Kotlin
Next level of Java










www.leanpub.com/effectivekotlin

www.kt.academy
Kotlin history
2010
2011
2012
JetBrains unveiled Kotlin
Start Development
Open sourced
Feb 2016




Feb 2016
May 2016
May 2017
Official Android Support

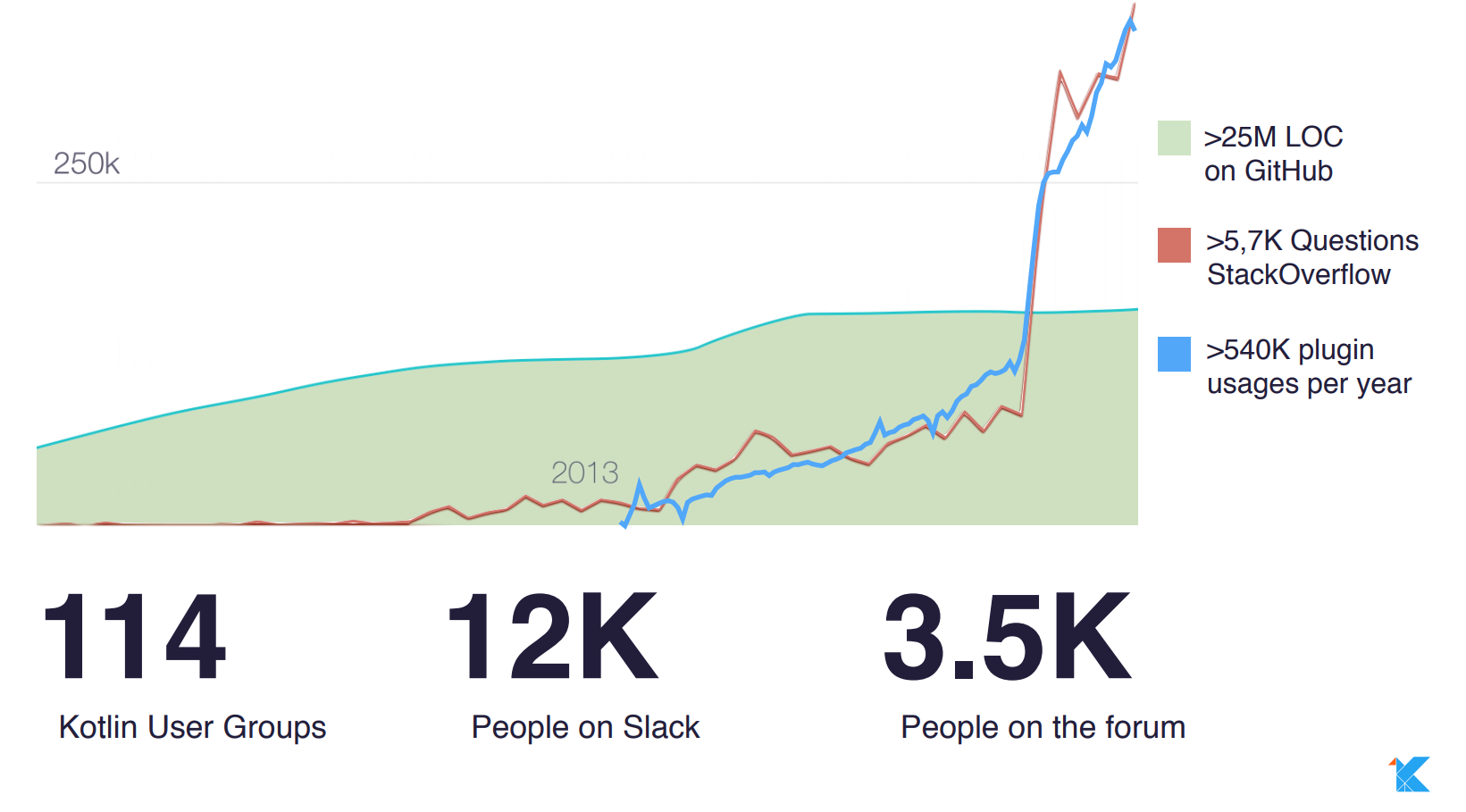
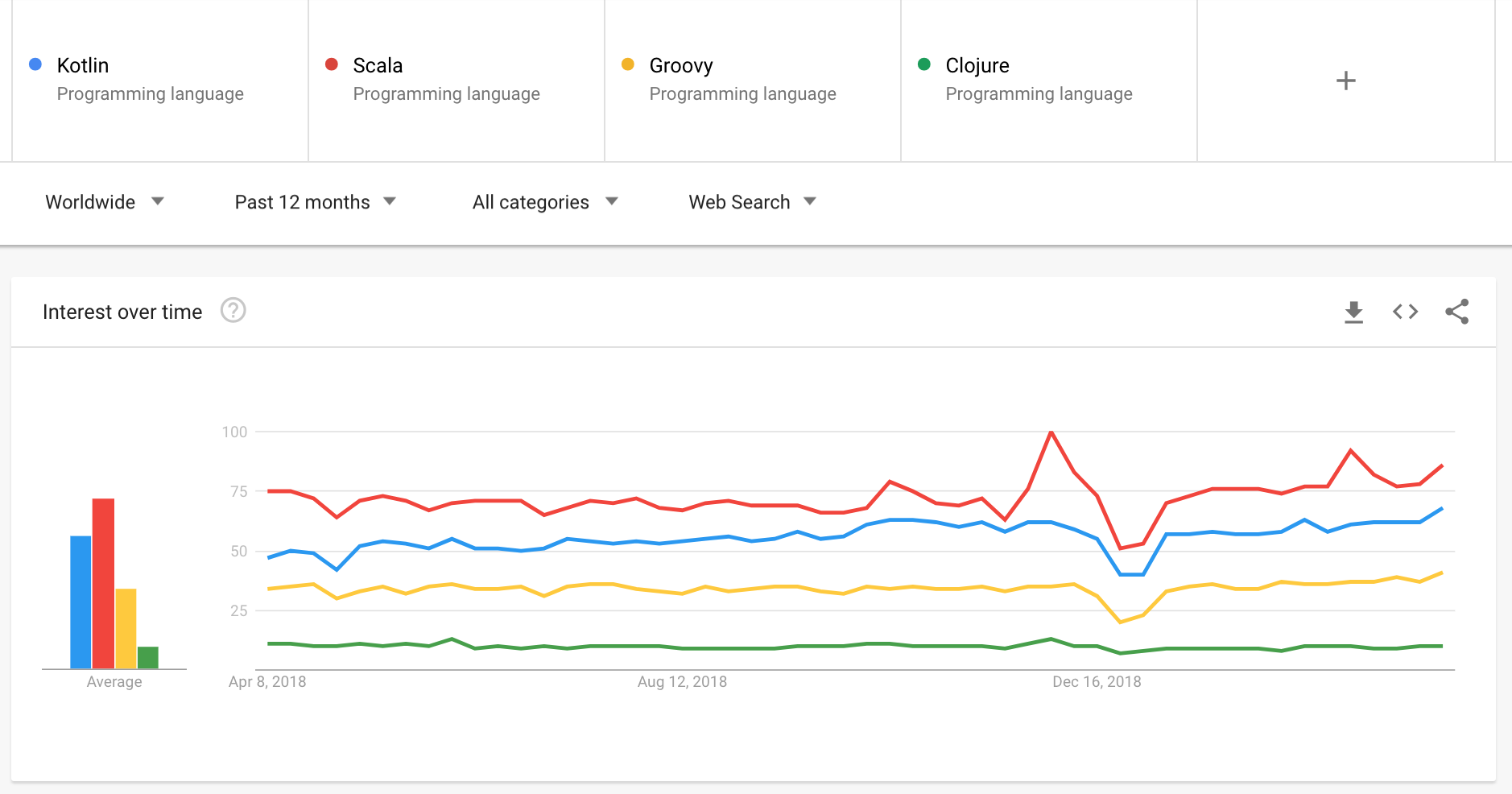
https://trends.google.com/

https://android-developers.googleblog.com/2018/10/
kotlin-momentum-for-android-and-beyond.html
Safeness
Language safeness - more errors can be prevented by checks at compile time instead of falling at run time. Also language is referred as safe when it is promoting way of coding that is know as more secure.
Billion-dollar mistake

Sir Charles Hoare
"This has led to innumerable errors, vulnerabilities, and system crashes, which have probably caused a billion dollars of pain and damage in the last forty years."
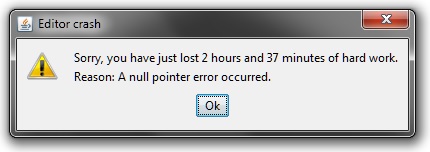
Null safety
var person: Person
Must be inilialized
var person: Person = null
Not null type cannot be null
var person: Person? = null? after type makes it nullable
person.name
Nullable must be unpacked
Null safety
person?.nameSafe call (null if person is null)
person!!.nameUnsafe call (exception if person is null)
if(person != null) {
person.name
}Smart Cast (after nullability check, object is casted to not-null)
if(person == null)
return
person.nameif(person != null && person.name == "Marcin")if(person == null || person.age < 18)person?.school?.nameElvis operator
val name = person?.name ?: "unknown"val name = person?.name ?: throw Error("No person or name is null")
val name = person?.name ?: returnRead-only properties
val name: String = "Marcin"Read only
var name: String = "Marcin"Read-write
val list = listOf("A", "B", "C")
val name: String by lazy { getNameFromForm() }Read-only properties
MutableListMutable
ListImmutable
var list = listOf("A", "B", "C")
list += "D"
list -= "A"val list = mutableListOf("A", "B", "C")
list.add("D")
list.remove("A")Object-Oriented
Kotlin
Classes
Classes
// Java
public class PersonJava {
private String name;
private String surname;
private int age;
PersonJava(String name, String surname, int age) {
this.setName(name);
this.setSurname(surname);
this.setAge(age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSurname() {
return surname;
}
public void setSurname(String surname) {
this.surname = surname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}Classes
class Person {
var name: String
var surname: String
var age: Int
constructor(name: String, surname: String, age: Int) {
this.name = name
this.surname = surname
this.age = age
}
}class Person(name: String, surname: String, age: Int) {
var name: String = name
var surname: String = surname
var age: Int = age
}class Person(var name: String, var surname: String, var age: Int)Classes
// Kotlin
class Person(
var name: String,
var surname: String,
var age: Int
)// Java
public class PersonJava {
private String name;
private String surname;
private int age;
PersonJava(String name, String surname, int age) {
this.setName(name);
this.setSurname(surname);
this.setAge(age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSurname() {
return surname;
}
public void setSurname(String surname) {
this.surname = surname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}Data Classes
data class Person(
var name: String,
var surname: String,
var age: Int
)- toString
- equals / hashCode
- copy
class Person(
var name: String,
var surname: String,
var age: Int
)Data Classes - toString
val person = Person("Johny", "Bravo", 34)
println(person)normal classs: Person@5305068a
data class: Person(name=Johny, surname=Bravo, age=34)
Data Classes - equals
val person1 = Person("Johny", "Bravo", 21)
val person2 = Person("Johny", "Bravo", 21)
println(person1 == person2)Java default behaviour: false
Kotlin data class behaiour: true
Data Classes - copy
val person1 = Person("Johny", "Bravo", 21)
val person2 = person1.copy(surname = "Cage")
println(person1)
println(person2)Prints:
Person(name=Johny, surname=Bravo, age=21)
Person(name=Johny, surname=Cage, age=21)
val person1 = Person("Johny", "Bravo", 21)
val person2 = person1.copy()
println(person1)
println(person2)Prints:
Person(name=Johny, surname=Bravo, age=21)
Person(name=Johny, surname=Bravo, age=21)
Conciseness and
code reusability
Java Utils hell
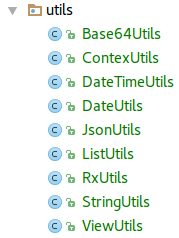
Java Utils hell
Arrays.asList(1,2,3);listOf(1,2,3)List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);Java Utils hell
view.visibility = View.GONEview.hide()ViewUtils.hide(view)Java Utils hell
val replacedStr = StringUtils.replaceAll(str, "name" to name, "surname" to surname)
val capitalizedStr = StringUtils.capitalize(replacedStr)str.replaceAll("{name}" to name, "{surname}" to surname)
.capitalize()

Kotlin extension functions
fun String.noLongerThen(max: Int): String {
return this.substring(0, Math.min(max, this.length))
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
println("Joe".noLongerThen(4)) // Joe
println("James".noLongerThen(4)) // Jame
println("Ashley".noLongerThen(4)) // Ashl
}fun View.hide() {
this.visibility = View.GONE
}Functions everywhere
fun double(i: Int) = i * 2
class A() {
fun triple(i: Int) = i * 3
fun twelveTimes(i: Int): Int {
fun fourTimes() = double(double(i))
return triple(fourTimes())
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
double(1) // 2
A().twelveTimes(2) // 24
}Top-level function
Mamber function
Local function
Kotlin extension properties
val Context.inflater
get() = getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE) as LayoutInflatervar View.isVisible: Boolean
get() = visibility == View.VISIBLE
set(value) {
visibility = if (value) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE
}context.inflaterprogress.isVisible = trueHigher level of code extraction
fun sum(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
var sum = 0
for (i in a..b) {
sum += i
}
return sum
}
fun product(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
var product = 1
for (i in a..b) {
product *= i
}
return product
}Higher level of code extraction
fun sum(a: Int, b: Int) = fold(a, b, 0, { acc, i -> acc + i })
fun product(a: Int, b: Int) = fold(a, b, 1, { acc, i -> acc * i })
fun fold(a: Int, b: Int, initial: Int, operation: (Int, Int)->Int): Int {
var acc = initial
for (i in a..b) {
acc = operation(acc, i)
}
return acc
}Higher level of code extraction
fun sum(a: Int, b: Int) = (a..b).fold(0) { acc, i -> acc + i }
fun product(a: Int, b: Int) = (a..b).fold(1) { acc, i -> acc * i }//Imperative
val filteredList = arrayListOf<String>()
for (fruit in list) {
if (fruit.startsWith('A'))
filteredList.add(fruit)
}Collection stream processing
//Declatative
val filteredList = list.filter{ it.startsWith("A")}val list = listOf("Apple", "Lemon", "Avocado")Collection stream processing
val filteredList = students
.filter { it.passing }
.filter { it.averageGrade > 4.0 }
.sortedBy { it.averageGrade }
.take(10)inline fun <T, R> Iterable<T>.map(transform: (T) -> R): List<R> {
val destination = ArrayList<R>()
for (item in this) destination.add(transform(item))
return destination
}
inline fun <T> Iterable<T>.filter(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): List<T> {
val destination = ArrayList<T>()
for (item in this) if(predicate(item)) destination.add(item)
return destination
}
...Collection stream processing
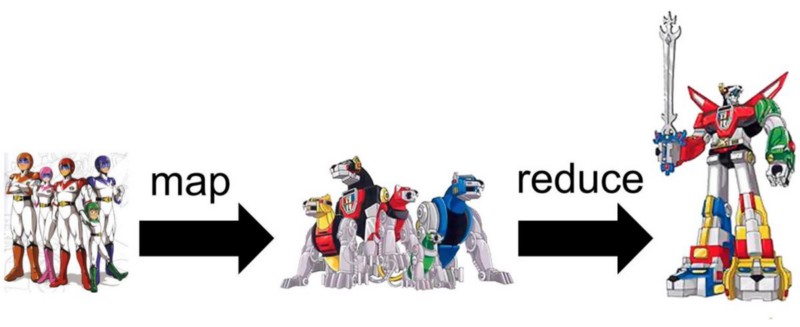
"This is Sparta".map { it.toUpperCase() }.toString() // THIS IS SPARTA
Collection stream processing
String processing
val str = list.joinToString("|", "(", ")", 2, "...", { it.toUpperCase() })
val str = list.joinToString(separator = "|")Result: Apple|Lemon|Avocado
val str = list.joinToString(separator = "|", prefix = "(", postfix = ")")Result: (Apple|Lemon|Avocado)
val str = list.joinToString(separator = "|", transform = { it.toUpperCase() })Result: APPLE|LEMON|AVOCADO
Collection sorting
val personList: List<Person> = listOf(...)val sortedList = personList.sortedWith(compareBy({ it.surname }, { it.name }))val sortedList = personList.sortedWith(compareBy(Person::surname, Person::name))val sortedList = personList.sortedBy { it.fullName }Multiplatfom development
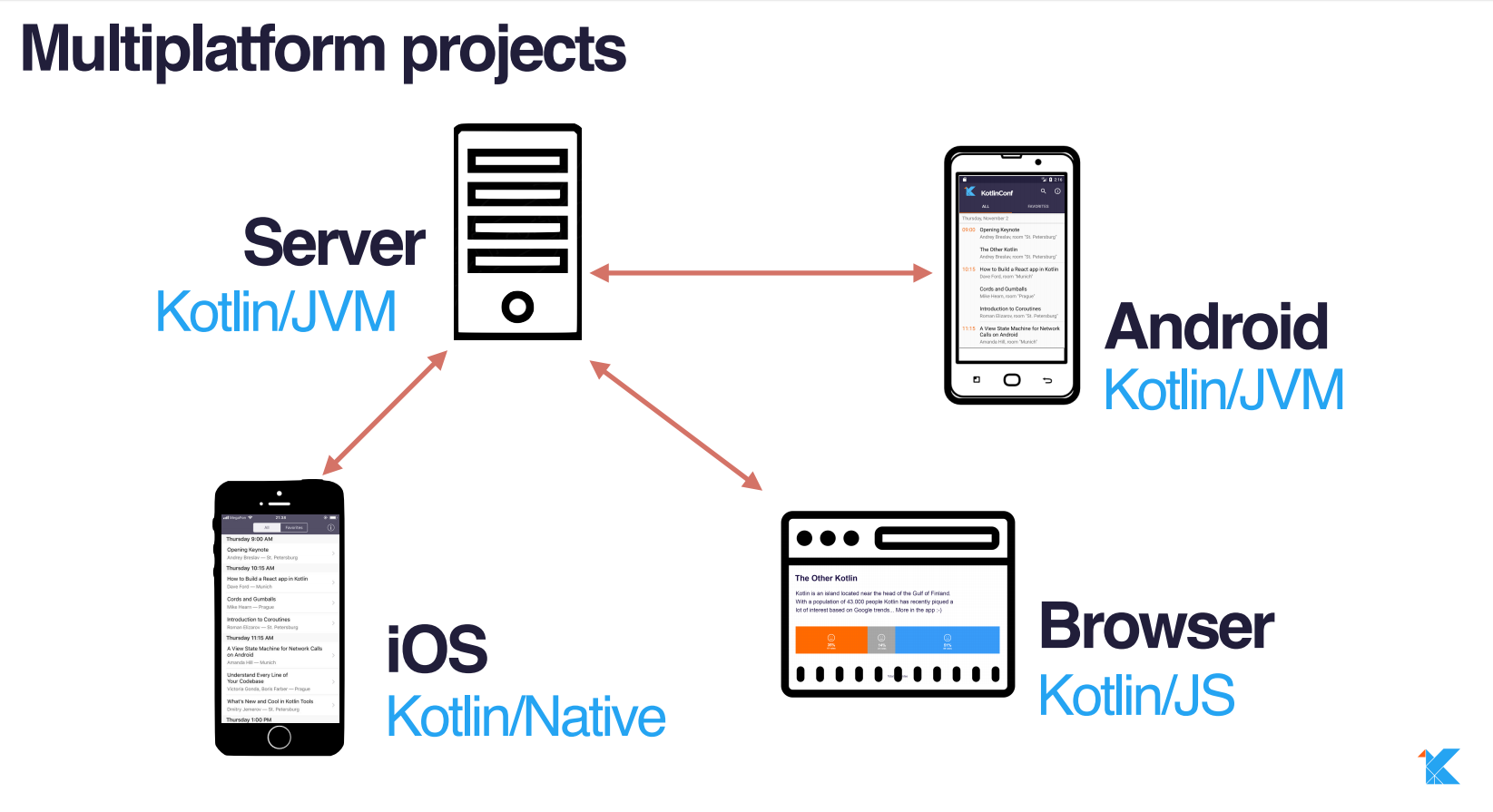
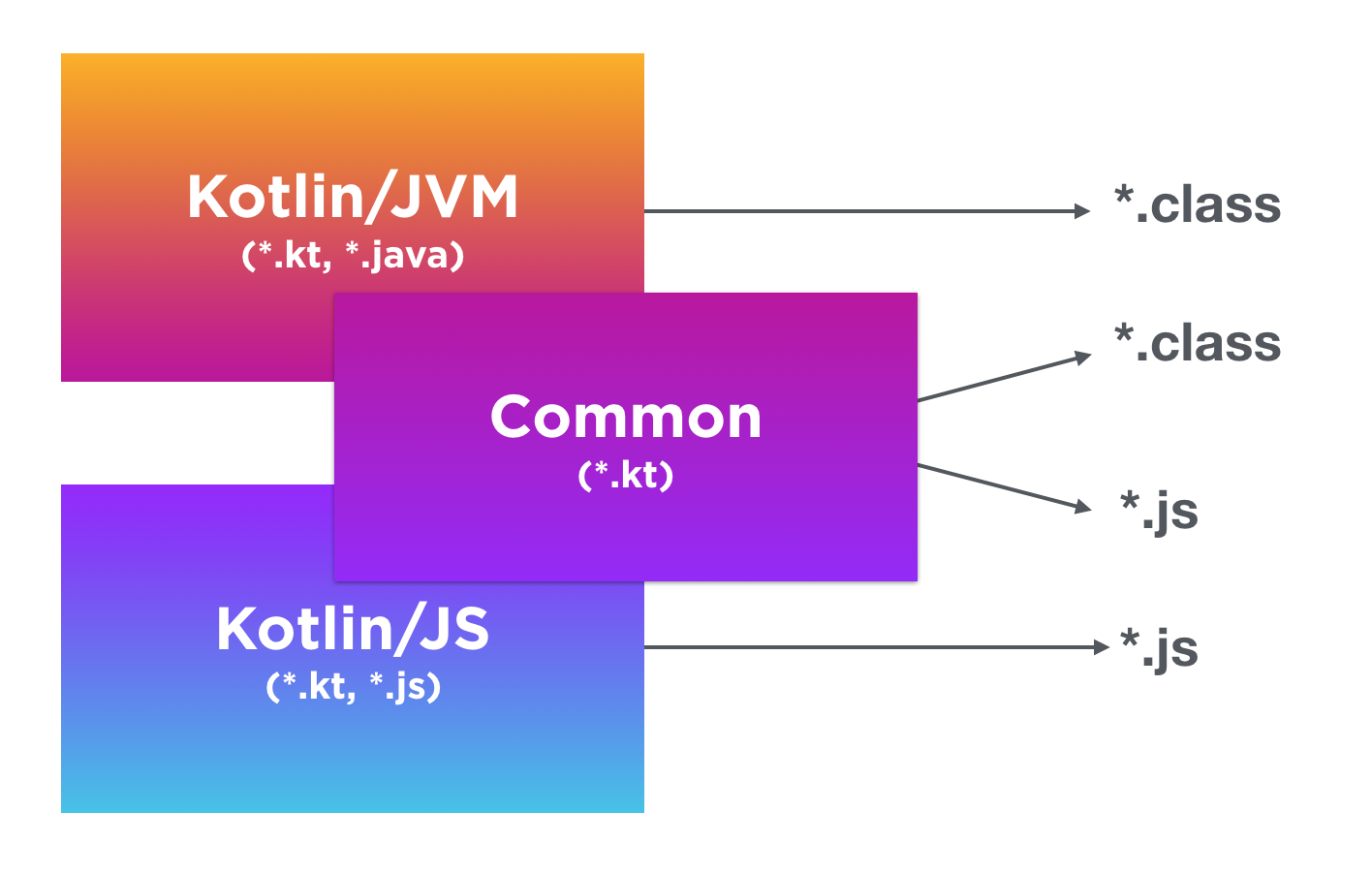



Native development
Native bytecode
We can easily use all platform-specific libraries and solutions
We use native libraries and solutions like OpenGL or GLES
Let's start using Kotlin
Website
IDE


Android
Studio
Intellij
Idea
Eclipse

CLion
IDE
Interoperability


Project








Java 2 Kotlin Converter


- Whole classes
- Paste code

Resources
References
Getting started with Kotlin on Android
https://developer.android.com/kotlin/get-started.html
Kotlin language reference
https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/
Kotlin Koans


www.kt.academy
blog.kotlin-academy.com
Biggest Medium publication dedicated to Kotlin
Questions?
@marcinmoskala
marcinmoskala.com
contact@kt.academy
Warsaw "Kotlin: Next level of Java"
By Marcin Moskala
Warsaw "Kotlin: Next level of Java"
- 1,400



