Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction
M. Rocha
Physics 4B
Magnetism
Magnets are Fun!

How do magnets work?
Origin of Magnetic Force
When electric charges move they create a magnetic field

The magnetic field is due to "distortions" in the electric field caused by motion

The right hand rule tells you the direction of the magnetic field due to a positive moving charge
Magnetism as a Consequence of Special Relativity
When electric charges move they create a magnetic field
The magnetic field is due to "distortions" in the electric field caused by motion

The right hand rule tells you the direction of the magnetic field due to a positive moving charge

Spinning charges are moving charges, thus create magnetic fields
Origin of Magnetic Force
Checkpoint
A proton travels in a circular path counterclockwise as shown below. What is the direction of the magnetic field lines at the center?

+
Away from the screen (towards you)
Magnetic Poles
North Pole: Side where field lines point away from the source
South Pole: Side where field lines point into the source

Magnetic Forces
As with electric charges, like poles (N&N, S&S) repel and opposites (N&S) attract.
Unlike electric charges, cannot have just a North or just a South pole




How do Magnets Work?
An iron atom has four electrons whose spin magnetism is not canceled. Each iron atom is a tiny magnet. The same is true to a lesser degree for the atoms of nickel and cobalt.
How do Magnets Work?
An iron atom has four electrons whose spin magnetism is not canceled. Each iron atom is a tiny magnet. The same is true to a lesser degree for the atoms of nickel and cobalt.

How do Magnets Work?
Each iron atom is a tiny magnet. Interactions among adjacent iron atoms cause large clusters of them to line up with one another.


clusters of aligned atoms are called magnetic domains
How do Magnets Work?
Magnetic domains can be induced to align by an external magnetic field

Defining the Magnetic Force Field
A magnetic field is defined by the force that a charged particle experiences moving in this field
The magnitude of this force is proportional to the amount of charge q, the speed of the charged particle v, and the magnitude of the applied magnetic field. The direction of this force is perpendicular to both the direction of the moving charged particle and the direction of the applied magnetic field. Based on these observations, we define the magnetic field strength B based on the magnetic force 𝐅⃗ on a charge q moving at velocity 𝐯⃗ as the cross product of the velocity and magnetic field, that is,
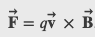
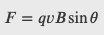
where θ is the angle between the velocity and the magnetic field.

Also you may find the images below useful when computing cross products using unit vectors
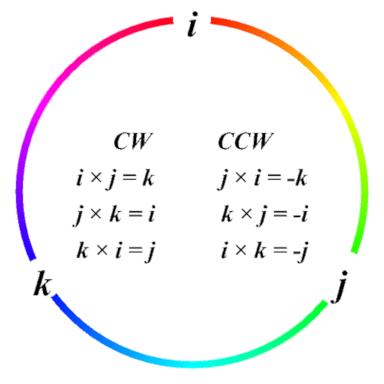
Magnetic Field Units
The SI unit for magnetic field strength B is called the tesla (T), where
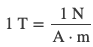
A smaller unit, called the gauss (G) is sometimes used for small magnetic field strengths
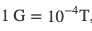
Magnetic Force on Moving Charges
Moving electric charges deflect by magnetic fields


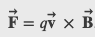
Checkpoint
An electron travels to the right within a magnetic field pointing towards the screen, in which direction would it be deflected?
_
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
Magnetic Field
It gets deflected down


A cosmic-ray electron moves at 7.5×10^6 m/s perpendicular to Earth’s magnetic field at an altitude where the field strength is 1.0×10^−5T. What is the radius of the circular path the electron follows?
Checkpoint
Magnetic Force on a Currents-Carrying Conductor
Moving charges in an electric current experience a force due to magnetic field


Magnetic Force on a Currents-Carrying Conductor
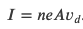

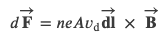
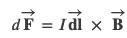
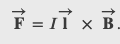
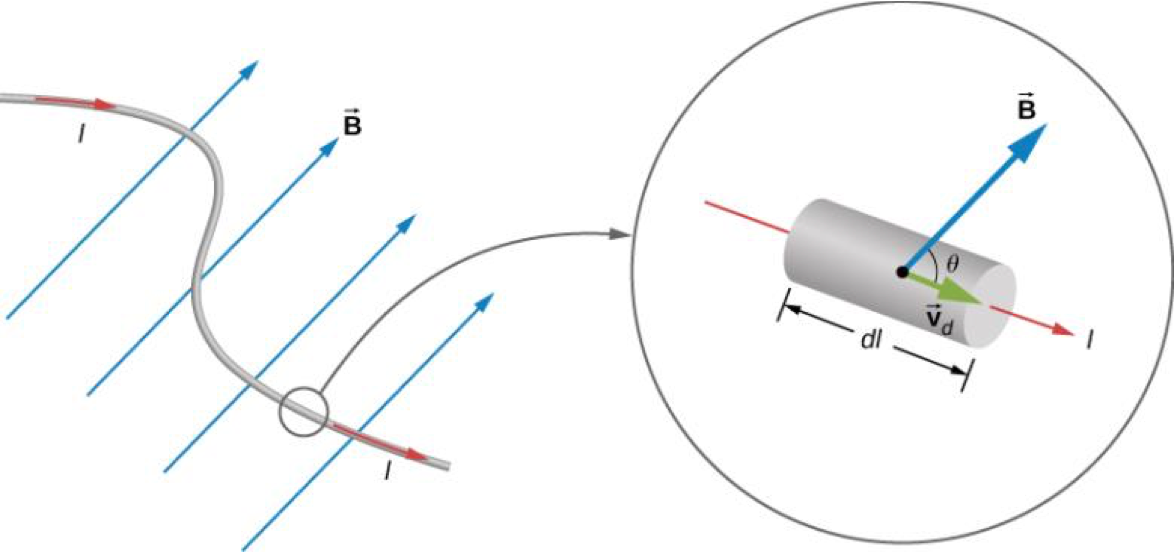
For an infinitesimal section of wire 𝑑𝑙, the volume is 𝑉 =𝐴·𝑑𝑙, so the number of charge carriers is given by 𝑛𝐴·𝑑𝑙.
The magnetic force on any single charge carrier is 𝑒𝐯⃗×𝐁⃗ , so the total magnetic force 𝑑𝐅⃗ on the 𝑛𝐴·𝑑𝑙 charge carriers in the section of wire is
or
Using the equation of current
For a straight wire in a uniform magnetic field
Electric Motors


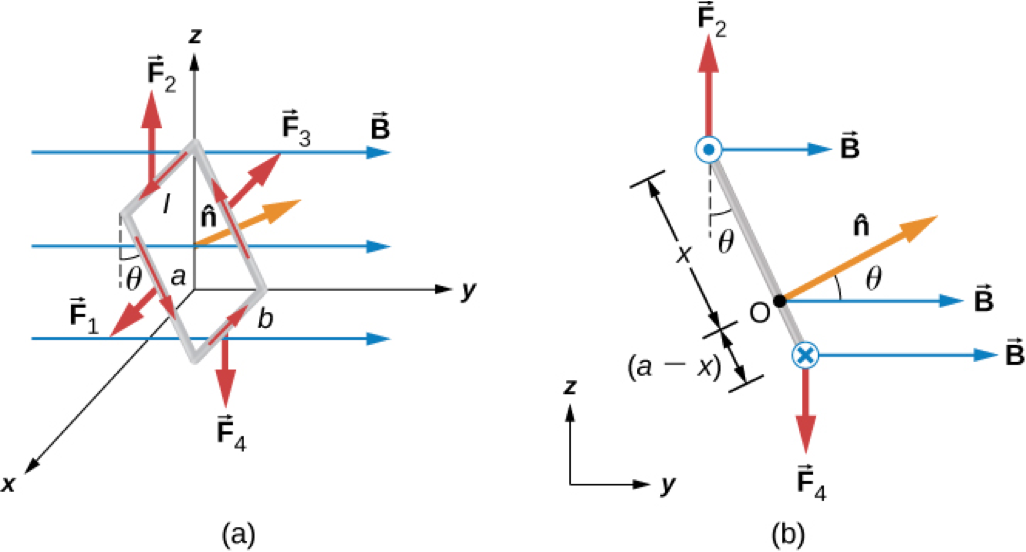
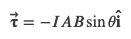
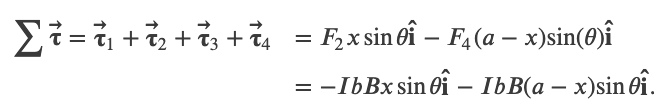
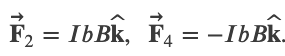
Net torque on a current loop within a magnetic field
or
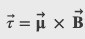
where
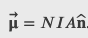
Checkpoint
What is the maximum torque on a 150-turn square loop of wire 18.0 cm on a side that carries a 50.0-A current in a 1.60-T field?
Speakers

Oscillations are created by variations in electrical current, which cause an electromagnet to be pulled towards and away from a second, permanent magnet
These oscillations cause the membrane of the speaker to vibrate with the same frequency as the oscillations in the electrical current.
Magnetic Fields Due To Currents
Electric Currents and Magnetic Fields
An electric current produces a magnetic field

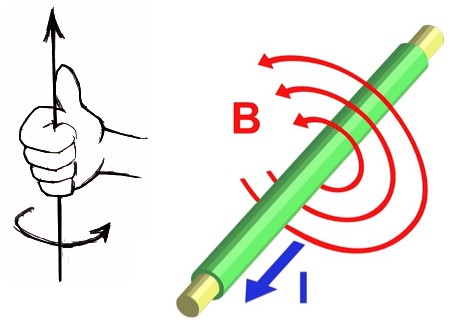
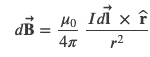
Biot-Savart Law
The magnitude and direction of the magnetic field 𝑑𝐁⃗ due to an element 𝑑𝐥⃗ of current-carrying wire is given by
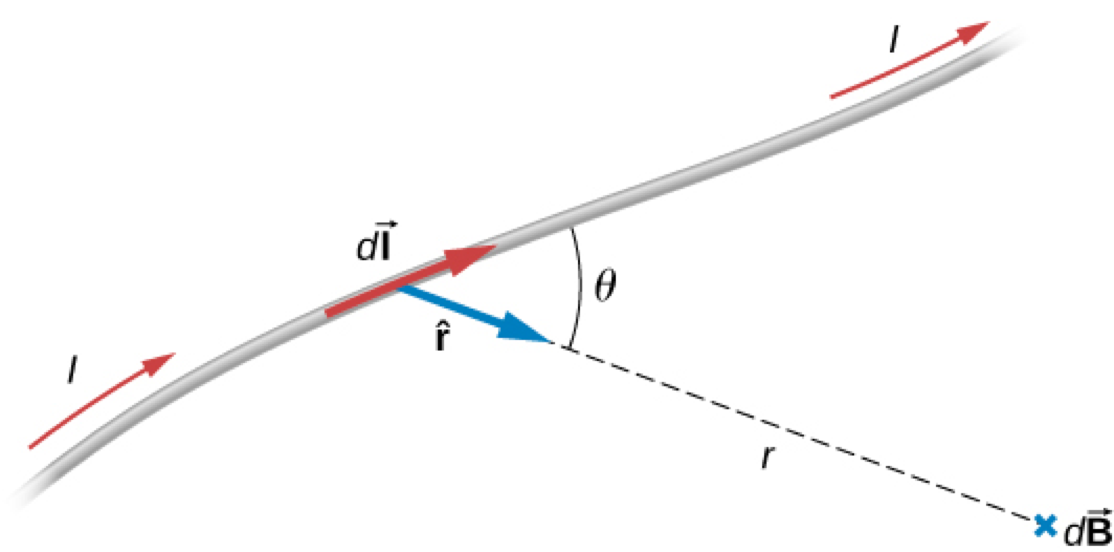

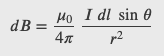
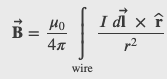
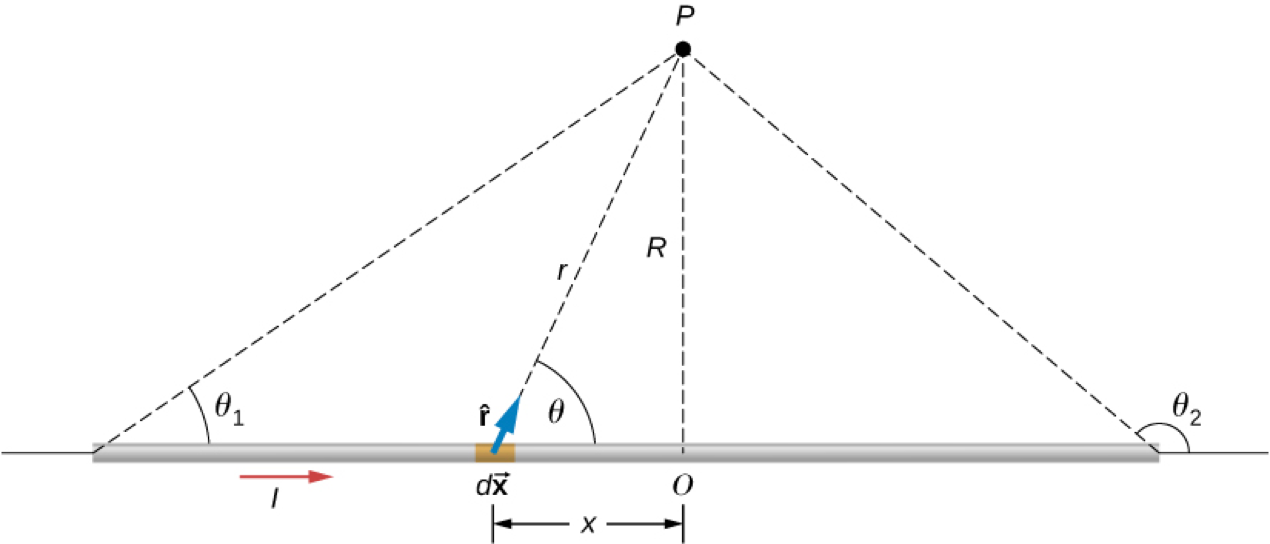
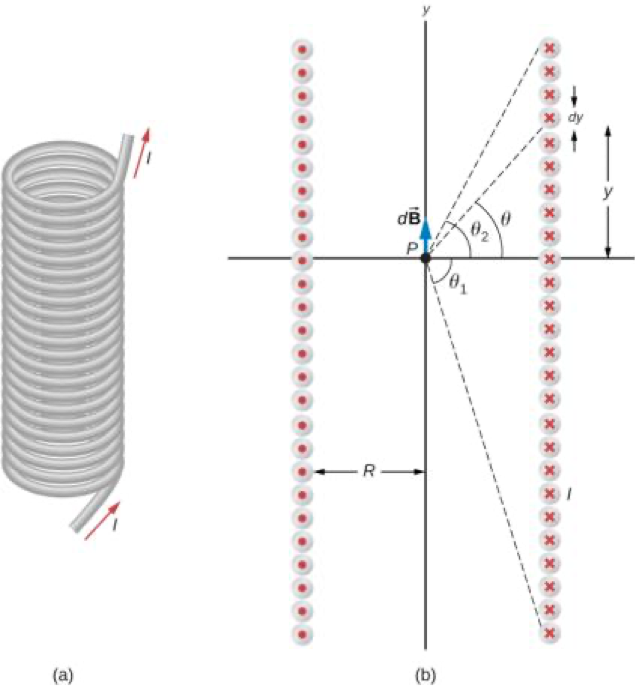
Magnetic Field Due to a Thin Straight Wire
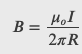
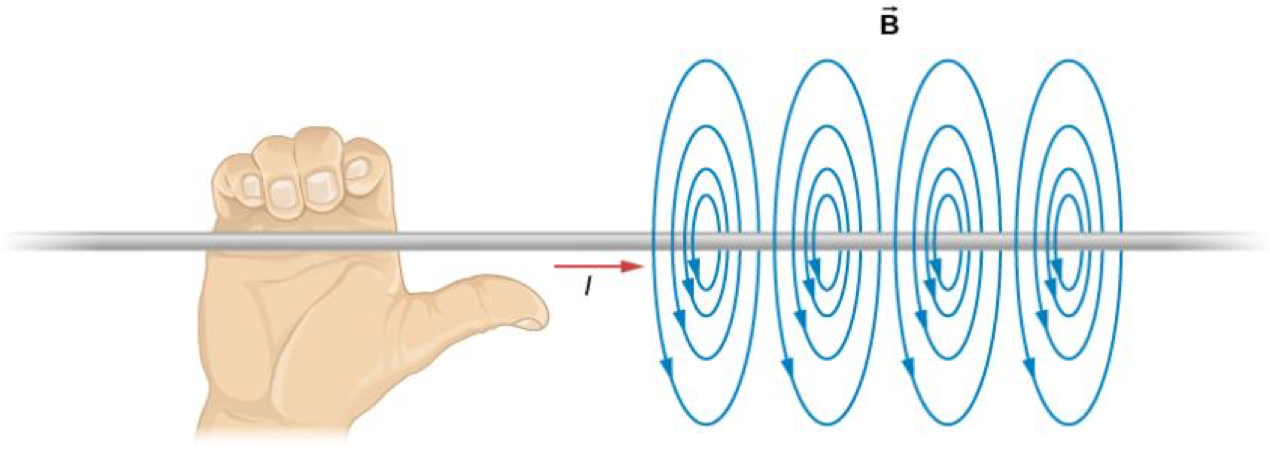
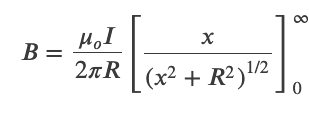
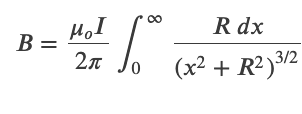
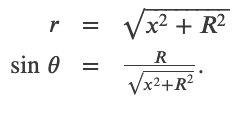
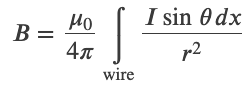
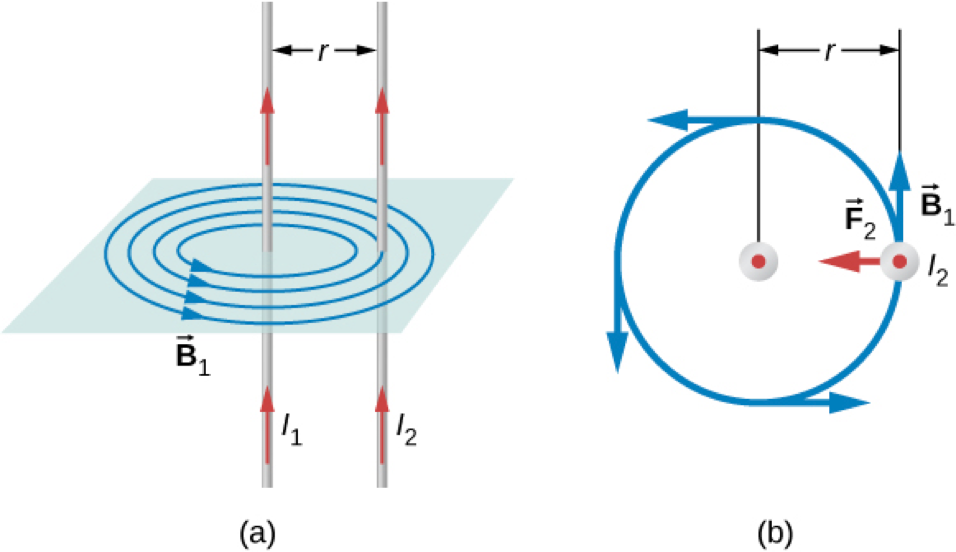
Force between Two Parallel Currents
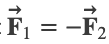
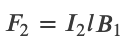
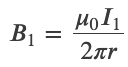
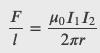
Magnetic Field of a Current Loop
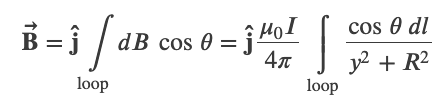
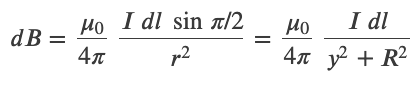
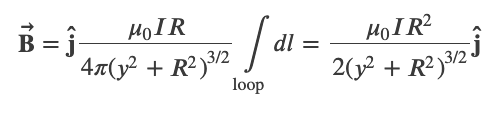
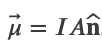
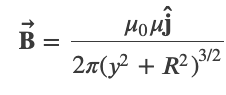
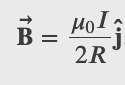
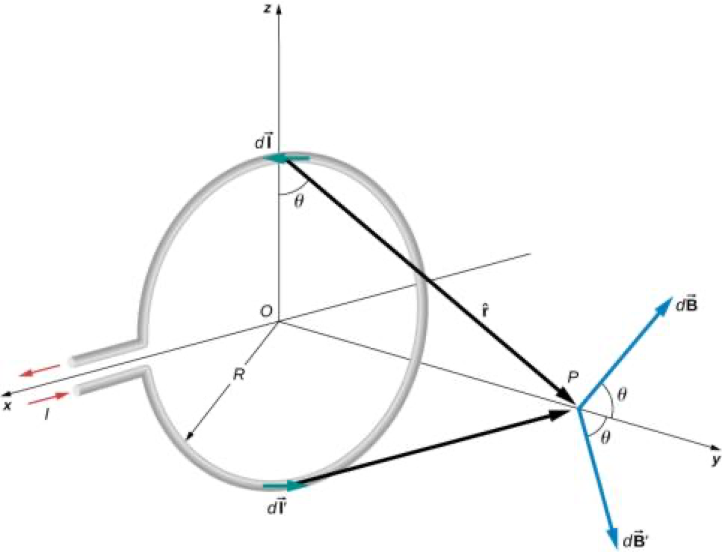
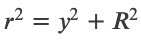
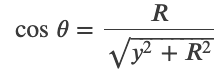
At the center of the loop (y = 0)
where
or
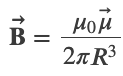
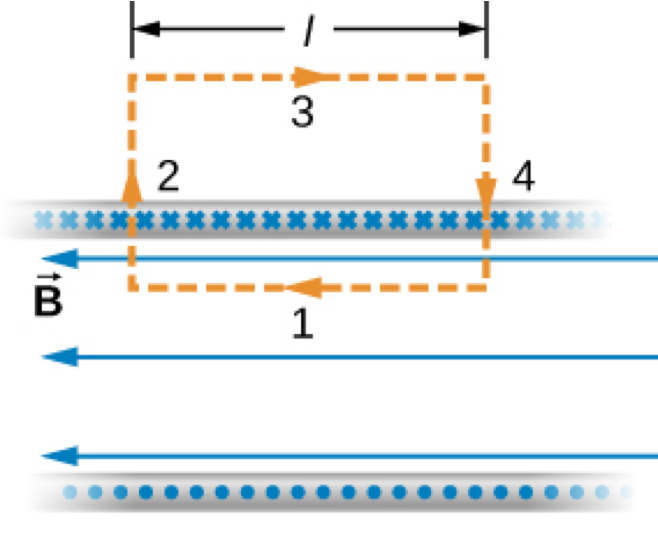
Amperes Law
Ampere's Law
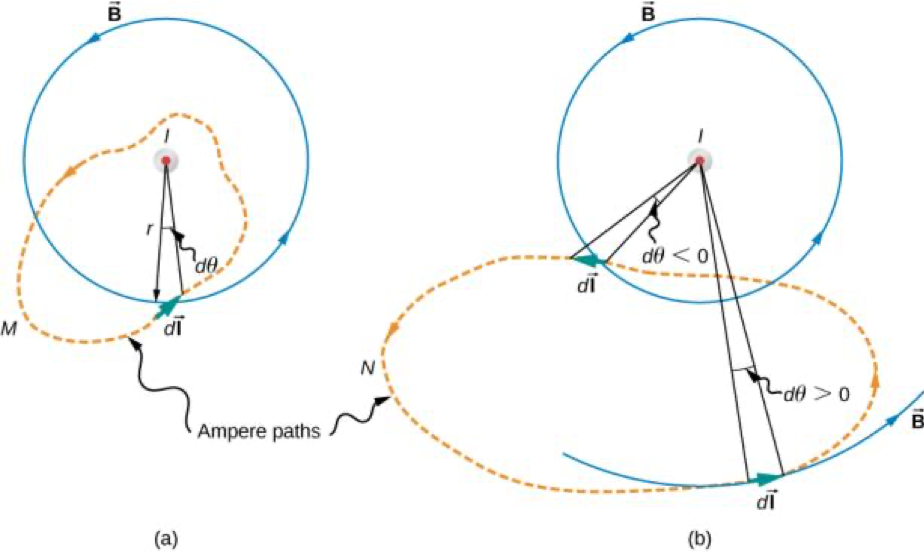
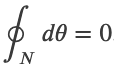
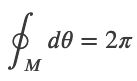
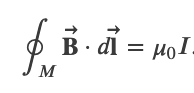
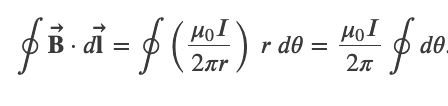
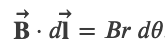
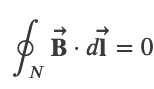
,
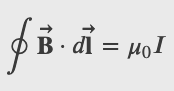
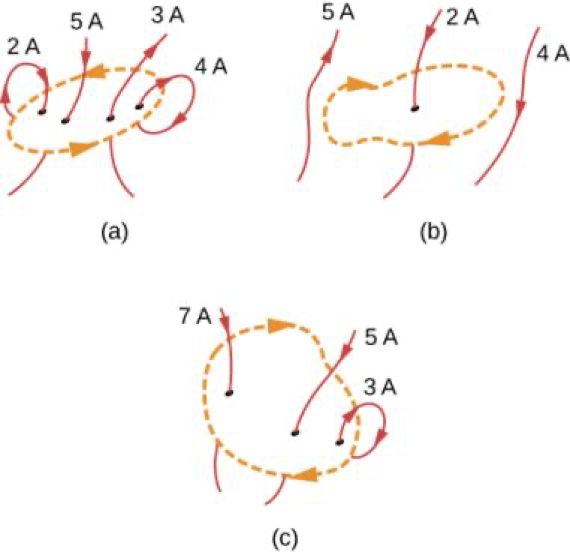
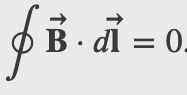
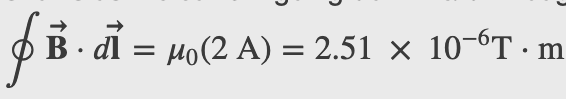
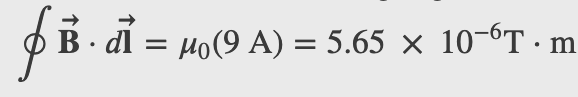
Magnetic Field Within a Solenoid
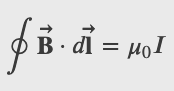
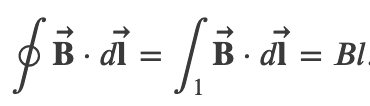
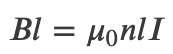
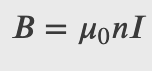
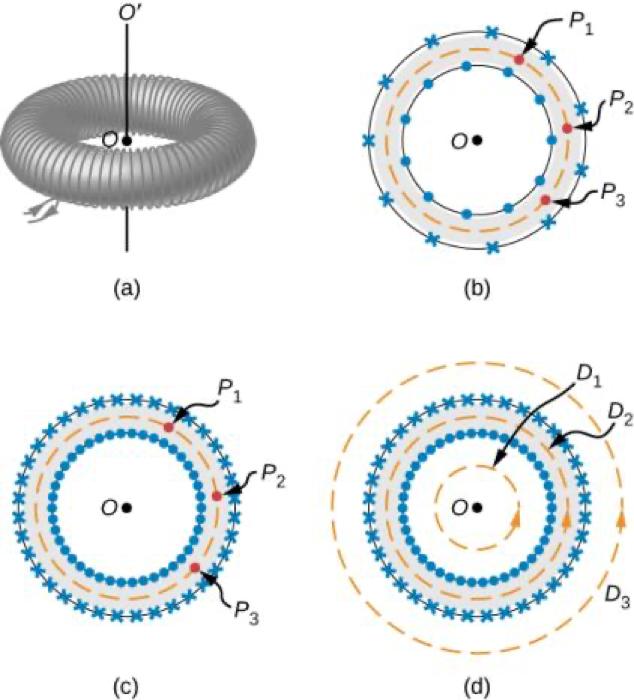
Magnetic Field Within a Toroid
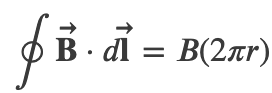
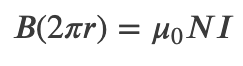
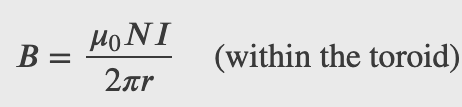
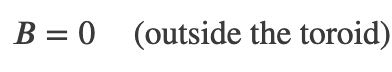
Electromagnets
Electromagnets
Electric current in a coil of wire creates a magnetic field similar to a bar magnet

Current In
Current Out
Origin of Earth's Magnetic Field
Earth is a giant electromagnet

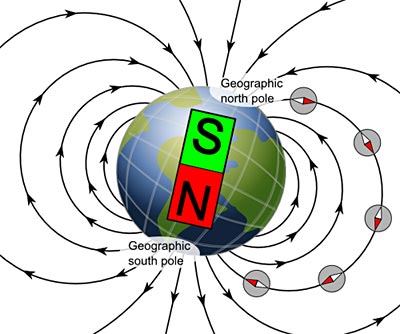
Earth's Magnetic Field Reversal

Northern Lights (Aurora)
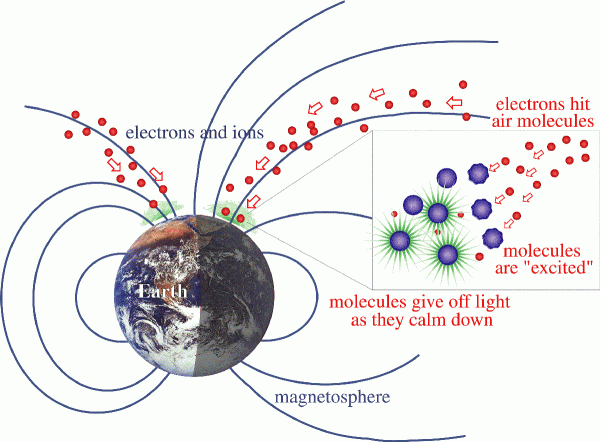

Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic Induction
Just like moving charges (currents) produce magnetic fields, moving magnetic fields produce voltages and currents

Electromagnetic Induction

Voltage is induced whether a magnetic field moves past a conductor, or the conductor moves through a magnetic field.
The results are the same for the same relative motion
Electromagnetic Induction

Twice as many loops results in twice as much voltage induced. For a coil with three times as many loops, three times as much voltage is induced
The induced current is proportional to the number of loops
2 v
4 v
6 v
Faraday's Law
The induced voltage in a coil is proportional to the product of the number of loops, the cross-sectional area of each loop, and the rate at which the magnetic field changes within those loops
How fast magnetic field changes
Faraday's Law
then the induced emf or the voltage generated by a conductor or coil moving in a magnetic field is by
where Φm is the magnetic flux, a measurement of the amount of magnetic field lines through a given surface
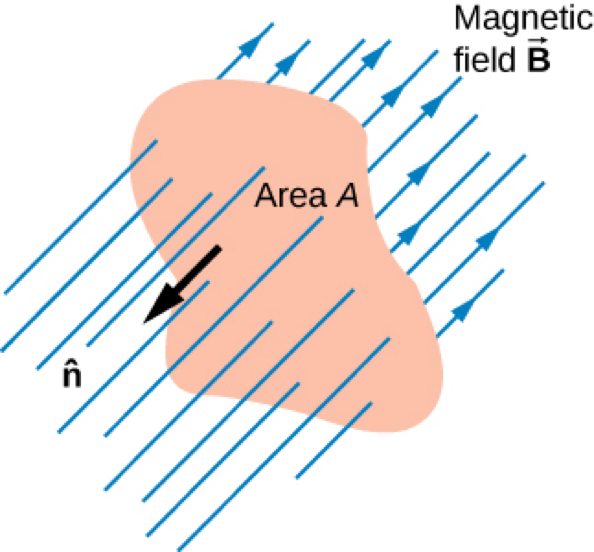
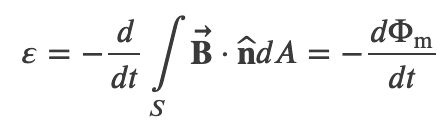
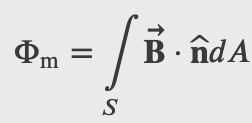
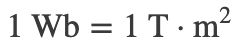
The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (Wb)
Faraday's Law
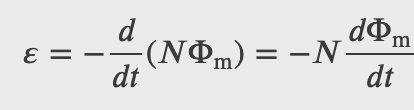
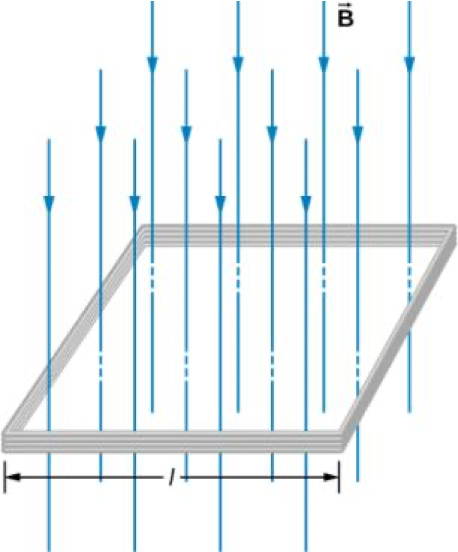
In many practical applications, the circuit of interest consists of a number N of tightly wound turns. Each turn experiences the same magnetic flux. Therefore, the net magnetic flux through the circuits is N times the flux through one turn, and Faraday’s law is written as
Checkpoint 1
When a coil with 200 loops is subject to a changing magnetic field it produces 0.5 v. Another coil with 400 loops but half the area is then subject the same changing magnetic field, what is the induced voltage?
Same, 0.5 v
Electromagnetic Induction
We don’t get something (energy) for nothing by simply increasing the number of loops

More difficult to push the magnet into a coil with more loops because the magnetic field of each current loop resists the motion of the magnet
The work done is proportional to the number of loops
When a current is induced by a changing magnetic field, that current itself produces its own magnetic field. This effect is called self-induction
Self Induction


The self-induced magnetic field is always opposed to the primary magnetic field that induced it
Lenz's Law
The direction of the induced emf drives current around a wire loop to always oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes the emf.
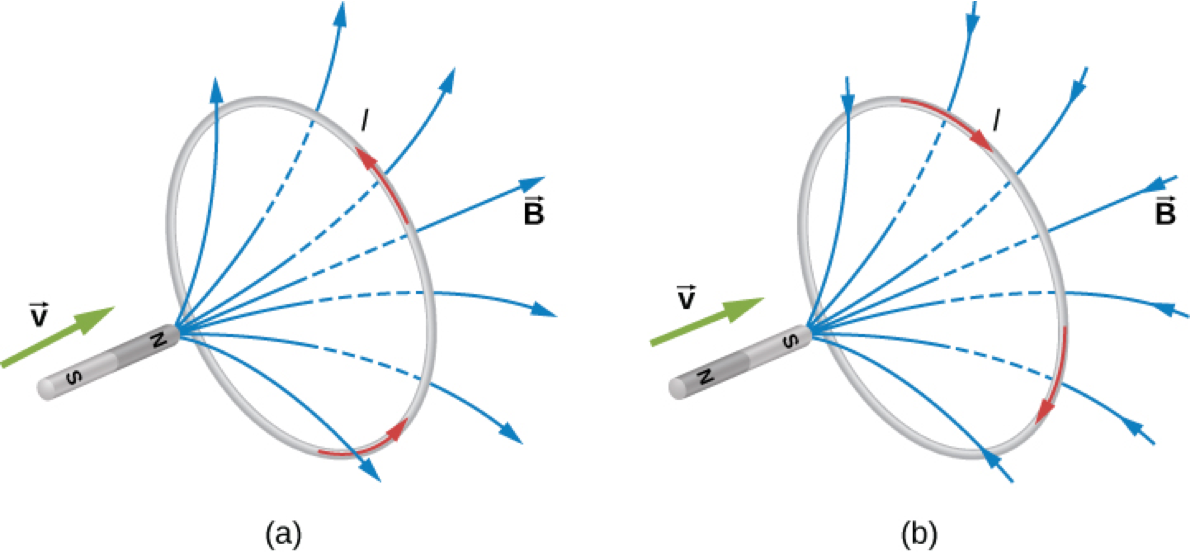

Eddy Currents

Changing magnetic field induces eddy currents within any conductor.
These internal currents produce self-induced magnetic fields

Metal detectors induce eddy currents on metals and detect the self-induced magnetic fields
Electric Guitars



Electric Generators

Electric generators move a conductor in a magnetic field to produce voltage via electromagnetic induction
Electric Generators

Electric Generators

As the loop rotates, the magnitude and direction of the induced voltage (and current) change
The direction of the current and magnitude of the voltage reverses each half rotation, the result is an alternating current
Current
Electric Motors

An electric motor is the same as a generator but instead converting mechanical energy to electrical energy, it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
Transformers

A transformer consist on a primary coil connected into alternating power source, and a secondary coil that produces a voltage by induction
If we place an iron core inside both coils, alignment of its magnetic domains intensifies the magnetic field
Transformers
A transformer consist on a primary coil connected into alternating power source, and a secondary coil that produces a voltage by induction
If the iron core forms a complete loop, guiding all magnetic field lines through the secondary, the transformer is more efficient

Transformers
A transformer consist on a primary coil connected into alternating power source, and a secondary coil that produces a voltage by induction
Voltages may be stepped up or stepped down with a transformer

Transformers

Voltages may be stepped up or stepped down with a transformer, but the power is always constant!
N = Number of loops on coil
Checkpoint 2
If the primary coil of a transformer has 10 loops and is connected to a outlet providing 120 v, what would be the output voltage (secondary voltage) if the secondary coil has only 1 loop?
12 v
Checkpoint 3
1 A
What would be the output (secondary) current if the input (primary) current is 0.1 A?

Power transmission uses transformers to increase voltage for long-distance transmission and decrease it before it reaches your home
Power Transmission
High voltage allows for less current for the same power (P = IV). Less current = less heat (less power loss)
The End

Since force on a wire due to a magnetic field depends on the current, we can use this effect to design a meter to measure current (an ammeter)

Electric Meters
Copy of Magnetic Sources and Electromagnetic Induction (4B)
By Miguel Rocha
Copy of Magnetic Sources and Electromagnetic Induction (4B)
Physics 4B
- 731



