Electromagnetic Waves,
Light and Color
M. Rocha
Physics 1 - Chapters 26 -27
Electromagnetic Waves
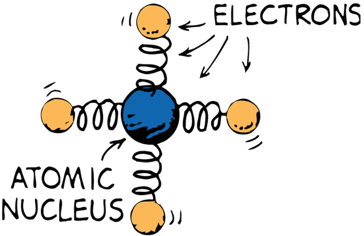
Moving charges produce magnetic fields

and moving magnetic fields produce electric fields
Current
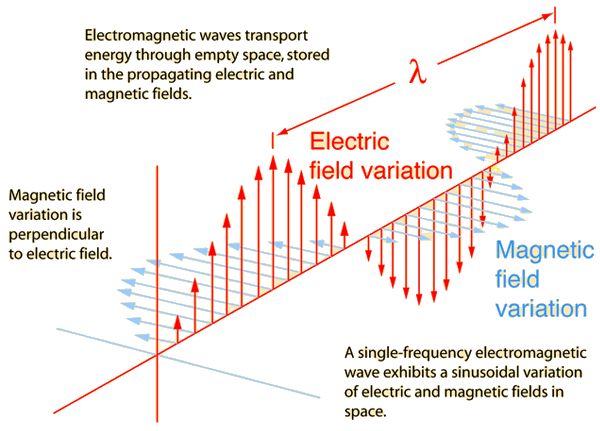
Electromagnetic Waves
Oscillating charges create oscillating magnetic fields, which in turn create oscillating electric fields



The result are oscillating electric and magnetic fields that regenerate each other while traveling on space
Electromagnetic Waves
E&M waves need not material medium to travel!
They can travel on vacuum
E&M waves have the standard properties of waves, but they all travel at the same speed, the speed of light
Electromagnetic Spectrum

Wavelength (m)
Light :

E&M waves in the visible range of the spectrum

Normal: Line perpendicular to interface
Checkpoint
What color of light has the highest frequency?
Violet
Checkpoint
What color of light has the shortest wavelength?
Violet
Refraction and Dispersion of Light
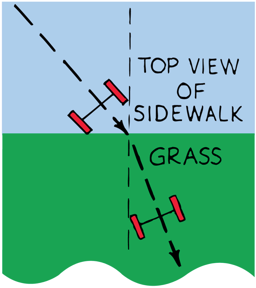
Wave Refraction
The bending of waves due to change of speed


Refraction of Light
Light rays refract (bend) when they pass from one medium to another at an oblique (not straigth) angle
Refraction is the result of waves changing speed as they cross from one medium to anoter
Direction of Refraction
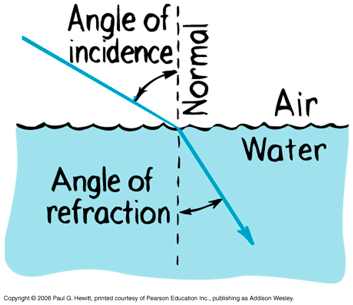
Waves bend towards the normal when going from fast to slow
and
away from the normal when going from slow to fast
Checkpoint 3
If you want to spear a fish from above the water, do you have to aim higher or lower?



Image
Actual
Lower

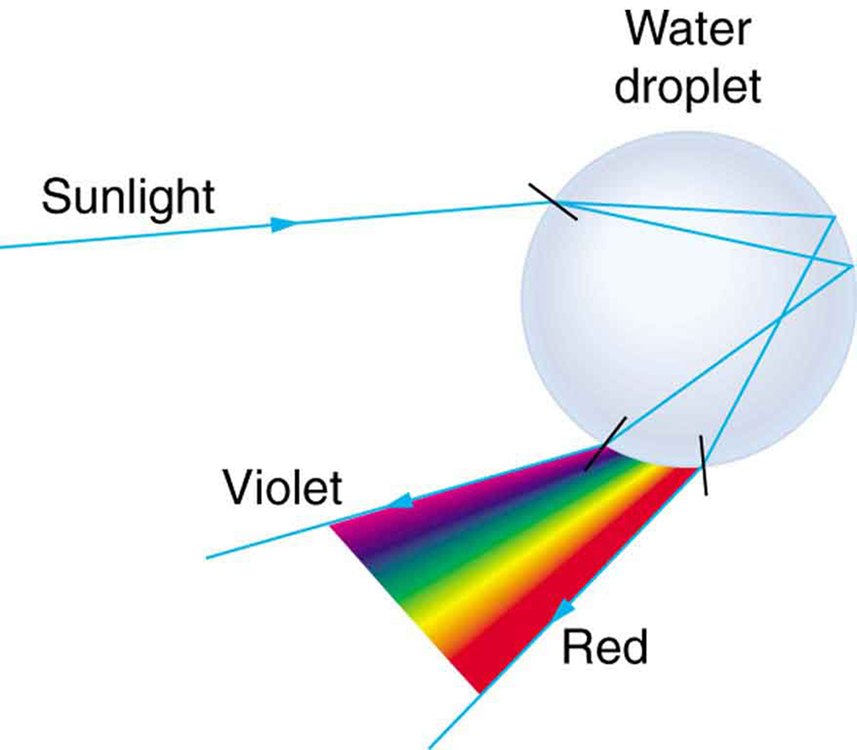
Dispersion happens because the refraction of light is frequency dependent
This is because higher frequencies travel slower inside the prism
Slowest
Fastest
Dispersion of Light
Vision and Color
Primary and Complementary Colors
Primary Colors:
Complementary Colors:
Red
Green
Blue
White - Red = Cyan
White - Green = Magenta
White - Blue = Yellow
Y
C
M

Selective Reflection
Most materials absorb light of some frequencies and reflect the rest
A red ball for example absorbs light of most visible frequencies and reflects red

Red ball seen under white light
Red ball seen under red light
Red ball seen under green light
Selective Transmission
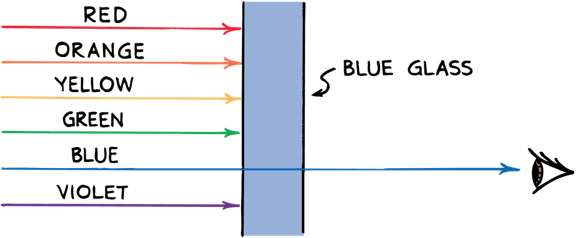
Blue glass transmits only energy of the frequency of blue light. Energy of the other frequencies is absorbed and warms the glass

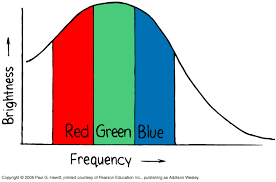
The radiation curve of sunlight is a graph of brightness versus frequency. Sunlight is brightest in the yellow-green region.
Sunlight
Why are sunsets are red?
As light from the sun travels through the atmosphere more and more blue/green light is scattered away

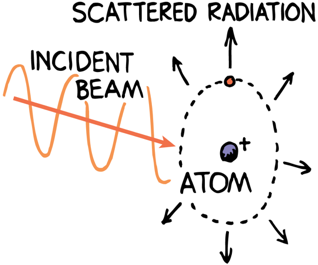

Why is the sky blue?
The molecules of our atmosphere scatter high frequency light (blue) more than low frequency light (red)


Checkpoint 4
Why are clouds white?
Because water droplets scatter light of all frequencies the same

Color of Water?
Water molecules scatter infrared and to some extent red light
White - Red = Cyan
The End
Transparent vs. Opaque Materials


How a materials responds to light depends on the frequency of light and the natural frequency of electrons in the material
Glass is transparent to all the frequencies of visible light
Some opaque materials absorb certain frequencies while others reflect certain frequencies
Transparent Materials
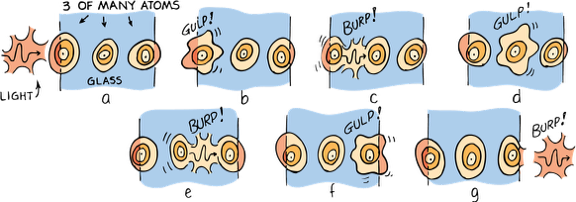
In transparent materials, the frequency of the reemitted light is identical to that of the light that produced the vibration to begin with
A light wave incident upon a pane of glass sets up vibrations in the atoms.
Because of the time delay between absorptions and reemissions, the average speed of light in glass is less than c
Opaque Materials
In opaque materials, any vibrations from light are either absorbed and turned into internal energy or reflected

In metals, the outer electrons of atoms are not bound to any particular atom. When light shines on metal and sets these free electrons into vibration, their energy is reemitted as light
Electromagnetic Waves, Light and Color
By Miguel Rocha
Electromagnetic Waves, Light and Color
Physics 1 - Week 12 - Chapters 26-27
- 1,817



