nuclear
radiation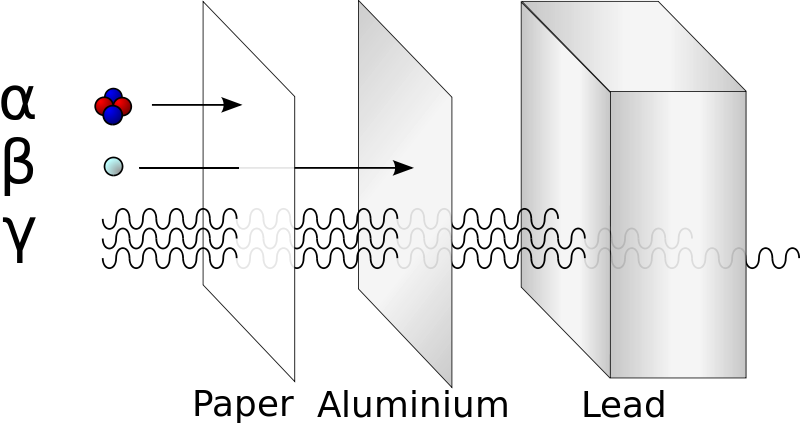
radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which EM waves travel through a vacuum or through matter-containing media; the existence of a media to propagate the waves is not required.
Tips:
vacuum:an empty area or space
matter-containing:not empty...
EM:electromagnetic(电磁的)
propagate:spread
Ralated knowledge:
-
Radiation is widespread in our daily life, any object does have radiation.
- Most of the radiation is harmless, such as radio waves, visible light, and the infrared(红外) waves …
- Well, some of them can also be fatal. For example, the nuclear radiation.
WHAT IS NUCLEAR
RADIATION?
In physics, the nuclear radiation was called radioactive decay, also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity, is the process by which a nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting particles(粒子) of ionizing(电离) radiation.
Tips:
decay:become weaker or less good (衰变)
unstable:likely to change, unsettled (不稳定的)
emitting particles of ionizing radiation:电离辐射放出粒子
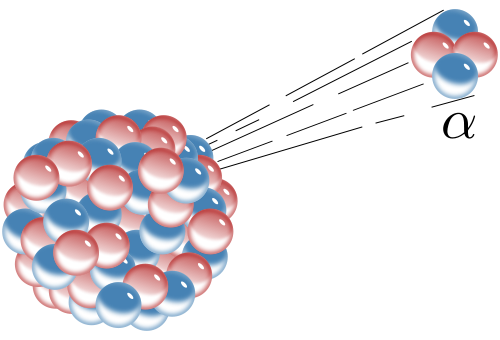
Alpha decay is one example type of radioactive decay, in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle, and thereby transforms (or 'decays') into an atom with a mass number(质量数) decreased by 4 and atomic number(原子序数) decreased by 2.
some beneficial uses
- Medicinal, such as radio therapy(放疗) and X-rays
- In smoke detectors (do you remember that boy?)
- In tracing locations of gas or liquid leaks or
- Tracing locations of malfunctioning in the body (isotope)
- Sterilization(消毒) of medical instruments or bacteria or moulds(霉菌) in foods (ultraviolet light)
printf("制作人(不分先后):\n");
cout<<"李敏成"<<endl;
echo "徐瑞阳"
print "张全琛"
sys.stdout.write("Thanks For Watching!")
nuclear radiation
By magine
nuclear radiation
- 311



