Vue.js
Introduction
Vue (pronounced /vjuː/, like view) is a progressive MVVM framework for building interactive user interfaces.
Introduction
- Intuitive
- Fast
- Composable
Comparison
Getting start
-
Import Vue.js
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script> -
Add Dom
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div> -
Give its data
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script><div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})One-way binding
v-bind
Two-way binding
v-model
Using JavaScript Expressions
{{ number + 1 }}
{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}
<div v-bind:id="'list-' + id"></div>Conditionals and Loops
-
v-if
-
v-for
<li v-for="todo in todos">
{{ todo }}
</li>
<li v-for="todo in todos">
{{ todo }}
</li><p v-if="seen">Now you see me</p>Composing with Components
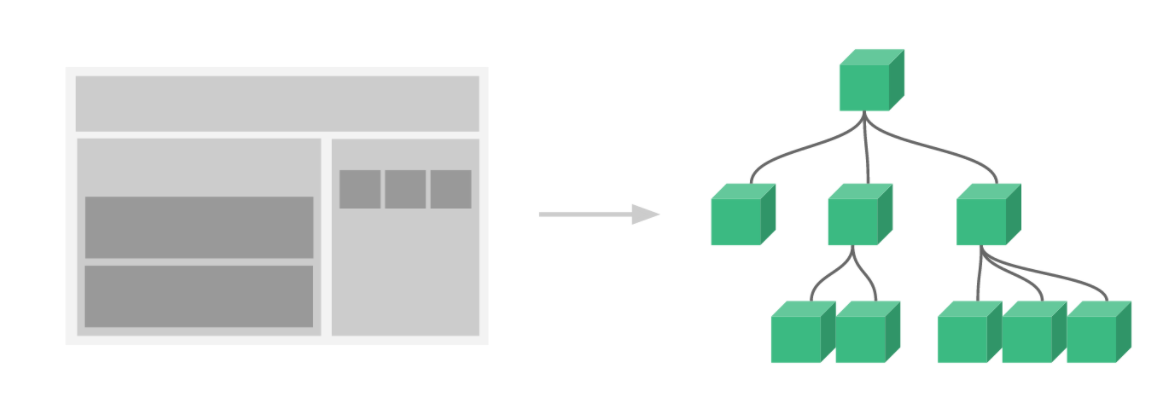
Define a component
// Define and register a global component
Vue.component('todo-item', {
template: '<li>This is a todo</li>'
})
// Define and register a scoped component
var TodoItem = {
template: '<li>This is a todo</li>'
}
new Vue({
// ...
components: {
// only be available in parent's template
'my-component': Child
}
})Props
Vue.component('todo-item', {
// The todo-item component now accepts a
// "prop", which is like a custom attribute.
// This prop is called todo.
props: ['todo'],
template: '<li>{{ todo.text }}</li>'
})Props Validation
Vue.component('example', {
props: {
// basic type check (`null` means accept any type)
propA: Number,
// multiple possible types
propB: [String, Number],
// a required string
propC: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// a number with default value
propD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// custom validator function
propE: {
validator: function (value) {
return value > 10
}
}
}
})


Lifecycle Hooks
Single File Components
- All in one(HTML, JS, CSS)
- CommonJS modules
- Component-scoped CSS

Content Distribution
<app>
<app-header></app-header>
<app-footer></app-footer>
</app>
Slot
Compilation Scope
Everything in the parent template is compiled in parent scope; everything in the child template is compiled in child scope.
Normal Slots
- The provides the content for the slot, including the data
- The child can only decide where to render the received content with <slot>
Scoped Slots
- The parent provides a template for the slot
- In this template, props are accepted.
- The child can pass data for these props to the slot
- The parent only provides the template markup, and the child provides the data.
Let's see how does vue work in those pain-points of our projects.
Binding HTML Classes
React
<header className={`rui-clearfix${this._isWebview() ? ' webview' : ''}`}>Vue
<header class="rui-clearfix" v-bind:class="classObject">
new Vue({
data: {
classObject: {
webview: this._isWebview()
}
}
}React
Vue
Dynamic Components
_renderListingPropertiesFromData(property) {
return property.isProject ?
( <ProjectProfileCard key={property.listingId} data={property} /> )
:
( <PropertyListingCard key={property.listingId} data={property} /> );
}
<div className="rui-grid-row">
{ this._renderListingPropertiesFromData(propertyData) }
</div><component v-bind:is="currentView">
<!-- component changes when vm.currentView changes! -->
</component>
var vm = new Vue({
data: {
currentView: 'home'
},
components: {
ProjectProfileCard: { /* ... */ },
PropertyListingCard: { /* ... */ }
}
})Serial Workshop
What's more?
vuejs
By melonq
vuejs
- 483



