What's new in ReactJS 16
And how does it affect our work?
Overview
-
New Core Algorithm
-
Error Boundary
-
Fragments
-
Portals
-
Better SSR
-
Other new feature
New Core Algorithm
Stack reconciliation VS Fiber reconciliation
Reconciliation
The "diffing" process of virtual DOM in React is called reconciliation
Reconciliation

Stack VS Fiber
Stack VS Fiber
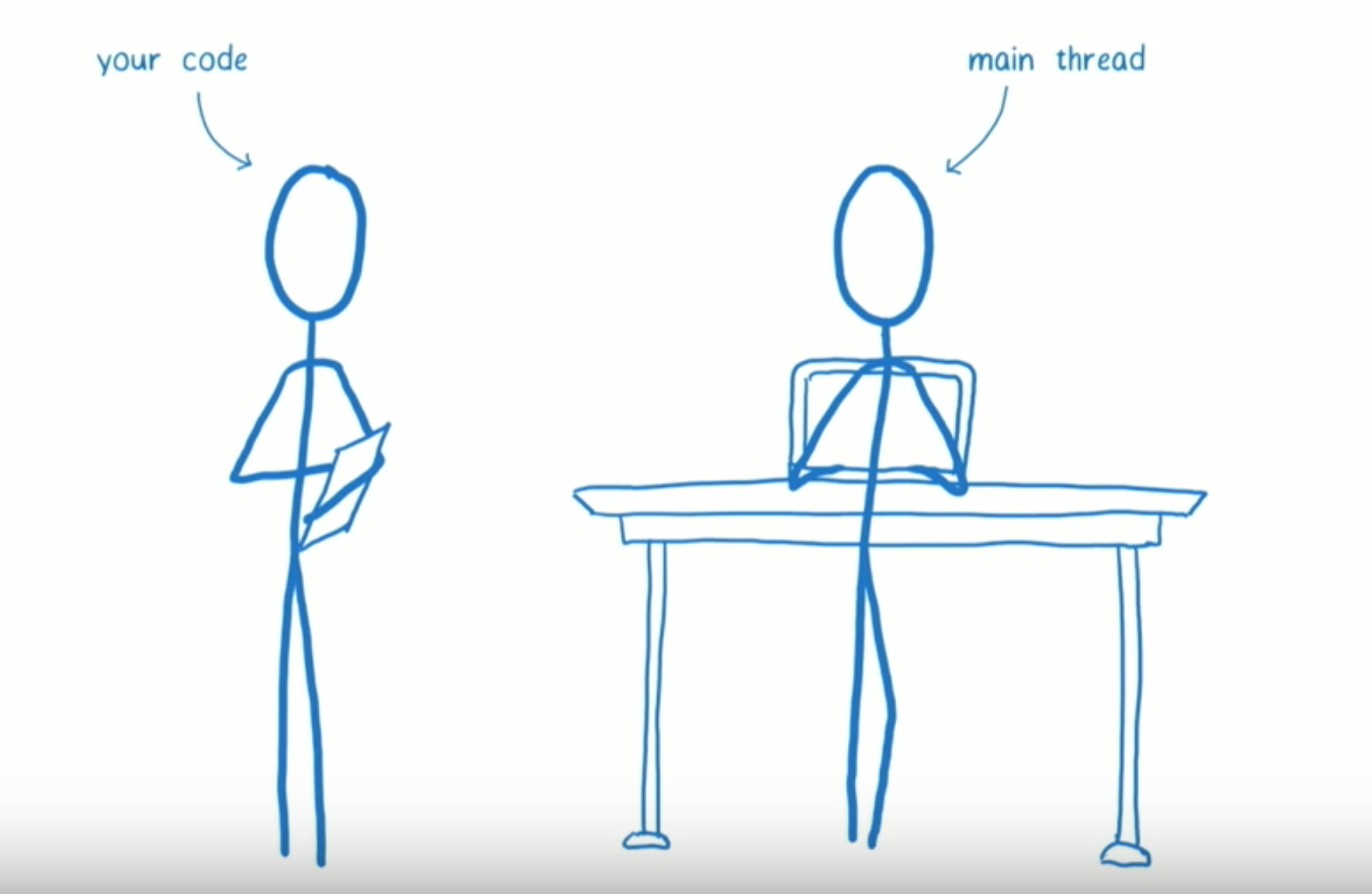
Stack reconciliation
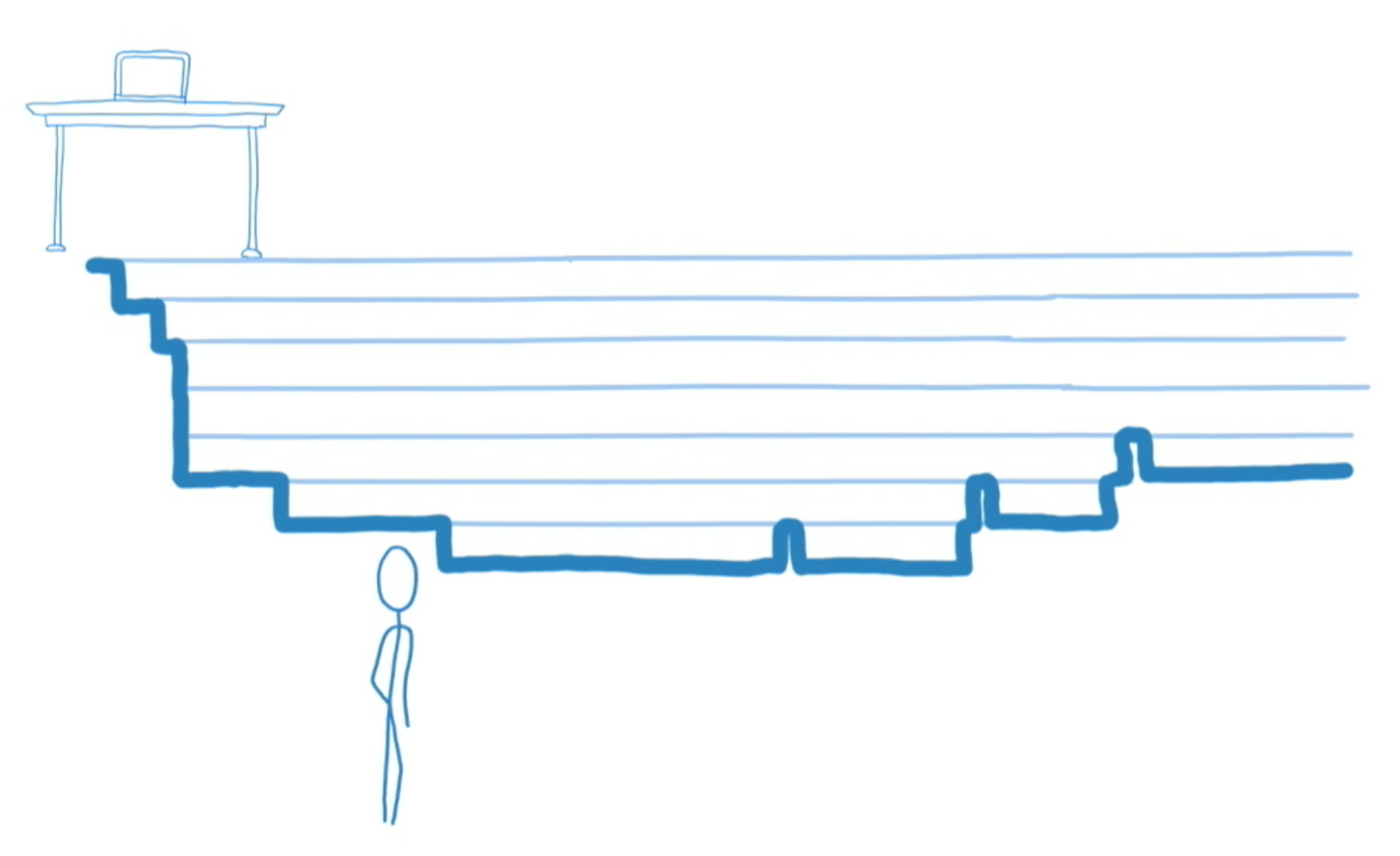
Fiber reconciliation
Cooperative scheduling
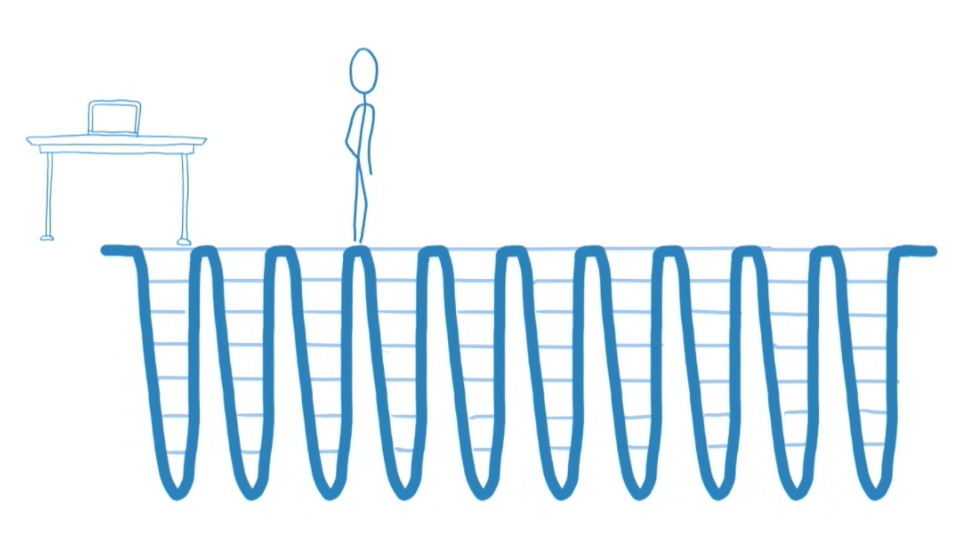
Async Rendering
To split the rendering work into chunks and spread out over multiple frames
Phases
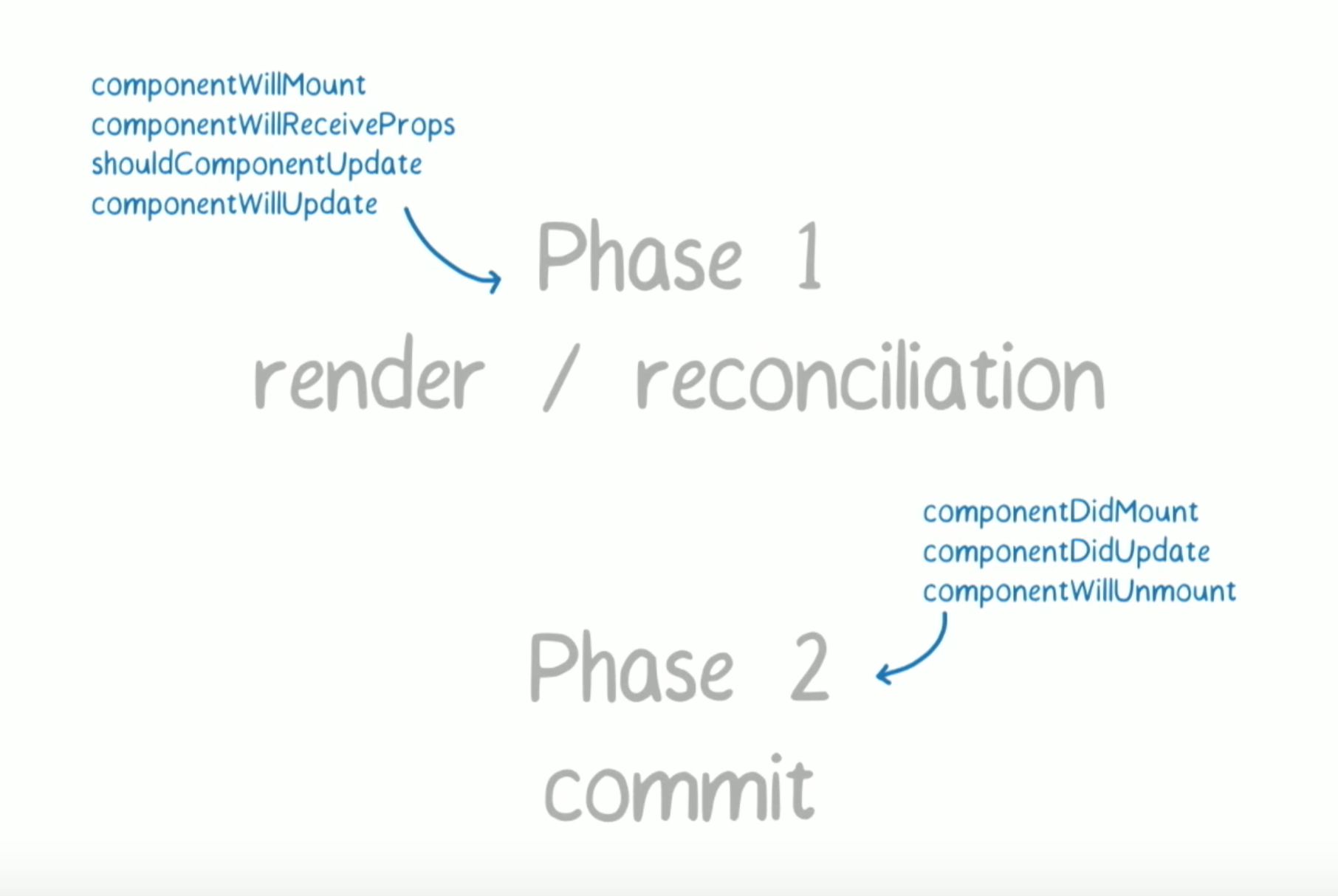
Phases
The commit phase is usually very fast, but rendering can be slow. For this reason, the upcoming async mode (which is not enabled by default yet) breaks the rendering work into pieces, pausing and resuming the work to avoid blocking the browser
Concurrency

Life Cycle Hooks

The life cycle methods may not fire in the same order you expected.
References
Error Boundary
What?😲 LOL
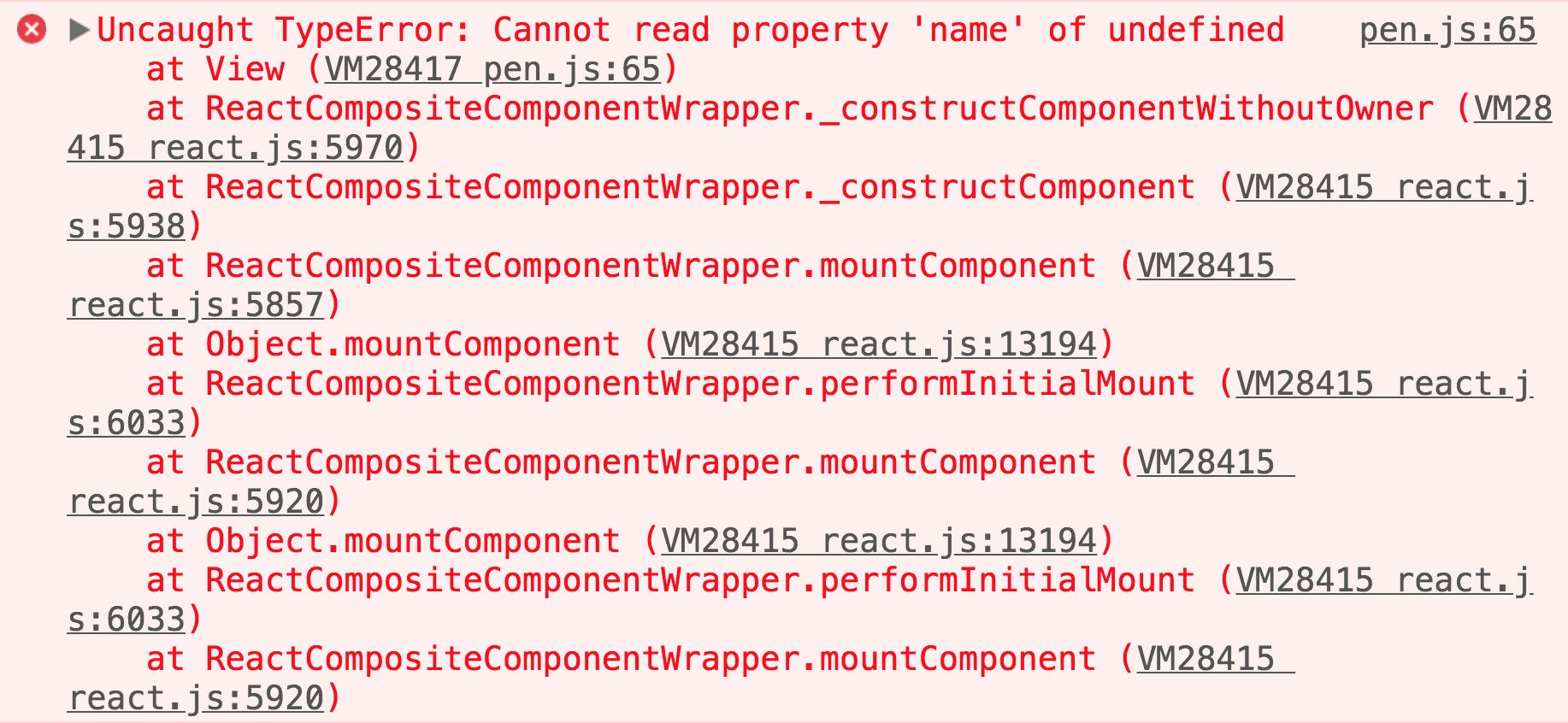
Robust and actionable errors
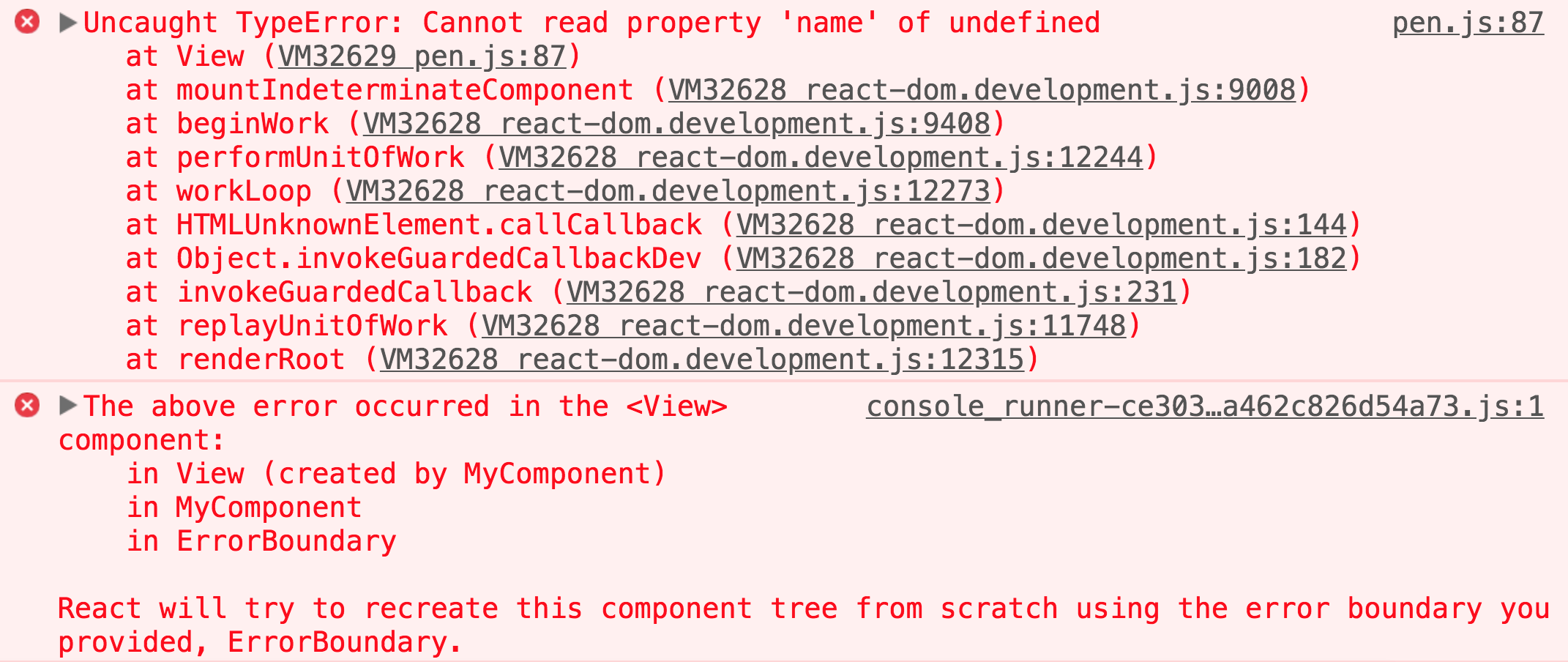
componentDidCatch(error, info)
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
this.setState({ hasError: true });
console.log(error, info);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
const entry =
document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(
<ErrorBoundary>
<MyWidget></MyWidget>
</ErrorBoundary>,
entry
);<div id="root">
<!-- This div's content will
be managed by React. -->
</div>const MyWidget = () => {
return <h2>My Widget</h2>;
}Let's have a try
React 15.1.0: https://codepen.io/melonq/pen/WzWpmM
React 16.3.1: https://codepen.io/melonq/pen/WzWpgd
Error boundaries do not catch errors for
- Event handlers
- Asynchronous code (e.g. requestAnimationFrame or setTimeout callbacks)
- Server side rendering
- Errors thrown in the error boundary itself (rather than its children)
References
The return types of render method
- A single React element
- Booleans, Null, and Undefined
- Strings
- Array
- Fragments
- Portals
Title Text
renderTitles() {
return (
<div>
<h2>MainTitle</h2>
<h3>SubTitle</h3>
</div>
);
}
renderItems() {
return (
<div>
{this.props.items.map((item, index) =>
<ItemElement data={item} key={index} />)
}
</div>
);
}
renderChildren() {
return (
<div>{this.props.children}</div>
);
}
Return an array
render() {
// Don't forget the keys
return [
<li key="A">First item</li>,
<li key="B">Second item</li>,
<li key="C">Third item</li>,
];
}Fragments
render() {
// No need for comma and keys
return (
<React.Fragment>
<li>First item</li>
<li>Second item</li>
<li>Third item</li>
</React.Fragment>
);
}
The shorter syntax sugar - 16.2.0
render() {
return (
<>
Some text.
<h2>A heading</h2>
More text.
<h2>Another heading</h2>
Even more text.
</>
);
}Portals
ReactDOM.createPortal
Portals provide a first-class way to render children into a DOM node that exists outside the DOM hierarchy of the parent component.
Let's have a try
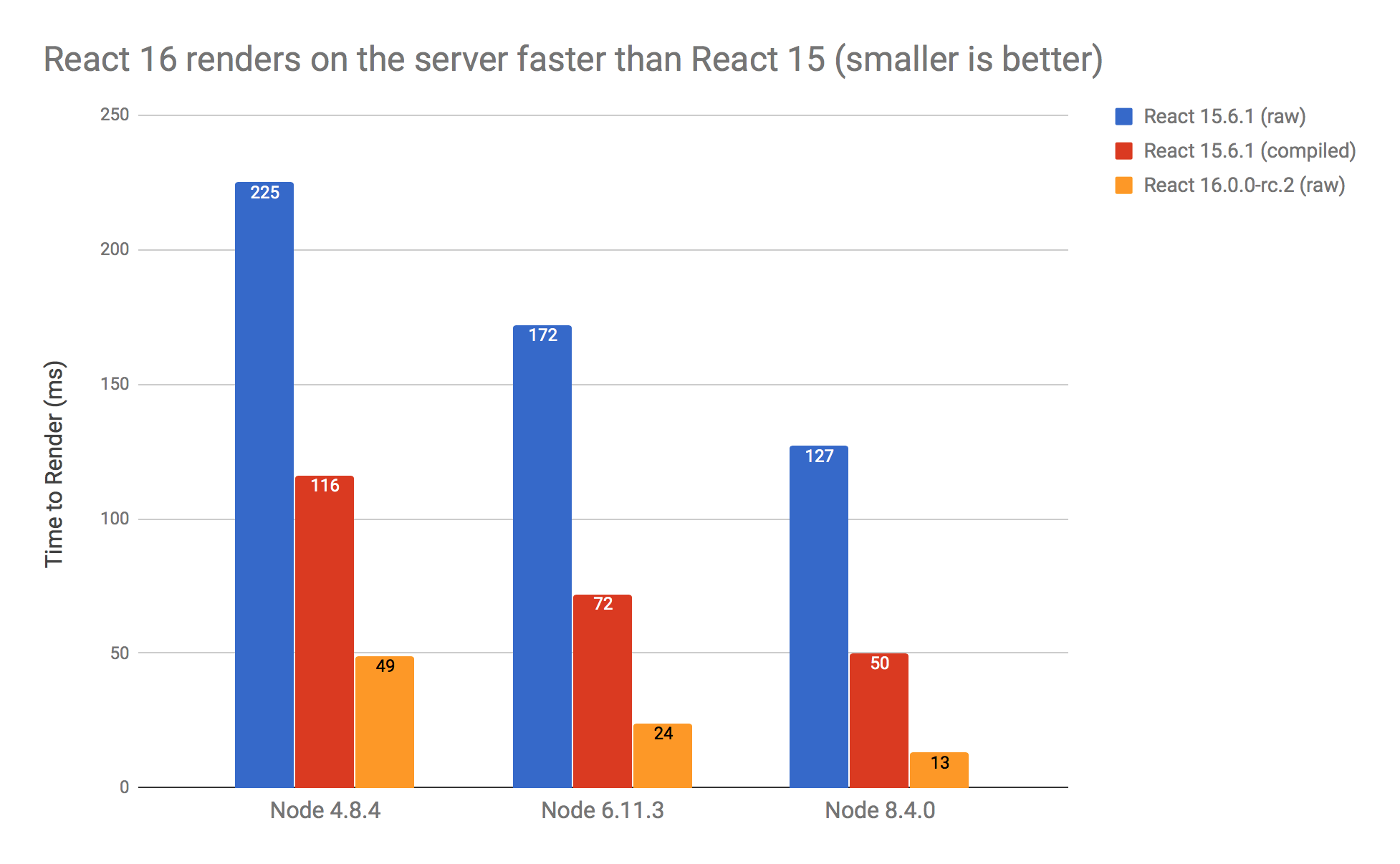
Better SSR
A completely rewritten server renderer
- Support streaming
- Compiles away `process.env` checks
- render() => hydrate()
- Faster
render() => hydrate()
// using Express
import { renderToString } from "react-dom/server"
import MyPage from "./MyPage"
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.write(renderToString(<MyPage/>));
res.end();
});import { render } from "react-dom"
import MyPage from "./MyPage"
const rootDom = document.getElementById("content");
render(<MyPage/>, rootDom);If you’re reviving server-rendered HTML, use ReactDOM.hydrate instead of ReactDOM.render. Keep using ReactDOM.render if you’re just doing client-side rendering.
References
Other new features
- Calling setState with null no longer triggers an update. This allows you to decide in an updater function if you want to re-render.
customCallback(newCount) {
if (newCount !== 0) {
this.setState((prevState, props) => {
return { count: prevState.count + newCount }
});
}
}
customCallback(newCount) {
this.setState((prevState, props) => {
return (newCount !== 0) ? { count: prevState + 1 } : null;
});
}
<div whatever-you-like="anyData">123</div>// Yes, please
<div tabIndex="-1" />
// Warning: Invalid DOM property `tabindex`.
// Did you mean `tabIndex`?
<div tabindex="-1" />createRef() - v16.3
class AutoFocusTextInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.textInput = React.createRef();
}
componentDidMount() {
this.textInput.current.focusTextInput();
}
render() {
return (
<CustomTextInput ref={this.textInput} />
);
}
}Official Context API - v16.3
const Context = React.createContext();
render() {
return (
<Context.Provider value={this.state.contextValue}>
{this.props.children}
</Context.Provider>
);
}render() {
return (
<Context.Consumer>
{context => <Child context={context} />}
</Context.Consumer>
)
}- Identifying components with unsafe lifecycles
- e.g: componentWillMount
- Warning about legacy string ref API usage
- Detecting unexpected side effects
That amounts to a combined 32% size decrease compared to the previous version (30% post-gzip).
Notes
- SSR Doesn’t Support Error Boundaries or Portals.
- React 16 Performs Less Strict Client-Side Checking.
- React16 is backwards compatible.
Feedback is welcome essential

ReactJS 16
By melonq
ReactJS 16
- 832



