The research Data Lifecycle:
From Planning to Sharing


Mercè Crosas, IQSS, Harvard University @mercecrosas

Every two years, the amount of new digitized data is equal to all of the data ever collected before. The world’s knowledge is at our fingertips, and data science allows us to effectively and efficiently make use of that knowledge. This is facilitating a societal shift as big as the Industrial Revolution.

Phil Bourne, Data Science Director, UVA, Former Director for Data Science, NIH; UVA Today, Q&A, August 21, 2017
REsearch DATA ARE AN ASSET TO RESEARCHERS and To the University, AND need to be Handled with CARE
Library
Information Sciences
HandLING Data with CARE,
A COLLAborative effort
Information TechnologY
Research
Vice-Provost for Research
Data Governance
Authorship,
data citation
Data Science
Security
Storage
Computation
Repositories
Sponsored Research
Data Agreements
Software
Tools
Privacy
Research data management concerns the organization of data, from its entry to the research cycle through the dissemination and archiving of valuable results. It aims to ensure reliable verification of results, and permits new and innovative research built on existing information.
Whyte, A., Tedds, J. (2011). ‘Making the Case for Research Data Management’. DCC Briefing Papers. Edinburgh: Digital Curation Centre
Research Data management AIMS
Data Collection, Acquisition
Support for the data lifecycle must accommodate differences across research domains, data types, and methodologies:
- natural, physical, social sciences, humanities, health, biomedicine
- qualitative vs quantitative data and methods
- small, medium (MB to GB) vs large (TB to PB)
- structured vs unstructured, static vs streaming
Storage and
Analysis
Data Sharing and Archiving
Planning
The Research Data Lifecycle
Data Collection,
Acquisition
- A Data Management Plan (DMP) helps you think how to organize, store, and share the data from your research project.
- A DMP is required by most research funding organizations.
- A DMP is a living document.
- The DMPTool assists you with requirements and templates
Storage and Analysis
Data Sharing and Archiving
Planning
In 2018, InTernational DMPTool LAUNCHES


https://dmptool.org/

First, rigorously collected, well-preserved data sets — including meaningful descriptors or metadata — will help the data owners to reach solid, meaningful results. Second, they will help future investigators to make sense of and reuse data, thereby enhancing utility and reproducibility. Preserving comprehensive data, ideally for many years, also reduces the risk of duplicating science done by others.
Data Collection, Acquisition
Storage and
Analysis
Data Sharing and Archiving
Planning
- When data are collected by the researcher, consider using data collection tools (e.g., Electronic Lab Notebooks).
- When data are acquired from third party, consider defining a Data Use Agreement.
Data USe Agreement, as Defined at Harvard
Data Use Agreements govern access to and treatment of data:
- provided by an outside organization to your organization for use in your organization’s research, or
- provided by your organization to an outside organization for use in its research.
Data Collection, Acquisition
Storage and Analysis
Data Sharing and Archiving
Planning
- Provide secure storage for sensitive datasets.
- Hybrid model for research computing incresingly popular: self-owned + public cloud options
- Consider offering consulting and training for research computing and data science (statistical models, machine learning, computational tools)
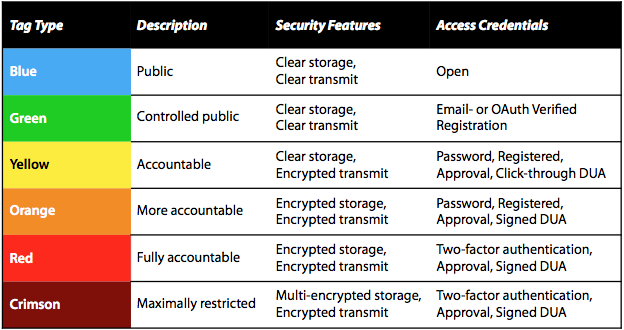
Sweeney L, Crosas M, Bar-Sinai M. Sharing Sensitive Data with Confidence: The DataTags System. Technology Science. 2015101601. October 16, 2015. http://techscience.org/a/2015101601
DataTags proposes 6 standard levels To SUPPORT sensitive/Restricted data
Data Collection, Acquisition
Storage and Analysis
Data Sharing and Archiving
Planning
- Make open research data the default, "as open as possible, as closed as needed" (Horizon 2020).
- Many funding organizations and journals require data sharing.
- Reward researchers when sharing data by giving them credit.
- Use trusted data repositories aligned with FAIR data principles.


https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata201618
FAIR Principles:
4 principles, 15 sub-principles

FAIR Principles For Humans and Machines:
In Brief
-
Findable
- Globally unique, resolvable, and persistent identifier
- Machine-readable descriptions to support structured search
-
Accessible
- Metadata is accessible beyond the lifetime of the dataset
- Clearly defined access and security protocols (FAIR != Open)
-
Interoperable
- Extensible machine interpretable formats for data + metadata
- Use FAIR vocabularies and link to other resources
-
Reusable
- Provide licensing, provenance, and use community-standard
FAIR slides acknowledgement: Michel Dumontier
Some research communities are taking the LEAD

http://copdess.org
"we commit to these goals:
Ensuring that Earth, space, and environmental science research outputs, including data, software, and samples or standard information about them, are open, FAIR, and curated in trusted domain repositories .."
Enabling FAIR DATA in EARTH, SPACE, and Environmental Sciences
Technology can Help

A Solution for Data Sharing and Archiving
Aligned with FAIR data principles
DATAVERSE IS A REPOSITORY
for finding, citing, and publishing data
Dataverse is A Platform
for building your own data repository
DATAVERSE IS A Community
which facilitates data access and data sharing around the world
Community
Features
Data
Projects
Dataverse.ORG
35 Dataverse Repositories sites around the world

Dataverse Community GROWTH
2006
Dataverse Development starts at Harvard's Institute for Quantitative Social Science (IQSS)
2
Dataverse sites
2015
14
Dataverse sites
2017
23
Dataverse sites
2018
35
Dataverse sites
2016
18
Dataverse sites
First Annual Dataverse Community Meeting
4 developers
First release
74 contributors
30 releases
12,807 commits
Global Dataverse Community Consortium
In 2018, a new international consortium is formed to support and coordinate efforts across Dataverse Repositories.
http://dataversecommunity.global (coming soon!)
Community
Features
Data
Projects
Data Citation:
Credit as an incentive to Share Data
- A formal data citation automatically generated
- Attribution to data creators and data providers
- Persistent identifier (e.g., DOI) resolves to dataset landing page
- Version in citation
- Universal Numerical Fingerprint (UNF): a checksum independent of file format, for tabular data files
- Compliant with the Joint Declaration of Data Citation Principles

Download data citation ready to be used in reference manager
Metadata TO FIND AND REUSE DATA
At multiple Levels:
- Citation metadata
- Custom metadata
- File metadata
- Variable-level metadata

With multiple Standards:
- Data Documentation Initiative (DDI)
- Dublin Core
- Schema.org
Download metadata in multiple formats
Schema.org USed BY GOOGLE DAtaset SearcH
- Schema.org JSON-ld embedded in HTML of dataset landing page
- Datasets become discoverable through Google Dataset Search

Metadata from schema.org in Dataverse dataset landing page
Versioning OF DATASETS AND FILES
- Major and minor versions
- Major versions show in the data citation
- Track both metadata changes and files changes

TIERED ACCESS to Data
- Default access is public, with CC0 waiver
- Allow public and restricted files
- Descriptive metadata always public for discoverability
- Custom Terms of Use, when needed
- Optional Guestbook to collect information from users

Public
Restricted
Tabular data exploration
- Variable metadata automatically extracted
- Descriptive statistics automatically computed


Metadata Extraction from Astronomy files
Metadata (instrument information) is extracted automatically from FITS files header upon data upload

Metadata from FITS Header
MANAGE and customize your own Dataverse
- Create a dataverse to manage your own collection of datasets
- Brand your dataverse or embed in your website

Extensive API to Enable Tool Integration
http://guides.dataverse.org








Community
Features
Data
Projects
a wide Variety of Data and Dataverses
- Dataverse for Journals
- Dataverse for Researchers
- Dataverse for Research Communities
- Dataverse for one or multiple Institutions
Data Policies IN social science Journals

Crosas, Gautier, Karcher, Kirilova, Otalora, Schwartz, 2018. Data Policies of highly-ranked social science journals
More than 50% of the top 50 journals in anthropology, economics, psychology, and political sciences have data policies that either encourage or require to share the data associated with the article.
Dataverse for a Journal
Hosted at Harvard Dataverse repository (80 journal dataverses)

Dataverse for a Researcher
Hosted at Harvard Dataverse repository

Dataverse for A RESEARCH COMMUNITY: Strucural Biology
Hosted SBGrid Consortium, Harvard Medical School

Dataverse For multiple Universities
Hosted by Texas Digital Libraries, a consortium of Texas Higher-Education Institutions

Harvard Dataverse:
OPEN to ALL the RESearch COMMUNITY
Hosted by Harvard University, in collaboration with Harvard Library, HUIT, and IQSS
http://dataverse.harvard.edu

# DatAsets Deposited at Harvard Dataverse:
30,000
Average # Released Datasets per Month (in 2018):
250
# of total DOWNLOADs:
5M
Average # downloads per month (in 2018):
150,000
Community
Features
Data
Projects
On-GOIng Projects
- Large data
- Sensitive data
- Data Quality, Reproducibility, Reusability
- Open Source 'Health' Index
Large Data
More ways to upload data
- rsync
More ways to access data:
- Local access
- Compute in the cloud
- Compute in institutional
research computing
More storages:
- Remote secure storage; data enclaves
Funded partially by Helmsley Charitable Trust, with focus on biomedical data, in collaboration with Piotrek Sliz



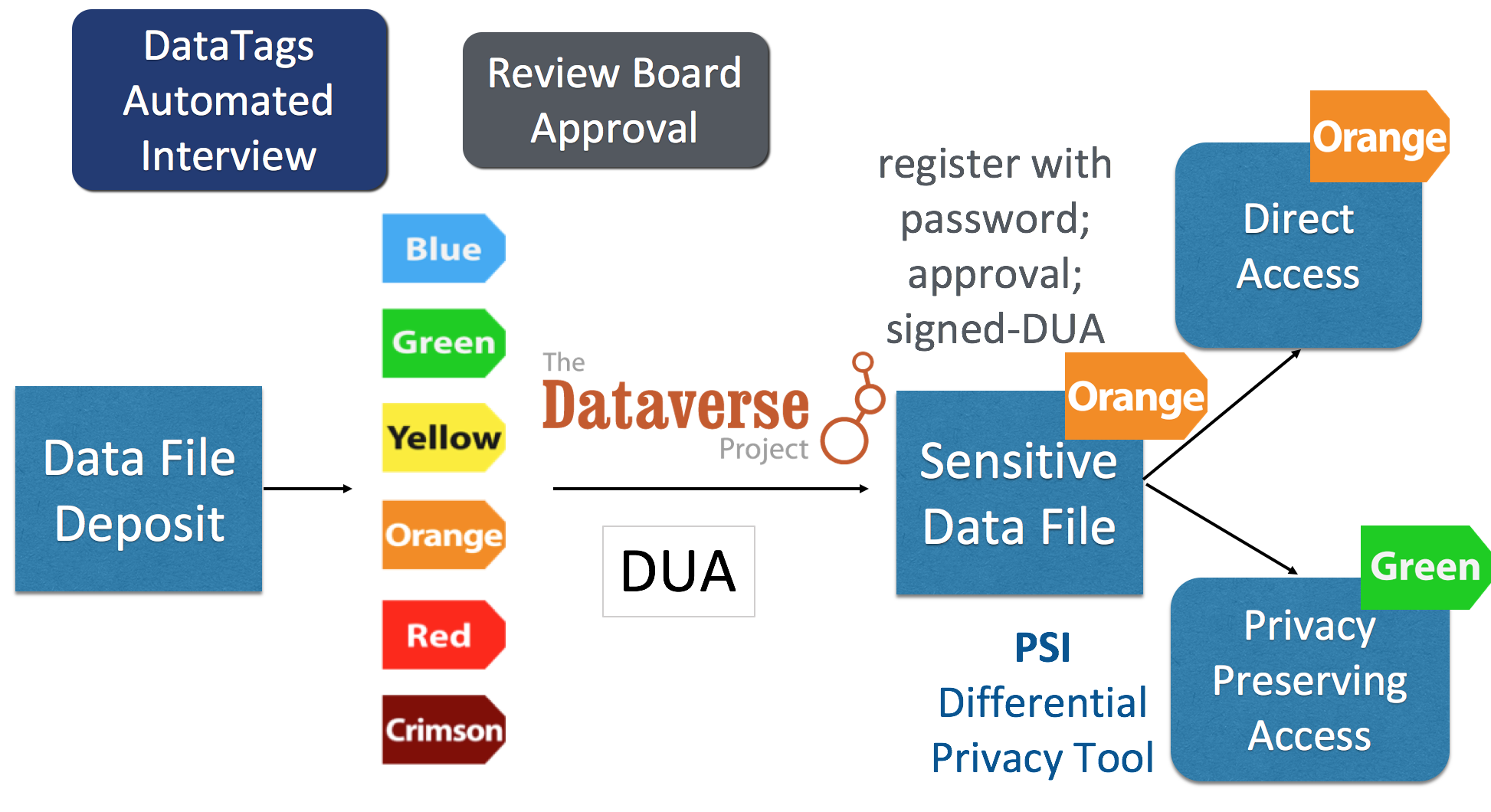
Sensitive Data: DataTaGS
Funded partially by National Science Foundation,
in collaboration with Latanya Sweeney
Standardize data security and access levels


Sensitive Data: Privacy Preserving Tools
Funded by National Science Foundation,
in collaboration with Harvard Privacy Tools Project

Integration with reprodUcibility Tools:
Code Ocean
Funded by Sloan Foundation, in collaboration with CodeOcean


Integration with repRODUCIBILITY Tools:
Encapsulator
Funded by Sloan Foundation, in collaboration with Margo Seltzer


Integration with reproducibility Tools:
CORE2
Funded by Sloan Foundation, in collaboration with the ODUM institute at UNC Chapel Hill


OPEN Source 'Health' Index
- A quantitative study to determine a health index for open source projects
- Leverage previous work (e.g., LYRASIS project and Qualification and Selection of Open Source Software (QSOS) )
Funded by IMLS

Thank YOu!
dataverse.org
dataverse.harvard.edu
The Dataverse Team @IQSS
https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/dataverse-community
scholar.harvard.edu/mercecrosas
@mercecrosas
The Research Data Lifecycle: From planning to sharing
By Mercè Crosas
The Research Data Lifecycle: From planning to sharing
- 1,870



