Introduction to JavaScript
Outline
HTML/CSS Review
JavaScript Overview
JavaScript Variables
Advanced Array Functionality
Manipulating HTML Elements
HTML
HyperText Markup Language
Uses <tags> to describe rendering
Organize content into a tree structure


Style
Selectors
By ID
li { /* all <li> elements */
property:value;
}By class
.my-class { /* all elements with class "my-class" */
property:value;
}By element type
#my-id { /* element with id "my-id" */
property:value;
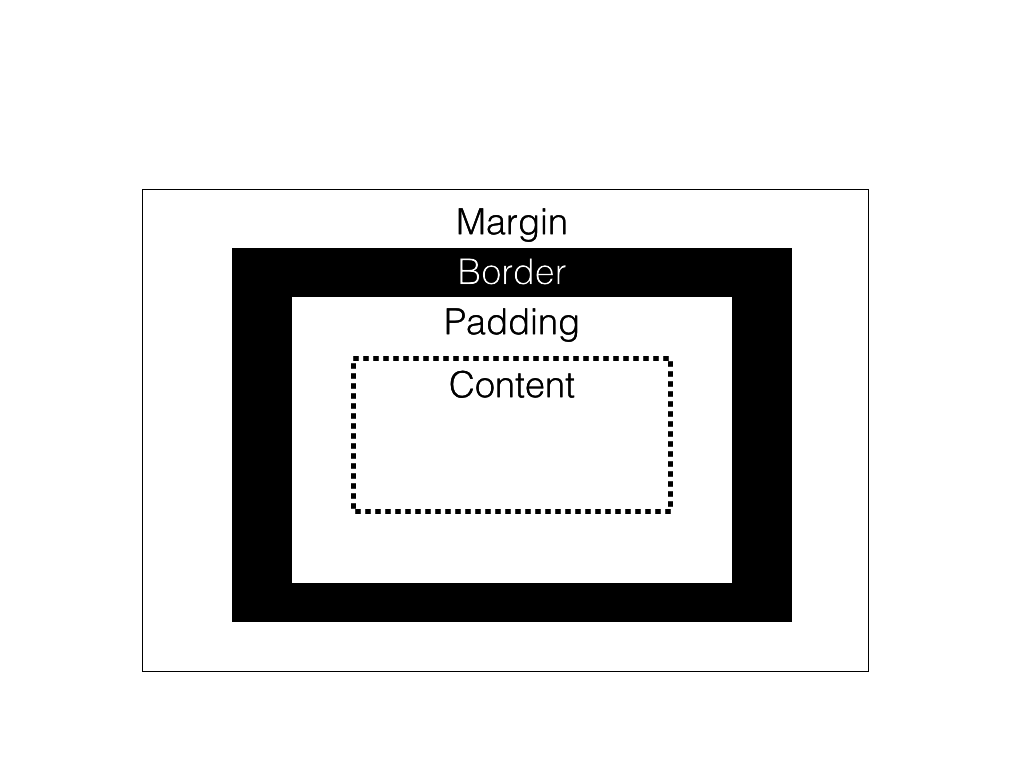
}The box model
{JavaScript Overview}
Javascript(JS)
The most popular programming language in the world
Most of the code you write will be JS
Can be used to create, manipulate, and remove HTML elements
Program behaviors of the webpage
Handle data
Written in a separate file, referenced by index.html
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/my-script.js"></script>Javascript is a scripting language
Differs substantially from markup languages
Creates variables which are not represented in the DOM
Supports structured programming (ie, conditional
if, else)statementsWe will aim for a functional understanding of JS
{JavaScript variables}
Variable types
Numeric: single quantitative value
var x = 13;String: characters, in quotes (', or ")
var str = "hello there";Array: Set of items in a vector (string or numeric)
var timesTwo = function(value) { return value * 2}Object: Item that holds key-value pairs
var arr = [13, 'fourteen', 15];var obj = {name:'steve', job:'lobbyist'};Function: Executable block of code, returns a value
Properties and Methods
Properties describe a feature of an element
var characters = "This is a string"
characters.length // Returns the length of the variable
var arr = [1,2,3]
arr.length // Returns the number of items in the arrayMethods are actions that variables can perform
var chars = "This is a string"
chars.replace("This", "Here") // Replaces "This" with "Here"
var arr = [1,2,3]
arr.push(4)// Pushes 4 into the array as the last elementNumbers
Only one type of JavaScript number
var num = 1;
typeof(num) // returns 'number'
var num = 1.2;
typeof(num) // returns 'number'
var num = 1e8
typeof(num) // returns 'number'Mathematical operations can be used
var num = 2*14 // num is 28
var num = 2/4 // num is .5Advanced Math operations
var num = Math.sqrt(4) // num is 2Strings
Create string variables with single or double quotes
var str = 'using single quotes'
var str = "using double quotes"Lots and lots and lots of string functions
var name = "Mike"
var greeting = "Hello, my name is " + name // concatenation
var greeting2 = greeting.replace("Hello", "Sup") // replacingArrays
Comma separated items, denoted by square brackets []
var x = [13, 14, 15];
var x = ['one', 'two'];Access values by index, starting at 0
var x = [13, 14]
x[0] // 13
x[1] // 14Objects
Data items with key-value pairs
var person = {
firstName:'Anna',
lastName:'Smith',
height:"5'4",
}
Access values by referencing the key
person.firstName // Anna
person['firstName'] // AnnaCan be nested
var person = {
firstName:'Anna',
favorites:{
music:'bluegrass',
food:'pizza'
}
}
person.favorites.food // 'pizza
Functions
Perform blocks of code on parameters
var myFunction = function(a,b) {
return a*b
}Execute function using this syntax
var result = myFunction(2,4) // returns 8Return a single item (object, array, etc.)
Conditional statements
Execute statements only if a condition is true (if)
if(a<b) {
// execute some action
}Provide a default alternative (else)
if(a<b) {
// take some action
}
else if(a==b) {
// another action
}
else {
// default
}Functions can take functions as parameters
You have a function that compares values
var comparison = function(a,b) {
if(a>b) {
return 'a is greater that b'
}
else {
return 'b is less than or equal to a'
}
}var comparison = function(a,b, callback) {
if(a>b) {
callback()
return 'a is greater that b'
}
}Pass that action in as a parameter
{advanced array manipulation}
Execute a function on each element of an array by using the "map" method
-
The map method is a built in alternative to writing loops
-
Each array value is passed to a provided function
-
Values in the array are unchanged
var arr = [1,2,3]
var timesTwo = function(d) {return d*2}
var doubleArr = arr.map(timeTwo) // returns [2,4,6]Map functions can also be written in-line
var arr = [1,2,3]
var doubleArr = arr.map(function(d) {
return d*2
})Filtering
var arr = [1,2,3]
var greaterThanTwo = arr.filter(function(d) {
return d>2
})Filtering only returns values that meet a given conditionality:
Same format as .map
{connection to HTML}
JavaScript DOM Manipulation
Get values using JavaScript
document.getElementById('my-input').valueSet properties using JavaScript
document.getElementById("demo").style.fontSize = "25px";
Libraries will make this less cumbersome (jQuery, D3, etc.)
Summary
-
Properties and methods of JavaScript variables
-
The use of functions
-
The ability to manipulate HTML elements
Assignment
Map-challenge (due before first class next week)
javascript
By Michael Freeman
javascript
- 1,736




