action = {
action: 'TASKS_LOADED',
tasks: [
...
]
};Fire Action
Reducer(s)
BE & FE State
function reducer(state = [], action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'TASKS_LOADED':
state = Object.assign({}
, action.data);
return state;
default:
return state;
}
}View(s)
React - Redux
App Root
Page
Page
CompG
CompB
CompC
CompD
CompE
CompF
CompA
CompH
React State Tree
BE & FE State
Connect
props
dispatch
Redux Advantages
Single Source of truth
Time travel debugging
Persist-able State
Hot reloading of data
State is read only
State is read only
Thank You!
React: UI Library
By Madhan Ganesh L
React: UI Library
- 1,017



