Intro to Astronomy
M. Rocha
Astronomy 1 - Lecture 1
What is Astonomy?
The science that studies celestial objects, space and the physical universe as a whole.
Astronomy applies mathematics, physics, and chemistry on this effort .
Observational v.s. Theoretical Astronomy
Professional astronomy is split in two branches:
observational and theoretical
Observational astronomy: Focused on acquiring data from observations of astronomical objects.
Theoretical astronomy (Astrophysics): Oriented toward the development of physical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena.
The two fields complement each other, with theoretical astronomy seeking to explain observational results and observations being used to confirm theoretical results.

Observational Astronomer
1940s

Observational Astronomers
Today
The Big Picture
To begin our study of Astronomy, we must first attempt to understand our place in the Universe
The Big Picture
Cosmic Neighborhood
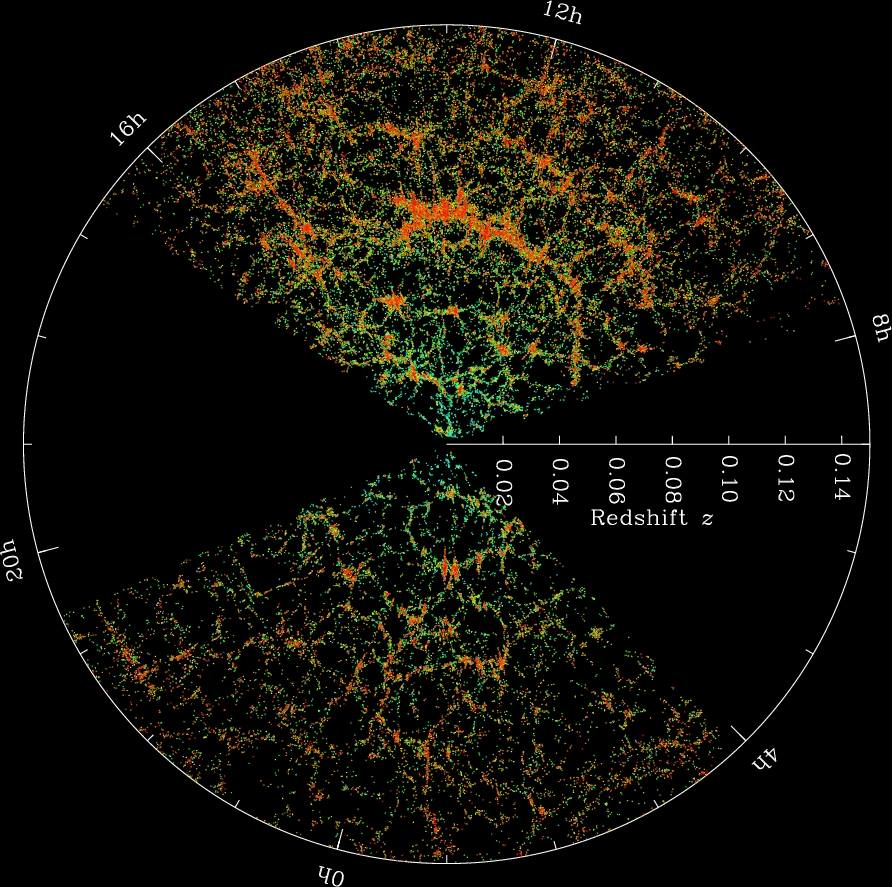


.04 light seconds
5 light hours
10 Mega ly (Mly)
40 light years (ly)
100,000 ly
3 Mega parsecs (Mpc)
55 Mly
17 Mpc
100 Mly
320 Mpc
The Big Picture
Our place in cosmic time
Our place in cosmic time
Astronomy knowledge is validated through Science
So what is Science?
Science is asking nature what is TRUE, and accepting its answer no matter what your believes, perception or ideologies are
We ask nature what is TRUE through experimentation and observations
What is Science?
Experimentation and observations yield evidence!
Science is the practice of only accepting as a FACT what has been shown to be TRUE via experimental or observational evidence
What is Science?
-
Recognize a question or a puzzle - such as unexplained fact.
-
Make an educated guess - a hypothesis - that might resolve/explain the puzzle/fact.
-
Predict consequences of the hypothesis.
-
Perform experiments or calculations to test the predictions.
-
Formulate the simplest general rule that organizes the three main ingredients: hypothesis, predicted effects, and experimental findings.
Scientific Method
A hypothesis becomes a theory or law only after many experiments have provided evidence for it not to be wrong

A hypothesis is only considered to be scientific if it can be proven wrong
Scientific hypothesis?
"Intelligent life exist on other planets somewhere in the universe"
"There is no other intelligent life in the universe"
No number of experiments can prove me right; a single experiment can prove me wrong"
-- Albert Einstein
Scientific hypothesis?
Can Science, Religion and Arts coexist in harmony?
Absolutely YES!
For as long as Religion and Art are open to accept/reject what nature has shown to be true/false
Science is not political, yet it can influence politics and culture
Science and Technology
Science
Technology
Technology is applied science
Technology enables science
It is humans who use the technology, and humans who are responsible for how technology is used
Science Induces Deep Thinking and Expands Our Cosmology
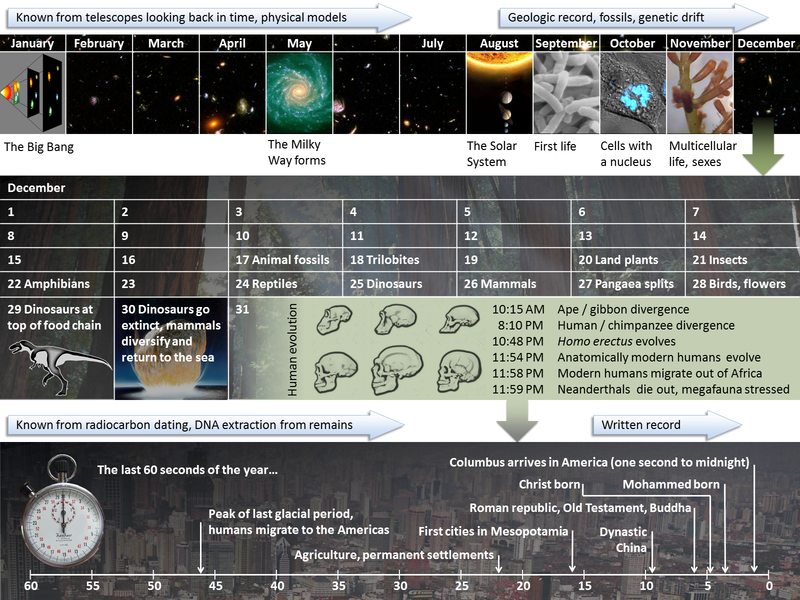
Beware of Pseudosciences
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that are claimed to be both scientific and factual, but are incompatible with the scientific method

Math Review
Math is the language of Physics/Astronomy
Math is the most abstract form of logic we have created.
Physics is understood through concepts, concepts are then represented in mathematical expressions.
Mass is a representation of Energy. How much energy is associated to the mass of an objects is given by multiplying the amount of mass by the speed of light squared.
For example:

What is the result of the following operation?
Checkpoint
Unit Analysis
Physical quantity = Value x [Unit]
Unit Analysis
Units Work!
Conversion of Units
1. Identify the equations that relate the units involved in the conversion.
2. Multiply by 1 in a way that the units you don't want cancel and the units you want remain.
3. Complete the operation by multiplying/dividing all the numbers involved in the conversion.
Conversion of Units
Conversion of Units
,
Alpha Centauri is the closest star to us. Alpha Centauri is about 4x10^16 meters (m) away from us. How far is Alpha Centauri in light years (ly) If 1 ly = 9.45x10^15 m?
Checkpoint
4.2 ly
For large distances astronomers prefer units of parsecs (pc) instead of light years (ly).
Andromeda (the closest spiral galaxy to us) is 2.4x10^22 m away. How far is Andromeda in Mega parsecs (Mpc) if 1 ly = 9.45x10^15 m and 1 pc = 3.26 ly ?
Checkpoint
0.8 Mega pc, or 0.8 Mpc
Trigonometry Review
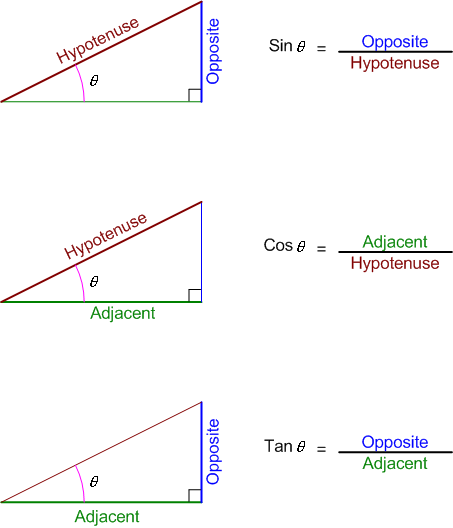
theta is the angle opposite to the right angle
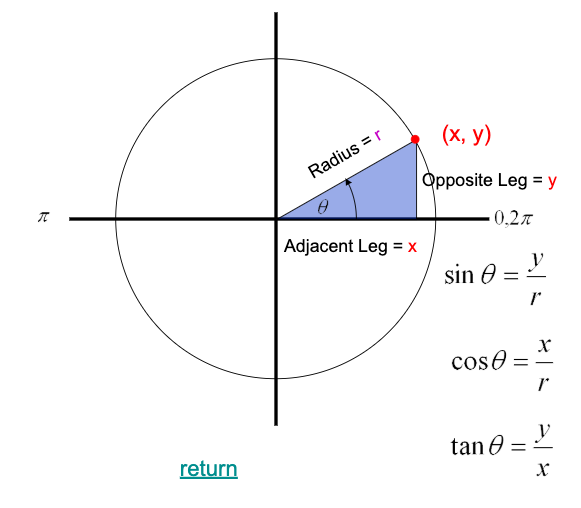
Circle Trigonometry

Small angle approximation
Arc Length = Angle in radians x Radius
r = Hypotenuse
Adjacent
Arc Length and The Small Angle Approximation
r
Oposite =
Oposite
L
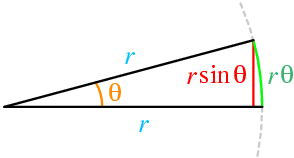
Checkpoint
What is the arc length L of a section of a circle with radius r = 4 meters, at an angle of
Some Impressive Measurements by The Greeks
Size of Earth
Size of the Moon
Distance to the Moon
Distance to the Sun
Size of the Sun
First measured by Eratosthenes ~235 B.C.
Aristarchus ~ 240 B.C.
Formulated how to do this measurements but was missing one key value, the Size of the Earth
Scientific Measurements
Scientific Measurements
Measurements take us from qualitative to quantitative knowledge
Qualitative knowledge
Quantitative knowledge
The Sun is much larger than the Earth and the Earth is much larger than the Moon
The Sun is a lot farther from Earth than the Moon
We need measurements to know !
By how much?
Scientific Measurements
Size of Earth
Size of the Moon
Distance to the Moon
Distance to the Sun
Size of the Sun
First measured by Eratosthenes ~235 B.C.
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.
Scientific Measurements
Size of Earth

First measured by Eratosthenes ~235 B.C.

Scientific Measurements
Size of Earth
First measured by Eratosthenes ~235 B.C.

Scientific Measurements
Size of Earth

First measured by Eratosthenes ~235 B.C.
,
Scientific Measurements
Size of the Moon
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.

During a total eclipse, it was observed that the moon traveled a distance equal to two and one half moon diameters while passing through the earth’s shadow.
Scientific Measurements
Size of the Moon
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.
During a total eclipse, it was observed that the moon traveled a distance equal to two and one half moon diameters while passing through the earth’s shadow.

Scientific Measurements
Size of the Moon
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.

Moon shadow tapers almost to a point in a solar eclipse
Scientific Measurements
Size of the Moon
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.

The shadows cast by the moon and the earth are similar isosceles triangles
Scientific Measurements
Size of the Moon
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.
This is a paralellogram, thus
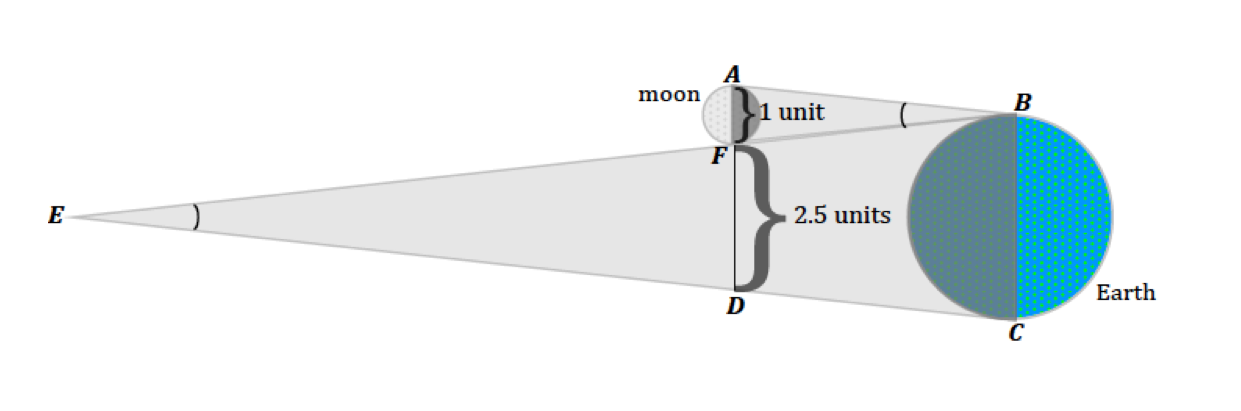
Scientific Measurements
Distance to the Moon
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.

Scientific Measurements
Distance to the Sun
First measured by Aristarchus ~240 B.C.

Scientific Measurements
Size of the Sun

Same as for the moon!
Because the sun is 400x farther than the moon but also 400x as big
d = diameter of sun image,
h = distance from pinhole to sun image

The apparent angular diameter of the sun is the same as that of the moon.
Scientific Measurements
Measurements take us from qualitative to quantitative knowledge
Qualitative knowledge
Quantitative knowledge
The Sun is much larger than the Earth and the Earth is much larger than the Moon
The Sun is a lot farther from Earth than the Moon
The sun 400 times farther away than the moon
Sun is 109 times larger than earth, and 400 times larger than the moon

Accuracy, Precision, Errors and Uncertainty
- Accuracy is how close a measurement is to the correct value for that measurement.
- The precision of a measurement refers to how close the agreement is between repeated measurements (which are repeated under the same conditions)s).
- Uncertainty is a quantitative measure of how much your measured values deviate from a standard or expected value. The uncertainty in a measurement, 𝐴, is often denoted as 𝛿𝐴, so the measurement result would be recorded as 𝐴±𝛿𝐴
- Errors are the source of uncertainty. Systematic Errors/Bias are reproducible inaccuracies that are consistently in the same direction for every measurement. Random Errors are statistical in nature.

The End!
Intro to Astronomy
By Miguel Rocha
Intro to Astronomy
Astro 1 - Intro to Astronomy, Science and Math Review Slides
- 1,644



