Smart Contracts - Solidity
Ming-der Wang
ming@Log4Analytics.com
mingderwang@gmail.com
集先鋒科技
5/25/2016
王銘德
本課程你能學到
- 至少能看得懂 Solidity 程式碼
- 動手做: 至少能寫你第一章"智能合約" Hello World
- 能執行你的合約, 跟別人交換合約來執行
如果你做了你的客製化 "tokens" (代幣)
- 透過你的Ether Wallet, 跟別個同學互相交換 tokens
Ethereum 網路
如何在 Ethereum 網路上開發應用?
也就是寫一個所謂的"智能合約“
那什麼是 "智能合約" - Smart Contracts?
什麼東西可以寫成或利用 S.C.
- 需要 3rd Party Trusts (“第三方信託") 時
- 需要公開透明, 卻又不能篡改的東西 (比如說, 歷史?)
- 你跟政府有簽合約嗎? 你為何相信政府的鈔票? (美金呢?)
例如:
- 眾籌募資: Digix , WeiFund, TheDAO
- 選舉, 選委員, 民主投票, 公證, 契約...
- 網路樂透,
- 想些超大的應用? 你生活周遭發生的事, 能用 S.C.來解決嗎?
開發環境
-
Use TEST-NET to Mine and Test Your Smart Contracts
-
Use Official Ethereum Wallet (Mist) to Run Your TEST-NET as Your Dev Env
-
Use Gist to Save Your Code
-
Use Solidity Real Time Compiler If You Want
-
Use eth or geth CLI When You Are An Expert
-
then, Deploy Your Code On Ethereum Main Network!
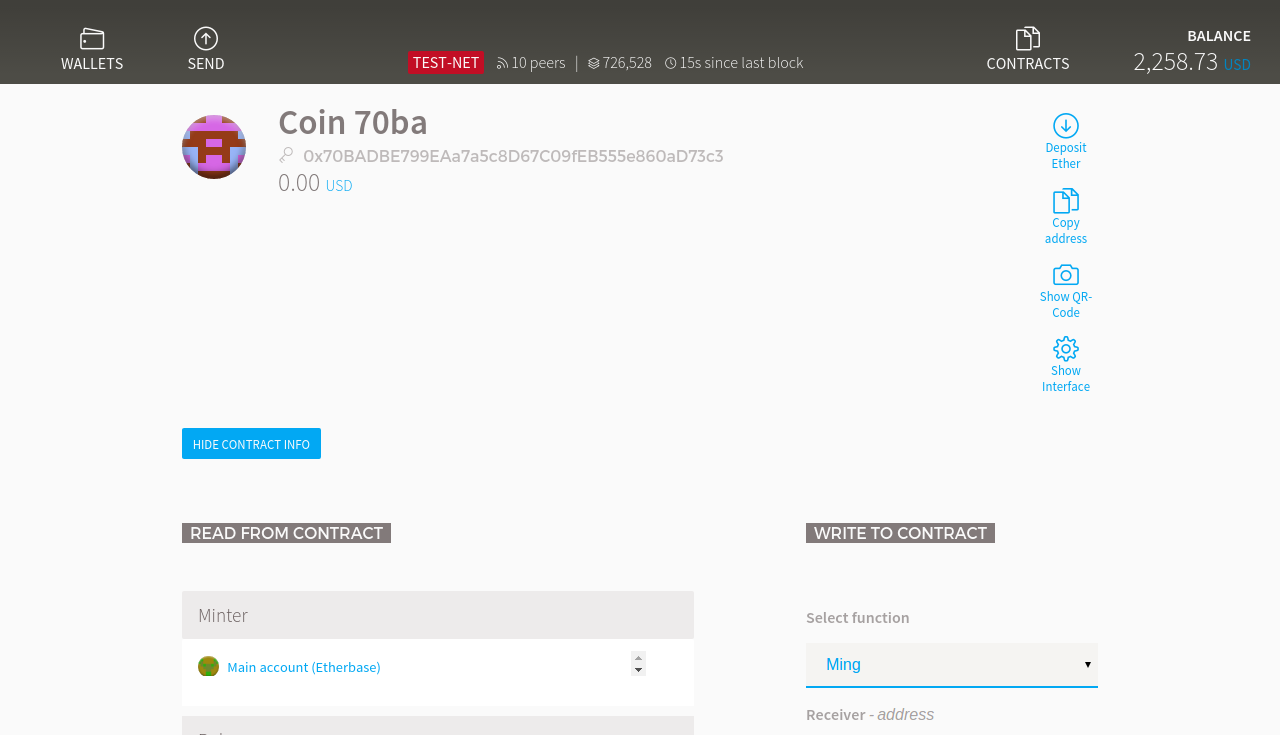
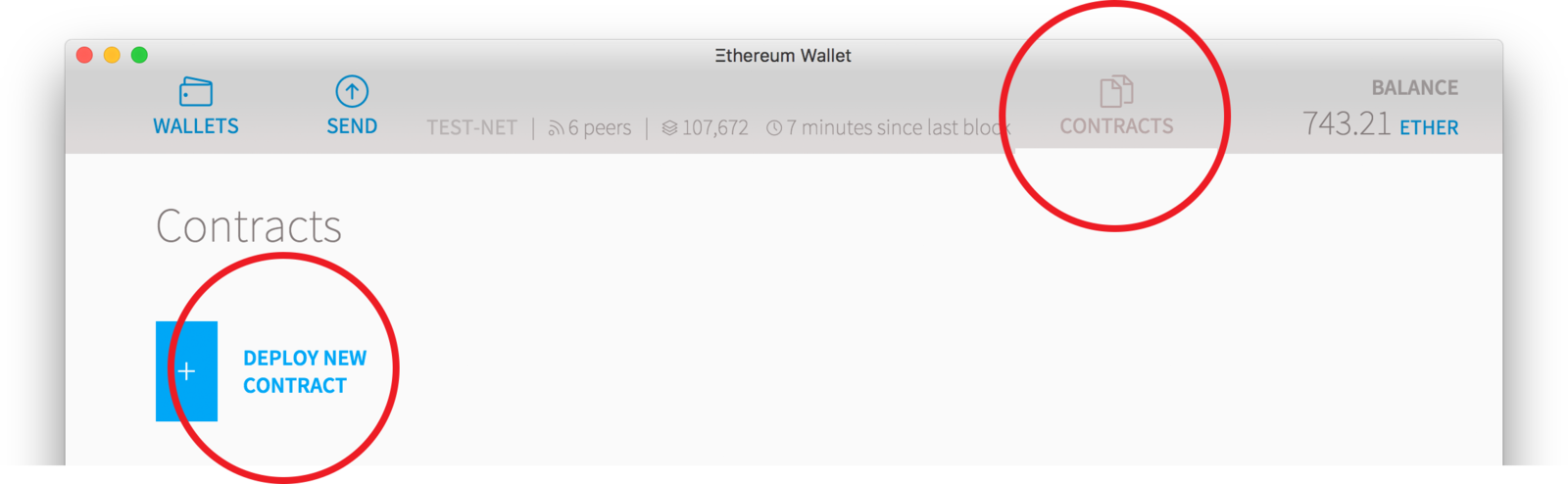
Ethereum Wallet
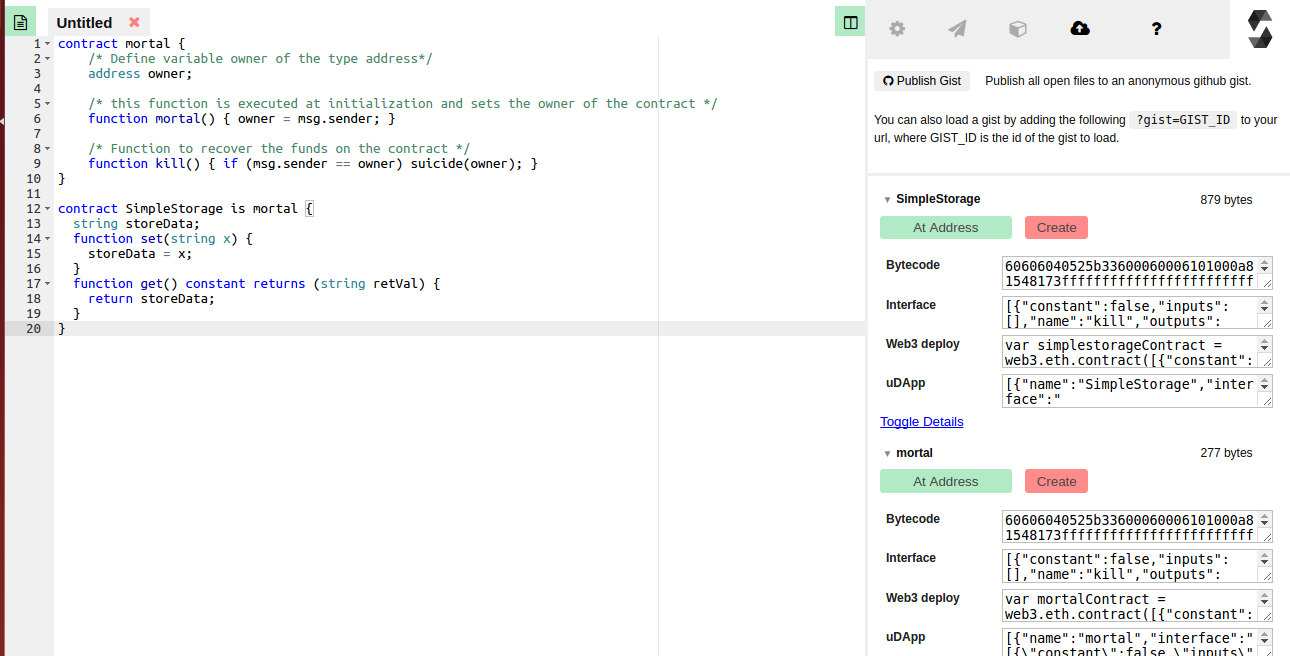
Solidity Realtime Compiler
Solidiy Features
- An object-oriented language
- Types
- Structs
- Mappings (a kind of Arrays)
- Arrays
- address' Methods
- Data Location
- Functions and Exceptions
- Good documents!
Mortal
contract mortal {
address owner;
function mortal() {
owner = msg.sender; }
/* Function to recover the funds on the contract */
function kill() {
if (msg.sender == owner)
selfdestruct(owner); }
}
HelloWorld
contract helloworld is mortal {
/* helloworld inherits all behaviors of mortal, such as function mortal(), kill() and owner */
string storeData;
function set(string x) {
storeData = x; }
function get() constant returns (string data) {
return storeData; }
}
Object-Oriented - inheritance
Types
bool
int8, int16, int24 ... int256
uint8, uint16, ... uint256
uint and int are aliases for uint256 and int256,
address
string
bytes1, bytes2, bytes3, ..., bytes32.
byte is an alias for bytes1
structs
struct Funder { address addr; uint amount; }
- NO rational number so far.
Implicit Conversions
- Compiler will do that for you if possible.
- In general, an implicit conversion between value-types is possible if it makes sense semantically and no information is lost.
- Any type that can be converted to uint160 can also be converted to address.
Explicit Conv.
int8 y = -3; uint x = uint(y);
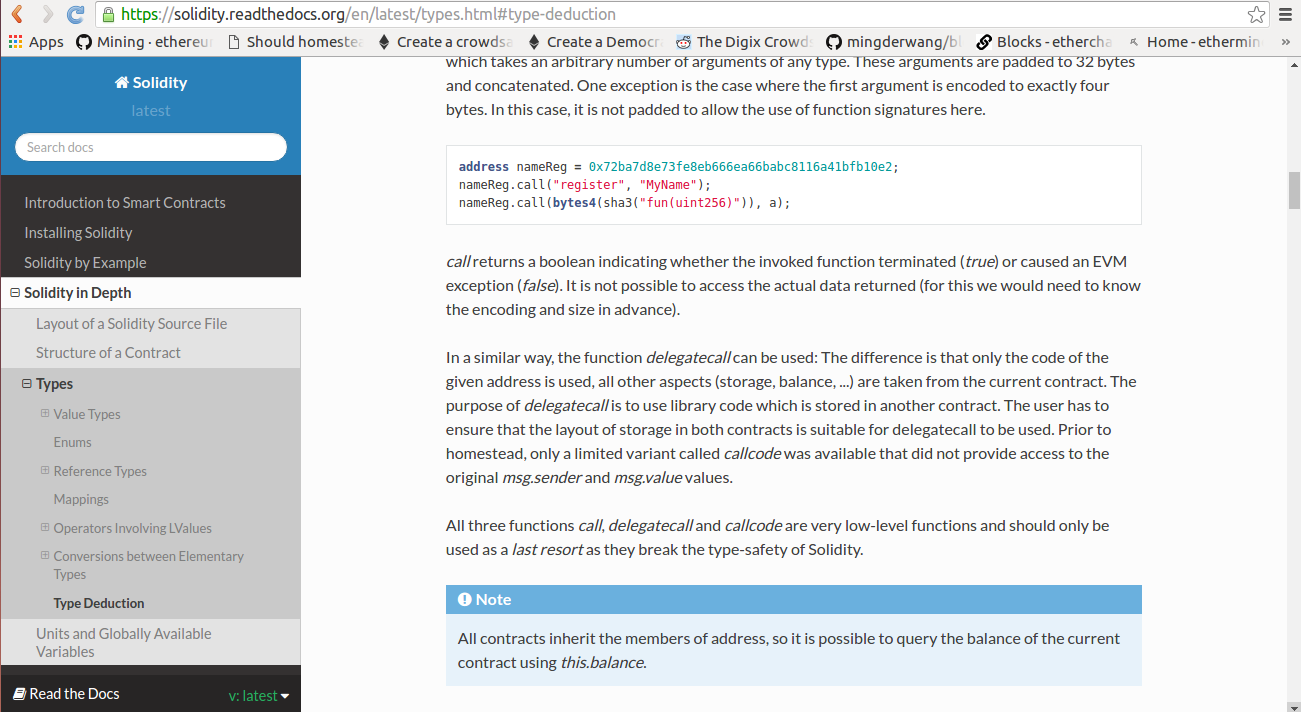
Type Deduction
uint20 x = 0x123; var y = x;
// y will be unit20 too
uint32 a = 0x12345678; uint16 b = uint16(a); // b will be 0x5678 now
- The type is only deduced from the first assignment, so the loop in the following snippet is infinite, as i will have the type uint8 and any value of this type is smaller than 2000. for (var i = 0; i < 2000; i++) { ... }
mappings
- Mapping types are declared as mapping (_KeyType => _ValueType), where _KeyType can be almost any type except for a mapping and _ValueType can actually be any type, including mappings.
- Mappings are only allowed for state variables (or as storage reference types in internal functions).
- no length
contract MyToken { /* This creates an array with all balances */
mapping (address => uint256) public balanceOf;
function MyToken() {
balanceOf[msg.sender] = 21000000; }
}
Arrays
contract C { function f(uint len) { uint[] memory a = new uint[](7); bytes memory b = new bytes(len);// memory // Here we have a.length == 7 and b.length == len a[6] = 8; } }
- An array of fixed size k and element type T is written as T[k], an array of dynamic size as T[].
bytes and string
Variables of type bytes and string are special arrays. A bytes is similar to byte[], but it is packed tightly in calldata. string is equal to bytes but does not allow length or index access (for now).
- So bytes should always be preferred over byte[] because it is cheaper.
- also, array has a member called, length and push.
- push is for appending elements.
Functions and Exceptions
contract Sharer { function sendHalf(address addr) returns (uint balance) { if (!addr.send(msg.value/2)) throw; // also reverts the transfer to Sharer return this.balance; } }
Hands-On
To create a new contract, such as "Greeter"
https://www.ethereum.org/token#the-code
Hands-On 2
To use "MyToken" contract to send tokens
address' Methods
address holds a 20 byte value (size of an Ethereum address). Address types also have members, like send()
address x = 0x123; address myAddress = this; if (x.balance < 10 && myAddress.balance >= 10) x.send(10);
All contracts inherit the members of address, so it is possible to query the balance of the current contract using this.balance.
if the address is a contract
address nameReg = 0x72ba7d8e73fe8eb666ea66babc8116a41bfb10e2; nameReg.call("register", "MyName"); nameReg.call(bytes4(sha3("fun(uint256)")), a);
- call returns a boolean indicating whether the invoked function terminated (true) or caused an EVM exception (false).
- delegatecall is to use library code which is stored in another contract.
- callcode was available that did not provide access to the original msg.sender and msg.value values.
Data Location
“calldata”, which is a non-modifyable non-persistent area where function arguments are stored. Function parameters (not return parameters) of external functions are forced to “calldata” and it behaves mostly like memory.
- memory (which is not persisting)
- storage (where the state variables are held).
- calldata
Every complex type, i.e. arrays and structs, has an additional annotation, the “data location”.
Data Location (continue)
- Depending on the context, there is always a default, but it can be overridden by appending either storage or memory to the type.
- The default for function parameters (including return parameters) is memory, the default for local variables is storage and the location is forced to storage for state variables (obviously).
Example
contract c {
uint[] x; // the data location of x is storage
// the data location of memoryArray is memory
function f(uint[] memoryArray) {
x = memoryArray; // works, copies the whole array to storage
var y = x; // works, assigns a pointer, data location of y is storage
y[7]; // fine, returns the 8th element
y.length = 2; // fine, modifies x through y
delete x; // fine, clears the array, also modifies y
y = memoryArray; // not working
delete y; // not working
g(x); // calls g, handing over a reference to x
h(x); // calls h and creates an independent, temporary copy in memory
}
function g(uint[] storage storageArray) internal {}
function h(uint[] memoryArray) {}
}
delete
contract DeleteExample {
uint data;
uint[] dataArray;
function f() {
uint x = data;
delete x; // sets x to 0, does not affect data
delete data; // sets data to 0, does not affect x which still holds a copy
}
uint[] y = dataArray;
delete dataArray; // this sets dataArray.length to zero, but as uint[] is a complex object, also
// y is affected which is an alias to the storage object
// On the other hand: "delete y" is not valid, as assignments to local variables
// referencing storage objects can only be made from existing storage objects.
}
}
contract Contract {
struct Data {
uint deadline;
uint amount;
}
Data data;
function set(uint id, uint deadline, uint amount) {
data.deadline = deadline;
data.amount = amount;
}
function clear(uint id) { delete data; }
}
delete for structure
Solidity Doc
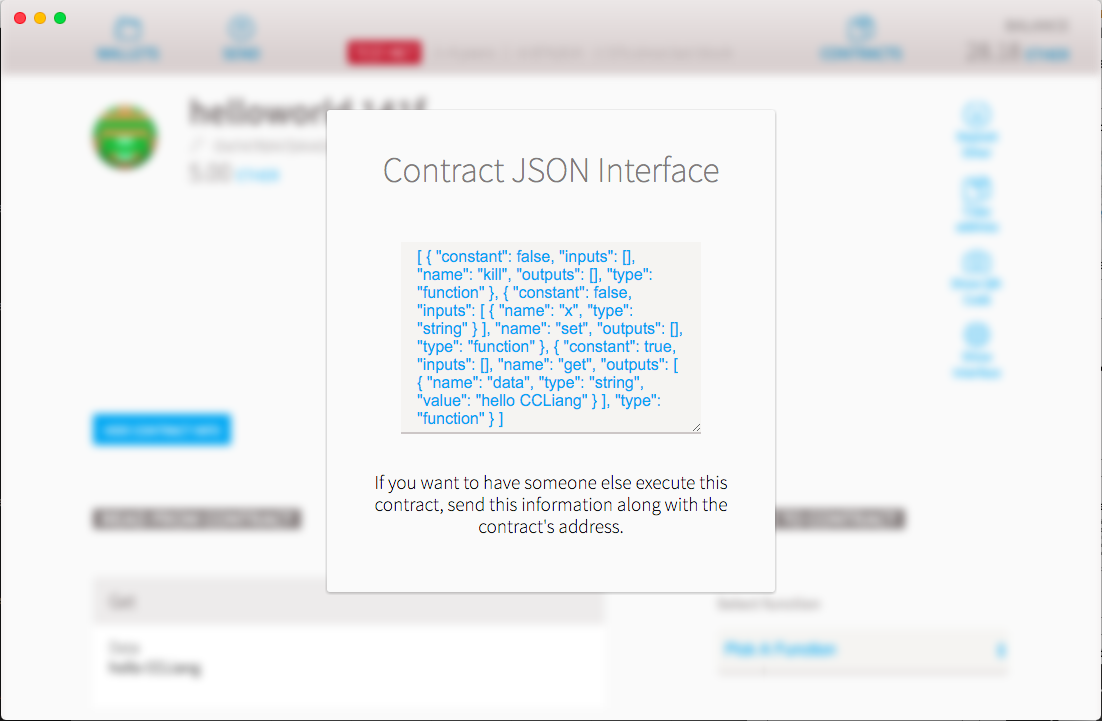
如何讓別人執行你的Contract
[ { "constant": false, "inputs": [], "name": "kill", "outputs": [], "type": "function" }, { "constant": false, "inputs": [ { "name": "x", "type": "string" } ], "name": "set", "outputs": [], "type": "function" }, { "constant": true, "inputs": [], "name": "get", "outputs": [ { "name": "data", "type": "string", "value": "hello CCLiang" } ], "type": "function" } ]
跟你的 Contract Address
0x141fd413A40a4163A8ecF1A02f902A1abE8ff7c5
寄給他們 Contract JSON
按 Show Interface
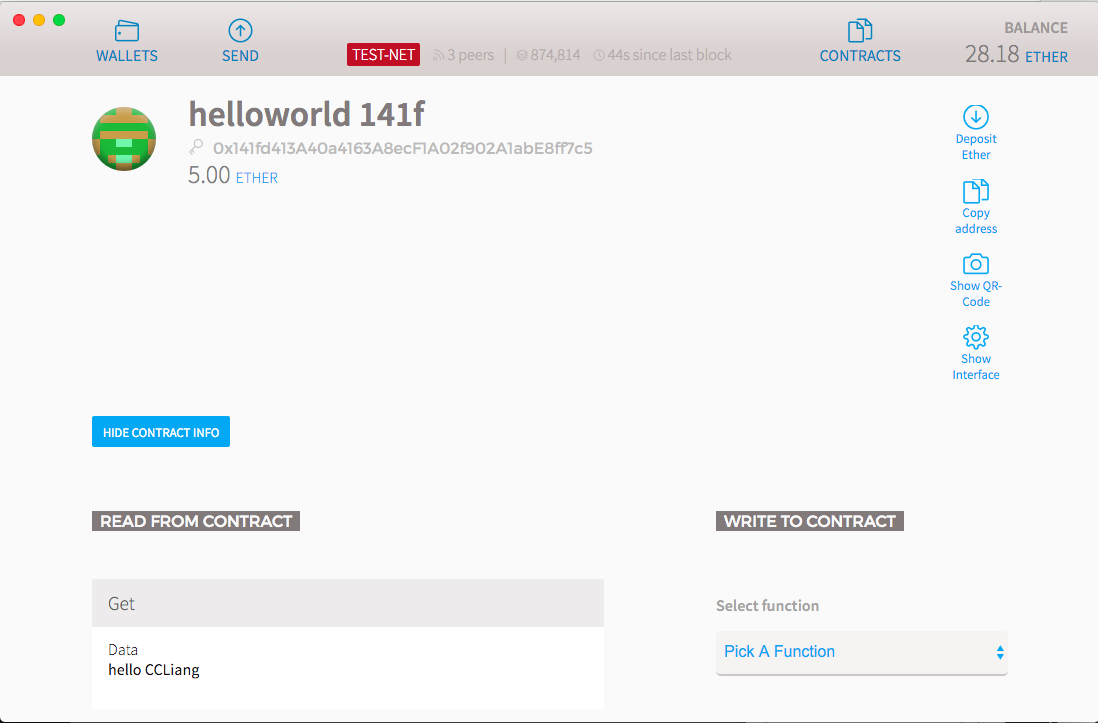
點擊
Contract Address
Contract JSON Interface
想執行別人的 Contract
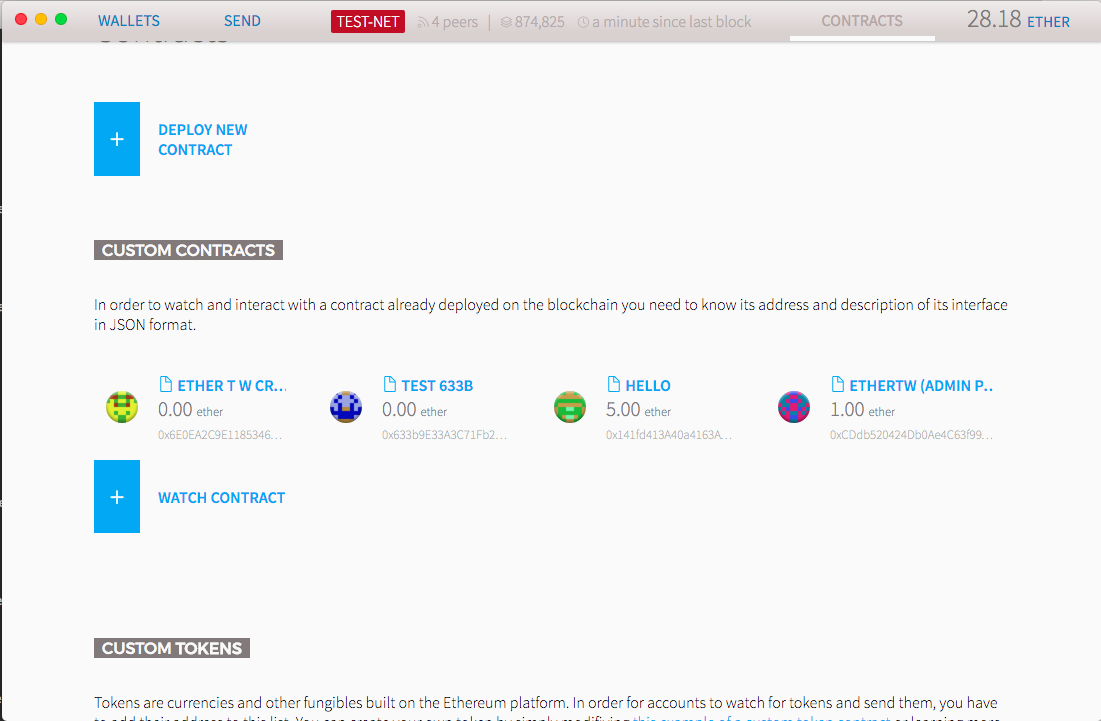
點擊
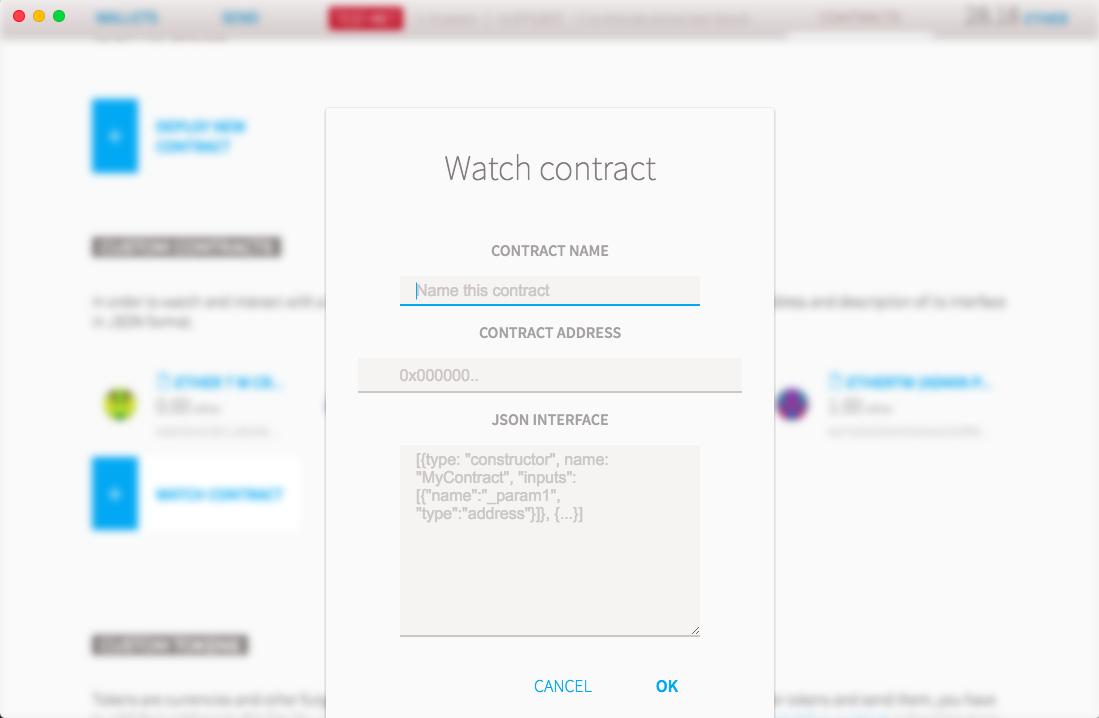
填如地址跟Contract JSON
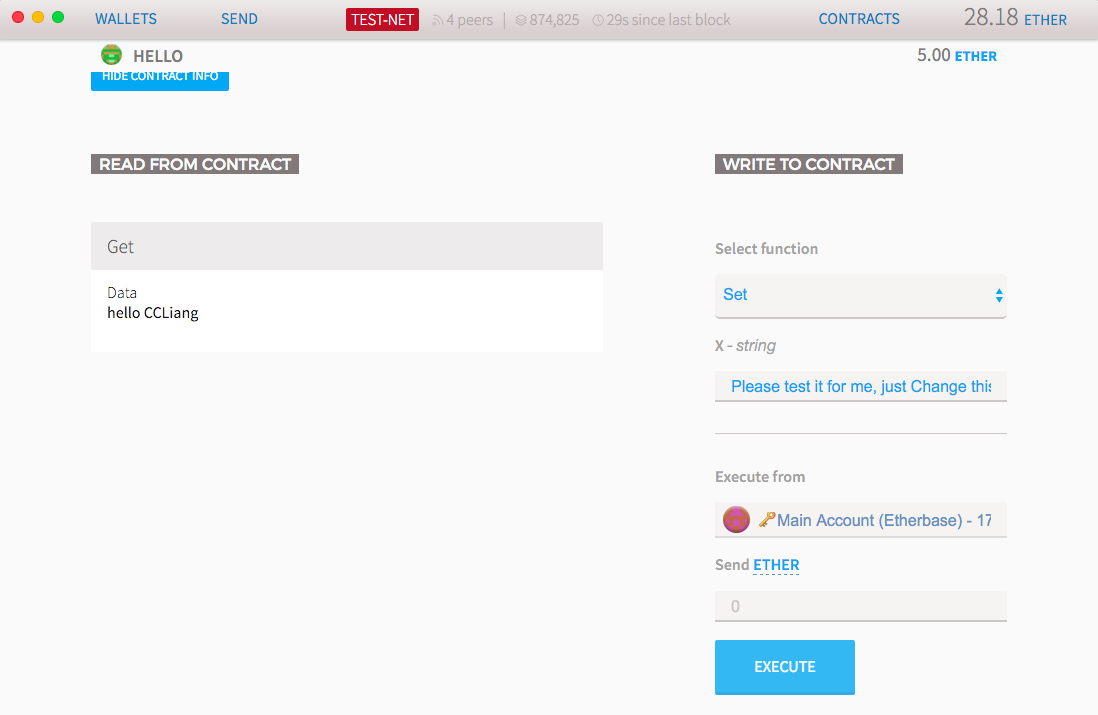
Hello Contract
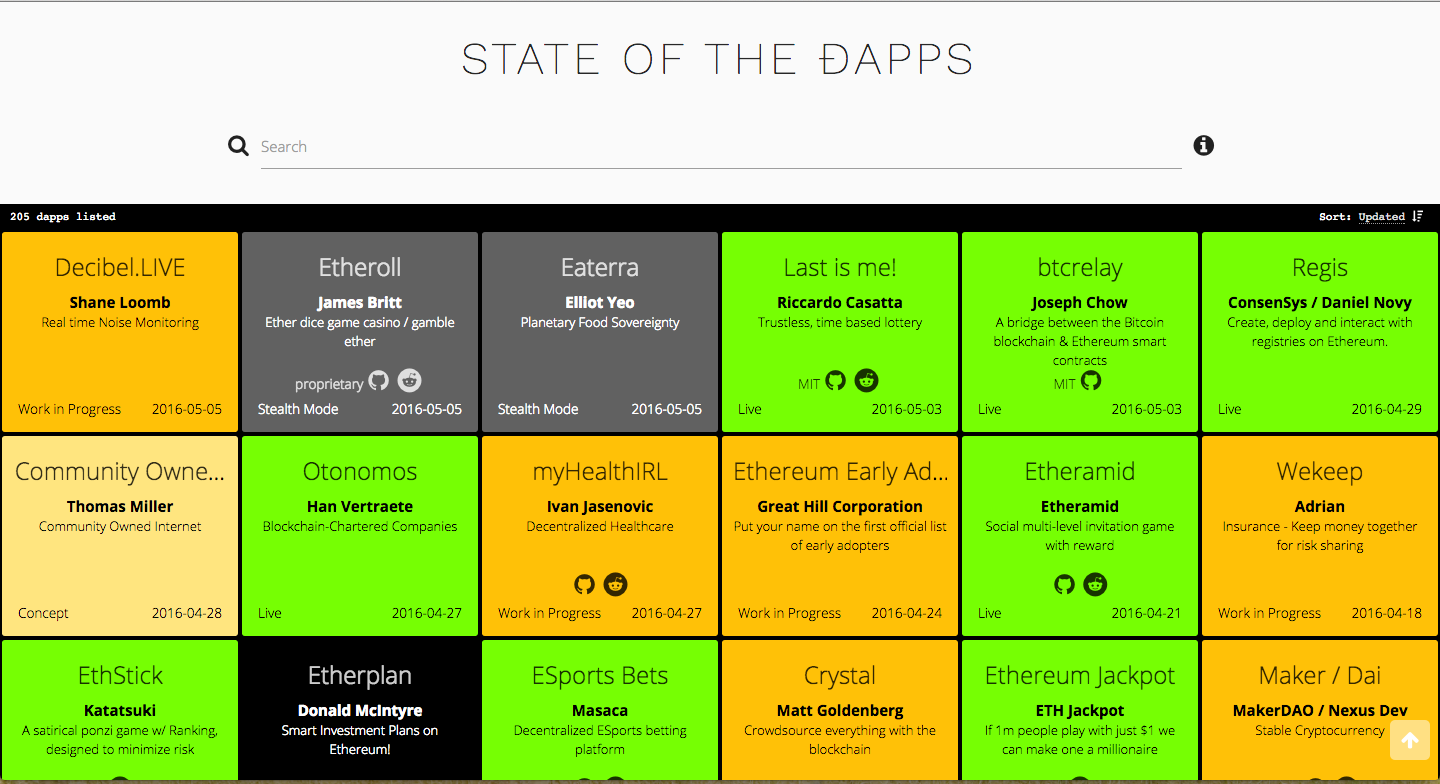
我有哪些 DApps 可以參考
http://dapps.ethercasts.com/
我還可以用其他語言寫 S.C. 嗎?
- Solidity - Javascript/C++ like
- Serpent - Python-like
- LLL - Lisp-like
-
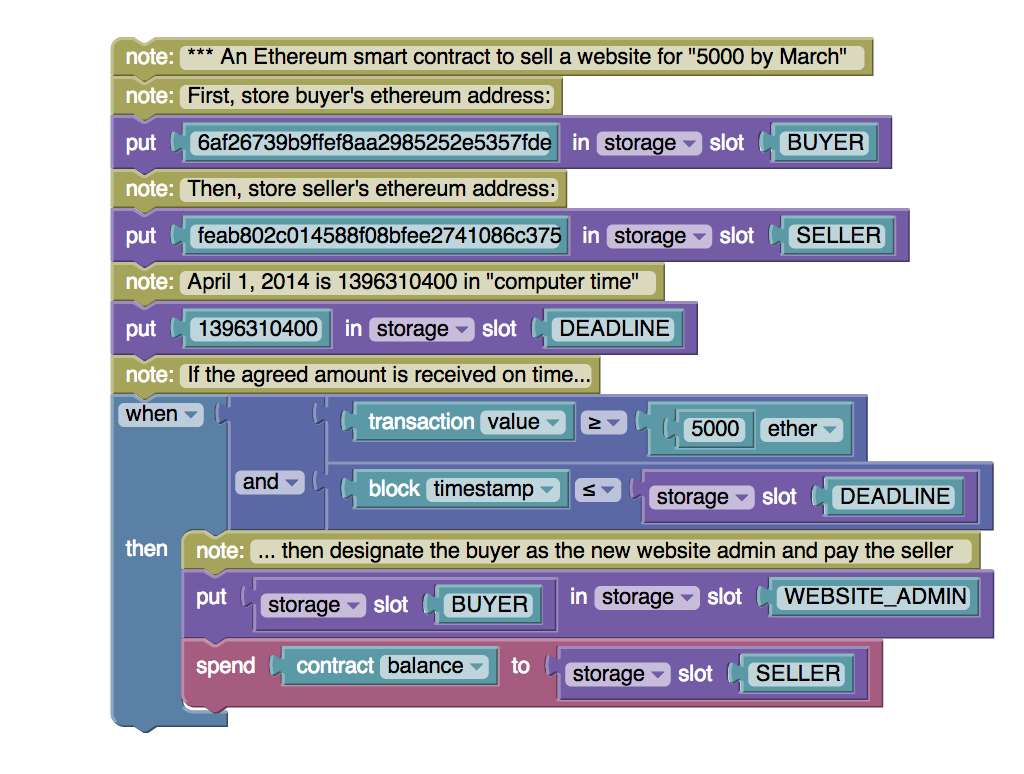
EtherScript - Scratch-like
- 類似早期的 Lego MindStroms
- eris
Ethereum-based
Bitcoin-based
- sidechain, counterparty, ...
Q & A
EtherTW.slack.com 線上討論
https://goo.gl/S6nhKv <---- 加入slack
ming@log4analytics.com
Further Reading:
Smart Contract - Solidity 5/25
By Ming-der Wang
Smart Contract - Solidity 5/25
- 1,411