Biomes

| by MingYang Li |
|---|
What is Biome?
A biome is a group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms.
- Scientists who study ecology have categorised and grouped places on Earth as biomes.
- The term biome means the main groups of plants and animals living in areas of certain climate patterns.

Mojave Desert, USA

Deciduous forest
o(* ̄▽ ̄*)ブ
- The actual species of plants and animals are similar because the climate conditions are similar. The climate helps determine which animals live in a particular place.

How many types biomes do we have?
Some ecologists have identified about 11 different biomes in the world. However, generally speaking, 5 -7 are agreed upon. The reason for the disagreement is that there is a zone between biomes where one blends into the other, and some ecologists think these zones are also separate biomes. However, the seven generally accepted biomes are:
•water (freshwater or ocean)
•rainforest (tropical or temperate)
•tundra
•desert
•taiga (coniferous forests)
•deciduous forests
•grassland
Rain Forest Biomes
※There are two types of rainforest biomes: temperate and tropical rainforests.
Tips:Rainforests are forests characterized by high rainfall, with annual rainfall between 250 and 450 centimetres (98 and 177 in). There are two types of rainforest: tropical rainforest and temperate rainforest.

Tropical Rainforests
Tropical rainforests are generally found between 30°N and 30°S latitudes, covering 6 - 7% of the Earth’s land surface. Tropical rainforests can be found around the world.
- Tropical rainforests are lush and warm all year long!
- Temperatures don’t even change much between night and day. The average temperature in tropical rainforests ranges from 70 to 85°F (21 to 30°C).
- Maintaining a high humidity of 77% to 88% year-round. The yearly rainfall ranges from 200 to 1000 cm, and it can rain hard. It can downpour as much as 5 cm in an hour!


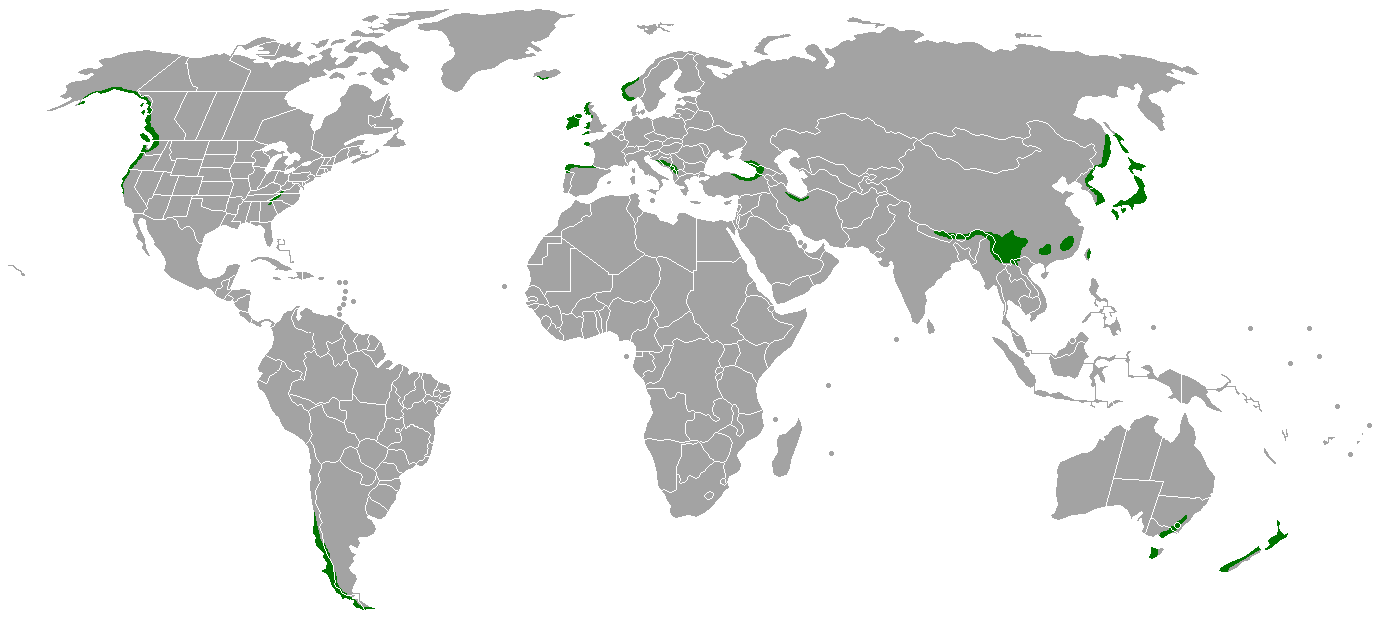
Temperate rainforests
Temperate rainforests are found along coasts in temperate regions. The largest temperate rainforests are on the Pacific coast in North America, stretching from Alaska to Oregon.
Temperate rainforests are also wet, but not as rainy as tropical rainforests. It rains about from 150 - 500 cm each year. Temperate rainforests are a lot cooler than tropical rainforests, but the temperatures are still mild. They often have two distinct seasons: one long wet winter, and a short drier summer.

Compare
Temperate Rainforest
Huge trees grow there, including cedars, red woods,and Douglas firs.
However, it is difficult to classify this region. Many ecologists refer to this ecosystem as a temperate rainforests. Mule deer are found there.
The term "temperate"means having moderate temperatures.
Tropical Rainforest

Although tropical rainforests cover only a small part of the planet, they probably contain more species of plants and animals than all the other biomes combined.

Desert Biomes
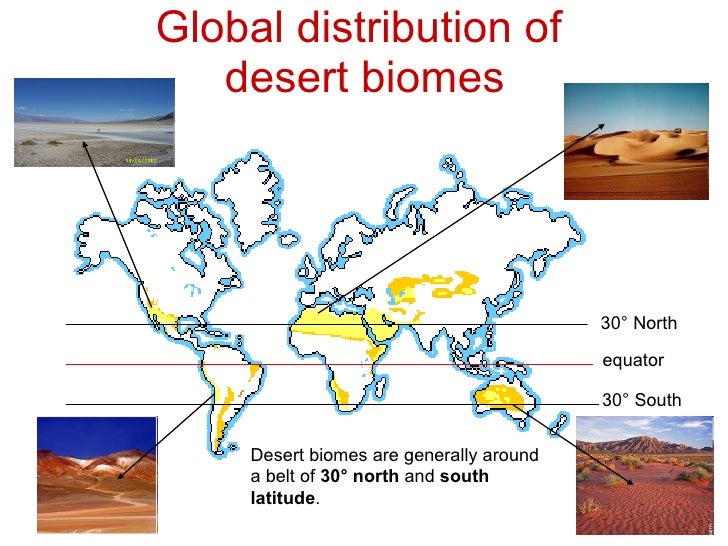
※A desert is an area that receives less than 25 centimeters of rain per year.
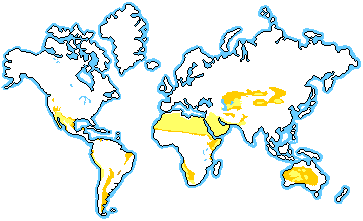
- Deserts cover about 20% of the Earth. There are four major types of desert in this biome - hot and dry, semiarid, coastal, and cold.
Interesting Desert Biome Facts:
| Although the daytime temperatures of the desert biome are very hot, they can get very cold at night. |
| The Sahara Desert is the largest desert in the desert biome. It covers over 300 million square miles. |
| The vegetation does not grow very tall so the desert biome can only accommodate small animals, rodents, and reptiles. These animals can escape the harsh Sun by hiding under small scrubs or hiding in burrows. Most animals active in night. |



Let see some pictures:)
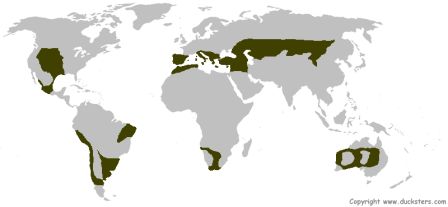
Grassland Biomes
- A grassland is an area that is populated mostly by grasses and other nonwoody plants.
- We usually call a grassy plain a prairie:)
- Ecologists classify prairies, which are generally found in the middle latitudes, as grassland.
- Fires and droughts are common in this biome.
- Grasslands that are located closer to the equator than prairies are known as savannas.
- A savannas receives as much as 120 cm of rain each year. Scattered shrubs and small trees grow on savannas along with grass.
- Grasslands are home to many of the largest animals on Earth--herbivores such as elephants, bison, antelopes, zebras, rhinoceroses, giraffes, and kangaroos.

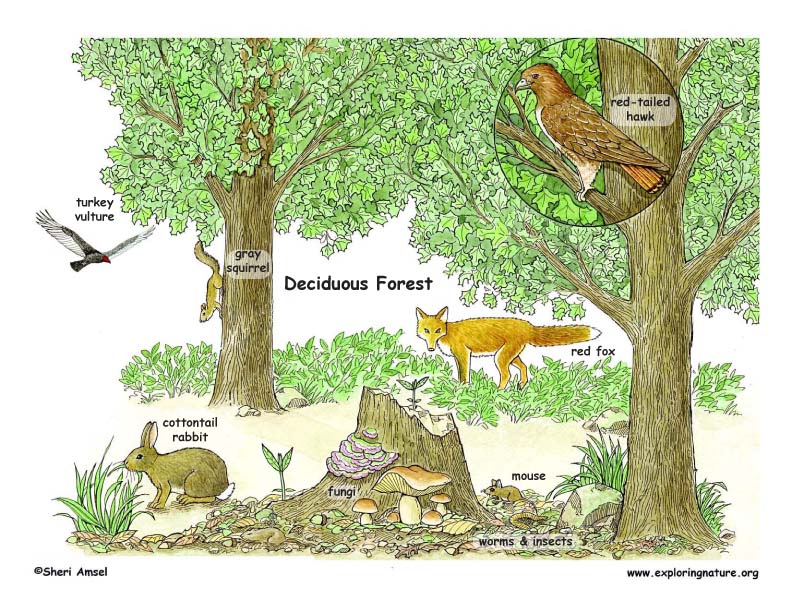
Deciduous Forest Biomes
※Many of the trees in this forests are deciduous trees.
Trees that shed their leaves and grow new ones each year. Ex:Oak, Maple
The growing season usually lasts five to six months.
Different species of birds live in different parts of the forests, eating the insects and fruits in their specific areas.
Mammals such as chipmunks and skunks live in deciduous forests. In a North American deciduous forest you might also see wood thrushes, white-tailed deer, and black bears.

Boreal Forest Biomes
※Most of the trees in the boreal forest are coniferous trees.
Trees that produce their seeds in cones and have leaves shaped like needles.
.jpg)

↣
The boreal forest is sometimes referred to by its Russian name, "Taiga".
Winters in these forests are very cold. The snow can even reach heights well over your head!
Animals include red squirrels, insects, and birds such as finches and chickadees
some herbivores such as snowshoe hares, moose, and beavers, eat tree bark and new shoots.
Many of the animals of the boreal forest eat the seeds produced by the coniferous trees

Boreal forests animals

↓
Tundra Biomes
Tundra are among Earth's coldest, harshest biomes.
Most of the soil in the tundra is frozen all year. This frozen soil is called permafrost.
During the short summer, the top layer of soil thaws, but the underlying soil remains frozen.
※Because rainwater cannot soak into the permafrost, there are many shallow ponds and marshy areas on the tundra in the summer.


☞
Plant and Animals

↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
Mosses, grasses, shrubs, and dwarf forms of a few trees, such as willows.
Insect-eating birds
foxes, caribou, wolves, and Arctic hares...


↓
Mountains and Ice...
Some areas are not part of any major biome.
These areas include mountain ranges and land that is covered with thick sheets of ice.

Mountains, such as these in Banff national park in Canada, are not part of any major biome. They do support ecosystems, however.

Wow!The end(o゜▽゜)o☆
- A biome is a group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms.
- Scientists who study ecology have categorised and grouped places on Earth as biomes.
- The term biome means the main groups of plants and animals living in areas of certain climate patterns.
- the seven generally accepted biomes are:
•water (freshwater or ocean)
•rainforest (tropical or temperate)
•tundra
•desert
•taiga (coniferous forests)
•deciduous forests
•grassland
It's just write down on your notebook≧ε ≦
Title Text
Tropical rainforests
- Tropical rainforests are lush and warm all year long!
- Temperatures don’t even change much between night and day. The average temperature in tropical rainforests ranges from 70 to 85°F (21 to 30°C).
Temperate rainforests
- Temperate rainforests are found along coasts in temperate regions. The largest temperate rainforests are on the Pacific coast in North America, stretching from Alaska to Oregon.
- Temperate rainforests are also wet, but not as rainy as tropical rainforests. It rains about from 150 - 500 cm each year. Temperate rainforests are a lot cooler than tropical rainforests, but the temperatures are still mild. They often have two distinct seasons: one long wet winter, and a short drier summer.
Desert Biomes
- A desert is an area that receives less than 25 centimeters of rain per year.
- Deserts cover about 20% of the Earth. There are four major types of desert in this biome - hot and dry, semiarid, coastal, and cold.
|
|
|
Grassland Biomes
- We usually call a grassy plain a prairie:)
- Ecologists classify prairies, which are generally found in the middle latitudes, as grassland.
- Fires and droughts are common in this biome.
- Grasslands that are located closer to the equator than prairies are known as savannas.
- A savannas receives as much as 120 cm of rain each year. Scattered shrubs and small trees grow on savannas along with grass.
- Grasslands are home to many of the largest animals on Earth--herbivores such as elephants, bison, antelopes, zebras, rhinoceroses, giraffes, and kangaroos.
Deciduous Forest Biomes
- Many of the trees in this forests are deciduous trees.
- The growing season usually lasts five to six months.
- Different species of birds live in different parts of the forests, eating the insects and fruits in their specific areas.
- Mammals such as chipmunks and skunks live in deciduous forests. In a North American deciduous forest you might also see wood thrushes, white-tailed deer, and black bears.
Boreal Forest Biomes
- Trees that produce their seeds in cones and have leaves shaped like needles.
-
Winters in these forests are very cold. The snow can even reach heights well over your head!
- Animals include red squirrels, insects, and birds such as finches and chickadees some herbivores such as snowshoe hares, moose, and beavers, eat tree bark and new shoots.
- Many of the animals of the boreal forest eat the seeds produced by the coniferous trees
Tundra Biomes
- Tundra are among Earth's coldest, harshest biomes.
- Most of the soil in the tundra is frozen all year. This frozen soil is called permafrost.
- During the short summer, the top layer of soil thaws, but the underlying soil remains frozen.
- Because rainwater cannot soak into the permafrost, there are many shallow ponds and marshy areas on the tundra in the summer.
Mountains and Ice...
- Some areas are not part of any major biome.

Finally! ☆*:.。. o(≧▽≦)o .。.:*☆
Thanks for watching and listening......


deck
By mingyangli
deck
- 2,147
