Maxwell Equations & EM Waves
Physics 4B
M. Rocha



Gasuss's Law
Gauss law for magnetism
Maxwell-Faraday equation (Faraday induction law)
Ampere’s Law (with the addition of Maxwell)
You already know most of Maxwell's Equations!





You already know most of Maxwell's Equations!
Gauss's Law for Magnetism

Magnetic Poles
North Pole: Side where field lines point away from the source
South Pole: Side where field lines point into the source

Not known magnetic Monopoles
Unlike electric charges, cannot have just a North or just a South magnetic pole

Maxwell-Faraday Equation (Induction Law)

Induced Electric Fields
- The induced emf due to changing magnetic fields is the result of the electric field doing work on the moving charges
- The work done by 𝐄⃗ in moving a unit charge completely around a circuit is the induced emf ε
- Faraday’s law can be written in terms of the induced electric field as


Maxwell-Ampere's Law

Maxwell's Addition To Ampere's Law



Ampere's Law
Maxwell suggested adding the displacement current




Gasuss's Law
Gauss law for magnetism
Maxwell-Faraday equation (Faraday induction law)
Ampere’s Law (with the addition of Maxwell)
Maxwell’s equations and the Lorentz force law together encompass all the laws of electricity and magnetism.

Lorentz force law
Electro-Magnetic Waves

In free space (no currents or charges), Maxwell's equations reduce to
,
,

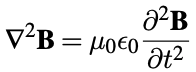


The speed of light
From maxwells equations in free space you can derive two symmetric wave equations (link to derivation)
Energy and Momentum of EM Waves



The time average of the energy flux is the intensity I of the electromagnetic wave and is the power per unit area.
where E0 and B0 are the maximum strengths/amplitude of the E and B fields and
The momentum can be found in terms of the Intensity of the EM wave, and is given by
The End
Maxwell Equations & EM Waves
By Miguel Rocha
Maxwell Equations & EM Waves
- 1,006



