Computation
@miloas
http://miloas.me
Outline
- Histroy
- Turing machine
- Lambda calculus
David Hilbert

Kurt Friedrich Gödel

Alan Mathison Turing

Turing machine
(Q, \Sigma, \Gamma, \delta, q_0, q_{accept}, q_{reject})
The Halting Problem
bool God_algo(char *program, char *input) {
if(<program> halts on <input>) return true;
return false;
}
bool Satan_algo(char *program) {
if(God_algo(program, program)) {
while(1);
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
Satan_algo(Satan_algo);
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor
| 1 | |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 |
a_{10}a_{11}a_{12}a_{13} ...
a_{20}a_{21}a_{22}a_{23} ...
a_{30}a_{31}a_{32}a_{33} ...
...
...
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | N | 1 | N | N | ... |
| M2 | 2 | 0 | N | 0 | ... |
| M3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ... |
| M4 | N | 0 | 5 | N | ... |
| ... |
构造新的图灵机P(i)
当Mi(i) halts时,P(i) = Mi(i)+1
否则,P(i) = 0
必然存在k使得Mk = P, 就会有:
Mk(k) = P(k) =
1+Mk(k) if Mk(k) halts
0 if Mk(k) doesn't halt
不管哪种情况都矛盾
Lambda calculus
(Y F) = (F (Y F))
Alonzo Church

lambda calculus BNF:
<expr> ::= <identifier>
<expr> ::= lambda <identifier-list> . <expr>
<expr> ::= (<expr> <expr>)
Haskell Brooks Curry

Y Combinator
"Why does it exist? Why does it work the way it does?"
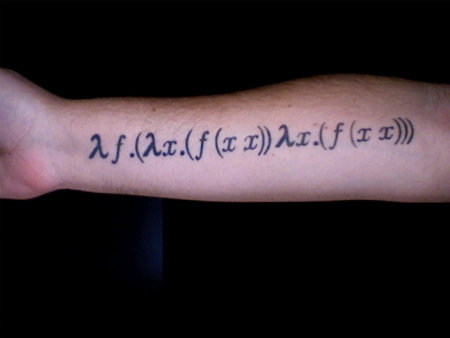
function f(n) {
return n == 0 ? 1 : n * f(n - 1)
} // lambda n. If_Else n == 0 1 n * f(n - 1)lambda n. If_Else n == 0 1 n * <self>(n - 1)let F = lambda n. If_Else n == 0 1 n * F(n - 1)let P = lambda self n. If_Else n == 0 1 n * self(self, n - 1) // P(P, 3)let P = lambda self n. If_Else n == 0 1 n * self(n - 1) // P(f, 3)
P(f) ??? excuse me ???
-----------> P(f)(3) == P(f, 3)
P(f) == lambda n. If_Else n == 0 1 n * f(n - 1) == f
Y(F) = f = F(f) = F(Y(F))let f_gen = lambda self. P(self(self))
f_gen(f_gen) = P(f_gen(f_gen))let Y = lambda F. {
let f_gen = lambda self. F(self(self))
return f_gen(f_gen)
}const Y = f => (x => f(v => x(x)(v)))(x => f(v => x(x)(v)))
(self => n => n ===0 ? 1 : n * self(n - 1))
Thanks.
computation
By miloas
computation
- 76


