The Zen of Cookies
Maxim Tsoy
Head of R&D at Surfly
Loves the Web
Cookies
ancient
sophisticated
don't make sense
Zen
ancient
sophisticated
don't make sense

1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API

1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
Set-Cookie: riddle=voldemort;Path=/;Domain=london.co.uk;httpOnly;Secure1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them
1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them

4.
1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them
4. Cookies contain sensitive data and should be protected
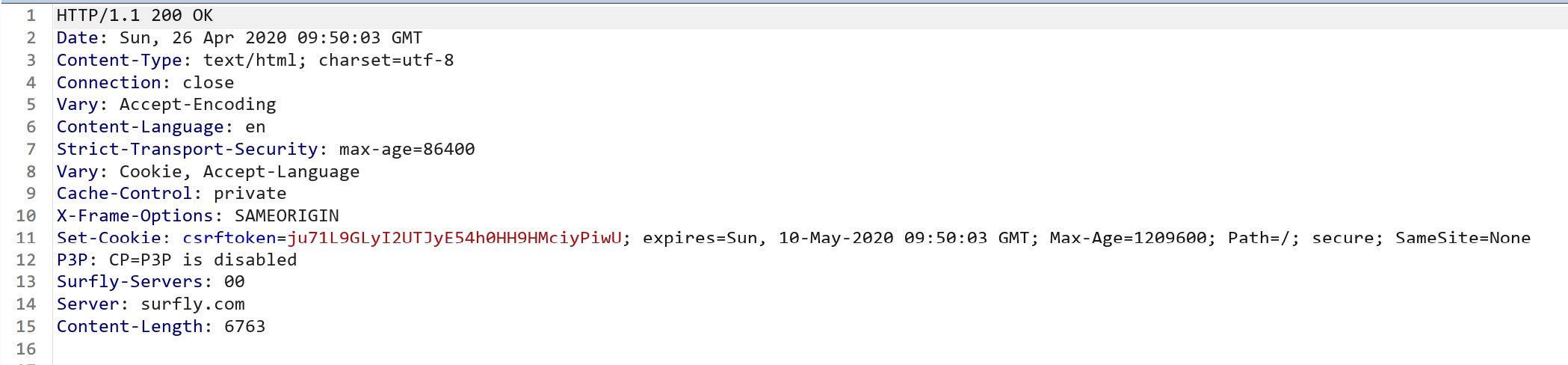
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Set-Cookie: super_secret=tomato-is-a-fruit!; Path=/cart/; httpOnly; Secure
Content-Length: 0
1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them
4. Cookies contain sensitive data and should be protected
1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them
4. Cookies contain sensitive data and should be protected
Browser extensions

HTML way
<meta http-equiv="Set-Cookie" content="name=value">Removed in Chrome in 2018:
Removed in Firefox in 2019:

HTML way
<meta http-equiv="Set-Cookie" content="name=value">
Still works in
document.cookie API

getter vs setter

no errors or useful return values
document.cookie

document.cookie
// cookie store jank example from
// https://github.com/WICG/cookie-store/blob/master/explainer.md#reacting-to-session-state-changes
function decode_document_cookie(value) {
// Simplified version of the code at https://github.com/js-cookie/js-cookie.
const cookie_strings = value.split('; ');
const cookies = {};
for (const cookie_string of cookie_strings) {
const index = cookie_string.indexOf('=');
const name = cookie_string.substring(0, index);
const encoded_value = cookie_string.substring(index + 1);
cookies[name] = decodeURIComponent(encoded_value);
}
return cookies;
}
let old_value = null;
function poll(duration_ms, cookie_name, handle_cookie_change) {
const cookies = decode_document_cookie(document.cookie);
const newValue = (cookie_name in cookies) ? cookies[cookie_name] : null;
if (old_value !== new_value) {
handle_cookie_change(new_value);
old_value = new_value;
}
setTimeout(() => {
poll(duration_ms, cookie_name, handle_cookie_change);
}, duration_ms);
}
is synchronous
Scope of existing cookies?
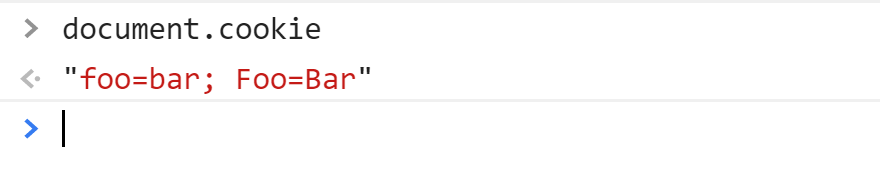
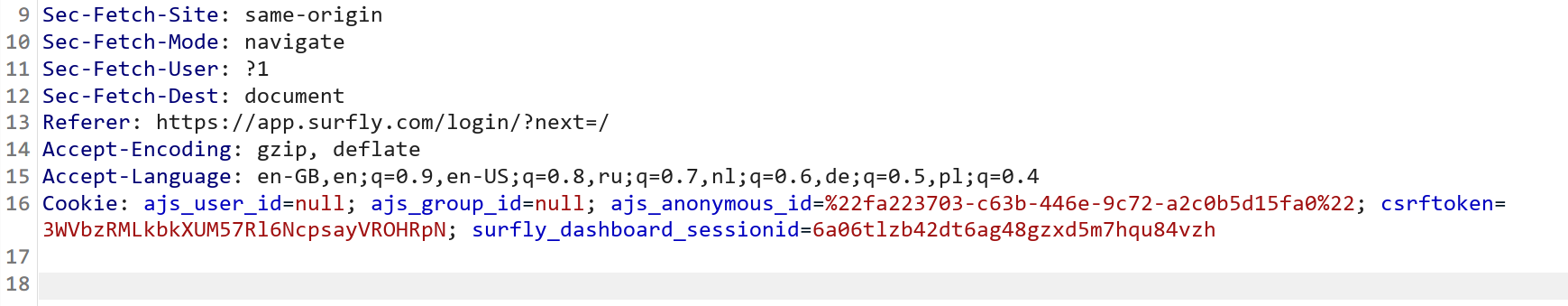
Cookie: foo=bar; Foo=BarJS:
HTTP:
Scope of existing cookies?
console.log(document.cookie) // -> "cat=dead"document.cookie = 'cat=alive'console.log(document.cookie) // -> "cat=dead; cat=alive"document.cookie = 'cat=dead; domain=example.com'1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them
4. Cookies contain sensitive data and should be protected
Set-Cookie format
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue; Path=/; Domain=cocobolo.com; HttpOnly; Secure
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue; Path=/; Domain=.cocobolo.com; HttpOnly; Secure
Set-Cookie: cookiename▓=▓cookievalue;▓Path▓=▓/;▓Domain▓=▓cocobolo.com;▓HttpOnly;▓Secure
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue;Path=/;Domain=cocobolo.com;HttpOnly;Secure
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue;pATh=/;DoMaIN=cocobolo.com;hTtPOnlY;seCURE
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue; Path=/; Domain=cocobolo.com; HttpOnly=really; Secure=forsure
Set-Cookie: __Secure-cookiename=cookievalue; Path=/; Domain=cocobolo.com; HttpOnly; Secure
Set-Cookie format
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue;;;;;;Path=/;;;;;;Domain=cocobolo.com;;;;;HttpOnly;;;;;Secure
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue; Path=/; Domain=cocobolo.com; HttpOnly; Secure
Set-Cookie: cookiename=cookievalue ; Path=/notthis/; Path=/notthiseither/; Path=/andnoteventhis/; Path=/; Domain=cocobolo.com; HttpOnly; Secure
Parsing implementations
rarely match the browser behaviour
Parsing implementations


Safari DevTools: (in recent versions, only "a" will be set)
cookie folding is still supported by many library implementations
Parsing caveats

Cookies with empty name
Parsing caveats
Cookies with empty value

Parsing caveats
Special characters

Parsing caveats
"=" is valid in the value

Parsing caveats
whitespaces

Parsing caveats
Only ASCII is allowed by the spec

Cookie: foo=春节回家路but all major browsers support UTF-8:
1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them
4. Cookies contain sensitive data and should be protected
Cookie scope
- name
- Path
- Domain
- httpOnly
- Secure
- SameSite
- Expires, Max-Age
Cookie attributes:
Name, Path and Domain define the cookie's identity
Cookie scope
These are all different cookies:
Set-Cookie: name=Dwalin; Path=/
Set-Cookie: name=Balin; Path=/profile/
Set-Cookie: name=Kili; Path=/profile/cart/;
Set-Cookie: name=Fili; Path=/profile/cart/change/;
Set-Cookie: name=Dori; Path=/; Domain=.example.com
Set-Cookie: name=Nori; Path=/profile/; Domain=.example.com
Set-Cookie: name=Ori; Path=/profile/cart/; Domain=.example.com
Set-Cookie: name=Oin; Path=/profile/cart/change/; Domain=.example.com
Set-Cookie: name=Gloin; Path=/; Domain=www.example.com
Set-Cookie: name=Bifur; Path=/profile/; Domain=www.example.com
Set-Cookie: name=Bofur; Path=/profile/cart/; Domain=www.example.com
Set-Cookie: name=Bombur; Path=/profile/cart/change/; Domain=www.example.comThe page at https://www.example.com/profile/cart/change/ will receive:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Cookie: name=Dwalin; name=Balin; name=Kili; name=Fili; name=Dori; name=Nori; name=Ori; name=Oin; name=Gloin; name=Bifur; name=Bofur; name=Bombur
Cookie scope
document URL vs cookie URL
https://example.com/healthy/
oatmeal=yes; Path=/healthy/
chocolate=no; Path=/tasty/
history.pushState({}, '', '/tasty/')Change the document URL:
https://example.com/tasty/
oatmeal=yes; Path=/healthy/
chocolate=no; Path=/tasty/
document.cookie == "oatmeal=yes"document.cookie == ???Cookie scope
document URL vs cookie URL
https://example.com/healthy/
oatmeal=yes; Path=/healthy/
chocolate=no; Path=/tasty/
history.pushState({}, '', '/tasty/')Change the document URL:
https://example.com/tasty/
oatmeal=yes; Path=/healthy/
chocolate=no; Path=/tasty/
document.cookie == "oatmeal=yes"document.cookie == "oatmeal=yes"
Cookie scope
document URL vs cookie URL
https://example.com/healthy/
oatmeal=yes; Path=/healthy/
chocolate=no; Path=/tasty/
history.pushState({}, '', '/tasty/')Change the document URL:
https://example.com/tasty/
oatmeal=yes; Path=/healthy/
chocolate=no; Path=/tasty/
document.cookie == "oatmeal=yes"document.cookie == "chocolate=no"
Cookie scope
<iframe src="about:blank"></iframe>
<iframe></iframe>
<iframe srcdoc="<p>Inner HTML</p>"></iframe>
<iframe
src="blob:https://example.com/432bd868-f211-417e-aae4-c94892c13945">
</iframe>
<iframe src="file:///C:/Users/muodov/Desktop/secret.html"></iframe>
<iframe src="data:text/html,<p>inner HTML</p>"></iframe>document.cookie = 'foo=bar' inside these iframes?
Cookie scope
<!-- Chrome, FF, Safari: inherit parent scope, IE11: empty -->
<iframe src="about:blank"></iframe>
<iframe></iframe>
<iframe srcdoc="<p>Inner HTML</p>"></iframe>
<!-- Firefox: inherit parent scope, Chrome and Safari: empty -->
<iframe
src="blob:https://example.com/432bd868-f211-417e-aae4-c94892c13945">
</iframe>
<!-- Chrome doesn't set cookies, others do -->
<iframe src="file:///C:/Users/muodov/Desktop/secret.html"></iframe>
<!-- Chrome raises DOMException, Firefox and Safari: empty -->
<iframe src="data:text/html,<p>inner HTML</p>"></iframe>document.cookie = 'foo=bar' inside these iframes?
1. Cookies can be set via Set-Cookie response header or JS API
2. Setting a cookie requires a special string format
3. Browsers send cookies back to the site that has set them
4. Cookies contain sensitive data and should be protected
Weak integrity
Set-Cookie: coca=cola; Path=/chuck/
• https://example.com/jimmy/ can set cookie on any other path:
Set-Cookie: coca=cola; Domain=.google.com // will be received by maps.google.com and mail.google.com
• https://google.com can set cookies on any subdomain:
Weak integrity
Set-Cookie: coca=cola; Path=/chuck/
• https://example.com/jimmy/ can set cookie on any other path:
Set-Cookie: coca=cola; Domain=github.io // will be set for annie.github.io and johnny.github.io
• https://github.io can set cookies on any subdomain:
Weak integrity
https://my-evil-app.herokuapp.com
could set cookies on all subdomains of .herokuapp.com:
Set-Cookie: coca=cola; Domain=.herokuapp.com
...affecting all other heroku apps like https://my-innocent-app.herokuapp.com
...unless herokuapp.com is an eTLD in the Public suffix list
(next to .com, .net, .co.uk, etc.)
your-own-space.random-hosting.com ?
Weak integrity
• http://example.com
can override Secure cookies set by https://example.com earlier
• httpOnly cookie cannot be overwritten from JS,
but if it was set, server cannot tell whether it is httpOnly or not
Cookie: coca=cola
SameSite cookies
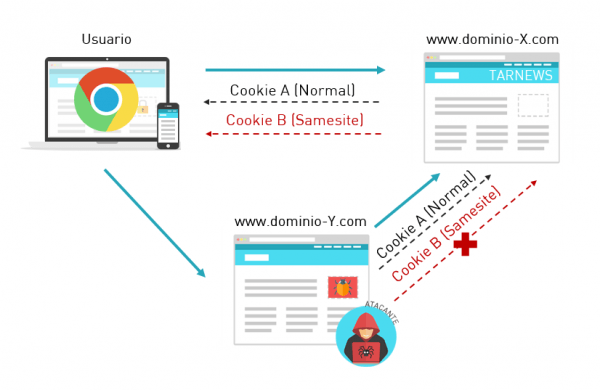
Cookies might be omitted in "cross-site" requests
SameSite cookies: same-site vs cross-site
https://subdomain.example.co.uk:4433/some/path/
SameSite cookies: same-site vs cross-site
https://subdomain.example.co.uk:4433/some/path/
SOP scope
SameSite cookies: same-site vs cross-site
https://subdomain.example.co.uk:4433/some/path/
SOP scope
Cookie scope
SameSite cookies: same-site vs cross-site
https://subdomain.example.co.uk:4433/some/path/
SOP scope
Cookie scope
"same-site" scope
SameSite cookies: same-site vs cross-site
https://evil.com
https://bank.com/sendmoney/
cross-site
http://example.com
https://example.com
same-site
http://example.com:1111
https://example.com:5555
same-site
https://jimmy.example.com
https://chuck.example.com
same-site
What's next?
What's next?
- Cookies are complicated, but there is a lot of ongoing work in Web standards space
- Reducing conflicts between the spec and actual implementations: RFC6265bis
- Asyncronous CookieStore API proposal
- HTTP State Tokens by Mike West

The Zen of Cookies
By Maxim Tsoy