Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
M. Rocha
CTEP Exploring Computer Science

- Scary smart dog robots
- Self-driving cars
- Super-human game players
Recent Advances in AI
Recent Advances in AI
- Early diagnosis and treatment of diseases (e.g cancer, diabetes, etc.)
- Drug discovery
- Cybersecurity
- Weather forecasting
- Asteroid discovery and monitoring
- Research (all fields and sciences)
AI is impacting all industries and transforming the world of technology!
- Marketing and user experience
AI and Automation will not take over the world. But they will take your job!
What is driving this new wave of developments in AI?
AI is nothing new, the theory behind all these recent developments was written 50 years ago!
Big Data: The scale/cost of data has increased/decreased dramatically, by many orders of magnitude.
So what is new?
High Performance Computing (HPC): We can now process these data to make decisions in time scales that make it practical for AI applications.
Stages of Data Analysis
- Exploration
- Manipulation and transformation ( a.ka. data wrangling/data jiu-jitsu)
- Analytics: discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data (creation of useful data tools and products)
From the Data Analysis lectures:
AI is a product of Data Analytics!
AI is algorithms making decisions based on DATA/INFORMATION
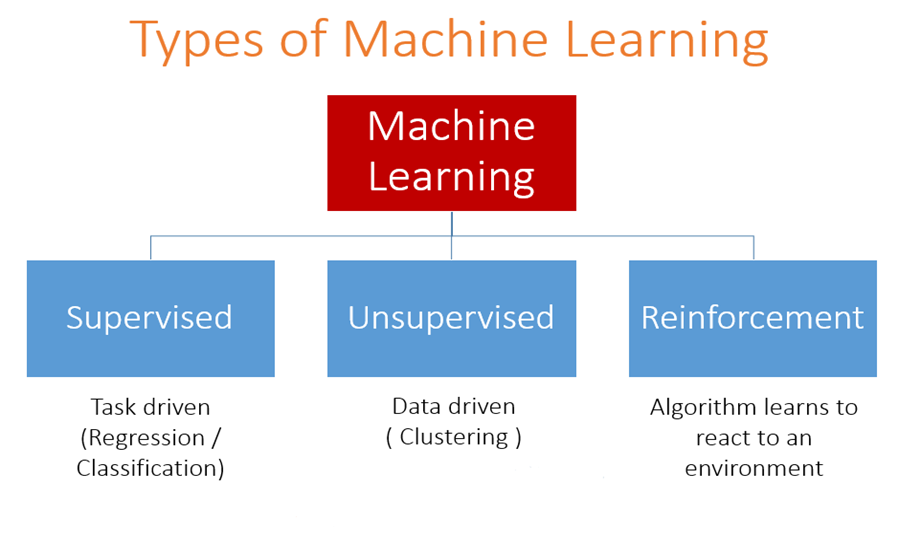
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is the formalism for writing algorithms that make decisions and predictions based on data, and that modify themselves to improve accuracy and performance

- Decisions
- Predictions
- Recommendations
- Pattern recognition
Input: Data
Output
Model with adjustable parameters
Model Optimization: The parameters of the model are adjusted by the ML algorithm to produce the most accurate output
Labeled data available for training.
Examples: Regression, Classification
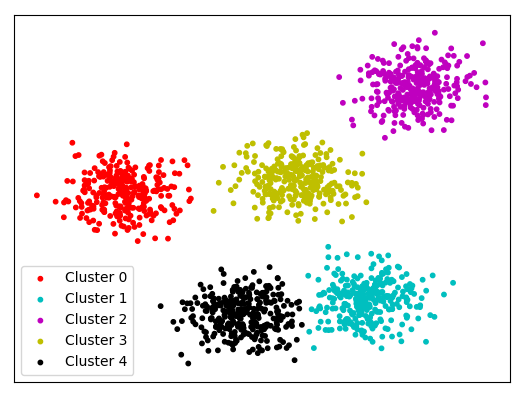
No labeled data for training.
Examples: Clustering (grouping based on patterns in the data)
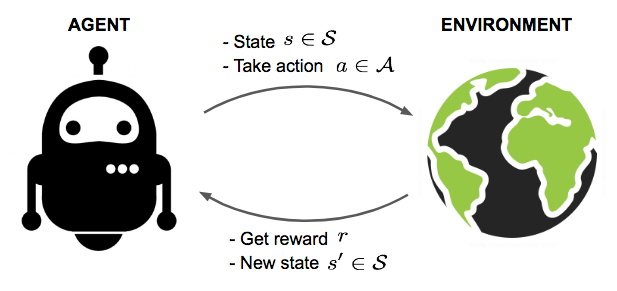
Algorithm learns to react to environment based on reward.
Examples: Robotic Navigation,
AlphaGo/AlphaZero

Building a Simple ML Model
Can we build a ML model that guess your height based on the length of your hand?
Lets try!
We first need some data

Measure your hand length
Measure height
Example data here:
Now we need a model
Lets try a simple linear regression model:
Further more we are trying to predict height, which is a continuous variable, thus we will use a regression model (if we wanted to tell tall v.s. short we would use a classification model)
We have some labeled data to train the model with, so we will use a supervised algorithm
In our case: y = Height, x1 = Hand Length
Training the Model
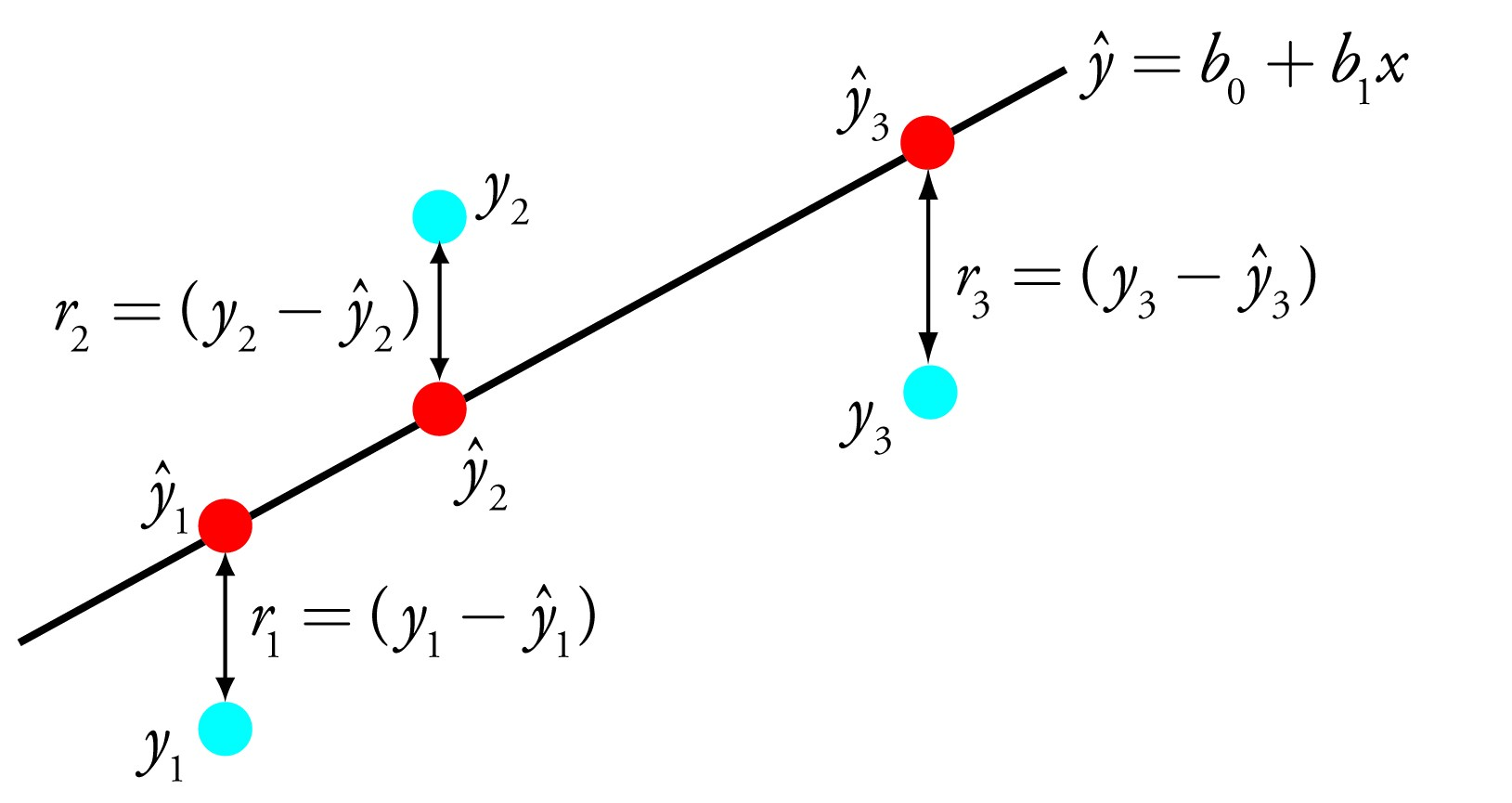
Training the model is the process of finding the set of coefficients that best fits our data
Model:
To do so we need to define a cost function:
Cost Function:
In the ML jargon, training the model is the process of minimizing the cost function
Gradient Descent
Gradient descent is the computational method used to find the minimum of the cost function efficiently
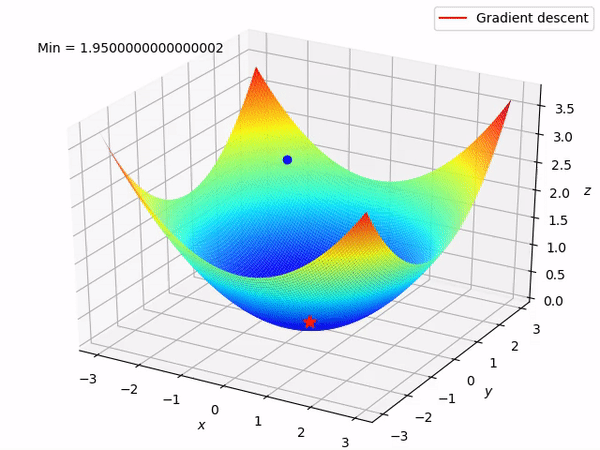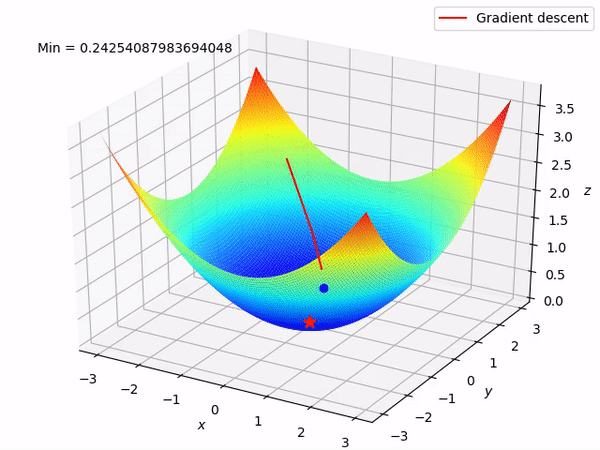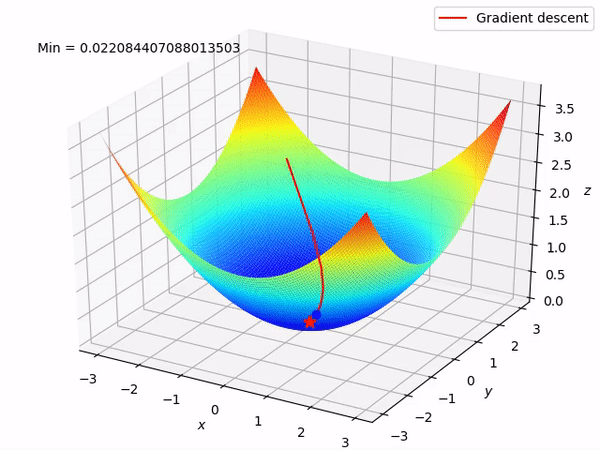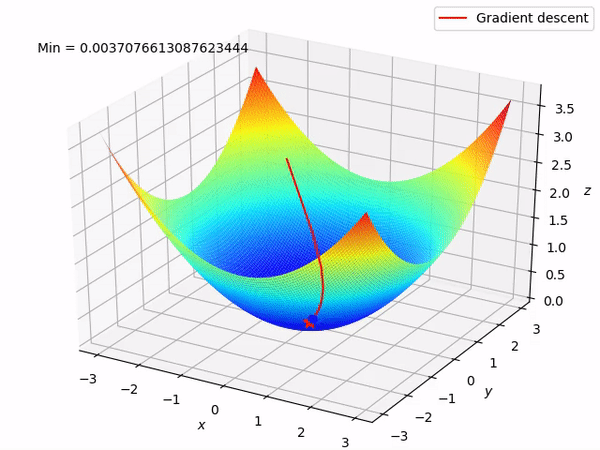

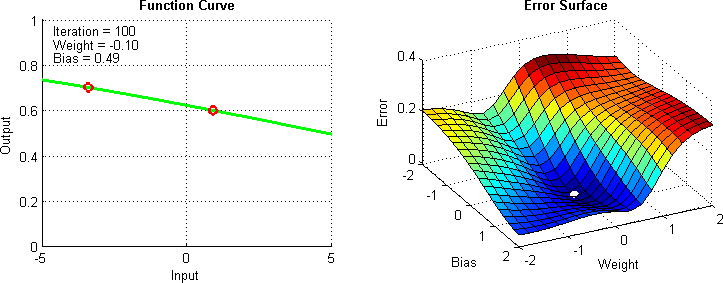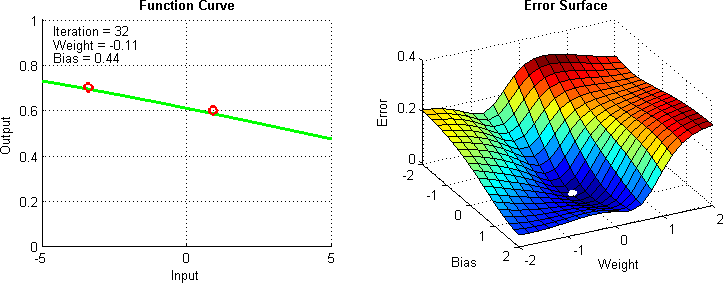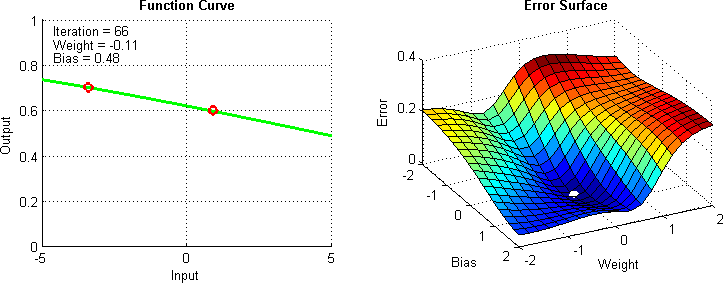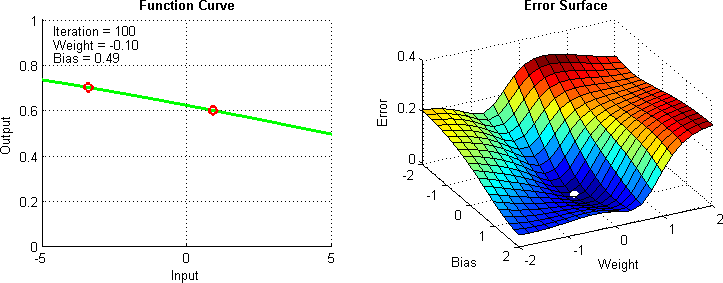
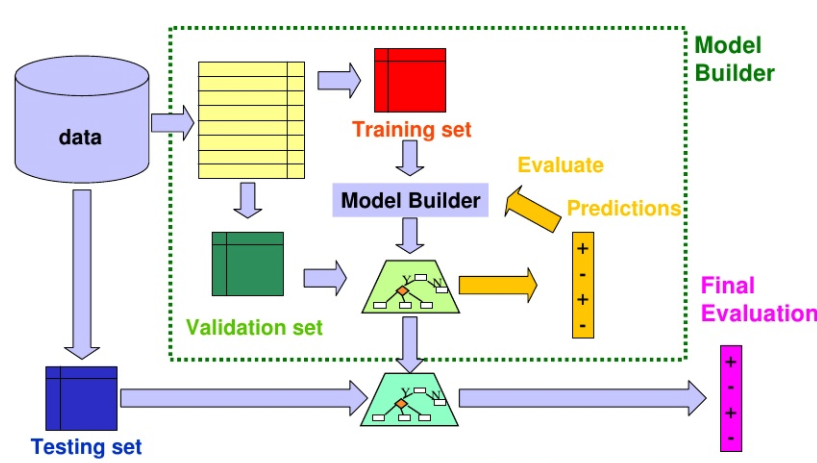
Data Split for Model Training, Validation and Evaluation
80%
20%
80%
20%
The 80:20 ratio for splitting your data is a good starting point but depends on the model and the amount of data
Assignment 14
Linear regression the Machine Learning way in Python
1. Get the height-length.csv data file
$ ipython33. Import the Numpy, Matplotlib and Scikit-learn packages
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg') # This is only required to use matplotlib on Cloud9
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
0. Clone the exploringcs-python-environment on Cloud9 (executed the command below if you get an error when importing scikit-learn)
$ wget https://mrocha.org/height-length.csv2. Open an Ipython terminal
$ sudo pip3 install scikit-learn# import model
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# import module to calculate model perfomance metrics
from sklearn import metrics
4. Import linear model from scikit-learn
5. Read the data and set the X and y
6. Split your data into training and testing sets
data = pd.read_csv("height-length.csv")
x = data["hand_length"]
y = data["height"]
# Splitting X and y into training and testing sets
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=1)
# We need to reshape our x array since it has only on feature
# (sci-kit learn expects more than one feature)
x_train = x_train.values.reshape(-1, 1)
x_test = x_test.values.reshape(-1, 1)8. Fit a linear model to the training part of your data
# Linear Regression Model
linreg = LinearRegression()
# Fit the model to the training data (learn the coefficients)
linreg.fit(x_train, y_train)9. Make predictions on the testing set and find the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
# make predictions on the testing set
y_pred = linreg.predict(x_test)
# compute the RMSE of our predictions
print(np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)))9. Test how well it tells your height based your hand length
your_height = linreg.predict(np.array(float(your_hand_length)).reshape(1,-1))[0]
print("Your predicted height is: {:.2f} in, {:.2f} ft".format(your_height, your_height/12))your_hand_length = input("What is your hand length in inches?\n")but your are not done!
That is cool
10. Create a file named predict-height.py and put all of the python commands of this assignment in it, then test it with the command
$ python3 predict-height.pyArtificial Neural Networks and
Deep Learning
Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are Machine Learning algorithms vaguely inspired on the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains
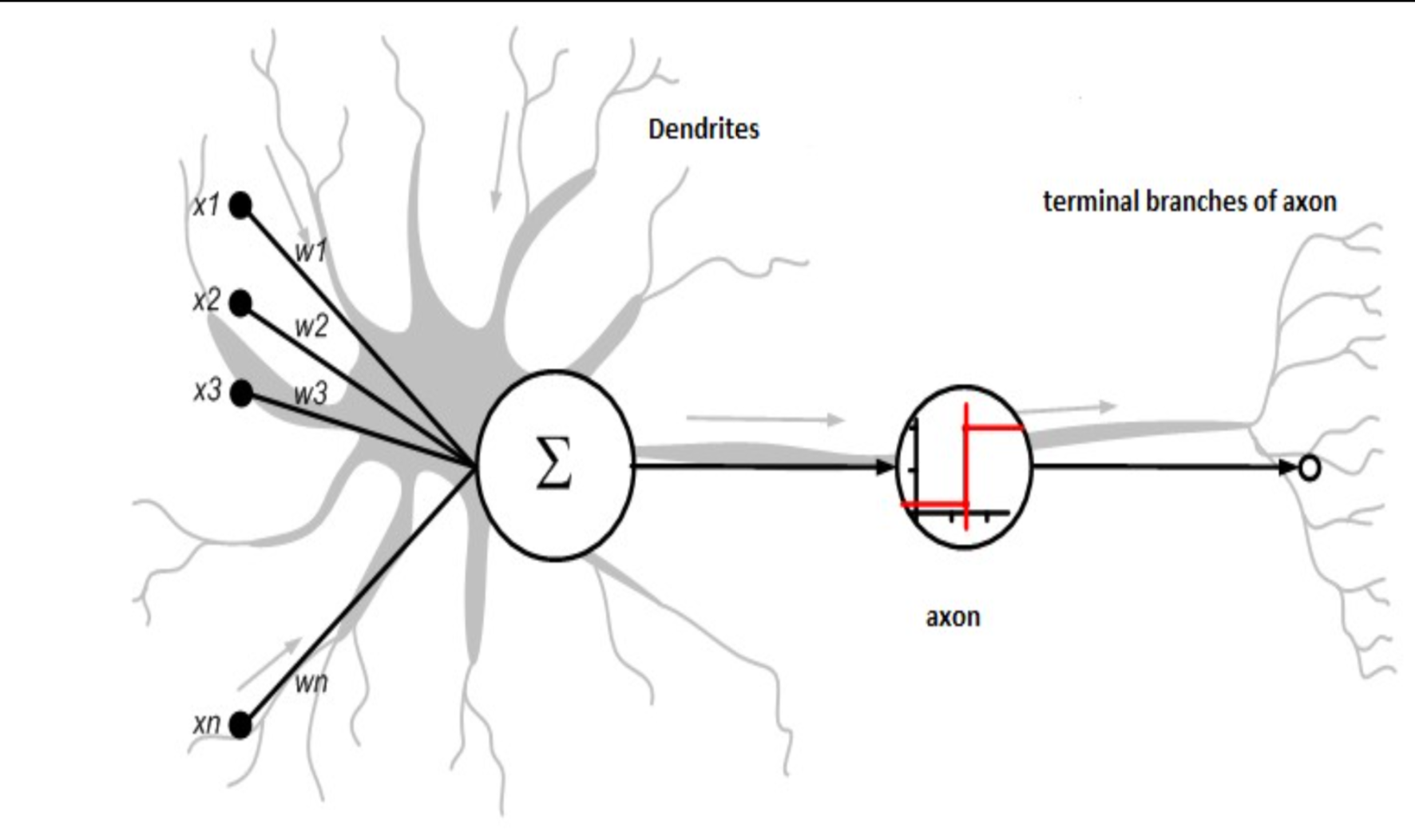
Nodes or Units
Synapses/Connections
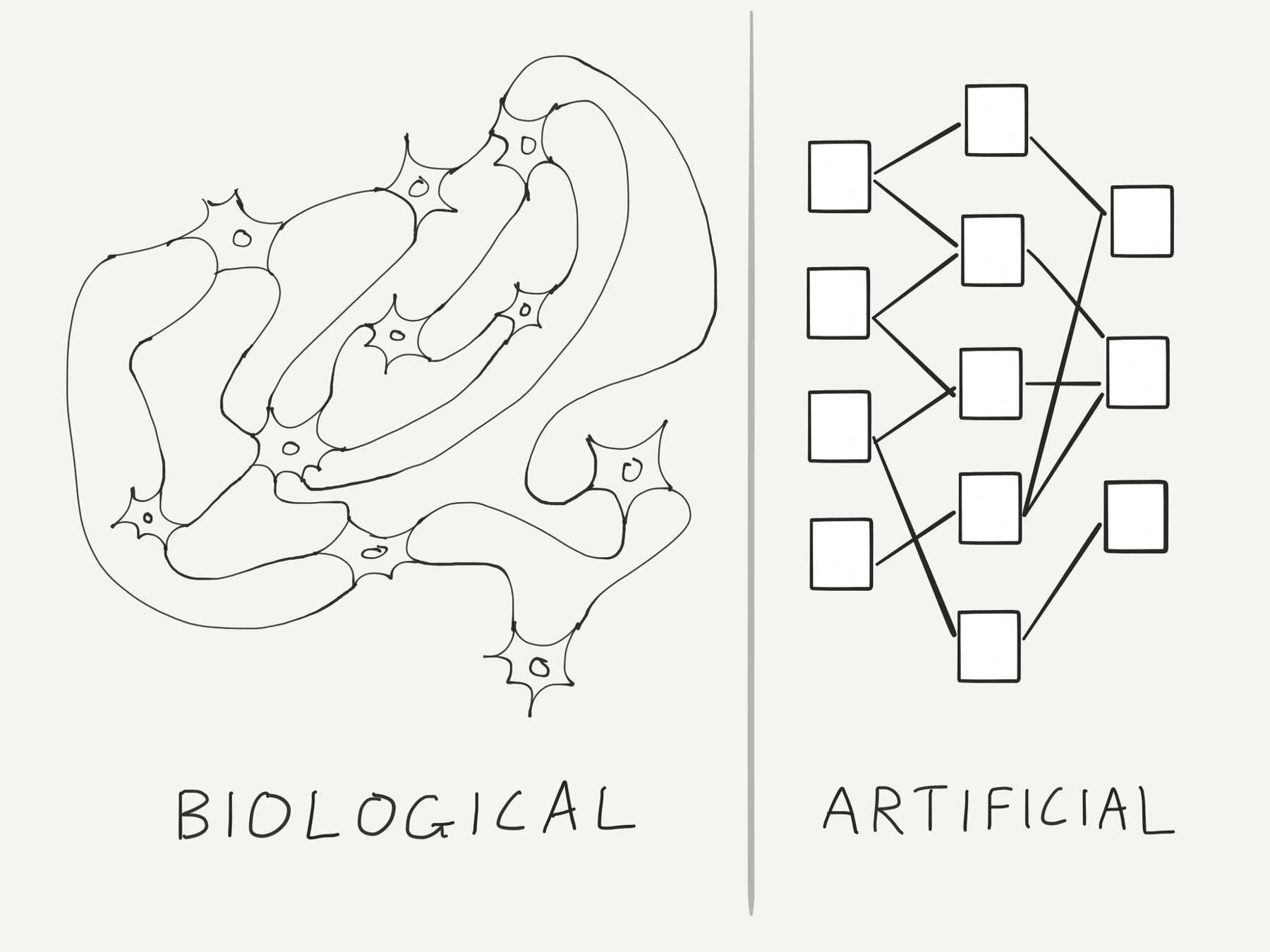
Artificial Neural Networks
Neural Networks
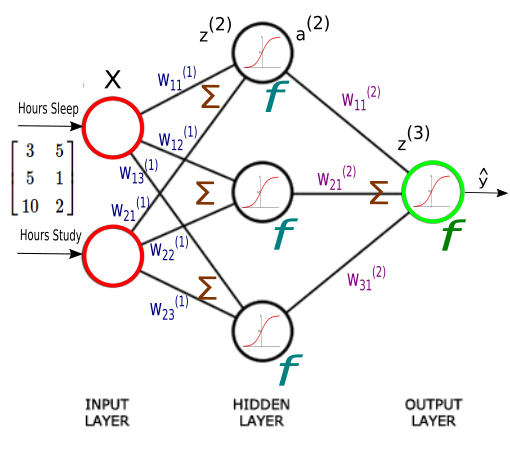
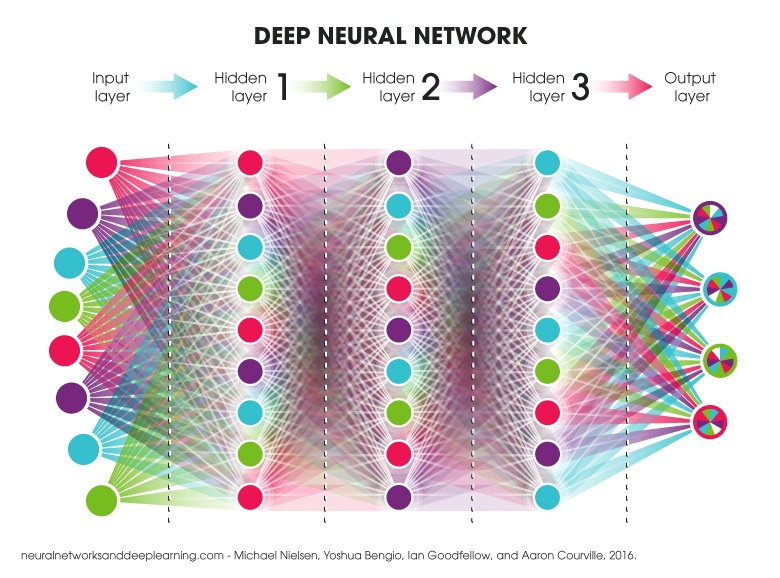
ANNs are arranged in layers. The first layer has input neurons which send data via synapses to the second layer of neurons, the last layer (output layer) outputs the results of the model.
Any layer between the input and output layer is called a hidden layer
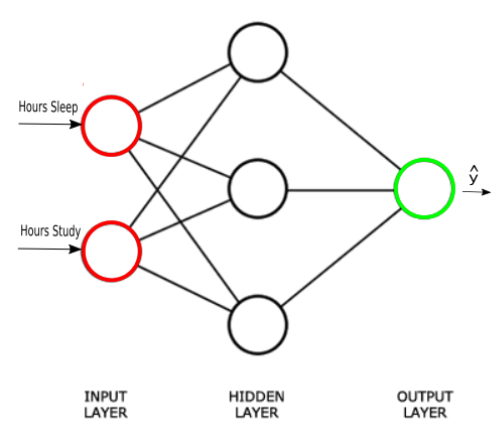
Test Score
x2: Hours of Sleep
x1: Hours of Study
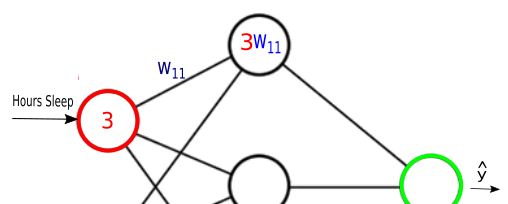
Synapses take a value from their input, multiply it by a specific weight, and output the result
Neural Operations
Synapses take a value from their input, multiply it by a specific weight, and output the result.
Nodes/Units add together the outputs of all their synapses, and then apply an activation function.
Test Score
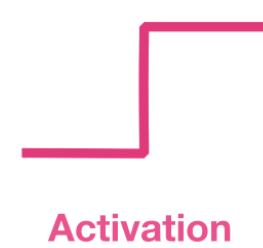
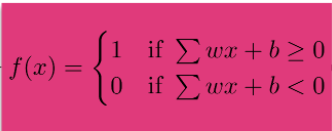
Activation Function
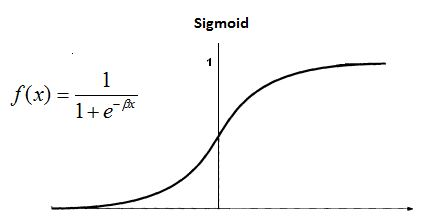
Sigmoid Activation Function
The sigmoid (or logistic) activation function gives you flexibility on how to define the threshold for activation
0.5
1
-x
x=0
Training the Network: The Backpropagation algorithm
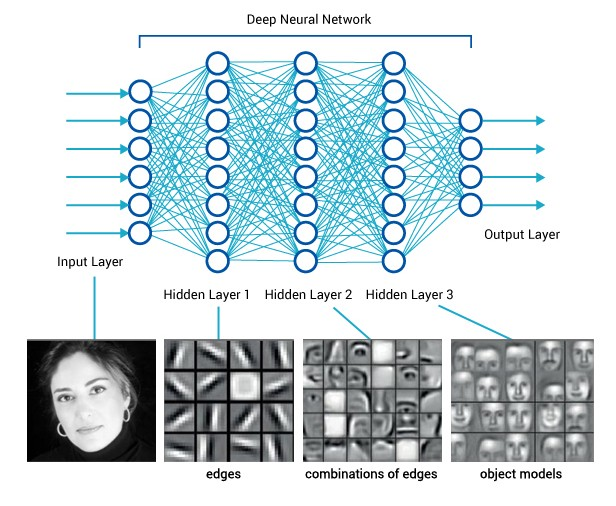
Deep Learning
DNNs use multiple hidden layers to model complex non-linear relationships
Graphical Processing Units (GPUs)

Deep Learning Tools

Assignment 15
Predicting diabetes onsets for Pima Indians from medical records
1. Get the Pima Indians Diabetes data file and rename it
$ ipython3$ source pyenv/bin/activate
$ pip3 install tensorflow keras0. Clone the exploringcs-python-environment on Cloud9 and Install tensorflow and keras on a isolated python enviroment
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jbrownlee/Datasets/master/pima-indians-diabetes.data.csv
$ mv pima-indians-diabetes.data.csv pima-indians-diabetes.csv2. Open an Ipython terminal
3. Follow the tutorial in this link: https://machinelearningmastery.com/tutorial-first-neural-network-python-keras/
4. When done create a file that executes all of the commands in the tutorial to reproduce the results, you can call this file keras_first_network.py, and run it by doing
$ python3 keras_first_network.pyMachine Learning and AI
By Miguel Rocha
Machine Learning and AI
Exploring Computer Science: lecture 17
- 800




