Intro to
Functional
JavaScript
Bianca Gandolfo
JavaScript Evangelist
slides: http://bit.ly/func-slides
exercises: http://bit.ly/func-exercises
Who is this for?
2-6mos experience learning JavaScript
Completed JS tutorial like Codecademy, CodeSchool, Khan Academy, or Bloc.io
Want to solidify fundamentals
Looking for more practice
Interested in getting into Hack Reactor

Part 1
Review and solidify core JS principles with project.
Part 2
Get started with functional methods.
After
Use foundation to grow as a JS engineer.


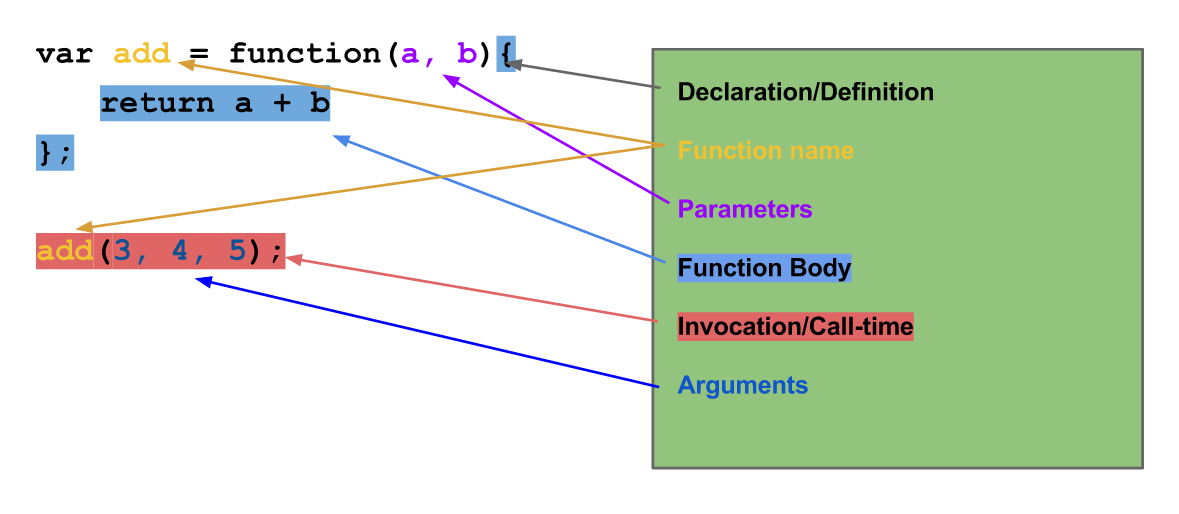
Anatomy
Scope
Overview
- Local
- Global
- Nested Scopes
- Precedence
- Block Scope


Local Scope
var func = function(){
var local = true;
};
console.log(local);var x = 'global!';var x = 'global!';
//inside a function
function encapsulate(){
z = 'global here, too!';
}var x = 'global!';
//inside a function
function encapsulate(){
z = 'global here, too!';
window.y = 'also global!';
}

Global Scope

Parent vs Child Scope
var g = 'global';
function blender(fruit) {
var b = fruit;
var y = 'yogurt';
function bs() {
alert( b + ' and ' + y + ' makes ' + b + ' swirl');
}
bs();
}
blender('blueberry');
Privacy
var g = 'global';
function blender(fruit) {
var b = fruit;
var y = 'yogurt';
function bs() {
alert( b + ' and ' + y + ' makes ' + b + ' swirl');
}
bs();
}
blender('blueberry');creating scopes


Precedence
var g = "global";
function go() {
var l = "local";
var g = "in here!";
alert(g + " inside go");
}
go();
alert(g + " outside go");
Block Scope
var inBlock = false;
for(var i = 0; i < 5; i++){
var inBlock = true;
};
if(inBlock){
console.log('Is there block scope? ' + !inBlock);
}Exercise Time

Questions

Closure
Closure Example
var closureAlert = function(){
var x = "Help! I'm a variable stuck in a closure!";
var alerter = function(){
alert(x);
};
alerter();
};
Closure Example
var closureAlert = function(){
var x = "Help! I'm a variable stuck in a closure!";
var alerter = function(){
alert(x);
};
setTimeout(alerter, 1000);
console.log('will still run right after');
};
Closure Example
var closureAlert = function(){
var x = 0;
var alerter = function(){
alert(++x);
};
return alerter;
};
var funcStorer = closureAlert();
var funcStorer2 = closureAlert();
funcStorer();
Closure Example
var add = function(num){
var num1 = num;
var addToNum1 = function(num2){
return num1 + num2;
};
return addToNum1;
};
Closure Example
function counter() {
var n = 0;
return {
count: function() { return ++n; },
reset: function() { n = 0; }
};
};
Closure Example
function counter() {
var n = 0;
return {
count: function() { return n++; },
reset: function() { n = 0; }
};
};
var c = counter(), d = counter(); c.count();
d.count();
c.reset();
c.count();
d.count();
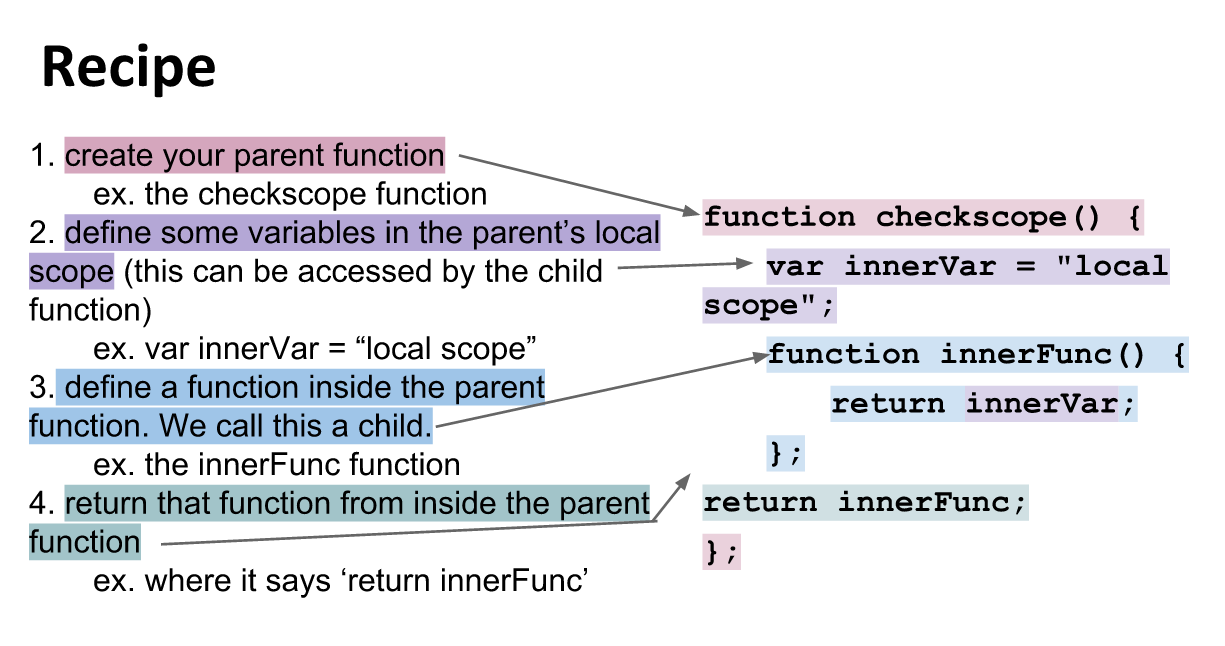
Recipe

Execution


Gotcha!
var sayAlice = function(){
var makeLog = function() {
console.log(alice);
};
var alice = 'Why hello there, Alice!';
return makeLog;
};
var makeStopwatch = function(){
console.log('initialized');
var elapsed = 0;
console.log(elapsed);
var stopwatch = function(){
console.log('stopwatch');
return elapsed;
};
var increase = function(){ elapsed++; };
setInterval(increase, 1000);
return stopwatch;
};
var x = makeStopwatch();
Module Pattern
var Module = function(){
var privateProperty = 'foo';
function privateMethod(args){
// do something
};
return {
publicProperty: "",
publicMethod: function(args){
// do something
},
privilegedMethod: function(args){
privateMethod(args);
}
};
};
Module Pattern
var Car = function(){
var gasolineLevel = 10;
function useGas(amt){
if(gasolineLevel - amt < 0){
console.log("out of gas :[");
} else {
gasolineLevel -= amt;
}
};
return {
radioStation: "104.5",
changeStation: function(station){
this.radioStation = station;
},
go: function(speed){ useGas(speed); }
};
};
Exercises
Questions
Higher- Order Functions and Callbacks
1. takes a function as an input (argument)
element.addEventListener("click", function(){
console.log("element clicked!");
});2. returns a function as the output
var add = function(num){
var num1 = num;
return addToNum1 = function(num2){
return num1 + num2;
};
};Higher-Order Functions

var ifElse = function(condition, isTrue, isFalse){
if(condition){
isTrue;
} else {
isFalse;
}
};
ifElse(true,
function(){ console.log(true);},
function(){ console.log(false);}
);Callbacks

var ifElse = function(condition, isTrue, isFalse){
if(condition){
isTrue();
} else {
isFalse();
}
};
var logTrue = function(){ console.log(true); };
var logFalse = function(){ console.log(false); };
ifElse(true,logTrue,logFalse);Callbacks

var increment = function(n){ return n + 1; };
var square = function(n){ return n*n; };
var doMathSoIDontHaveTo = function(n, func){ return func(n); };
doMathSoIDontHaveTo(5, square);
doMathSoIDontHaveTo(4, increment);Passing Arguments

var ifElse = function(condition, isTrue, isFalse){
if(condition){
isTrue();
} else {
isFalse();
}
};Passing Arguments

var ifElse = function(condition, isTrue, isFalse, arg){
if(condition){
isTrue(arg);
} else {
isFalse(arg);
}
};Passing Arguments

var ifElse = function(condition, isTrue, isFalse){
if(condition){
isTrue.apply(this, [].slice.call(arguments,3));
} else {
isFalse.apply(this, [].slice.call(arguments,3));
}
};[xtra credit]Passing Arguments

Exercises
Questions
Underscore.js
underscore.js
What is it? a utility library that provides functional methods for you to use in your JS.
Where is it? http://underscorejs.org/
Include it in your HTML:
Annotated Source:
http://underscorejs.org/docs/underscore.html

_.each() defined
_.each([1,2,3], function(val,i,list){
console.log(val);
});
- Iterates over a list of elements, yielding each in turn to an iterator function.
- Each invocation of iterator is called with three arguments: (element, index, list). If list is a JavaScript object, iterator's arguments will be (value, key, list).

_.each() usage
//_.each(list, iterator)
var pocketmon = ['Charisaur', 'Bulbazard', 'Twomew'];
_.each() usage
//_.each(list, iterator)
var pocketmon = ['Charisaur', 'Bulbazard', 'Twomew'];
var logger = function(val){
console.log(val);
};
_.each() usage
//_.each(list, iterator)
var pocketmon = ['Charisaur', 'Bulbazard', 'Twomew'];
var logger = function(val){
console.log(val);
};
_.each(pocketmon,logger);
Looping with _.each
function AnimalMaker(name) {
return {
speak: function () {
console.log("my name is ", name);
}
};
};
var animalNames = ['', '', ''];
var farm = [];
for(var i = 0; i < animalNames.length; i++){
farm.push(AnimalMaker(animalNames[i]));
}
Looping with _.each
function AnimalMaker(name) {
return {
speak: function () {
console.log("my name is ", name);
}
};
};
var animalNames = ['', '', ''];
var farm = [];
_.each(animalNames, function (name) {
farm.push(AnimalMaker(name));
});
_.map() defined
_.map([1,2,3], function(v,i,list){console.log(v)})
- Produces a new array of values by mapping each value in list through a transformation function (iterator).
- Each invocation of iterator is called with three arguments: (element, index, list). If list is a JavaScript object, iterator's arguments will be (value, key, list).

_.map() usage
//_.map(list, iterator)
var pocketmon = ['Charisaur', 'Bulbazard', 'Twomew'];
_.map() usage
//_.map(list, iterator)
var pocketmon = ['Charisaur', 'Bulbazard', 'Twomew'];
var excitedArr = function(val){
return val + '!!!';
};
_.map() usage
//_.map(list, iterator)
var pocketmon = ['Charisaur', 'Bulbazard', 'Twomew'];
var excitedArr = function(val){
return val + '!!!';
};
var excitedPocketmon = _.map(pocketmon,excitedArr);
Looping with _.map
function AnimalMaker(name) {
return {
speak: function () {
console.log("my name is ", name);
}
};
};
var animalNames = ['', '', ''];
var farm = []
_.each(animalNames, function (name) {
farm.push(AnimalMaker(name));
});
Looping with _.map
function AnimalMaker(name) {
return {
speak: function () {
console.log("my name is ", name);
}
};
};
var animalNames = ['', '', ''];
var farm = _.map(animalNames, function (name) {
return AnimalMaker(name);
});
_.map vs _.each
function AnimalMaker(name) {
return {
speak: function () {
console.log("my name is ", name);
}
};
};
var animalNames = ['', '', ''];
var farm = _.map(animalNames, function (name) {
return AnimalMaker(name);
});
_.each(farm, function (animal) {
animal.speak();
});
Exercises
Questions
Copy of intro to func
By Matthew Gutierrez
Copy of intro to func
- 351