Functional Programming
How I learned to stop worrying and love the monad
WHAT
Composition & Reusable functions
passing around class-objects with hidden state in for loops
Not
WHAT
Pure Functions
someObject.property1 = "hej"
const months = ['Jan', 'March'];
months.splice(1, 0, 'Feb');
console.log(months);
Array(3) [ "Jan", "Feb", "March"]- Side effects
WHAT
Pure Functions
- Side effects
- Deterministic
function add(first, second) {
first + second
}WHAT
Pure Functions
- Side effects
- Deterministic
WHAT
Immutability
Thou shalt not mutate
Performance losses? Don't worry about it
WHAT
Higher order functions

WHAT
Higher order functions
- A function that takes another function as argument
- .map(), reduce(), filter()
WHY (and why not)
WHY
Parallelization
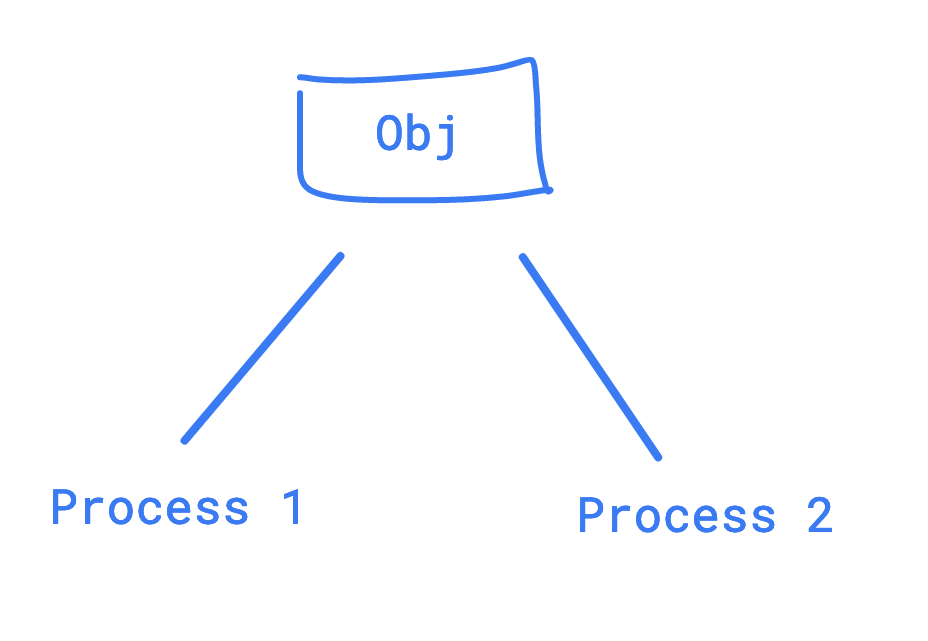
WHY
Parallelization
WHY
Composition
WHY
Composition
Frame
|> Put on wheels
|> Put on windows
|> Put on doors
|> Put on color
WHY
Testability
WHY
Why not
-
⠀
WHY
Why not
*Cricket Noise*
WHY
- Parallelization
- Tests
- Composability
HOW
HOW
React
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(prevCount => prevCount + 1);
}
return (
<button onClick={handleClick}>
You pressed me {count} times
</button>
);
}
HOW
React
What is useEffect?
HOW
Kubernetes
You set constraints
Kubernetes helps you fullfil them
HOW
More examples
HOW
function mailPreferences(arr) {
let result = [];
for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) {
const person = arr[index];
if (person.age >= 18) {
person.drink = "beer";
result.push(person);
}
}
if (result) {
sendMail(result);
} else {
console.log("nothing to send");
}
}HOW
function mailPreferencesFunc(arr) {
res = arr
.filter(({ age }) => age > 18)
.map((e) => {
e.drink = "beer";
return e;
});
if (res) {
sendMail(res);
} else {
console.log("nothing to send");
}
}HOW
function mailPreferencesFunc(arr) {
res = arr
.filter(({ age }) => age > 18)
.map((e) =>
Object.assign({
drink: "beer",
e,
})
);
if (res) {
sendMail(res);
} else {
console.log("nothing to send");
}
} function mailPreferences(arr) {
let result = [];
for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) {
const person = arr[index];
if (person.age >= 18) {
person.drink = "beer";
result.push(person);
}
}
if (result) {
sendMail(result);
} else {
console.log("nothing to send");
}
}HOW
function mailPreferencesFunc(arr) {
res = arr
.filter(({ age }) => age > 18)
.map((e) =>
if (e.age >= 20) {
return Object.assign({
drink: "wine",
e,
});
} else {
return Object.assign({
drink: "beer",
e,
});
}
);
if (res) {
sendMail(res);
} else {
console.log("nothing to send");
}
}function mailPreferences(arr) {
let result = [];
for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) {
const person = arr[index];
if (person.age >= 20) {
person.drink = "wine";
result.push(person);
} else if (person.age >= 18) {
person.drink = "beer";
result.push(person);
}
}
if (result) {
sendMail(result);
} else {
console.log("nothing to send");
}
}
HOW
function mailPreferences(arr) {
let result = [];
const drinkers = {
kombucha: 0,
wine: 0,
beer: 0,
};
for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) {
const person = arr[index];
if (person.age >= 40) {
const drink = "kombucha";
person.drink = drink;
result.push(person);
drinkers[drink] += 1;
} else if (person.age >= 20) {
const drink = "wine";
// Same thing as above
} else if (person.age >= 18) {
const drink = "beer";
// Same thing
}
}
for (const drink in drinkers) {
const nrOfDrinkers = drinkers[drink];
if (nrOfDrinkers > 0) {
console.log(
`${drink}Drinkers ${toPercentage(nrOfDrinkers, arr.length)} %`
);
}
}
console.log(
`excluded ${toPercentage(arr.length - result.length, arr.length)} %`
);
sendMail(result);
}HOW
function mailPreferencesFunc(arr) {
const drinkPreferences = getDrinkPreferences(arr)
const printDrinkerStats = (list, totalNr) =>
Object.entries(
list
.map(({ drink }) => drink)
.reduce((acc, drink) => {
if (!acc[drink]) {
acc[drink] = 1;
} else {
acc[drink] = acc[drink] + 1;
}
return acc;
}, {})
)
.map(([drink, drinkers]) => [drink, toPercentage(drinkers, totalNr)])
.map(([drink, percent]) => `${drink}Drinkers ${percent} %`)
.concat([`excluded ${toPercentage(totalNr - list.length, totalNr)} %`])
.map(printEntry);
printDrinkerStats(drinkPreferences, arr.length);
sendMail(drinkPreferences);
} const getDrinkPreferences = (arr) =>
arr
.filter(({ age }) => age > 18)
.map((e) => {
if (e.age >= 40) {
return Object.assign({
drink: "kombucha",
e,
});
} else if (e.age >= 20) {
return Object.assign({
drink: "wine",
e,
});
} else if (e.age >= 18) {
return Object.assign({
drink: "beer",
e,
});
}
});Summary
"All told, a monad in X is just a monoid in the category of endofunctors of X, with product × replaced by composition of endofunctors and unit set by the identity endofunctor."
Summary
Its up to you!
Functional Programming
By Mikael Gråborg
Functional Programming
- 147



