Webpack: A newcomer introduction

Mario Terron
Frontend developer at beezy

@marioterron_
About this talk

- What is webpack?
- How webpack does that?
- How to use Webpack?
- Core Concepts
- DEMO
- Q&A
What is webpack?

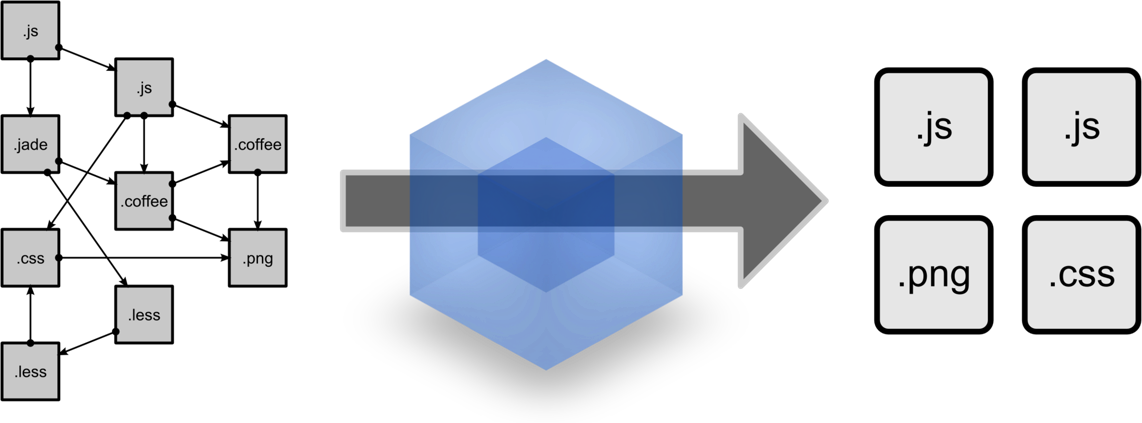
Module with dependencies
Static assets
And that's it?
tree shaking - unused code elimination
Hot module replacement - Makes it possible to swap modules live. For example can update your CSS WITHOUT FORCING A REFRESH
code splitting - Split your code into various bundles wich can then loaded on demand or in parallel
ASSET CACHING - Add Content hashes to every generated asset
how does webpack do that?

It takes an application (An entry poinT to an app)
Creates a dependency tree of all stuff is required
Proccess all stuff
Emits optimized assets representing this application




HOW TO USE WEBPACK?

Defining a config file
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry:'./src/index.js',
output: {
path: 'path.resolve(__dirname, 'build')',
filename: 'bundle.js'
}
}
BUT...
Since version 4, webpack does not require a configuration file to bundle your project
#0CJS
The core concepts

module.exports = {
entry: './path/to/my/entry/file.js'
};ENTRY
TELLS WEBPACK WHAT FILES TO LOAD FOR THE BROWSER

Output
Tells Webpack WHERE and HOW to distribute bundles
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './path/to/my/entry/file.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
}
};

Loaders
Tells Webpack HOW to interpret and translate files.
module: {
output: {
filename: 'my-first-webpack.bundle.js'
},
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, use: ‘babel-loader’ },
{ test: /\.css$/, use: ‘css-loader’ }
],
}
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.scss$/,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'sass-loader']
}
],
},
};
Chaining Loaders
styleLoader(cssLoader(sassLoader("source")))You can think of these as function calls. The output of one loader feeds as input into the next:
1. The test property identified wich file or files shoul be transformed
2. The use property indicates which loader should be used to do the transformig
AT A HIGH LEVEL, LOADERS HAVE TWO PURPOSES IN YOUR WEBPACK CONFIGURATION:
PLUGINS
Adds additional functionallity to compilations
module: {
output: {
filename: 'my-first-webpack.bundle.js'
},
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, use: ‘babel-loader’ },
{ test: /\.css$/, use: ‘css-loader’ }
],
}
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const webpack = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin(),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({template: './src/index.html'})
]
};
MODE
Allows you enable webpack's built-in optimizations that correspond to each environment
module.exports = {
mode: 'production'
};
DEMO

QUESTIONS?

References
-
webpack docs (https://webpack.js.org)
-
survivejs (https://survivejs.com/webpack)
-
wepback medium (https://medium.com/webpack)
-
webpack Tutorials (https://github.com/markerikson...)
-
WEBPACK Advanced Techniques (HTTPS://GITHUB.COM/MARKERIKSON...)
THANKS!

Webpack: A newcomer introduction
By Mario Terron
Webpack: A newcomer introduction
- 259

