Micro-Frontends
- What are Micro-Frontends?
- History of app development.
- Core Idea Behind Micro-Frontends.
- Advantages And Disadvantages.
- MF Frameworks.
- Module Federation
Micro-Frontends - What Are They?
Relatively new concept that extends the idea of Microservices to the frontend.
General idea behind the Micro-Frontend is to split one frontend application into multiple so that they can be worked on and deployed separately.
Monolith Frontend - One big application.
Micro-Frontends - Multiple small applications.
History Of App Development
At first, apps were monolith and contained both frontend and backend application.
They would later be split vertically to frontend and backend.
Backend applications were then split horizontally into microservices.
History Of App Development
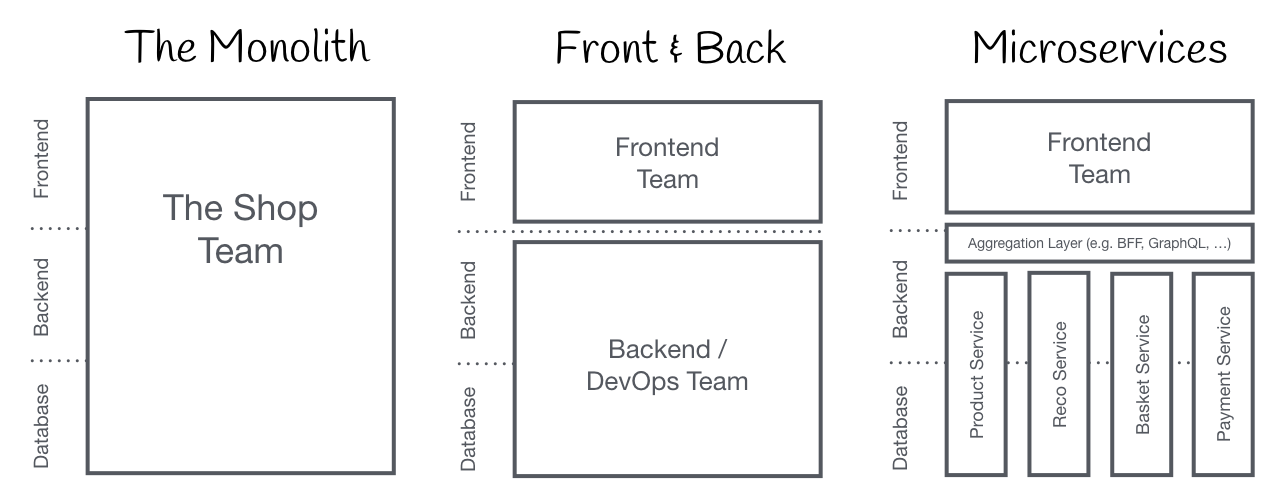
At first, apps were monolith and contained both frontend and backend application.
They would later be split vertically to frontend and backend.
Backend applications were then split horizontally into microservices.
Core Idea Behind Micro-Frontends
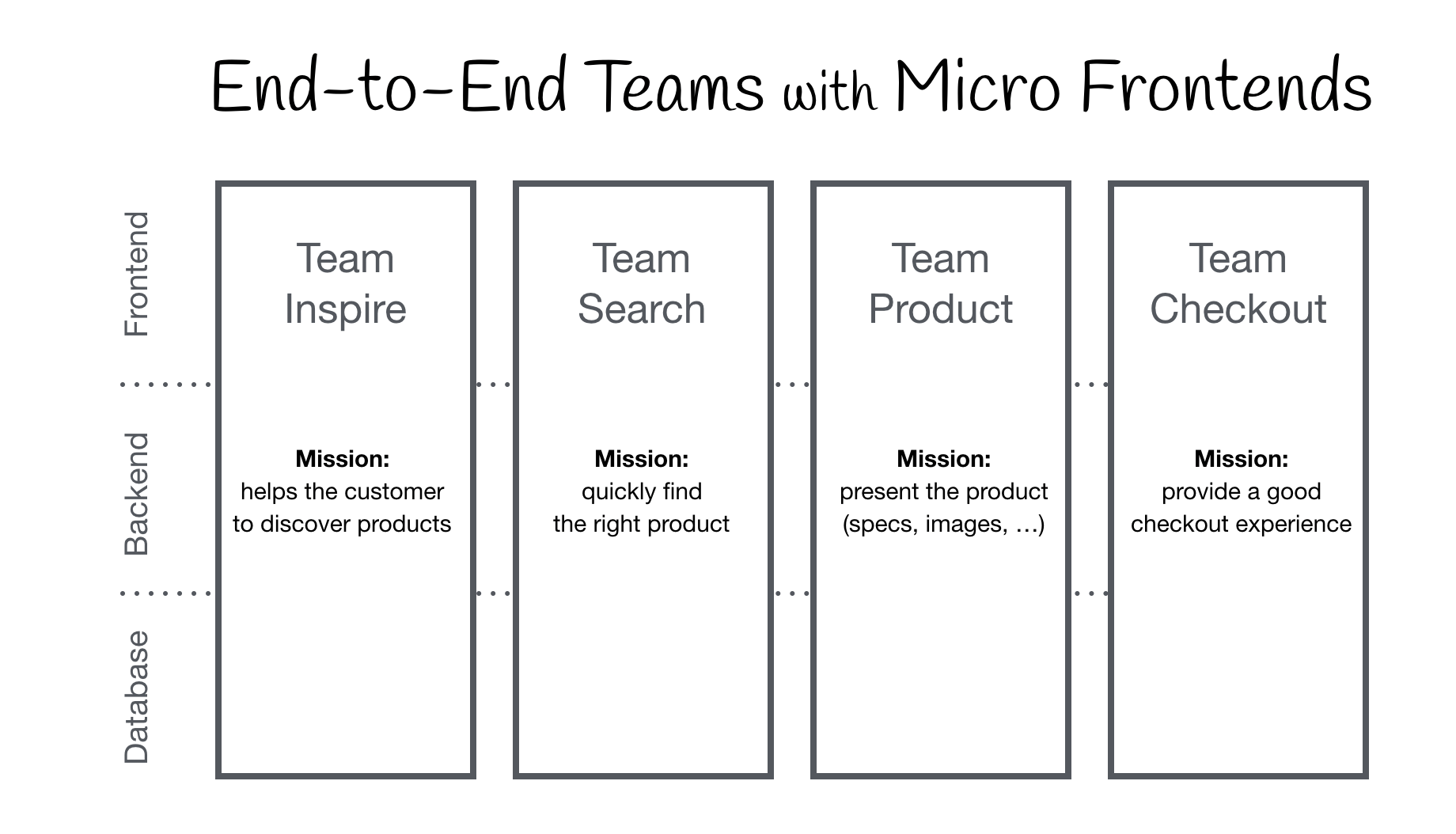
The idea behind Micro-Frontends follows the idea behind microservices.
After splitting monolith frontend, the entire application is split horizontally which allows each team independent End-to-End development.
Core Idea Behind Micro-Frontends
The idea behind Micro-Frontends follows the idea behind microservices.
After splitting monolith frontend, the entire application is split horizontally which allows each team independent End-to-End development.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Adventages:
1. Technology agnostic - different Micro-Frontends can use different programming languages, frameworks and libraries.
2. Loosely coupled - change in one Micro-Frontend does not require change in oters.
3. Independent deployment - each MF-end can be deployed separately, independent of others.
Disadvantages:
1. Complexity
2. An emerging developer community
3. No standards
MF Frameworks
Most popular MF frameworks:
1. Bit
2. Module Federation
3. Single SPA
4. Open Components
Module Federation
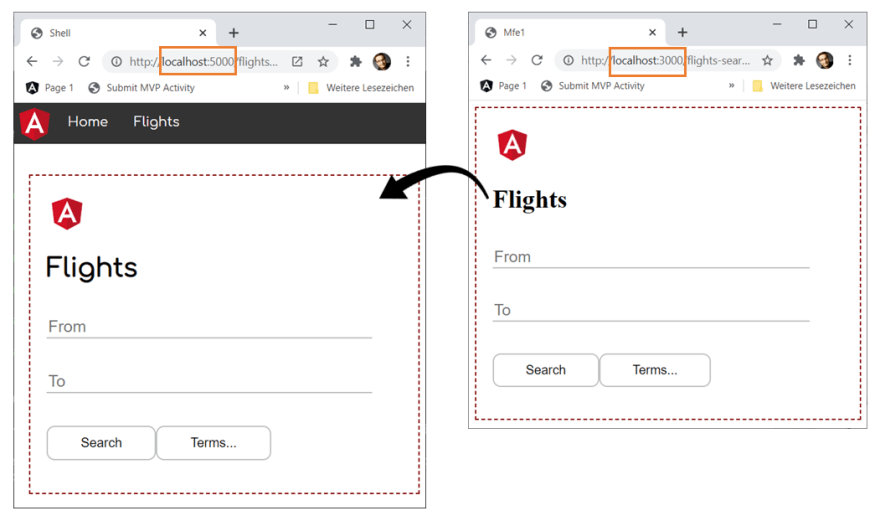
Module Federation is made out of 2 types of MF-end applications, host(shell) and remotes.
Host application is used as "backbone" and loads MF-ends when needed.
Module Federation
Module Federation is made out of 2 types of MF-end applications, host(shell) and remotes.
Host application is used as "backbone" and loads MF-ends when needed.
NX Library
# NX LIBRARY
- tool for building enterprise-scale applications with Angular
- faster builds
- minimize the downsides that come with Module Federation
Create a new NX workspace
npx create-nx-workspace@latest wedofinanceCreate a shell application
npx nx g @nrwl/angular:host shell --dynamicCreate a microfrontend application
npx nx g @nrwl/angular:remote excels --host=shell
...Create library for shared code between shell and remotes
nx g @nrwl/angular:lib shared/auth
...# NX LIBRARY
Generated files:
- standard Angular application files
- project.json (updated the build target - @nrwl/angular:webpack-browser)
- webpack.config.js
- module-federation.config.js
- bootstrap.ts
# NX LIBRARY
//apps/shell/webpack.config.js
const withModuleFederation = require('@nrwl/angular/module-federation');
const moduleFederationConfig = require('./module-federation.config');
module.exports = withModuleFederation({
...moduleFederationConfig,
});//apps/shell/module-federation.config.js
module.exports = {
name: 'shell',
remotes: [], //dinamicki
//remotes: ['excels', 'transactions', 'graphs'], //staticki
};//apps/excels/module-federation.config.js
module.exports = {
name: 'excels',
exposes: {
'./Module': 'apps/excels/src/app/remote-entry/entry.module.ts',
},
};# NX LIBRARY
Communication
# COMMUNICATION
- module-federation.manifest.json
- remotes.d.ts
- main.ts (shell)
- app.routes.ts
- module-federation.config.js
- entry.routes.ts (microfrontents)
- index.ts (lib)
//module-federation.manifest.json
{
"excels": "http://localhost:4201",
"transactions": "http://localhost:4202",
"graphs": "http://localhost:4203"
}
//main.ts - shell
import { setRemoteDefinitions } from '@nrwl/angular/mf';
fetch('/assets/module-federation.manifest.json')
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((definitions) => setRemoteDefinitions(definitions))
.then(() => import('./bootstrap').catch((err) => console.error(err)));
manifest.json, remote.d.ts and main.ts
//remotes.d.ts
declare module 'excels/Module';
declare module 'transactions/Module';
declare module 'graphs/Module';
# COMMUNICATION
//app.routes.ts - shell
export const appRoutes: Route[] = [
{
path: 'excels',
loadChildren: () =>
loadRemoteModule('excels', './Module').then((m) => m.RemoteEntryModule),
}, ...
];
//app.routes.ts - microfrontend
export const remoteRoutes: Route[] = [
{
path: '',
loadChildren: () => import('../excel-upload/excel-upload.module')
.then(m => m.ExcelUploadModule)
},
{
path: 'approval',
loadChildren: () => import('../excel-approval/excel-approval.module')
.then(m => m.ExcelApprovalModule)
},
];
app.routes.ts
# COMMUNICATION
//index.ts - library
export * from './lib/shared-excel-lib.module';
export * from './lib/services/excel.service';
export * from './lib/services/upload-excel.service';
Important to add exports in library's index.ts so each new class can be accessible from outside of library
index.ts
# COMMUNICATION
Docker Containers
To use docker with MF application it is necessary to create docker container for each MF-end.
To create MF-end container we need to write Dockerfile as well as docker-compose file for it.
wedofinance-graphs.yml file
version: "3.8"
services:
#----------------------------------------------------------------
wedofinance-graphs:
build:
context: ./../wedofinance-frontend
dockerfile: apps/graphs/Dockerfile
container_name: wedofinance-graphs
restart: on-failure
expose:
- '4203'
ports:
- "4203:80"
networks:
- wedofinance-network
#----------------------------------------------------------------
networks:
wedofinance-network:YML file example
Graphs Dockerfile
FROM node:latest as node
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN npm install -g @nrwl/cli
RUN npm install --force
RUN npx nx build graphs --configuration=production
#stage 2
FROM nginx:alpine
COPY ./apps/graphs/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
COPY --from=node app/dist/apps/graphs /usr/share/nginx/htmlDockerfile example
Nginx config file
events{}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
}
}Nginx config
Problems in Dockerization
# PROBLEMS
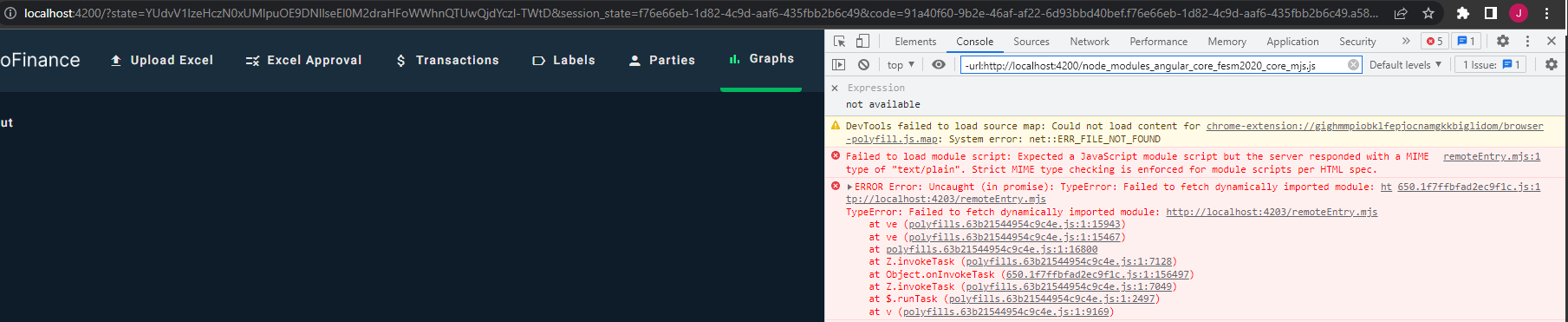
Failed to fetch module due to MIME mismatch
Solution:
# PROBLEMS
Solution:
# PROBLEMS
Adding MIME types to Nginx config file:
events{}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
types
{
text/html html htm shtml;
text/css css scss;
text/xml xml;
image/gif gif;
image/jpeg jpeg jpg;
application/javascript js mjs;
application/atom+xml atom;
application/rss+xml rss;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
}
}Source:
Module Federation
By Mitar Brankovic
Module Federation
- 211

