Thermodynamics
M. Rocha
Physics 4C
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Connecting heat to mechanical energy
The Thermodynamic System
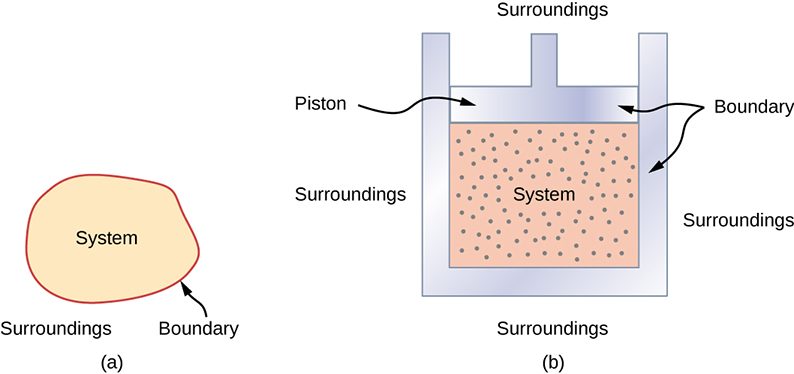
- Most systems are known as an open system, which can exchange energy and/or matter with its surroundings.
- The system is contained by a boundary, acting as a wall that separates the system and the environment
- Within the system, we assume thermal equilibrium .
Remember
Heat (Q) : Energy transfer due to temperature differences
Work (W): Energy transfer due to acting forces
First Law of Thermodynamics
Whenever heat is added to a system, it transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy
Energy is conserved!
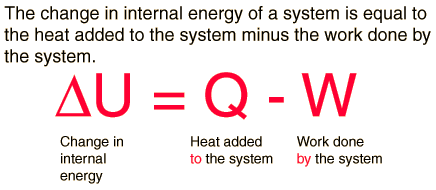
First Law of Thermodynamics
Whenever heat is added to a system, it transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy
Energy is conserved!
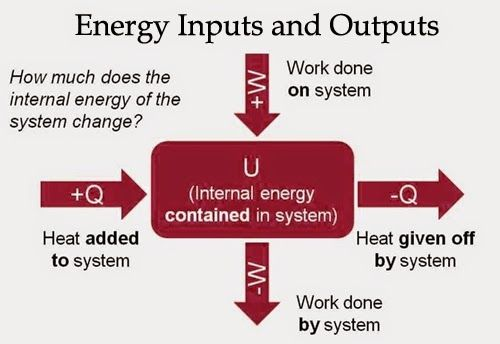
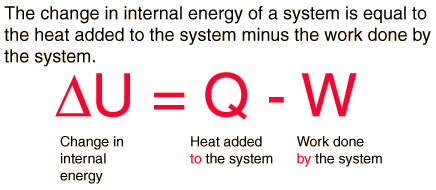
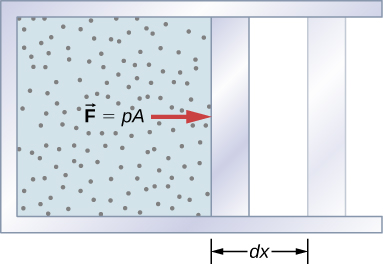
Work Done by a System
If the gas expands against the piston, it exerts a force through a distance and does work on the piston. If the piston compresses the gas as it is moved inward, work is also done—in this case, on the system. The work associated with such volume changes can be determined as follows:
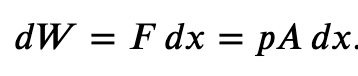
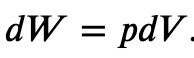
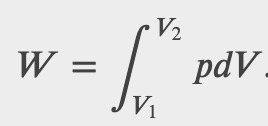
Where p is the gas pressure, V the volume of the system.
Work Done by a Perfect Gas
For a perfect gas, we have a well known equation of state relating pressure p and volume V
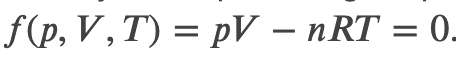
So we can define the work done by a perfect gas as
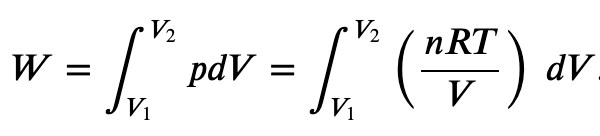
For a perfect gas, we have a well known equation of state relating pressure p and volume V
Notice the dependance of this integral on Volume (V) and Temperature (T). Because of this, the work done going from one point to another in the phase space is path dependent.
Work Done by a Perfect Gas
Isothermal process (constant Temperature):
If the gas is kept at a constant temperature T by keeping it in thermal equilibrium with a heat reservoir, then
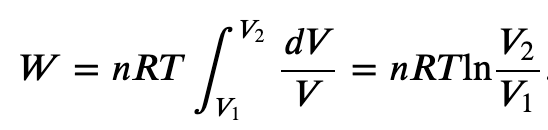
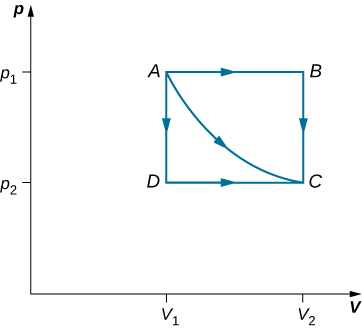
The path AC represents an isothermal process from points A to C
Work Done by a Perfect Gas
Isobaric process (constant Pressure):
If the gas is kept at a constant pressure p, then

The path AB represents an isobaric process from points A to B
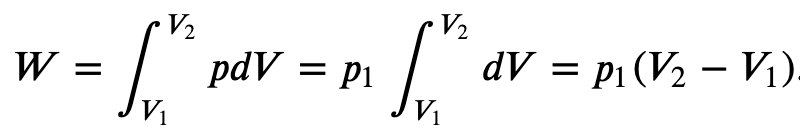
Work Done by a Perfect Gas
Isochoric process (constant Volume):
If the gas is kept at a constant volume V, then there is no work done as dV = 0

The path BC represents an isochoric process from points B to C
Work Done by a Perfect Gas
Thus, the work done for the transition A->C is path dependent

Work done by path AC:
Work done by path ABC:
Work done by path ADC:
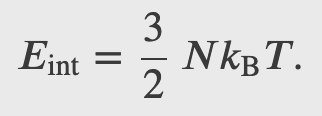
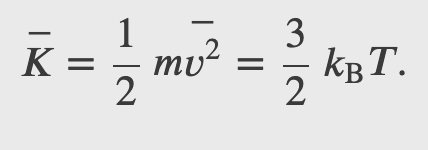
Internal Energy for an Ideal Monoatomic Gas
For a monoatomic ideal gas 𝑈𝑖 = 0, hence
The internal energy of a thermodynamic system is, by definition, the sum of the mechanical energies of all the molecules or entities in the system. If the kinetic and potential energies of molecule 𝐾𝑖 and 𝑈𝑖, respectively, then the internal energy of the system is the average of the total mechanical energy of all the entities:
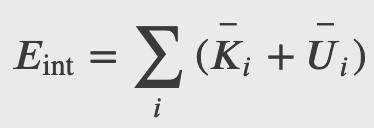
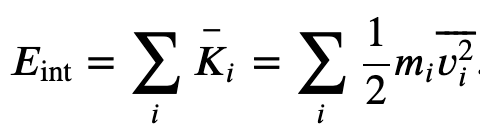
And using the result from the kinetic theory of gases
First Law of Thermodynamics for an Ideal Gas
The first law of thermodynamics tells us that by conservation of energy
Using the result of the internal energy for an ideal gas, then
Then the change in internal energy only depends in temperature (T), and since T = pV/Nk, the change in internal energy is path independent
The change in internal energy is path independent
First Law of Thermodynamics for an Ideal Gas
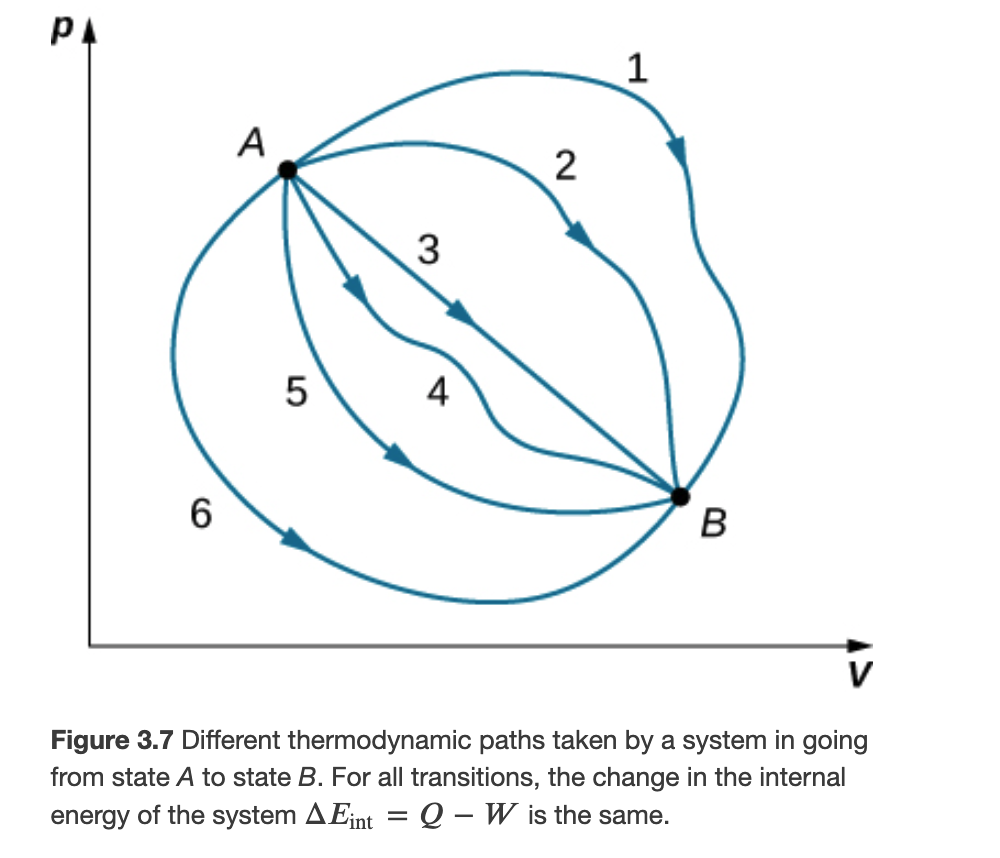
Although Q and W both depend on the thermodynamic path taken between two equilibrium states, their difference 𝑄−𝑊 does not.
Quasi-static vs Non-quasi-static Processes
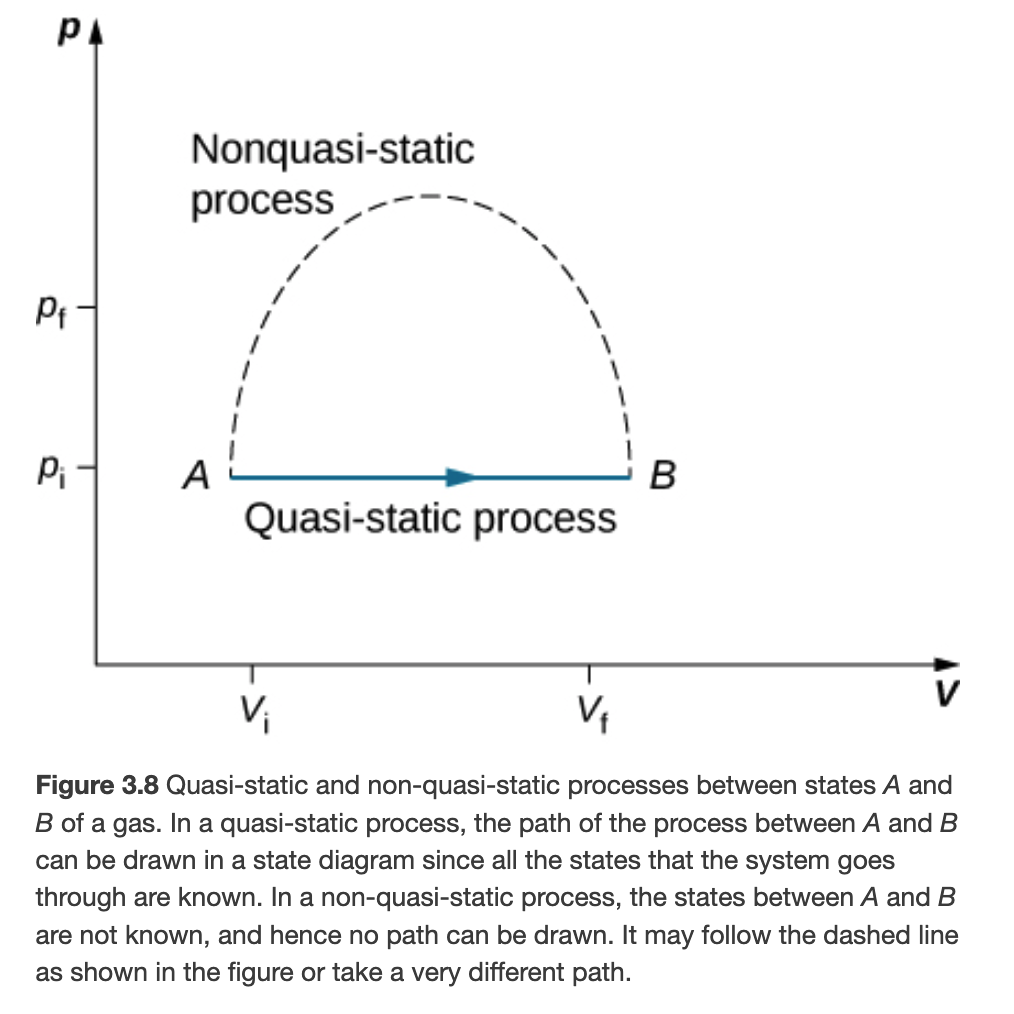
Adiabatic Process
Compressing or expanding a gas while no heat enters or leaves the system is said to be an adiabatic process

Adiabatic Process
When a gas adiabatically expands, it does work on its surroundings and gives up internal energy, and thus becomes cooler.

Cyclic Process
We say that a system goes through a cyclic process if the state of the system at the end is same as the state at the beginning. Therefore, state properties such as temperature, pressure, volume, and internal energy of the system do not change over a complete cycle:
Adiabatic Process for an Ideal Gas
Using the internal energy change we found in terms of Cv, we can write the first law of thermodynamics for an ideal gas in an adiabatic process (dQ=0) as follows:
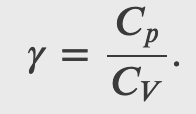
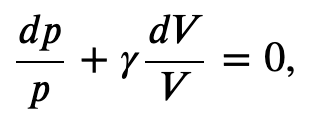
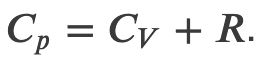
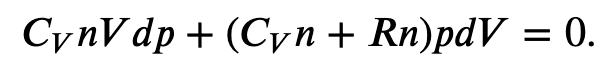
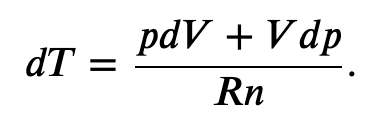
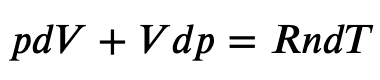
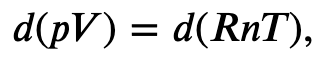
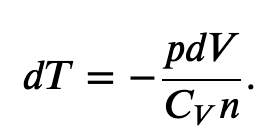
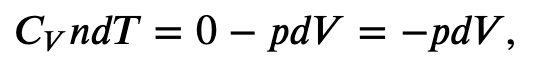
and solving for dT
But we also know from the ideal gas law that
so
and
Now we have two equations for dT, that equating together gives
Which can be written as
where
and
Adiabatic Process for an Ideal Gas
Integrating the previous result
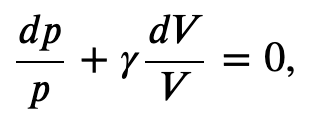
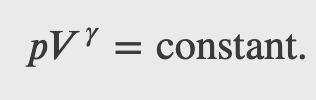
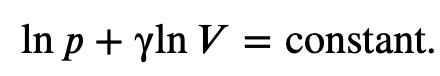
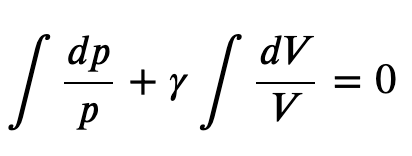
we get
Finally, using ln(𝐴^𝑥)=𝑥ln𝐴 and ln(𝐴𝐵)=ln𝐴+ln𝐵, we can write this in the form
This equation must be obeyed by an ideal gas going through adiabatic process
Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure
From the kinetic theory of gases, we found that the molar specific heat capacity of a gas at constant-volume is given by
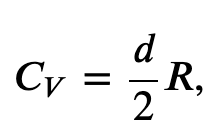
where d is the number of degrees of freedom of a molecule in the system.
Now, we can use the first law of thermodynamics to find a specific heat capacity at constant-pressure. We will do this for an ideal gas, but the result work as a good approximation non-monoatomic gases.
Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure
First we find the change in internal energy for a constant-volume process (W = 0):
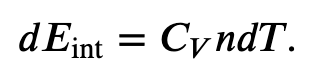
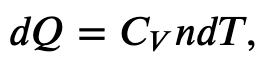
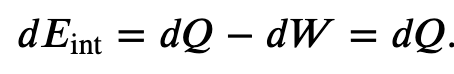
and
Now we know the change in internal energy, which is path independent for an ideal gas since it only depends on temperature, so must be the same for an constant-pressure process
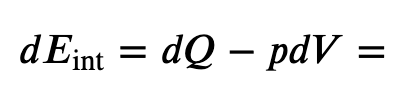
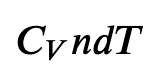
and for constant-pressure
then
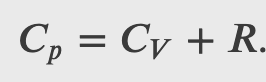
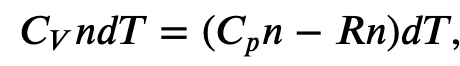
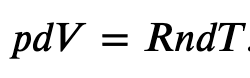
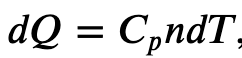
Since
where 𝐶𝑝 is the molar heat capacity at constant pressure of the gas.
Checkpoint
During a thermodynamic process, a system moves from state A to state B, it is supplied with 400 J of heat and does 100 J of work. (a) For this transition, what is the system’s change in internal energy? (b) If the system then moves from state B back to state A, what is its change in internal energy? (c) If in moving from A to B along a different path, 𝑊′𝐴𝐵=400 J of work is done on the system, how much heat does it absorb?
a) 300 J
b) -300 J
c) -100 J
Checkpoint
Consider the quasi-static expansions of an ideal gas between the equilibrium states A and C of If 515 J of heat are added to the gas as it traverses the path ABC, how much heat is required for the transition along ADC?
Assume that
𝑝_1=2.1×10^5 N/m^2, 𝑉_1=2.25×10^−3 m^3
𝑝_2=1.05×10^5 N/m^2, 𝑉_2=4.5×10^−3 m^3

Checkpoint
Heat is added to 1 mol of an ideal monatomic gas confined to a cylinder with a movable piston at one end. The gas expands quasi-statically at a constant temperature of 300 K until its volume increases from V to 3V. (a) What is the change in internal energy of the gas? (b) How much work does the gas do? (c) How much heat is added to the gas?

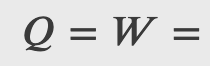
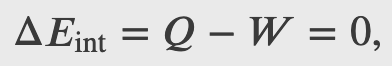
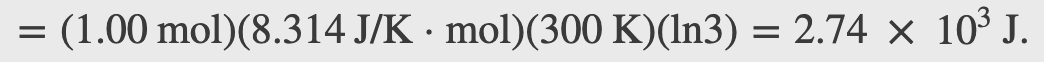
Checkpoint
When 1.00 g of ammonia boils at atmospheric pressure and −33.0°C, its volume changes from 1.47 to 1130cm^3. Its heat of vaporization at this pressure is 1.37×10^6 J/kg. What is the change in the internal energy of the ammonia when it vaporizes?
Checkpoint
A machinist polishes a 0.5 kg copper fitting with a piece of emery cloth for 2 min. He moves the cloth across the fitting at a constant speed of 1 m/s by applying a force of 20 N, tangent to the surface of the fitting. (a) What is the total work done on the fitting by the machinist? (b) What is the increase in the internal energy of the fitting? Assume that the change in the internal energy of the cloth is negligible and that no heat is exchanged between the fitting and its environment. (c) What is the increase in the temperature of the fitting?
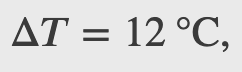

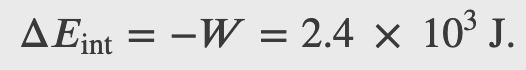

Second Law of Thermodynamics
Heat of itself never flows from a cold object to a hot object
The second law of thermodynamics describes the direction of heat flow in natural processes
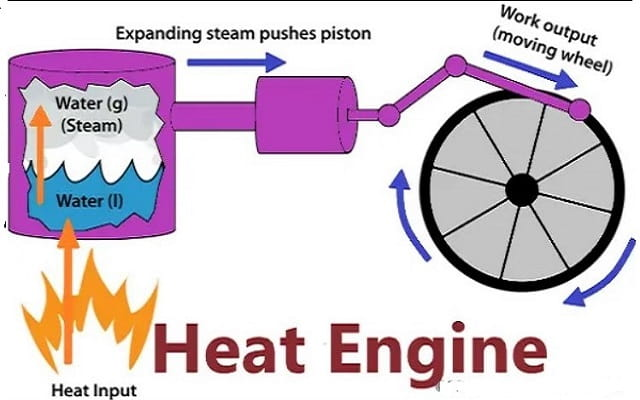
Heat Engine and Second Law
A heat engine is any device that changes internal energy into mechanical work
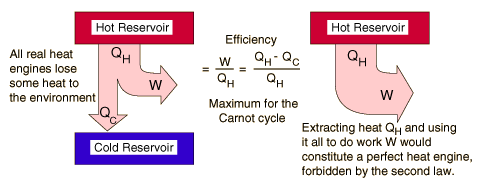
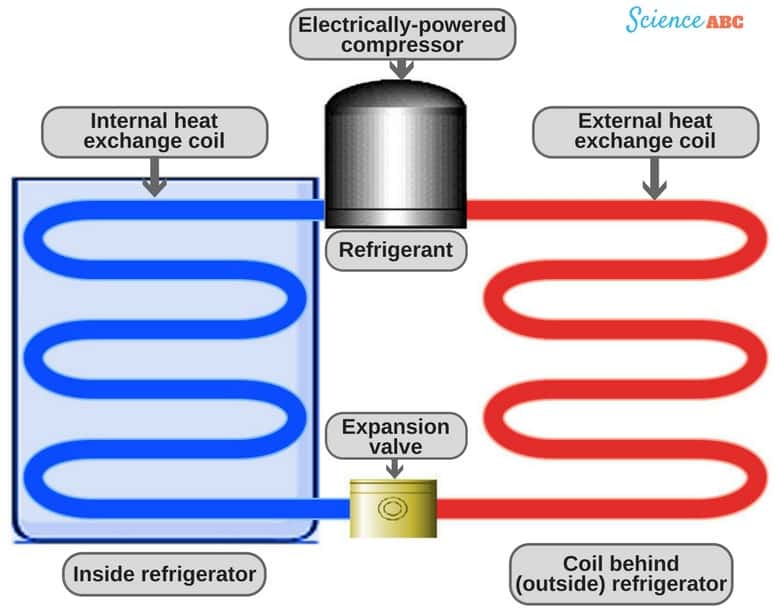
How a Refrigerator Works?
The End
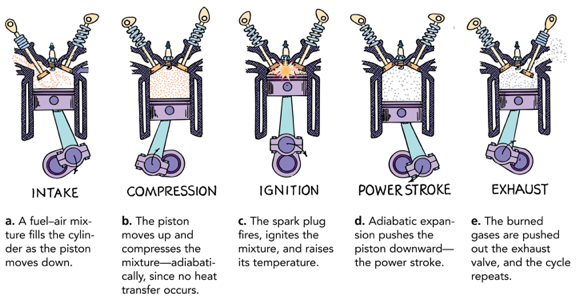
Adiabatic Process
Thermodynamics (Physics 4C)
By Miguel Rocha
Thermodynamics (Physics 4C)
Physics 1 - Week 7 - Chapters 17-18
- 754



