Electric Current, Resistance, Ohm's Law & Power
M. Rocha
Physics 4B
Electric Current
Electricity in motion
Electric Current
Just like water flows whenever there is a altitude difference, electric charge flows whenever there is a voltage difference
Electric
Potential Difference
(voltage)
Gravitational Potential Difference
Electric Current

Electric current is measured in amperes or amps (A)
An ampere is the flow of
1 coulomb of charge per second
1 coulomb = 6.24 x 10^18 e
= 6.24 billion billion electrons
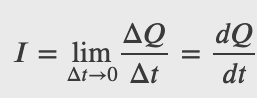
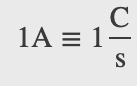
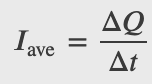
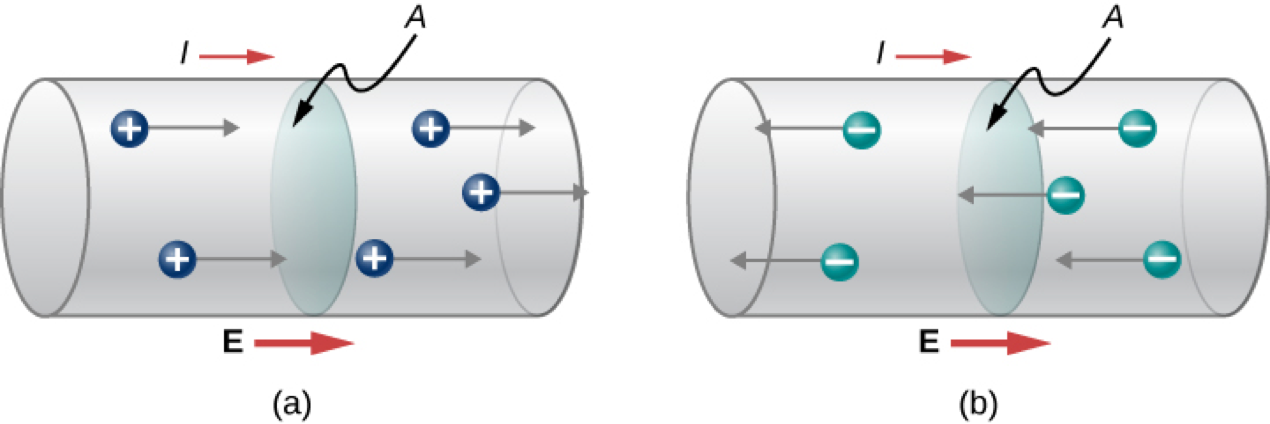
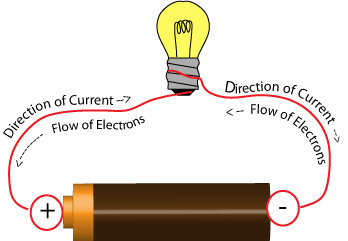
Electric Charge Flow
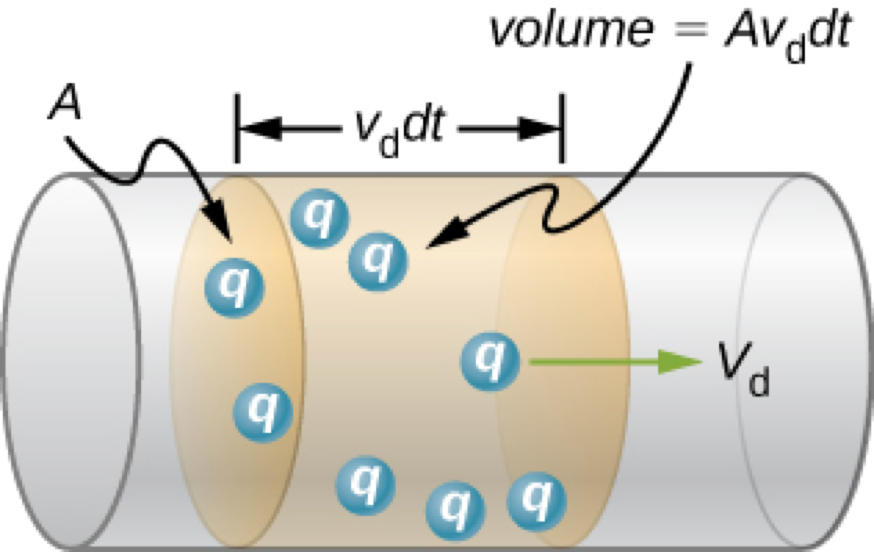
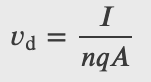
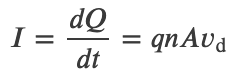
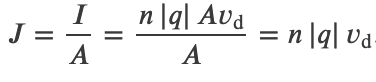
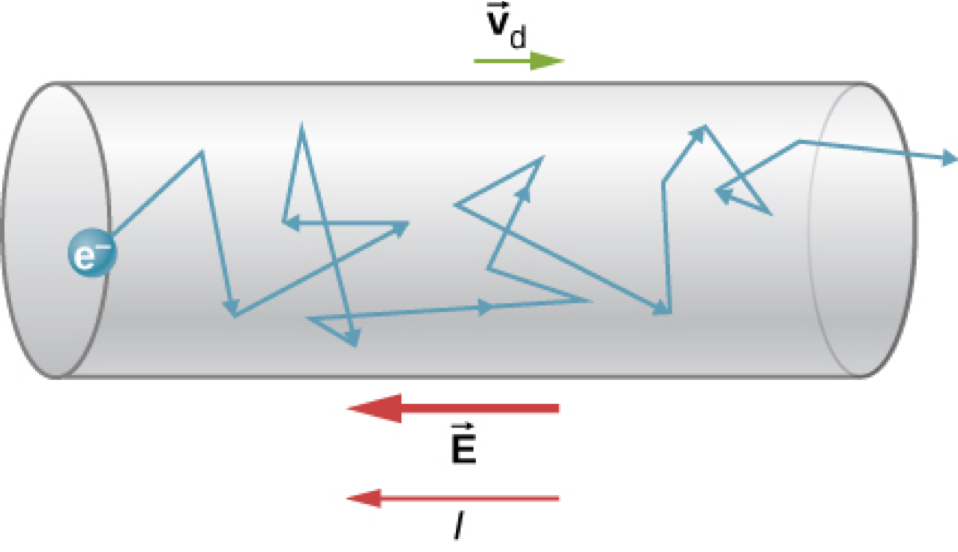
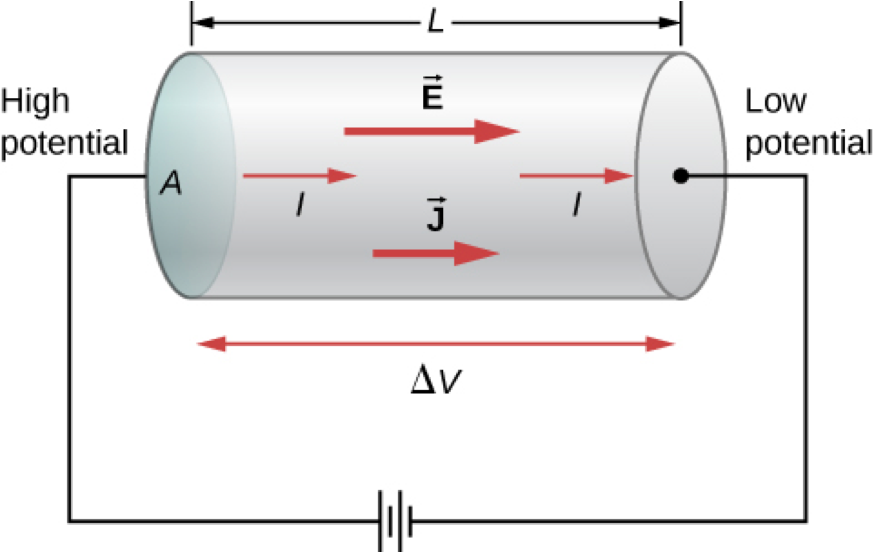
Drift Velocity and Current Density
Current:
Drift Velocity:
Current Density:
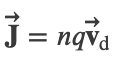
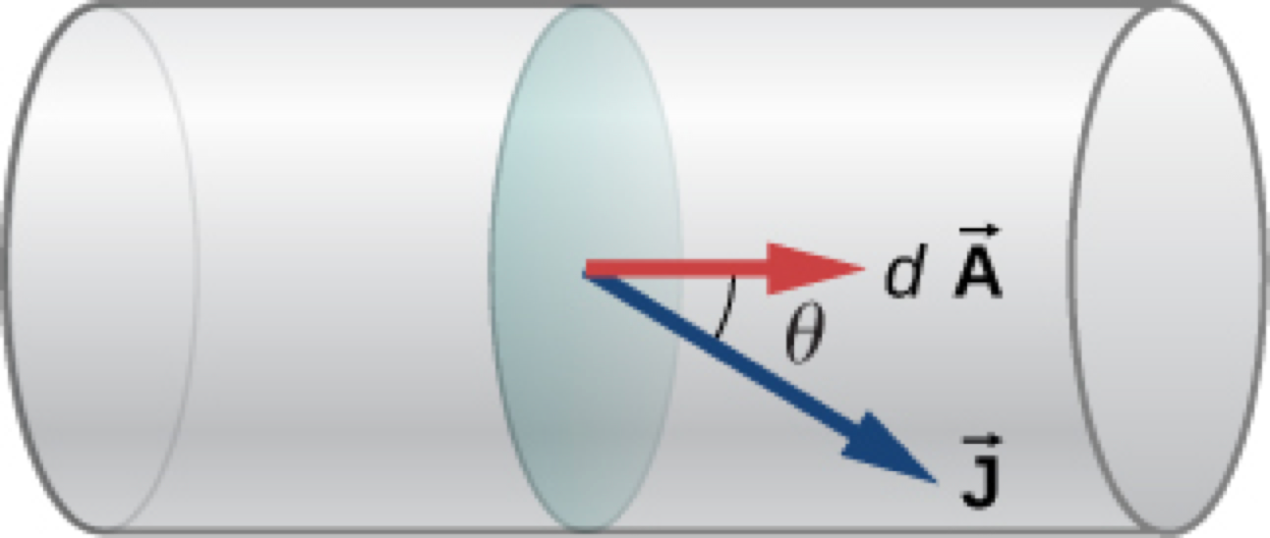
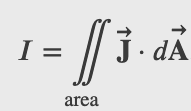
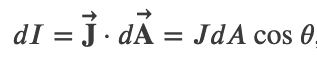
Current from Current Density
If uniform Current Density:
Electrical Resistance

For a given pressure, more water passes through a large pipe than a small one
Similarly, for a given voltage, more electric current passes through a large-diameter wire than a small-diameter one

Less resistance
More resistance
Electrical Resistance

Voltage Source
A simple hydraulic circuit is analogous to an electric circuit
Ohm's Law
The Current flow is proportional to the Voltage and inversely proportional to the Resistance
Units:
A potential difference of 1 volt across a circuit with a resistance of 1 ohm will produce a current of 1 ampere
Ohm (symbol Ω) is the unit of resistance
Checkpoint
A typical light bulb has a resistance of about 100 ohms. What is the current flow across a light bulb when connected to an electric socket providing 120 volts?
Checkpoint
If the resistance across your body is 1000 times greater than a typical light bulb, how much current would flow trough your body if you touch an electric socket? (current = 1.2 amps for the bulb)

Electric Shock
Ohmic Heating
Flowing electrons strike atoms in a conductor, heating the material. For a given voltage the higher the resistance the higher the heating


Toaster
Oven
Light bulb
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
A fuse is designed to melt (due to ohmic heating) when current is too large
Circuit breaker does same job without needing replacement; flip the switch to reconnect


Conductivity and Resistivity
The conductivity σ of a material tells you how much current density you get for given amount of E-field
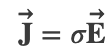
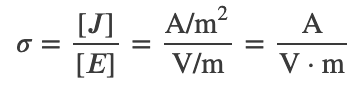
Units of σ :
The resistivity 𝜌 of a material is the inverse of its conductivity
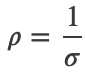
Units of 𝜌 :
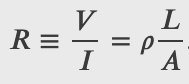
Electrical Resistance from Resistivity
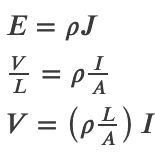

Circuit Resistors
Electric Power
Units:
Checkpoint
A kilowatt is 1000 watts, and a kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy consumed in one hour at the rate of 1 kilowatt. If electric energy costs 20 cents per kilowatt-hour, what does it cost to operate a 100 watt light bulb for 10 hours?
100 watts x 10 hours (20 cents/kilowatt-hour)
= 1 kilowatt-hour (20 cents/kilowatt-hour)
= 20 cents
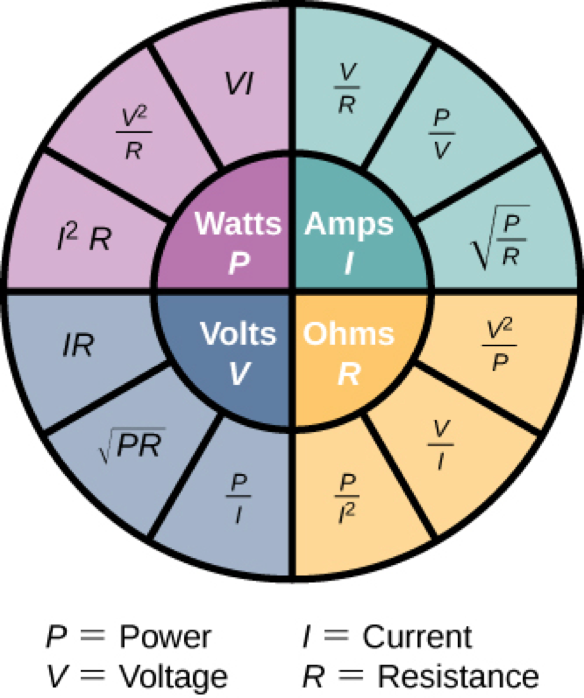
Summary of Relationships
Direct vs. Alternating Currents

Direct current (DC) is current that flows in only one direction
Alternating current (AC) is current that flows back and forth with alternating direction


The End
Electric Current
The instrument to measure current is called an Ammeter

Due to charge conservation, same current into and out of light bulb
Capacitors
Capacitors are used to store electric potential energy

They produce a short lived current while discharging
Electric Current, Resistance & Ohm's Law
By Miguel Rocha
Electric Current, Resistance & Ohm's Law
Physics 4B
- 1,063



