The Solar System
M. Rocha
Astronomy 1 - Lecture 3
The Solar System:
-
The Moon-Earth system
-
Eclipses
-
Tides
-
Formation of The Solar System
-
The Solar System Today
The Moon

The most visible object in the sky!
Lunar Pareidolia
Formation of The Moon

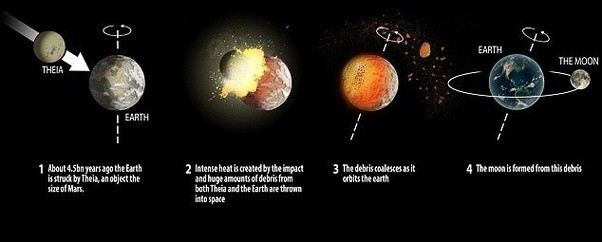
Giant Impact hypothesis:
The Moon originated from the debris left after a collision of a Mars-sized proto-planet with the proto-Earth about 4.5 billion years ago
Formation of The Moon
Moon's Composition
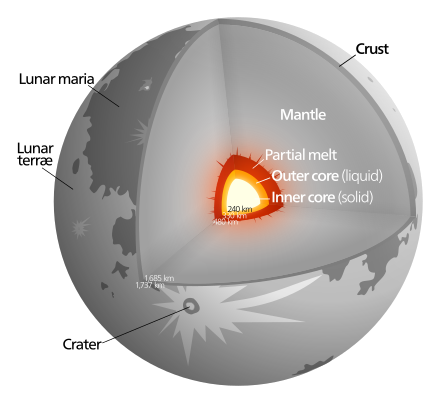
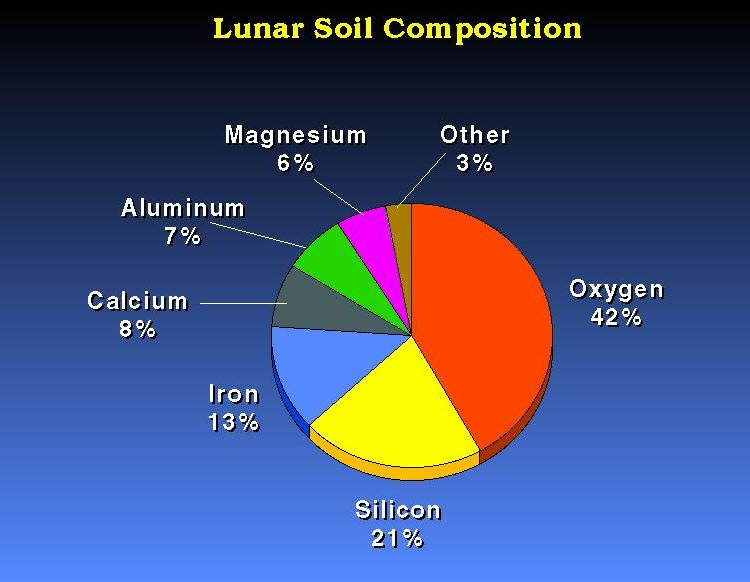
The Moon has a solid iron-rich inner core and a fluid outer core primarily made of liquid iron
The surface/crust of the Moon is mostly a rocky mixture of oxygen, silicon and iron
Checkpoint 1
It turns out that the composition of the Earth is nearly identical to that of the Moon, thus the Earth must be mostly made out of
Iron at the core with a crust made out of mostly oxygen, silicon and iron

- The moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth
- Its mean distance from the Earth is about 340,000 km (~ 30x the diameter of the Earth)
- It's radius is about 1740 Km (~ 1/4) the radius of the Earth
- The largest among planetary satellites relative to the size of the planet that it orbits. The fifth-largest natural satellite in the Solar System
Moon Facts:
- Daytime temperatures on the sunny side of the moon reach 273° F (134° C); on the dark side it gets as cold as -243° F (-153° C)
The Moon Orbit

The Moon appears 14% larger and 30% Brighter at perigee (Supermoon)
Phases of The Moon
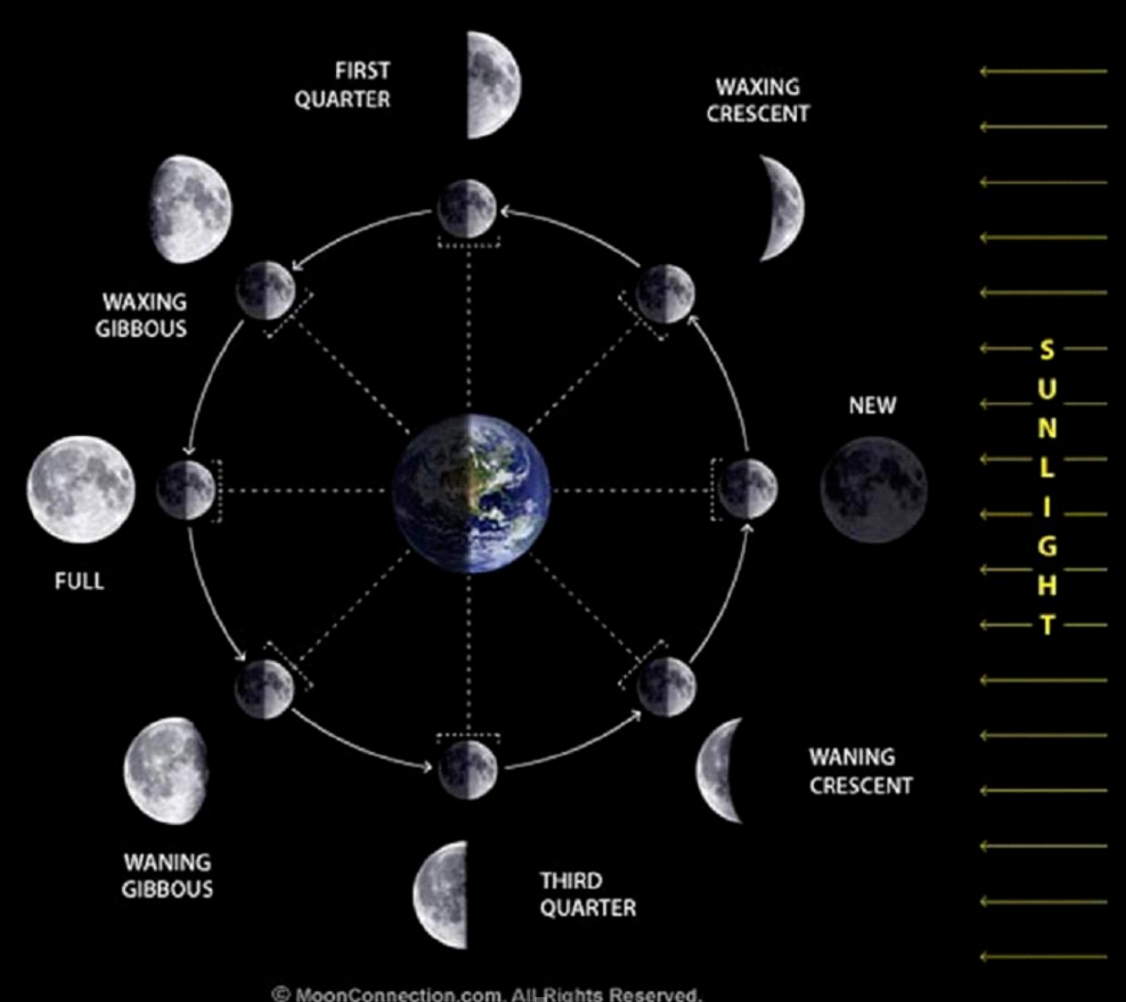
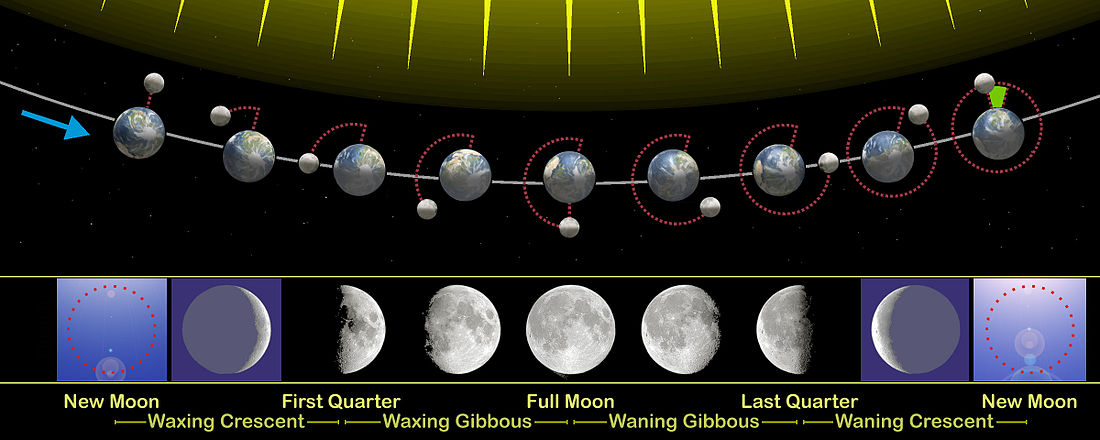
Phases of The Moon
The Moon's sidereal orbital period (the sidereal month) is ~27.3 days; this is the time interval that the Moon takes to orbit 360° around the Earth relative to the "fixed" stars. The period of the lunar phases (the synodic month), e.g. the new moon to new moon period, is longer at ~29.5 days
Text
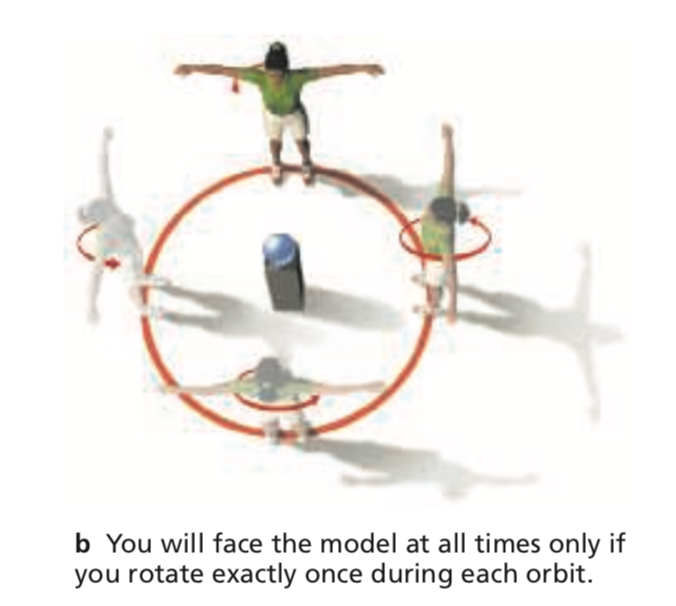
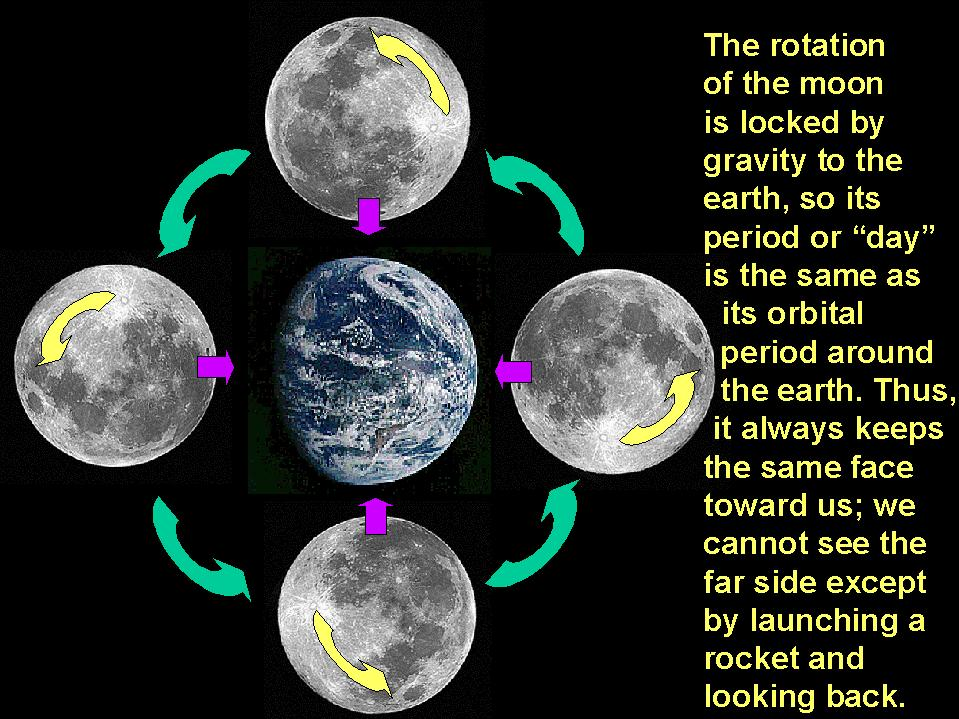

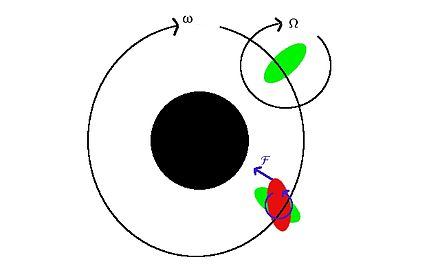
Tidal locking
Checkpoint 2
How long would a full day-night cycle last at the Moon (i.e. from sunrise to sunrise)?
About 28 days

The Two Sides of The Moon
Near Side: More volcanic activity
Far Side: More impact craters


There is virtually no atmosphere on the Moon (no wind!)
Craters from asteroid impacts, volcanic activity and shoe tracks do not erode


Eclipses


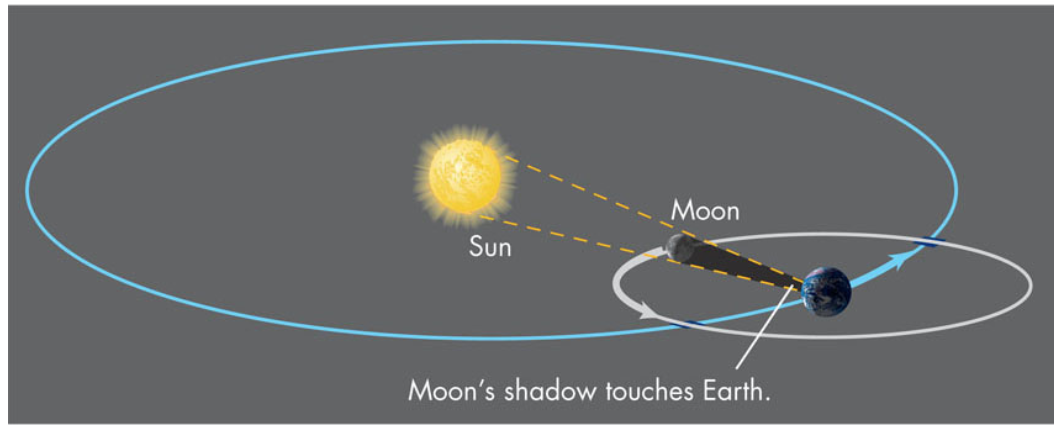
Solar Eclipses


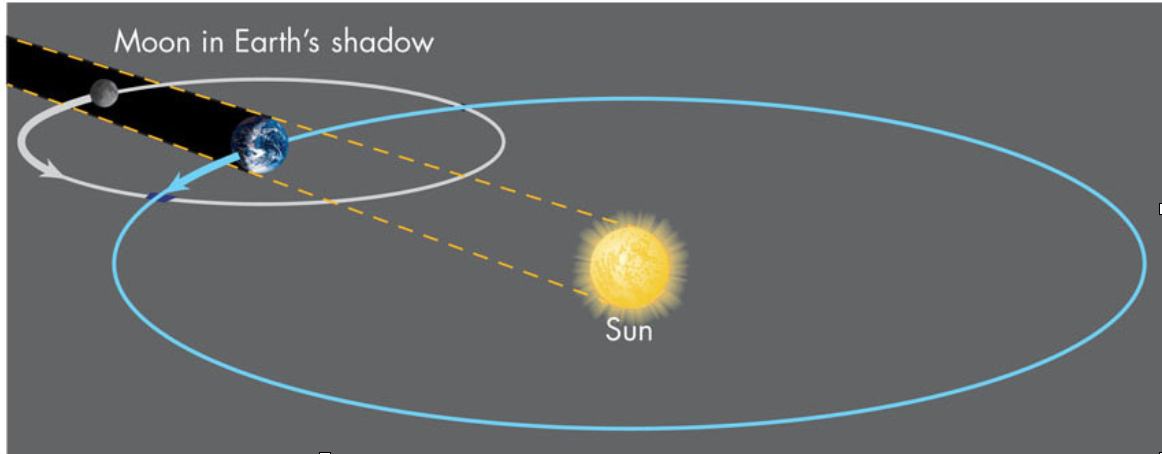
Lunar Eclipses


When the moon is being eclipsed it appears red, this is because the Earth's atmosphere scatters away purple, blue and green light, but lets red light pass and reach the Moon
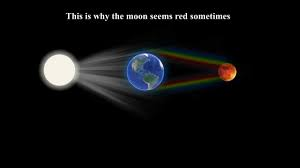

Why The Moon Looks Red?

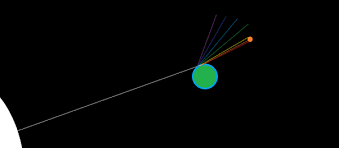
When the moon is close to the horizon it can appear red, this is because the Earth's atmosphere scatters away purple, blue and green light, but lets red light pass and reach the Moon
Why The Moon Looks Red?
The Moon Orbital Plane
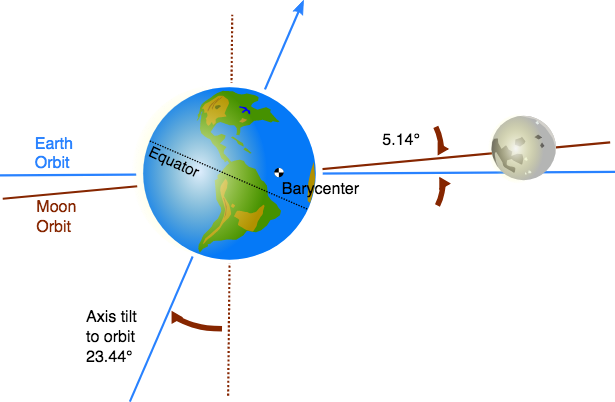
The Moon-Earth orbital plane is tilted about 5° with respect to the ecliptic (the Earth-Sun orbital plane)
The Moon Orbital Plane
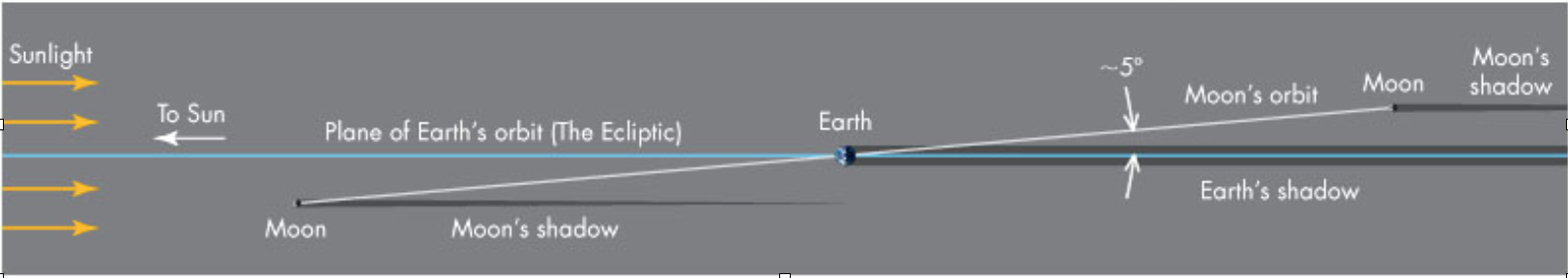

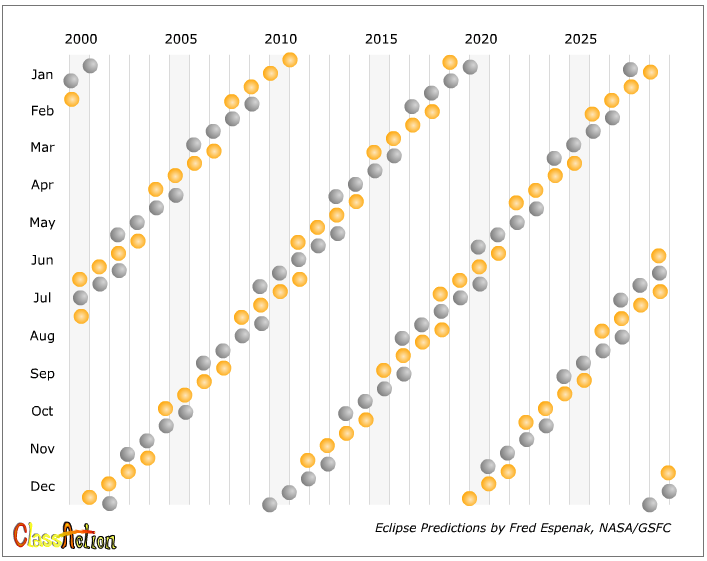
- Since the Moon’s orbit tilts nearly in the same direction through the year, twice a year the Moon’s orbit will pass through the Sun giving the possibility of an eclipse – these times are called eclipse seasons
- When a solar eclipse occurs at new Moon, conditions are right for a lunar eclipse to occur at the full Moon either before or after the solar eclipse
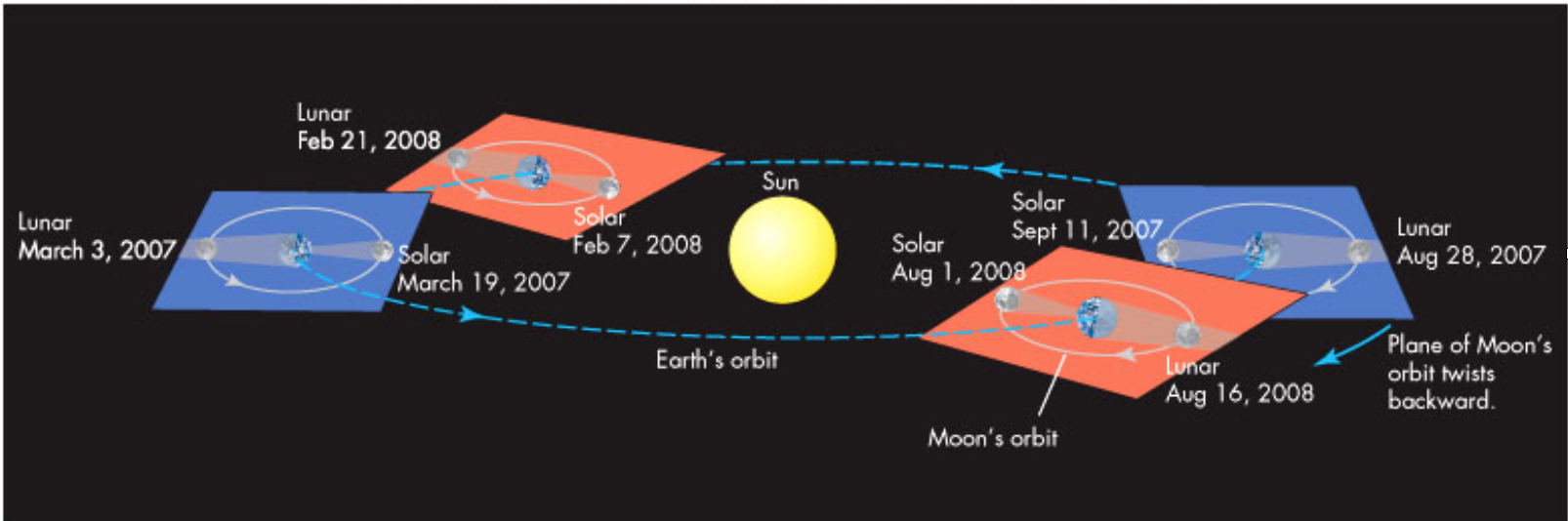
Eclipse Seasons
Checkpoint 3
On January 31st there was a lunar eclipse, when would you expect was the following solar eclipse?
About 14 days later, on February 14-15
Checkpoint 4
We had a lunar and solar eclipse at the beginning of the year (January-February), when would you expect was the next set of lunar and solar eclipses?
About 6 months later, on June-July
But it actually happened in July-August
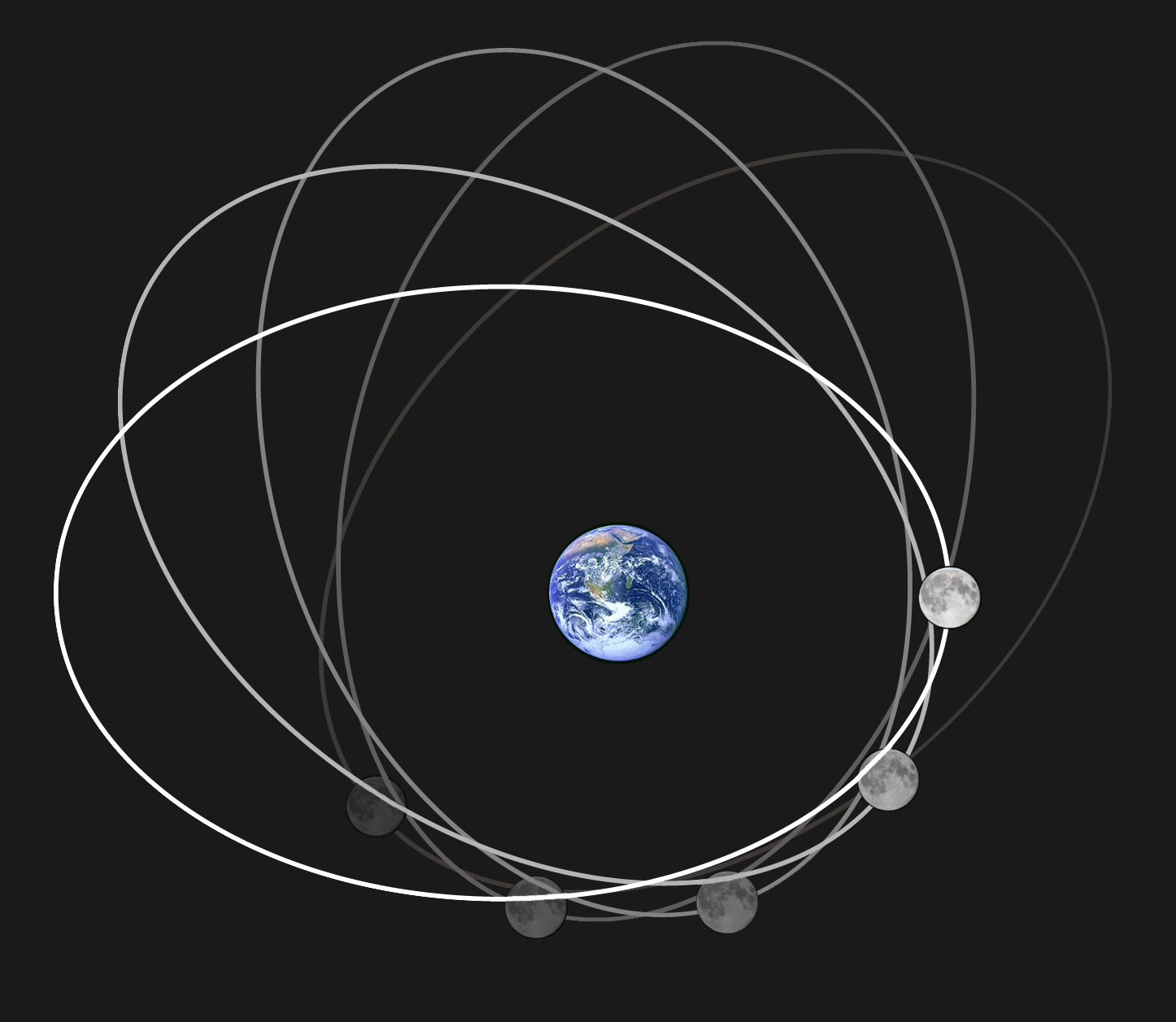
Precession of Lunar orbit
Moon's elliptic orbit rotates once every 8.85 years
Ocean Tides
The ocean tides are caused by differences in the gravitational pull of the moon on opposite sides of Earth
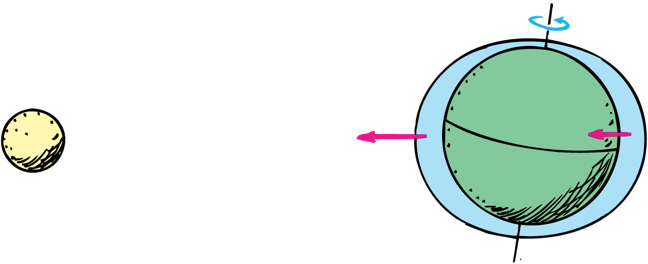
As the Earth rotates tides change during the day



Ocean Tides
When the sun, the moon, and Earth are aligned, spring tides occur

Ocean Tides
When the attractions of the sun and the moon are at right angles to each other (at the time of a half moon), neap tides occur

Ocean Tides
The sun also contributes to ocean tides, but only about half as much as the moon
The difference in gravitational pull by the sun on opposite sides of Earth is very small

The Sun's pull on Earth is 180 times greater than the moon’s pull on Earth, so why aren’t tides due to the Sun 180 times greater than tides due to the Moon?
Ocean Tides
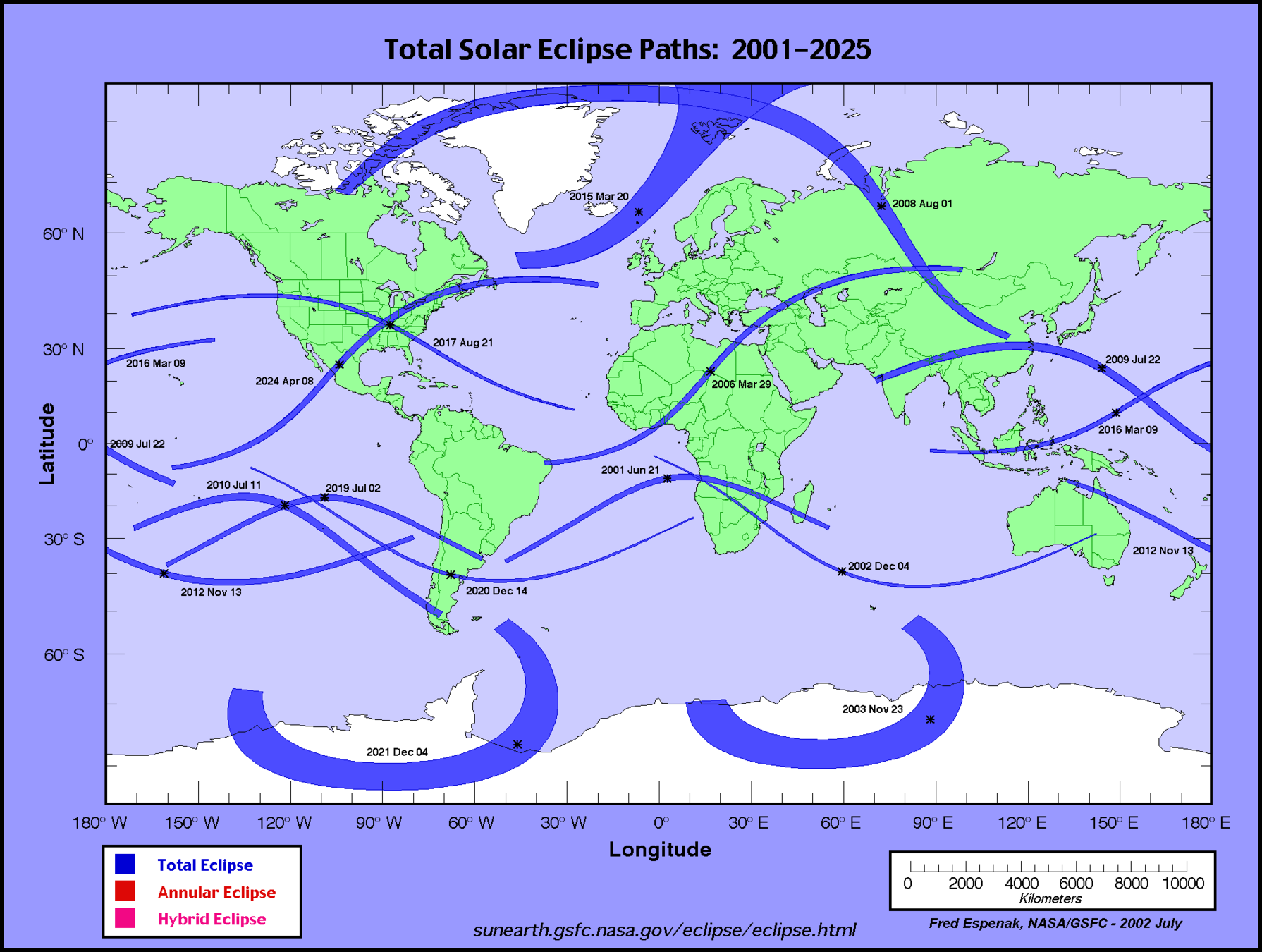
Tides are most noticeable in fjords and basins due to a funneling effect. The Bay of Fundy has some of the most extreme tide swings in the planet (15+ m/48+ ft)

The Solar System

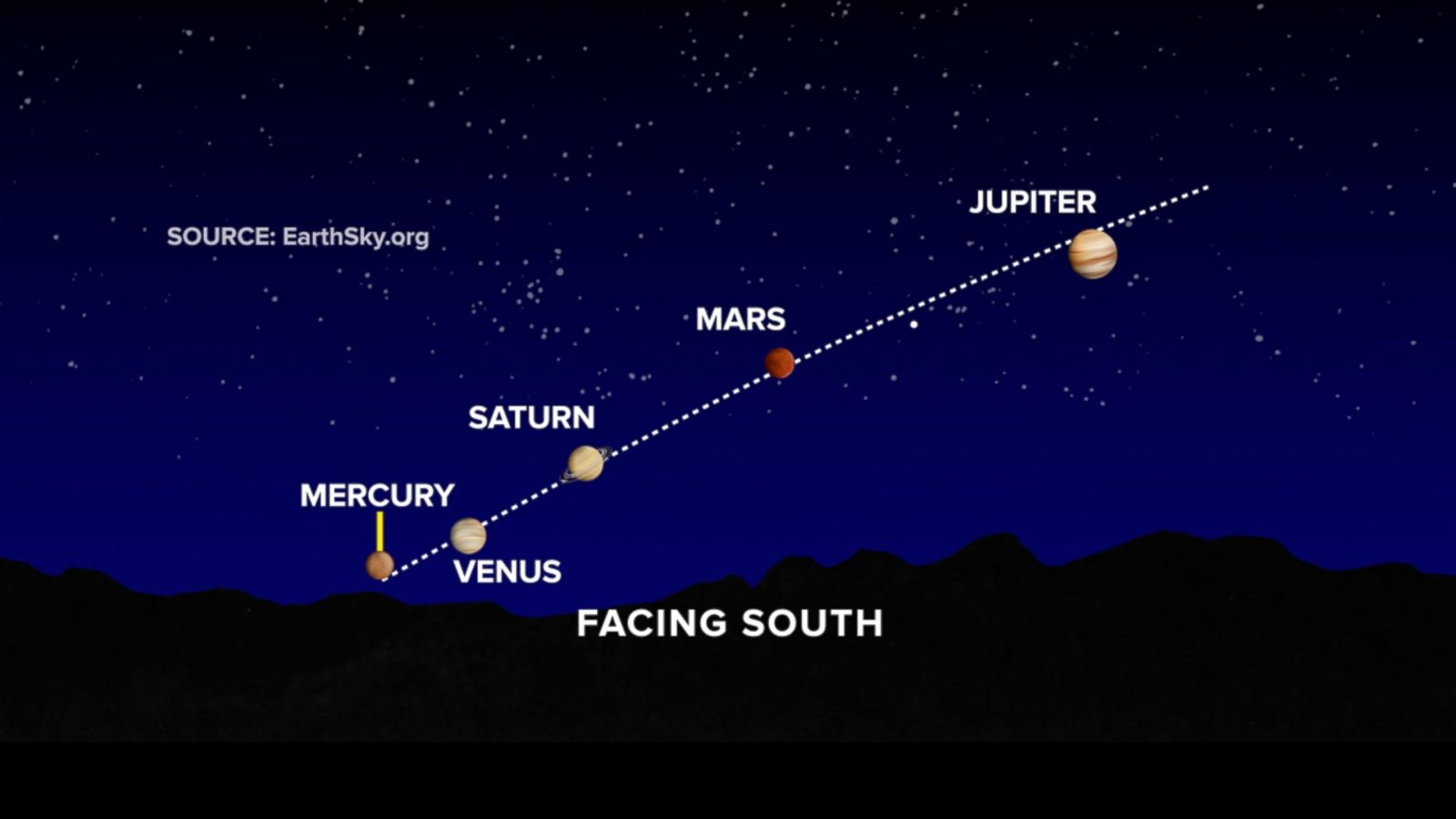
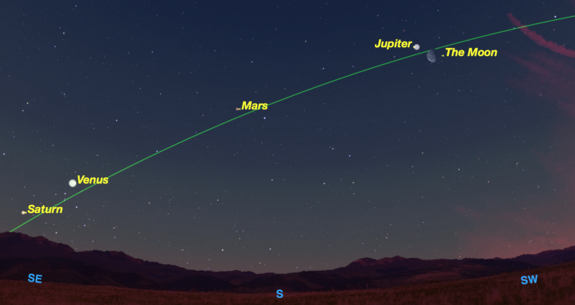
Checkpoint 1
What is the name of the line on the celestial sphere marking the path that all the planets follow on the sky?
The Ecliptic
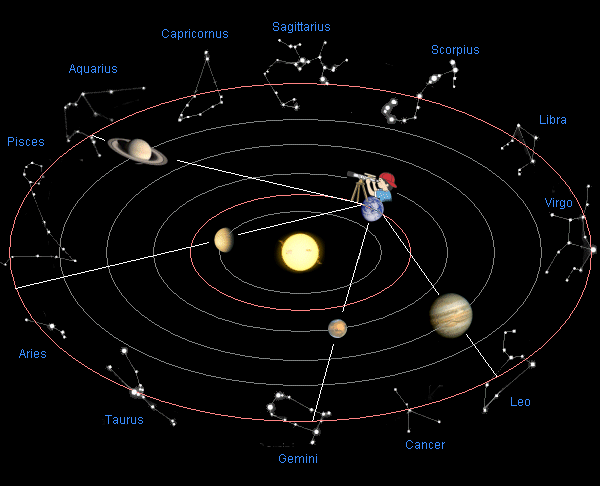
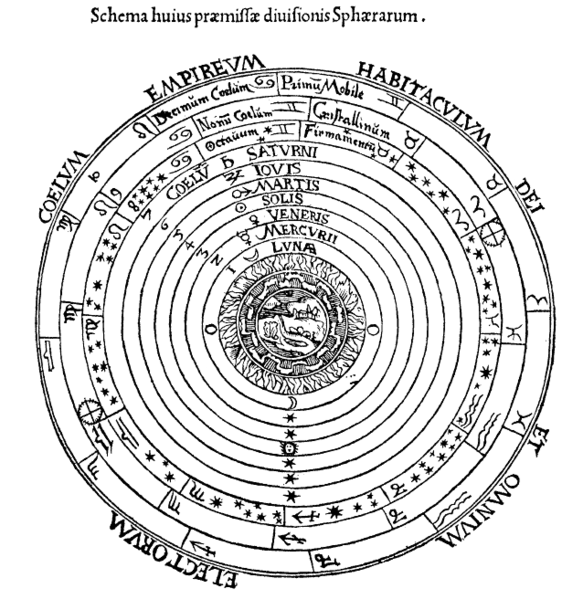
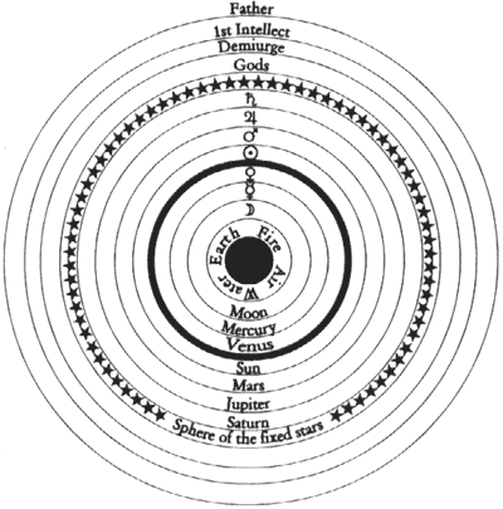
The Geocentric Model
Plato, Aristoteles and Heraclides ~350 BC

The church supported the geocentric model, so it became the stablished and most accepted cosmology for 2000+ years
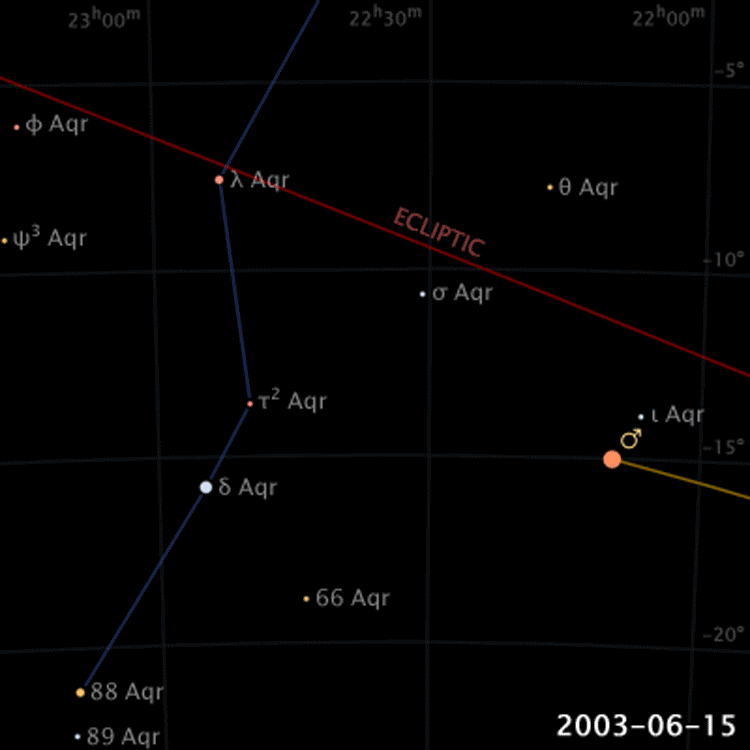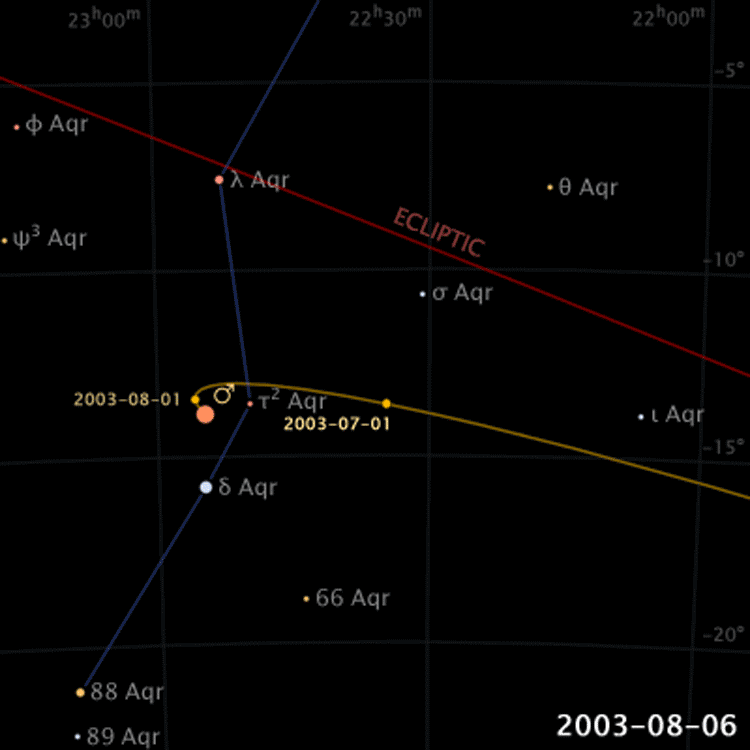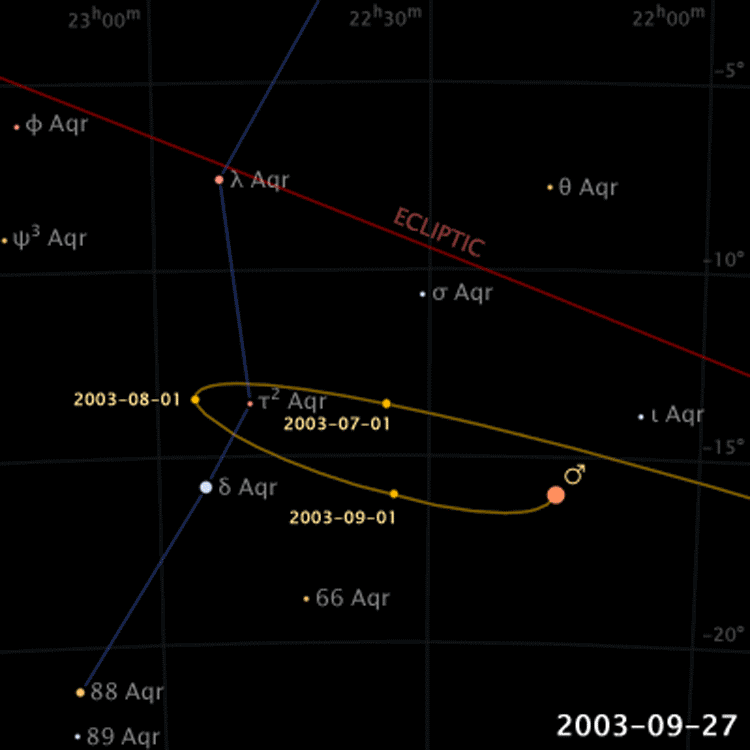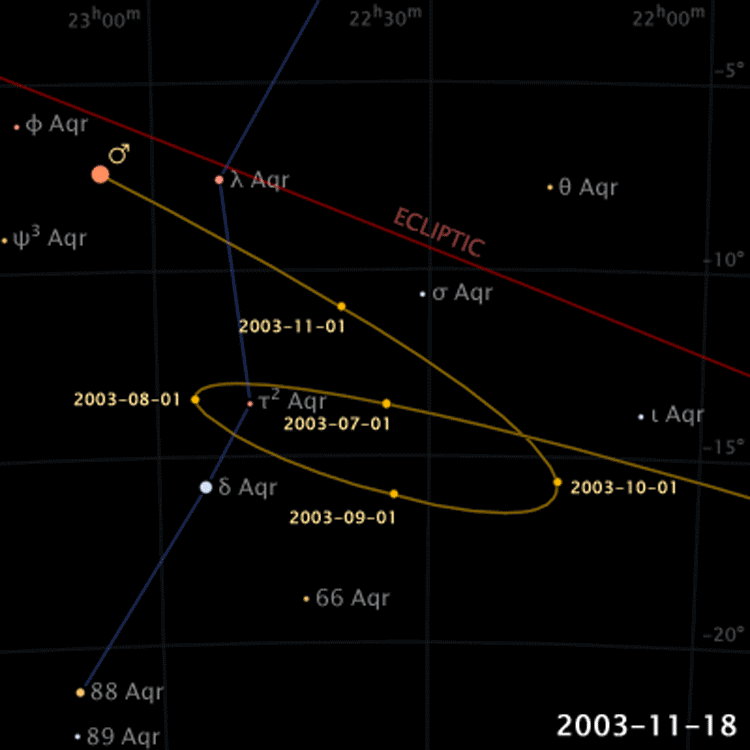
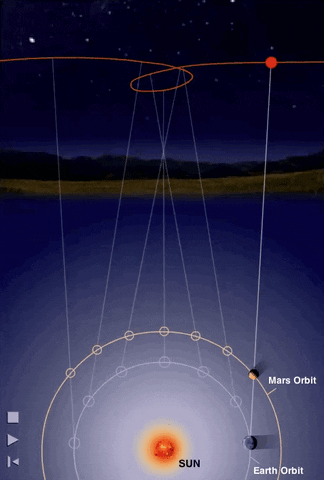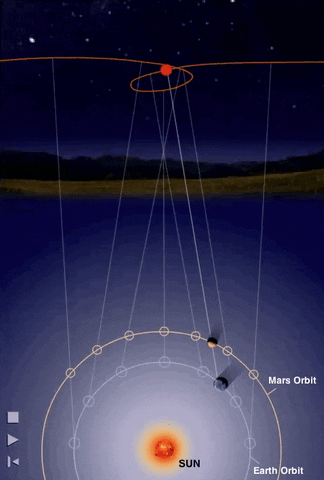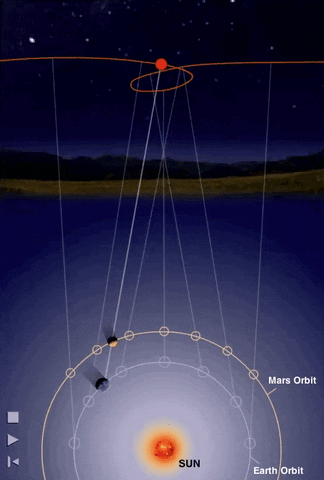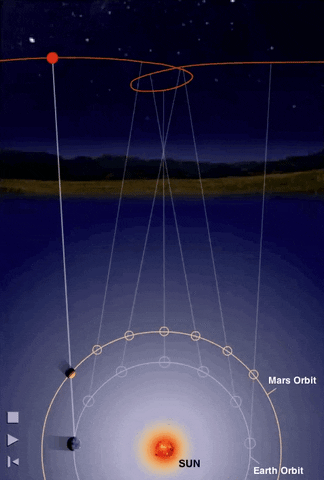
Retrograde Motion of Planets


Planets move backwards relative to its usual motion around the sky
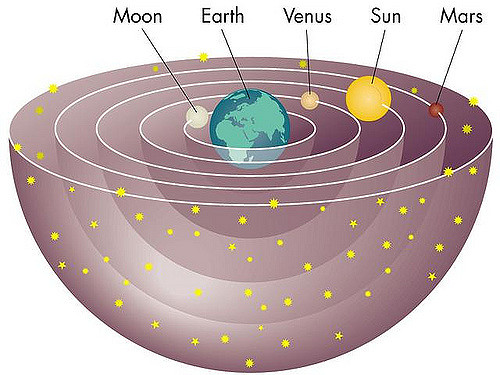
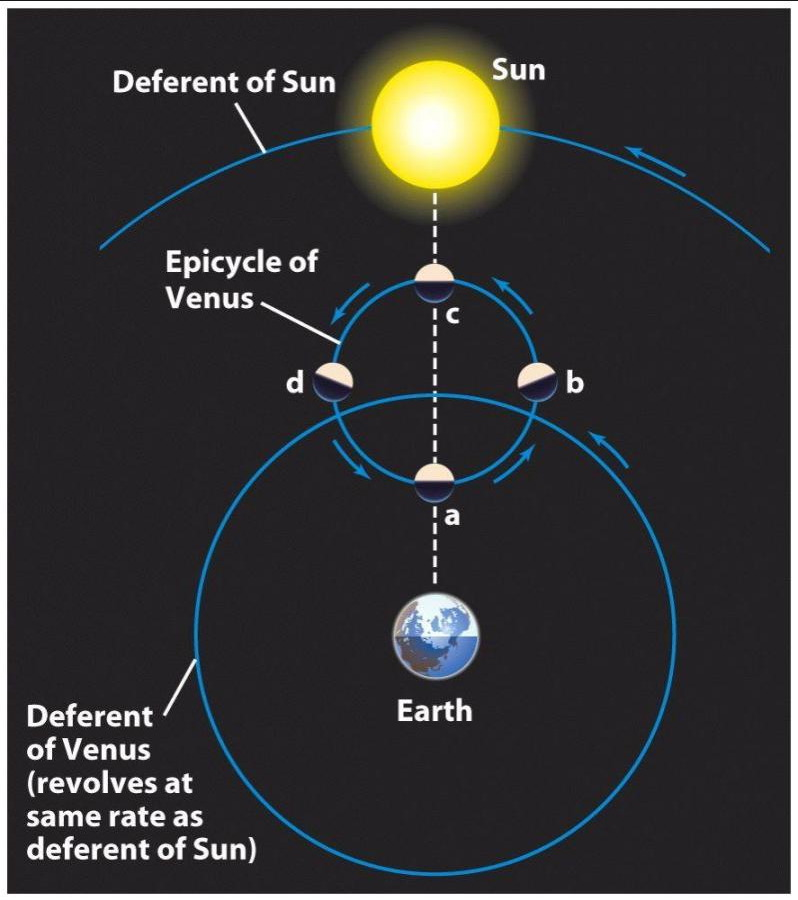
Ptolemy's Model
Ptolemy added epicycles to the Geocentric Model of the Greeks in order to explain retrograde motions

~150 AD
Retrograde Motion


Ptolemy proposed epicycles on on planetary orbits to explain retrograde motions
The Heliocentric Model
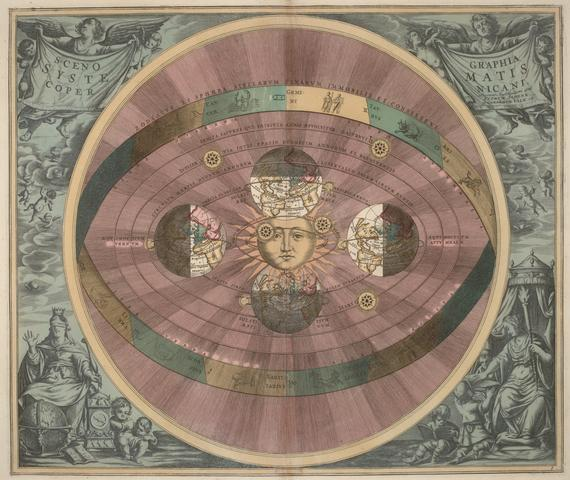
Pythagoras, Aristarchus and Copernicus

The Copernican Model
Copernicus introduced his heliocentric model of the Universe a few months before he died in 1543
The Heliocentric Model
The heliocentric model naturally explains retrograde motions
Mars
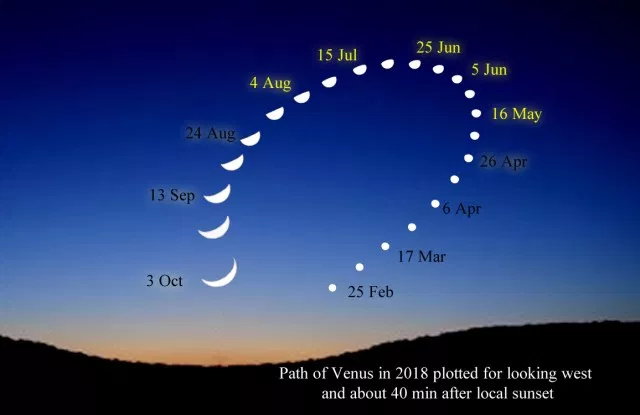
Venus
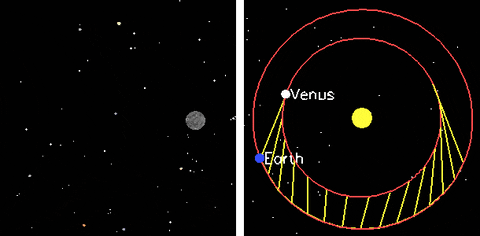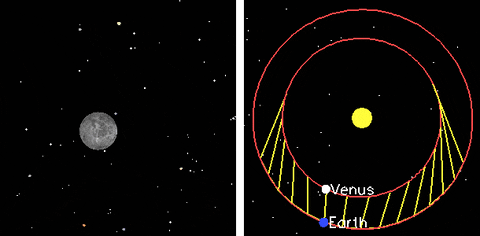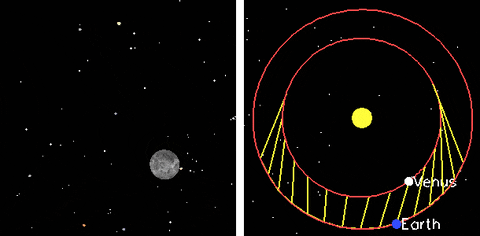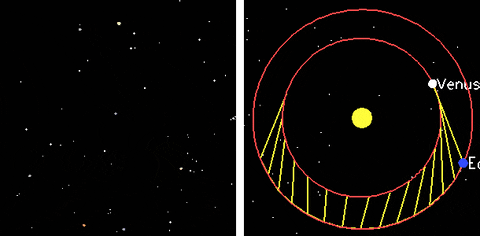
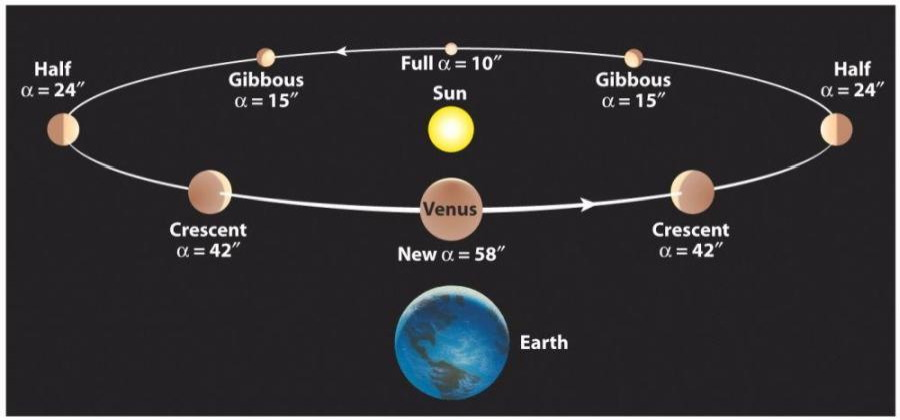
Phases of Venus
Galileo Galilei (~1600 AC) invented the telescope. With it he observed that Venus showed all phases, just like the Moon
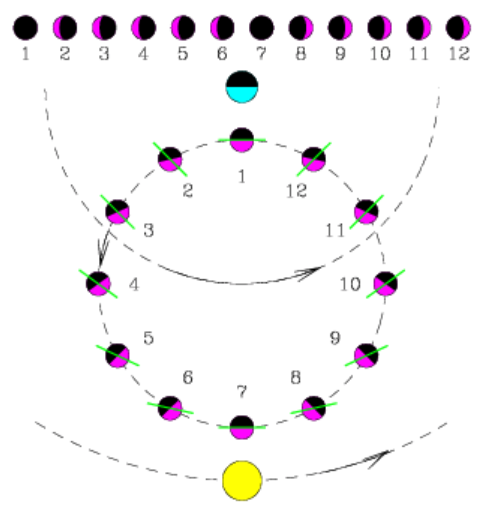
Ptolemy's model failed to explain this!

Moons of Jupiter
Galileo also discovered that Jupiter has Moons. Demonstrating that there are celestial objects orbiting something other than the Earth
Ptolemy's model failed to explain this!

The Heliocentric Model
The heliocentric model naturally explains the phases of Venus (and Mercury) without ad hoc modifications
Tycho Brahe's Model
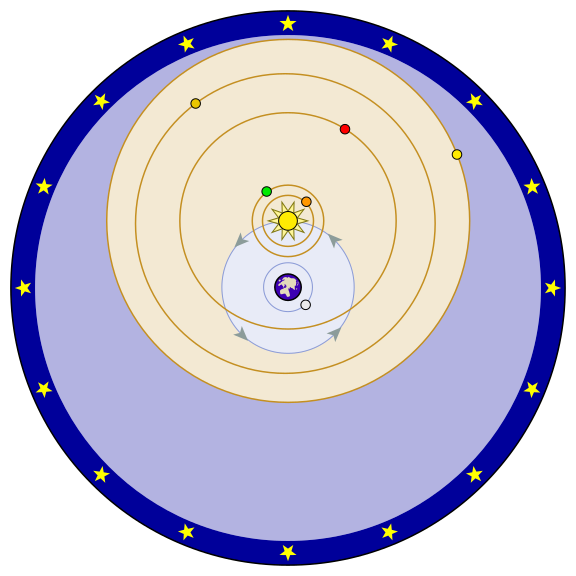
Tycho Brahe modified the Geocentric Model in order to explain Galilleo's observations of the phases of Venus
Tychonic Model: The objects on blue orbits (the moon and the sun) revolve around the Earth. The objects on orange orbits (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) revolve around the sun
~1600 AC
Checkpoint 3
Venus brightness on the sky is nearly constant all the time, even while is changing in phase and size. How would you explain that?
The closer and larger Venus gets, the less of it surface is reflecting light to us
Checkpoint 2
In both Ptolemys' and Tycho's geocentric models of the Solar System the Earth is at the center and is
Not moving
Smoking Gun Evidence in Favor of The Heliocentric Model: The Earth Moves!
- In 1725, James Bradley discovered stellar aberrations

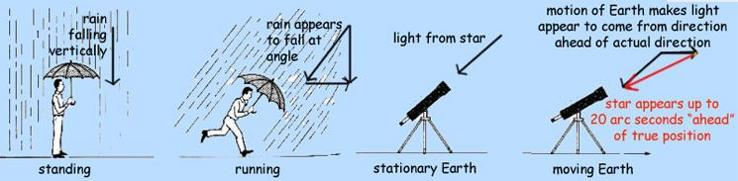
Smoking Gun Evidence in Favor of The Heliocentric Model: The Earth Moves!
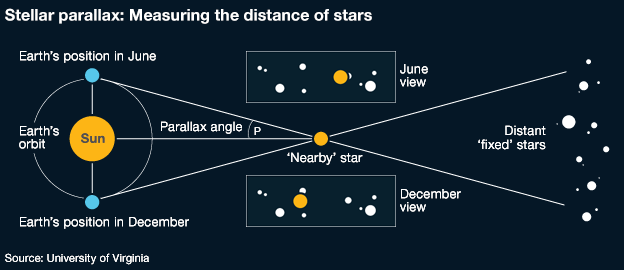
- In 1838, Friedrich Bessel made the first successful measurements of annual parallax
Smoking Gun Evidence in Favor of The Heliocentric Model: Orbits are not perfect circles!
- Kepler's work (1609 - 1619) demonstrated that planets orbits are elliptical and not perfect circles. Also explained why the orbital speed of planets varied.

Our Current Knowledge of the Solar System
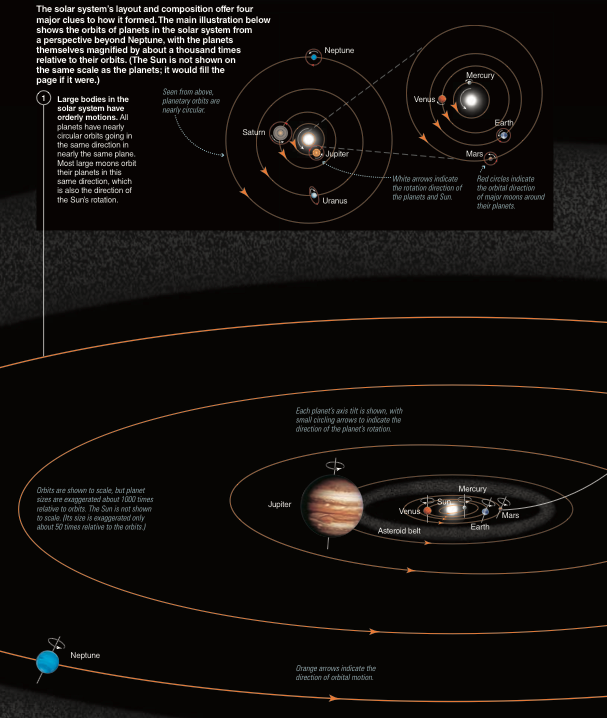
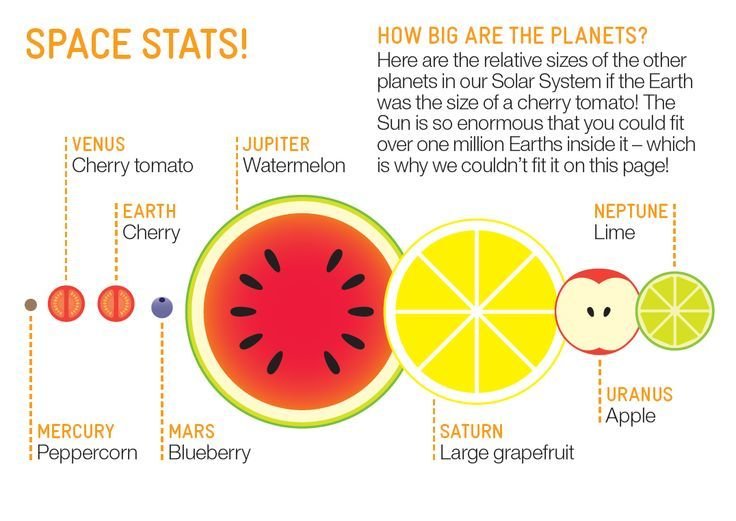

Our Current Picture of The Solar System
The Scale of The Solar System

Our Current Picture of The Solar System
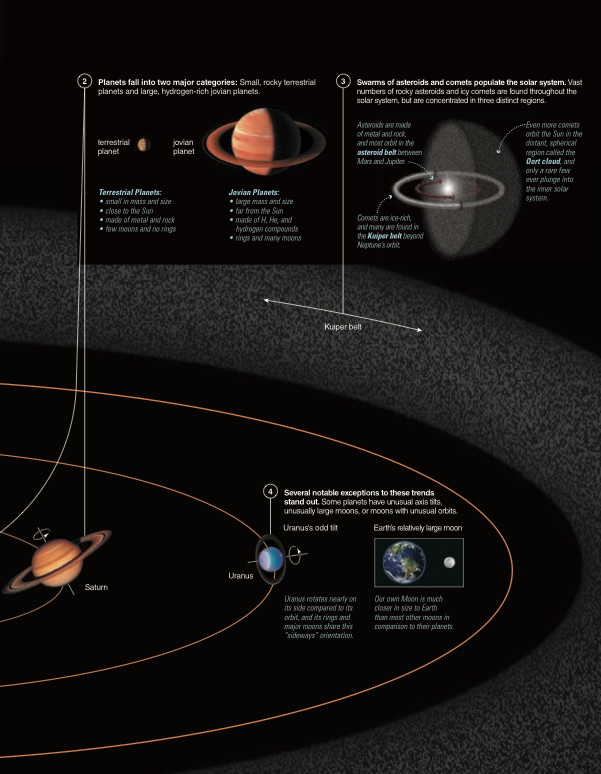
Terrestrial v.s. Jovian Planets
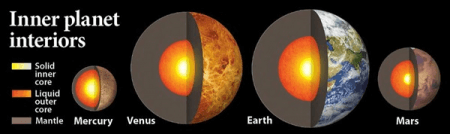

Terrestrial/Inner Planets
- Solid Surfaces
- Dense metallic cores
- Atmospheres abundant of carbon dioxide and nitrogen
Jovian/Giant Planets
- Gaseous surfaces of mostly hydrogen and helium
- Molten rock cores
- Rings
- Many moons
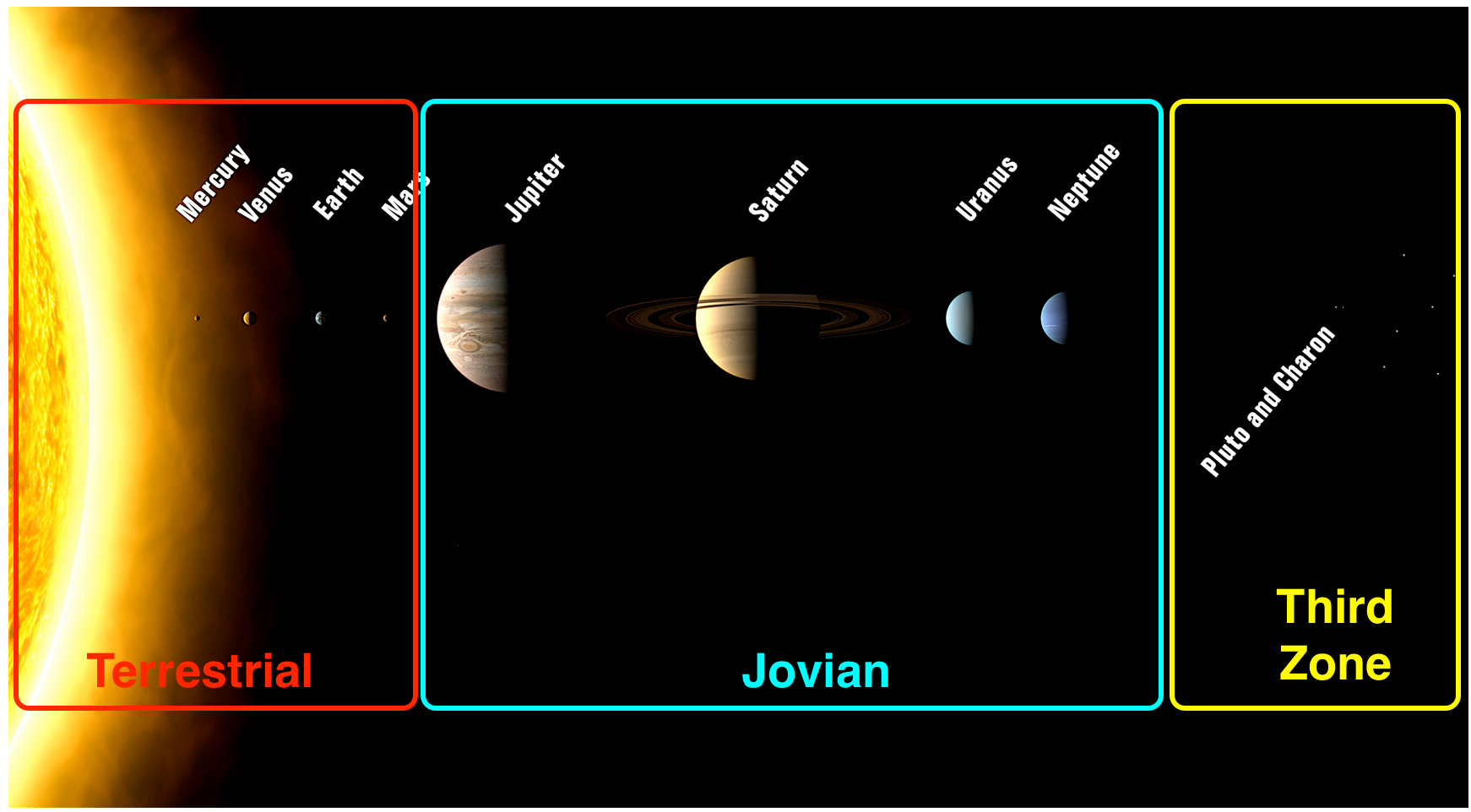
What about Pluto?
The discovery of Eris, a bigger Pluto-like planet farther away from Pluto, led the International Astronomical Union (IAU) to define the term "planet" formally in 2006. That definition excluded Pluto and reclassified it as a dwarf planet

Dwarf Planets

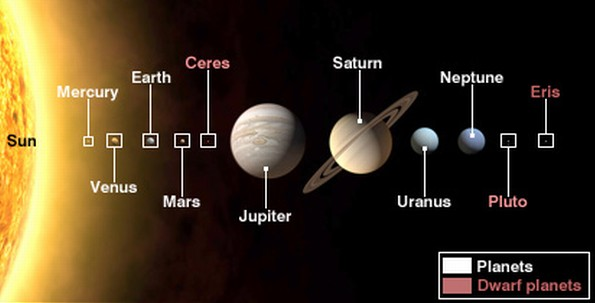
The Moon is not a dwarf planet, it is just here for size comparison
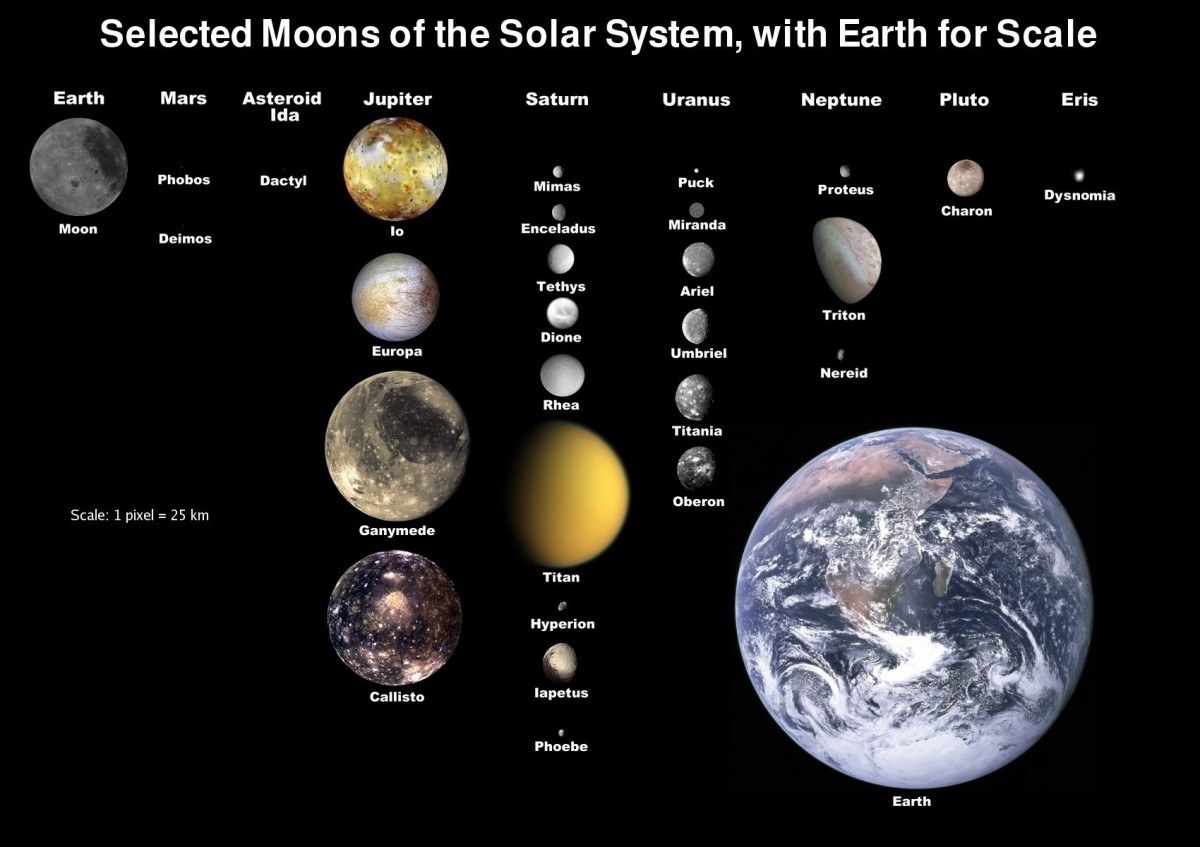
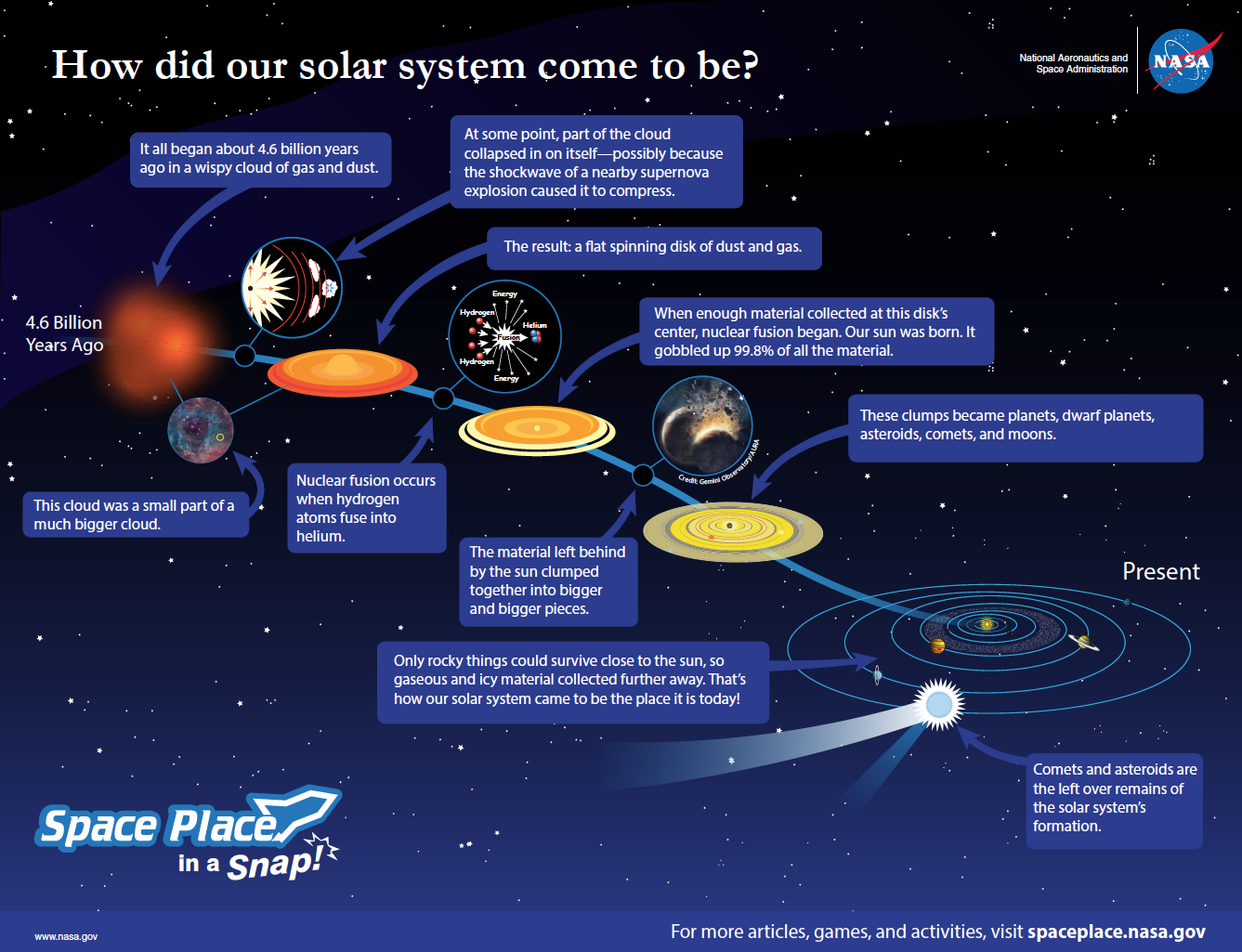

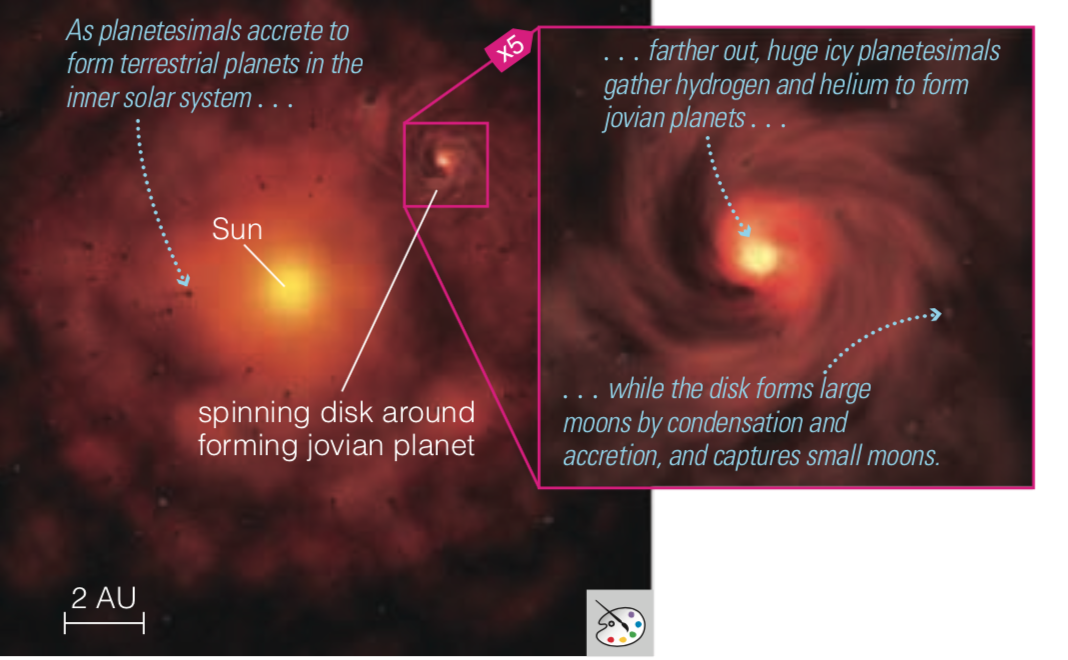

Checkpoint 1
Why do you think the direction of the rotation and orbit for all the planets, moons and the Sun is the same?
Because that was the initial rotation of the nebula from which they all formed


Nebulas in the process of forming planetary systems
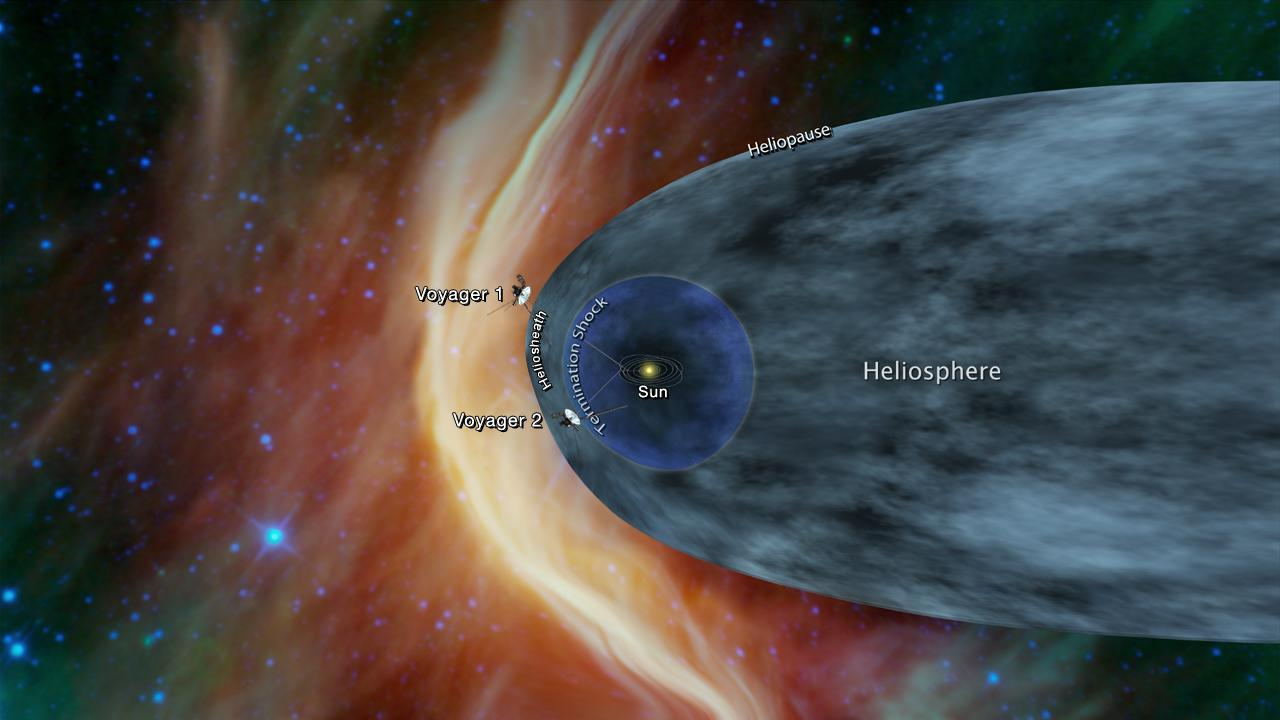
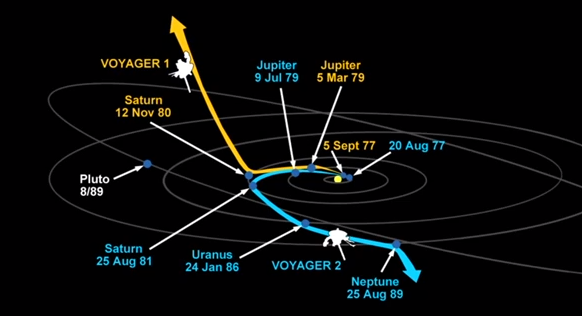
The Edge of the Solar System
Voyager 1 left the solar system on 2012. Voyager 2 left the solar system on November 2018

The End


Our Current Picture of The Solar System
The Solar System
By Miguel Rocha
The Solar System
Astro 1 - The Solar System Slides
- 2,472



