Data Mining Overview
Tables
Hypercubes
Metacube
Tables
Goals
- Data mining tables aggregate information from many feature tables to provide insight or answer a question
- Data mining tables are used to create hypercubes for analyzing experiments
Features
- Data mining tables do not affect the recommendation system in production
- Data mining tables are used for analysis of features during a sliding 90-day timeframe
Extract
Transform
Load
Extract

Transform


Load

Load to Redshift



Workflow Objects
- Inherits from:
- hive_workflow
- hive_daily_workflow
- Option to upload to Redshift
- Custom validation logic
Successes
- Easy to create a workflow
- Configurable
- Upstream validation
- Terminal validation
Regrets
- Latency in extract phase
- Source of truth is Redshift
- String transform in load to Redshift
- Formatting difficulties
- Many workflow objects
- Duplicated tests
The Future
Table Name
Schedule
Frequency
Dependencies
Validation
Hypercubes
Goals
- Hypercubes allow slicing, or dimension reduction
- Hypercubes allow drill-up/drill down; you can analyze one dimension or increase complexity by examining interaction between many dimensions
- Hypercubes allow roll up; you can summarize across one dimension
Features
- Hypercubes can be configured on the fly (CLI) or in a more permanent fashion (hypercubes.py)
- Hypercubes are self-building
- Hypercube queries are optimized for performance
- Hypercubes are shareable and can be combined
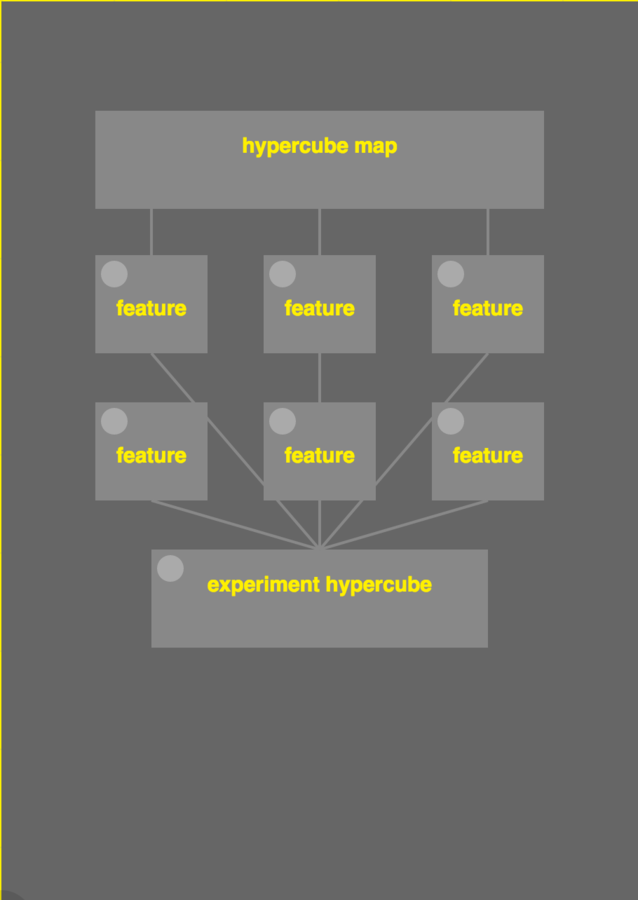
Hypercube Components
- Hypercube map
- Hypercube core
- Feature Hypercube
- Experiment Hypercube

Successes
- Configurable
- Componetized
Regrets
- High latency building multiple hypercubes, even with multiprocessing
The Future
Component
Experiment
Hashing
Measures
Features
Denominators
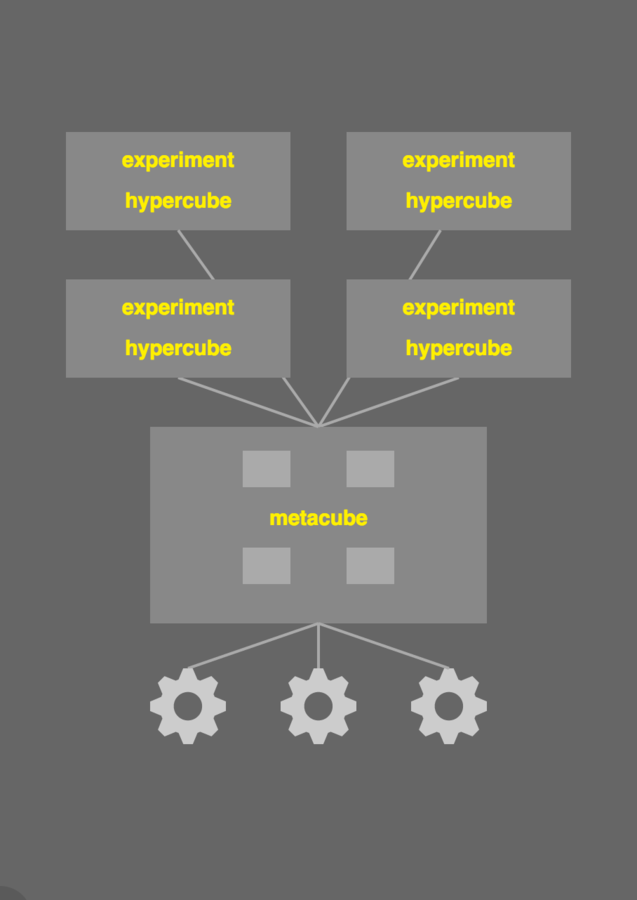
Metacube
Overview
The metacube combines all of the experiment hypercubes into one table for uploading to redshift, for use in Tableau, R, & Chartio.
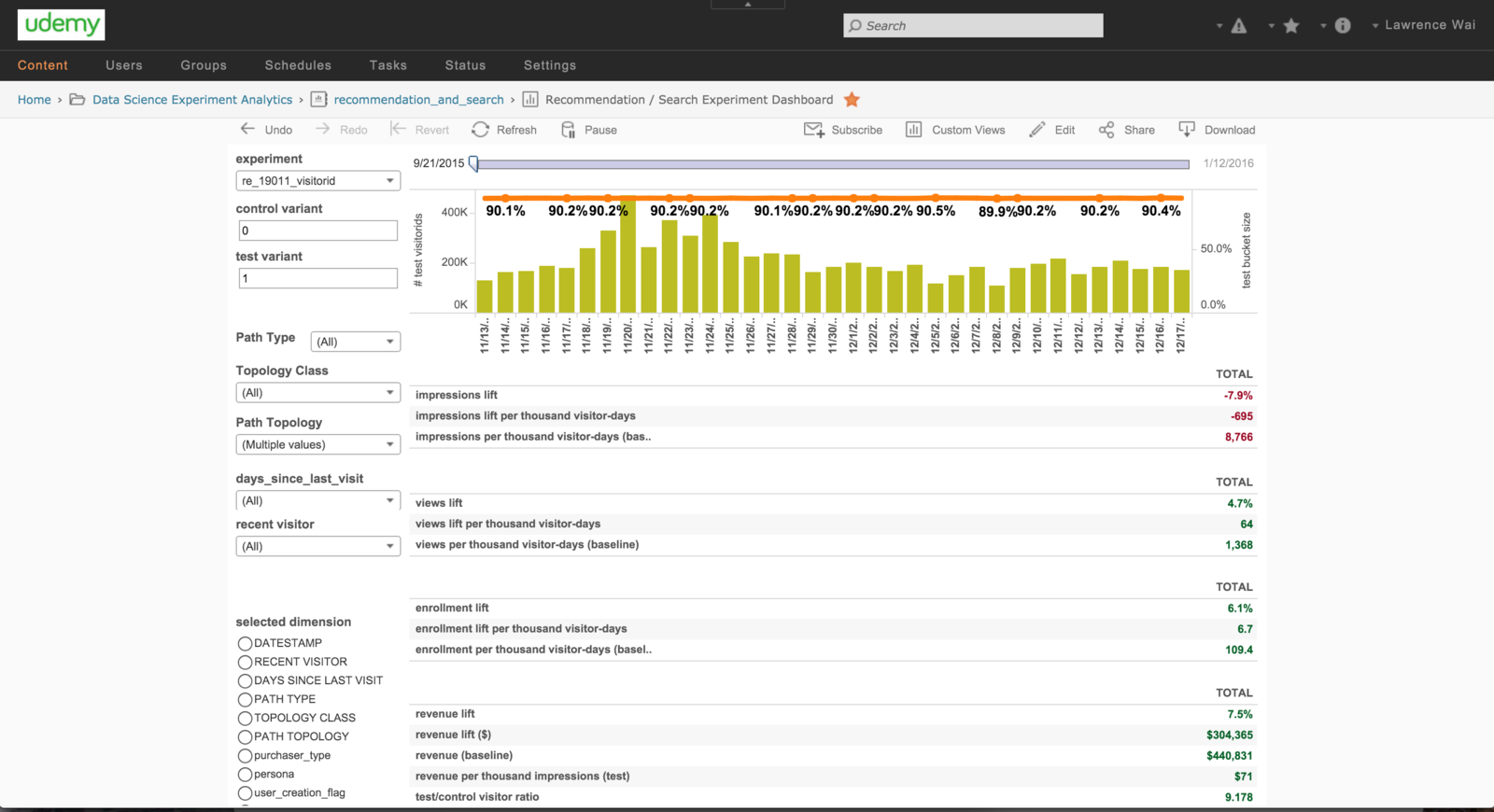
Experiment Workbook
Data Mining Overview
By marswilliams
Data Mining Overview
- 472



