APCS 實作題複習
當然,我的hackmd筆記:
here!
還有因為這是複習班,所以我不會仔細的講每個細節
題目的解釋我都會用講的 (因為再用打得我就要瘋了)
自我介紹??? (好像每個簡報都要放一下)
我是112班16號的翁釩予
成電38屆 教學+網管
興趣:打code、剪輯影片、玩minecraft
discord: @mlgnotcool
C++ 基礎語法
給1~2級分的
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//你的變數
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
//你的code
}
基礎架構:
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005小技巧:
define 很好用
#define int long long
signed main(){
...
}想開long long時
基礎資料結構
int n1; //整數,可以存(大約) -1e9 ~ 1e9
long long n2; //整數,可以存(大約) -1e18 ~ 1e18
string s; //字串,注意如果題目的字串長度很長就要用 字元的陣列
char c; //字元
double d; //小數,可以不要用就不要用
int arr[200005] //陣列,可以存一串數字基礎語法:
&& //and
|| //or
//如果條件,就做這件事
if (條件){
...
}else if (條件){
...
}else{
...
}
//如果條件,就一直做這件事直到不符合條件
while (條件){
...
}for (預設; 條件; 每次做什麼){
...
}其實二級是很簡單的!
我們來寫一下題目!
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int a, b, n, num, counter;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> a >> b >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> num;
if (num%(a+b) >= a) counter += b-(num%(a+b)-a);
}
cout << counter << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 1005
using namespace std;
int n, ans, cou, b[105];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n; b[0]=inf;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> b[i];
if (b[i] < b[i-1]){
cou++;
ans = max(ans, cou);
}else cou = 1;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int x, n, l, r, sf, minl = 100, minr = -100;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> x >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int a; cin >> a;
if (x > a) ++l;
else ++r;
minl = min(minl, a);
minr = max(minr, a);
}
cout << max(l, r) << " ";
if (l>r) cout << minl << endl;
else cout << minr << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 15
using namespace std;
int n, w1, w2, h1, h2, sum[maxn], dh[maxn], maxsum;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
cin >> w1 >> w2 >> h1 >> h2;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int a; cin >> a;
sum[i] = a+sum[i-1];
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if (sum[i] <= w1*w1*h1) dh[i] = sum[i]/(w1*w1);
else if (sum[i] <= w1*w1*h1 + w2*w2*h2) dh[i] = h1 + (sum[i]-w1*w1*h1)/(w2*w2);
else dh[i] = h1+h2;
maxsum = max(maxsum, dh[i] - dh[i-1]);
}
cout << maxsum << endl;
}
STL, 二維陣列
給3級分的
STL 是什麼,可以吃嗎???
STL 是在C++裡很好用的東西 (我相信你們可以自己看的)
通常在一二題會用到的有:
struct, vector, pair, set, stack, queue
而在後面比較會用到的有:
map, priority_queue, bitset, unordered_set, unordered_map
int m[105][105];通常來說
第二題考的都會是二維陣列
二維陣列要注意的:
不能超出邊界!
不能超出邊界!
不能超出邊界!
記得要檢查有沒有超出邊界!!!
二維陣列移動的方法:
int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k){
nxtx = x+dx[k]; nxty = y+dy[k];
}1. dx, dy:
如果往哪個方向都一樣的話,就可以用dx, dy陣列
2. 每個方向去討論:
如果每個方向都有特別的條件的話,就要一個一個去討論
int f = 0;
...
if (f==0){
...
}else if (f==1){
...
}else if (f==2){
...
}else if (f==3){
...
}二維陣列的重點:
要有耐心,完全看懂題目,小心答題,
並且好好的debug和抓edge case
如果你有耐心,其實三級是很簡單的!
我們來寫一下題目!
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int m, n, k, r, c, diamond, score, a[101][101], facing=1; bool turning=true;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n >> k >> r >> c;
for (int i=0; i<m; ++i) for (int j=0; j<n; ++j) cin >> a[i][j];
while (a[r][c] != 0){
if(facing == 1){
if ((score+a[r][c]) % k == 0 && turning){facing ++; turning = false;}
else{
if (c+1 >= n || a[r][c+1] == -1) facing ++;
else{
turning = true;
score += a[r][c];
++diamond;
--a[r][c];
++c;
}
}
}else if(facing == 2){
if ((score+a[r][c]) % k == 0 && turning){facing ++; turning = false;}
else{
if (r+1 >= m || a[r+1][c] == -1) facing ++;
else{
turning = true;
score += a[r][c];
++diamond;
--a[r][c];
++r;
}
}
}else if(facing == 3){
if ((score+a[r][c]) % k == 0 && turning){facing ++; turning = false;}
else{
if (c-1 < 0 || a[r][c-1] == -1) facing ++;
else{
turning = true;
score += a[r][c];
++diamond;
--a[r][c];
--c;
}
}
}else if(facing == 4){
if ((score+a[r][c]) % k == 0 && turning){facing ++; turning = false;}
else{
if (r-1 < 0|| a[r-1][c] == -1) facing ++;
else{
turning = true;
score += a[r][c];
++diamond;
--a[r][c];
--r;
}
}
}
if (facing > 4) facing = 1;
}
cout << diamond << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 25
using namespace std;
int h, w, n, a[maxn][maxn];
int r, c, t, x;
int main() {
cin >> h >> w >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> r >> c >> t >> x;
++r; ++c;
for (int j = 1; j<=h; j++) {
for (int l = 1; l<=w; l++) {
if (abs(j-r) + abs(l-c) <= t) a[j][l] += x;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i<=h; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j<=w; j++) {
if (j==w) cout << a[i][j] << endl;
else cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int m, n, k, x, y; string nest[22]; int steps[101]; set<char> cou;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n >> k; x=m;
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i) cin >> nest[i];
for (int i=1; i<=k; ++i) cin >> steps[i];
for (int j=1; j<=k; ++j){
int itr = steps[j];
if (itr == 0){
if (x-1 >= 1){
cout << nest[x-1][y];
cou.insert(nest[x-1][y]);
--x;
}else {cout << nest[x][y]; cou.insert(nest[x][y]);}
}else if (itr == 1){
if (y+1 <= n-1){
cout << nest[x][y+1];
cou.insert(nest[x][y+1]);
++y;
}else {cout << nest[x][y]; cou.insert(nest[x][y]);}
}else if (itr == 2){
if (x+1 <= m && y+1 <= n-1){
cout << nest[x+1][y+1];
cou.insert(nest[x+1][y+1]);
++x; ++y;
}else {cout << nest[x][y]; cou.insert(nest[x][y]);}
}else if (itr == 3){
if (x+1 <= m){
cout << nest[x+1][y];
cou.insert(nest[x+1][y]);
++x;
}else {cout << nest[x][y]; cou.insert(nest[x][y]);}
}else if (itr == 4){
if (y-1 >= 0){
cout << nest[x][y-1];
cou.insert(nest[x][y-1]);
--y;
}else {cout << nest[x][y]; cou.insert(nest[x][y]);}
}else{
if (x-1 >= 1 && y-1 >= 0){
cout << nest[x-1][y-1];
cou.insert(nest[x-1][y-1]);
--x; --y;
}else {cout << nest[x][y]; cou.insert(nest[x][y]);}
}
}
cout << endl;
cout << cou.size() << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 45
using namespace std;
int n, m, a[maxn][maxn], cnt; bool del[maxn][maxn], clean;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >>n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j) cin >> a[i][j];
}
while (!clean){
clean = 1;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
if (del[i][j]) continue;
for (int k=i+1; k<=n; ++k){
if (a[k][j] == a[i][j]){
del[i][j] = 1;
del[k][j] = 1;
cnt += a[i][j];
clean = 0;
}
if (!del[k][j]) break;
}
for (int k=i-1; k>=1; --k){
if (a[k][j] == a[i][j]){
del[i][j] = 1;
del[k][j] = 1;
cnt += a[i][j];
clean = 0;
}
if (!del[k][j]) break;
}
for (int k=j+1; k<=m; ++k){
if (a[i][k] == a[i][j]){
del[i][j] = 1;
del[i][k] = 1;
cnt += a[i][j];
clean = 0;
}
if (!del[i][k]) break;
}
for (int k=j-1; k>=0; --k){
if (a[i][k] == a[i][j]){
del[i][j] = 1;
del[i][k] = 1;
cnt += a[i][j];
clean = 0;
}
if (!del[i][k]) break;
}
}
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 55
using namespace std;
int n, m, a[maxn][maxn]; vector<pair<int, int>> v;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j) cin >> a[i][j];
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
int cnt=0;
for (int x=1; x<=n; ++x){
for (int y=1; y<=m; ++y){
if (abs(x-i) + abs(y-j) <= a[i][j]){
cnt += a[x][y];
}
}
}
if (cnt%10 == a[i][j]) v.push_back({i-1, j-1});
}
}
cout << v.size() << endl;
for (pair<int, int> i:v){
cout << i.first << " " << i.second << endl;
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 55
using namespace std;
int r, c, n, t, cnt, emp; char ch; bool a[maxn][maxn], f;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> r >> c >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> ch >> t; f=false;
if (ch == 'A'){
if (t >= r-3) ++cnt;
else{
for (int j=c+1; j>=1; --j){
if (a[t+1][j-1] == 1 || a[t+2][j-1] == 1 || a[t+3][j-1] == 1 || a[t+4][j-1] == 1) f=true;
if (f && j>c){f=false; break;}
if (f || j==1){
a[t+1][j] = 1;
a[t+2][j] = 1;
a[t+3][j] = 1;
a[t+4][j] = 1;
f=true;
break;
}
}
}
}else if (ch == 'B'){
if (t >= r) ++ cnt;
else{
for (int j=c+1; j>=1; --j){
if (a[t+1][j-1] == 1) f=true;
if (f && j>c-2){f=false; break;}
if (f || j==1){
a[t+1][j] = 1;
a[t+1][j+1] = 1;
a[t+1][j+2] = 1;
f=true;
break;
}
}
}
}else if (ch == 'C'){
if (t >= r-1) ++ cnt;
else{
for (int j=c+1; j>=1; --j){
if (a[t+1][j-1] == 1 || a[t+2][j-1] == 1) f=true;
if (f && j>c-1){f=false; break;}
if (f || j==1){
a[t+1][j] = 1;
a[t+2][j] = 1;
a[t+1][j+1] = 1;
a[t+2][j+1] = 1;
f=true;
break;
}
}
}
}else if (ch == 'D'){
if (t >= r-1) ++ cnt;
else{
for (int j=c+1; j>=1; --j){
if (a[t+1][j+1] == 1 || a[t+2][j-1] == 1) f=true;
if (f && j>c-2){f=false; break;}
if (f || j==1){
a[t+1][j+2] = 1;
a[t+2][j] = 1;
a[t+2][j+1] = 1;
a[t+2][j+2] = 1;
f=true;
break;
}
}
}
}else if (ch == 'E'){
if (t >= r-2) ++cnt;
else{
for (int j=c+1; j>=1; --j){
if (a[t+1][j] == 1 || a[t+2][j-1] == 1 || a[t+3][j-1] == 1) f=true;
if (f && j>c-1){f=false; break;}
if (f || j==1){
a[t+2][j] = 1;
a[t+3][j] = 1;
a[t+1][j+1] = 1;
a[t+2][j+1] = 1;
a[t+3][j+1] = 1;
f=true;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!f) ++cnt;
}
for (int i=1; i<=r; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=c; ++j){
if (a[i][j] == 0) ++emp;
}
}
cout << emp << " " << cnt << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
string s; int n, op;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> s >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> op;
if (op==0){
for (int j=0; j<s.size(); j+=2) swap(s[j], s[j+1]);
}else if (op==1){
for (int j=0; j<s.size(); j+=2){
if (s[j] > s[j+1]) swap(s[j], s[j+1]);
}
}else{
string temp="";
for (int l=0, r=s.size()/2; r<s.size(); ++l, ++r){temp += s[l]; temp += s[r];}
s = temp;
}
}
cout << s << endl;
}
三級分以上的重點
演算法
第三和第四題都會是演算法,
並且還會把好幾個演算法塞在一題內,
因此接下來的章節會用演算法來分
以下會是一些要注意的東西:
1. 把全部的STL都學會
看文案
一定會用到的有:
struct, vector, pair, set, stack, queue, map, priority_queue, unordered_set, unordered_map
2. 學會如何計算時間複雜度:
這樣不但可以看你的方法會不會TLE,
甚至有時候可以猜出題目要考的演算法。
舉例來說:
n<=10,可以猜我們是把所有可能爆出來 O(n!)解
n<=20,可以猜我們是要用遞迴或回朔法 O(2^n) 解
n<=100~500,可以猜我們是三層迴圈 O(n^3)解
n<=5000,可以猜我們會是 O(n^2)解
** n<= 100000~1000000,可以猜我們是 O(n logn)解,
同時也可以猜我們會用到sort,或是二分搜
n更大,通常會是O(n)解
3. 多做題目!
看到題目時就不太會緊張,
還比較容易想到怎麼做
前綴和,差分
前綴和:
num為原本的數字
設一個新的陣列為pre,pre[i] = num[1] + num[2] + … + num[i]
若要找num[l] + … + num[r]的值
就會 = pre[r] - pre[l-1]
*提供區間查值,不能更改
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll n, num, nums[maxn]; int k;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> num;
nums[i] = nums[i-1] + num;
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if (i==n) cout << nums[i] << endl;
else cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 300005
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, num[maxn], sub[maxn], total, ans;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> num[i];
total += num[i];
sub[i] = sub[i-1] + num[i];
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
ans += num[i] * (total-sub[i]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 505
using namespace std;
int n, m, sum[maxn][maxn], a, b, c, d;
//sum[i][j] 會是(1, 1)到(i, j)的數字加起來
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
while (cin >> n >> m){
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=n; ++j){
cin >> a;
sum[i][j] = sum[i-1][j] + sum[i][j-1] - sum[i-1][j-1] + a;
}
}
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
cout << sum[c][d] - sum[c][b-1] - sum[a-1][d] + sum[a-1][b-1] << endl;
}
}
}
差分:
sub[i] = num[i] - num[i-1],而num就會是sub的前綴和
如果要區間[l, r]加值x,我們只要將sub[l]+=x, sub[r+1]-=x;
如果要單點查值,就1加到要查的值
*區間更改,單點查值
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll n, num[maxn], sub[maxn]; int k;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> num[i];
sub[i] = num[i] - num[i-1];
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if (i==n) cout << sub[i] << endl;
else cout << sub[i] << " ";
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int n, cnt, ans; vector<pair<int, int>> p;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
p.push_back({a, 1});
p.push_back({b, -1});
}
sort(p.begin(), p.end());
for (pair<int, int> i:p){
cnt += i.second;
ans = max(ans, cnt);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int n, cnt, prevx, l; vector<pair<int, int>> v;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
v.push_back({a, 1});
v.push_back({b, -1});
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i=0; i<v.size(); ++i){
if (l==0) prevx = v[i].first;
l += v[i].second;
if (l==0) cnt += v[i].first - prevx;
}
cout << cnt <<endl;
}
二分搜
有兩種主要的考法:
用lower_bound, upper_bound找最接近的值
要用二分搜找出某一個東西的最小可能值
C++中有一個好東西叫lower_bound和upper_bound
(***只能用在sort好的陣列)
lower_bound: 找到第一個 >= 的數字
upper_bound: 找到第一個 > 的數字
vector<int> v;
int a[maxn]; //1~n
...
lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), k) - v.begin(); //回傳第一個在v裡>=k的數字的index
upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), k) - v.begin(); //回傳第一個在v裡>k的數字的index
lower_bound(a+1, a+1+n, k) - a; //回傳第一個在a裡>=k的數字的index
upper_bound(a+1, a+1+n, k) - a; //回傳第一個在a裡>k的數字的index# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005
using namespace std;
int n, m, p, sum[maxn], curidx;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int a; cin >> a;
sum[i] = sum[i-1] + a;
}
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
cin >> p;
if (sum[curidx] + p > sum[n]){
curidx = lower_bound(sum+1, sum+n+1, p-(sum[n]-sum[curidx])) - sum;
}else{
curidx = lower_bound(sum+1, sum+n+1, sum[curidx]+p) - sum;
}
}
cout << curidx%n << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 30005
using namespace std;
int n, curx, cury, f, cnt;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> x, y;
unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, int>> mp;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n; f = 1; curx=0; cury=0;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;
swap(a, b);
mp[a][b] = c;
x[b].push_back(a);
y[a].push_back(b);
}
for (auto i=x.begin(); i!=x.end(); ++i) sort(i->second.begin(), i->second.end());
for (auto i=y.begin(); i!=y.end(); ++i) sort(i->second.begin(), i->second.end());
while (true){
if (f==0){
if (x[cury].empty()) break;
int it = upper_bound(x[cury].begin(), x[cury].end(), curx) - x[cury].begin();
if (it>=x[cury].size()) break;
else{
curx = x[cury][it];
if (mp[curx][cury] == 0) f = 1;
else f = 3;
}
}else if (f==1){
if (y[curx].empty()) break;
int it = upper_bound(y[curx].begin(), y[curx].end(), cury) - y[curx].begin();
if (it>=y[curx].size()) break;
else{
cury = y[curx][it];
if (mp[curx][cury] == 0) f = 0;
else f = 2;
}
}else if (f==2){
if (x[cury].empty()) break;
int it = lower_bound(x[cury].begin(), x[cury].end(), curx) - x[cury].begin() - 1;
if (it<0) break;
else{
curx = x[cury][it];
if (mp[curx][cury] == 0) f = 3;
else f = 1;
}
}else if (f==3){
if (y[curx].empty()) break;
int it = lower_bound(y[curx].begin(), y[curx].end(), cury) - y[curx].begin() - 1;
if (it<0) break;
else{
cury = y[curx][it];
if (mp[curx][cury] == 0) f = 2;
else f = 0;
}
}
++cnt;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
假設題目要你k的最小值,並且k從0到最大值有單調性
(eg. 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1),就可以用二分搜找答案
while (l < r){
mid = (l+r)/2;
if (nums[mid] > a) r = mid;
else l = mid+1;
}
return r;在這裡介紹的方法(最常用的),是左閉右開:
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 50005
using namespace std;
int n, k, nums[maxn], l=1, r, m, d;
int check_diameter(int r){
int x=1, curidx=nums[1];
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if (curidx+r < nums[i]){
++x;
curidx = nums[i];
}
}
return x;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> nums[i];
r = max(r, nums[i]);
}
sort(nums+1, nums+1+n);
while (l < r){
m=(l+r)/2;
d=check_diameter(m);
if (d <= k) r = m;
else if (d > k) l = m+1;
}
cout << r << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 305
using namespace std;
struct coord{
int x, y, d, dep;
};
int n, a[maxn][maxn], l, r, ans, dist, finald; queue<coord> q; bool vis[maxn][maxn];
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=n; ++j) cin >> a[i][j];
}
l=0, r=1000000;
while (l < r){
while (!q.empty()) q.pop();
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=n; ++j) vis[i][j] = 0;
}
q.push({1, 1, 0, 0});
int m=(l+r)/2; ans=-1, dist=-1;
while (!q.empty()){
if (q.front().x == n && q.front().y == n){
ans = q.front().d; dist=q.front().dep;
break;
}
int x=q.front().x, y=q.front().y, d=q.front().d, dep=q.front().dep; q.pop();
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k){
int nxtx = x+dx[k], nxty = y+dy[k];
if (nxtx < 1 || nxtx > n || nxty < 1 || nxty > n) continue;
if (!vis[nxtx][nxty] && abs(a[x][y]-a[nxtx][nxty]) <= m){
vis[nxtx][nxty] = 1;
q.push({nxtx, nxty, max(d, abs(a[x][y]-a[nxtx][nxty])), dep+1});
}
}
}
if (ans == -1){
l = m+1;
}else r = m;
if (dist != -1) finald = dist;
}
cout << r << endl << finald << endl;
}
遞迴
如果有認真上數學課的話,因該就知道遞迴是什麼了,
而在C++裡就是在函式裡面再叫另一個函式,一直遞迴下去
小注意:遞迴的數量是有上限的,如果你覺得太多
有可能被爆掉,有可能就要換另一種方法
(ex: dfs -> bfs)
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn
using namespace std;
int curi, cnt; string s;
int calc(string s){
int tmp = 0;
if (s=="f"){
cin >> s; tmp = 2*calc(s) - 3;
return tmp;
}else if (s=="g"){
cin >> s; tmp += 2*calc(s);
cin >> s; tmp += calc(s) - 7;
return tmp;
}else if (s=="h"){
cin >> s; tmp += 3*calc(s);
cin >> s; tmp -= 2*calc(s);
cin >> s; tmp += calc(s);
return tmp;
}else return stoi(s);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> s;
cout << calc(s) << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 50
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int n, depth=1; ll cnt;
void dfs(int x){
int num;
for (int i=1; i<=2 + (x%2); ++i){
cin >> num;
if (num != 0){
cnt += abs(x-num);
dfs(num);
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
dfs(n);
cout << cnt << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 2000005
#define maxm 10005
#define int long long
using namespace std;
struct t{
int l, r;
};
int n, m, w[maxn], op[maxm], curnode; t v[maxn];
void dfs(int x, int k){
if (x >= n){
w[x] += k;
curnode = x;
return;
}
if (w[v[x].l] <= w[v[x].r]) dfs(v[x].l, k);
else if (w[v[x].l] > w[v[x].r]) dfs(v[x].r, k);
w[x] += k;
return;
}
void build(int x){
if (w[v[x].l] == -1) build(v[x].l);
if (w[v[x].r] == -1) build(v[x].r);
w[x] = w[v[x].l] + w[v[x].r];
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=2*n-1; ++i) w[i] = -1;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> w[i+n-1];
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i) cin >> op[i];
for (int i=1; i<=n-1; ++i){
int a; cin >> a;
cin >> v[a].l >> v[a].r;
}
build(1);
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
dfs(1, op[i]);
if (i==m) cout << curnode << endl;
else cout << curnode << " ";
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
string k, s, tmp; int n; set<string> st; bool f;
void dfs(string a, int d){
if (f) return;
if (d==n){
if (st.find(a) == st.end()){
cout << a << endl;
f = true;
}
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<k.size(); ++i){
if (f) return;
dfs(a+k[i], d+1);
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> k >> n >> s;
for (int i=0; i<s.size(); ++i){
tmp = "";
for (int j=i; j<=i+n-1; ++j) tmp += s[j];
st.insert(tmp);
}
dfs("", 0);
}
滑動窗口
在APCS是很少見的 (只是上次有考到所以我還是放在這)
總而言之,就是想像一個區間的窗口在陣列移動,
找一個區間的某的值。
目標是用前一區間的值來算出這一區間的值,
比每次都重新找還快。
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005
using namespace std;
int m, n, cnt, finalcnt; string p[maxn];
unordered_map<string, int> mp;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> p[i];
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
mp[p[i]]++;
if (mp[p[i]] == 1) ++cnt;
}
if (cnt==m) ++finalcnt;
for (int i=m+1; i<=n; ++i){
mp[p[i-m]]--;
if (mp[p[i-m]] == 0) --cnt;
mp[p[i]]++;
if (mp[p[i]] == 1) ++cnt;
if (cnt==m) ++finalcnt;
}
cout << finalcnt << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005
#define inf 1e18
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, k, nums[maxn], place[maxn], prevp, dp[maxn], mincount;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> nums[i];
sort(nums+1, nums+1+n);
prevp=nums[1 + ((k-1)/2)]; place[1] = 0;
for (int i=1; i<=k; ++i) place[1] += abs(nums[i] - prevp);
for (int i=2; i<=n-k+1; ++i){
int mp=nums[i + ((k-1)/2)];
//用數學去算
if (k%2 == 0){
place[i] = place[i-1] + nums[i-1] + nums[i+k-1] - 2*mp;
}else{
place[i] = place[i-1] + nums[i-1] + nums[i+k-1] - prevp - mp;
}
prevp = mp;
}
dp[1] = place[1]; mincount = inf;
for (int i=2; i<=n-k+1; ++i){
dp[i] = min(dp[i-1], place[i]);
if (i>k) mincount = min(mincount, dp[i-k] + place[i]);
}
cout << mincount << endl;
}
貪心 greedy
greedy比較不像是演算法,但也是很重要的考點。
總而言之,就是我們用一種特定的方法去取東西,而不是把全部的可能爆出來,並且可以證明這樣的取法是最佳的方法。
舉簡單例子來說:
如果我們有1, 5, 10, 50元
且我們要花最少硬幣數退錢給客人,
則我們會greedy先取目前可以取的最大
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int n, m, l, r, w, t[maxn], sub[maxn], val[maxn]; ll cnt;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
cin >> l >> r >> w;
sub[l] += w;
sub[r+1] -= w;
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> t[i];
val[i] = val[i-1] + sub[i];
}
sort(val+1, val+n+1, greater<int>());
sort(t+1, t+n+1);
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cnt += t[i]*val[i];
cout << cnt << endl;
}
APCS 20171004
遇到這種要特定排序的greedy,就把他的comp函式比較寫出來,比較先選a和先選b的差別(甚至有些會被消掉),最後再做比較
假設我們目前在比較A, B哪個要排上和下,且他們上放的重量是W
A在上:
B在上:
假設我們目前在比較A, B哪個要排上和下,且他們上放的重量是W
並且可以發現可以消掉一些東西,最後要比較的就只剩這兩個:
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 200005
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, curw, cnt; pair<int, int> p[maxn];
bool comp(pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b){
return a.first*b.second < a.second*b.first;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> p[i].first;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> p[i].second;
sort(p+1, p+n+1, comp);
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cnt += curw * p[i].second;
curw += p[i].first;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
AP325 P-4-4
算比較經典的greedy題,重點就是要把結束最早的排在前面,因此這樣後面才比較有機會放更多活動
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 100005
using namespace std;
int n, counter, curtime; pair<int, int> times[maxn];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> times[i].second >> times[i].first;
sort(times+1, times+1+n);
curtime = -1;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if (curtime < times[i].second){
++counter;
curtime = times[i].first;
}
}
cout << counter << endl;
}
APCS 20230104
和上一題類似,甚至前40%都和上一題一樣
只是我們要都考慮一個greedy,就是我們這個活動要用的機器 (如果有的化)
就會是一台機器目前活動結束時間 小於且最靠近 現在考慮的活動開始時間
然後我們就可以發現:
我們可以用multiset來存機器的活動結束時間,
並且用二分搜來找到要使用的機器
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 100005
using namespace std;
int n, k, cnt; pair<int, int> p[maxn];
multiset<int> w;
bool comp(pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b){
if (a.second != b.second) return a.second < b.second;
else return a.first < b.first;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> p[i].first;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> p[i].second;
sort(p+1, p+1+n, comp);
for (int i=1; i<=k; ++i) w.insert(-1);
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
auto it = w.lower_bound(p[i].first);
if (it == w.begin()) continue;
--it;
++cnt;
w.insert(p[i].second);
w.erase(it);
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
單調隊列
直接帶題目:
AP325 P-3-4
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int n; long long counter; stack<pair<int, int>> p;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
p.push({INT_MAX, 0});
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int h; cin >> h;
while (h >= p.top().first){
p.pop();
}
counter += i-p.top().second;
p.push({h, i});
}
cout << counter << endl;
}
若大於等於stack上方的數字則去掉
並可以保證pop的數字都比那一個數字小
新的數字若大於上個數字,則可保證上次pop的數字都比新的還小
若比較小或等於,則pop掉舊的數字,且上次pop的數字也都比較小(也是跳過)
廣度優先搜尋 bfs
可以把它想像成一層一層去做,目前在的點會是目前距離可以抵達得地方
因此提到最短距離時就要想到BFS
舉例來說:
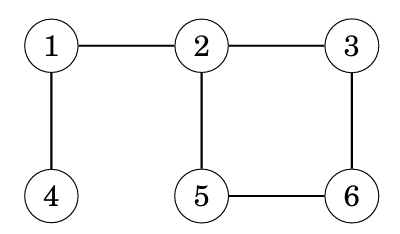
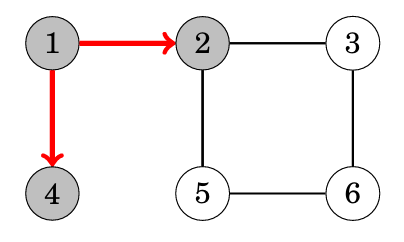
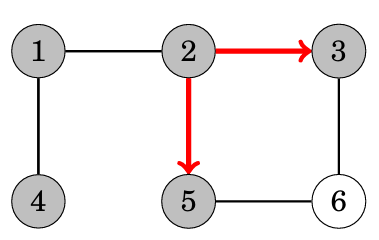
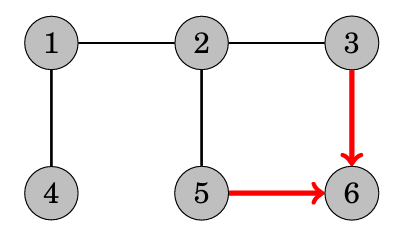
我們要使用queue來實作,用queue存放目前可以抵達的點,並且每次把queue最前面點的鄰近點丟回queue裡,
這樣就可以達到一層一層做的效果
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 805
using namespace std;
int n, m, n1, n2; bool found, vis[maxn];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
while(cin >> n >> m){
found=false; queue<int> q; vector<int> v[maxn];
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) vis[i] = 0;
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
v[a].push_back(b);
}
cin >> n1 >> n2; q.push(n1); vis[n1] = 1;
while (!q.empty()){
int x=q.front(); q.pop();
for (int i:v[x]){
if (vis[i] == 1) continue;
if (i == n2){
found=true;
break;
}
vis[i] = 1;
q.push(i);
}
if (found) break;
}
if (found) cout << "Yes!!!" << endl;
else cout << "No!!!" << endl;
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 105
using namespace std;
struct coord{
int x, y, dist;
};
int n, a[maxn][maxn]; queue<coord> q; bool vis[maxn][maxn], f;
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
string s; cin >> s;
for (int j=0; j<n; ++j){
if (s[j] == '.') a[i][j+1] = 1;
else a[i][j+1] = 0;
}
}
q.push({2, 2, 1}); vis[2][2] = 1;
while (!q.empty()){
int x = q.front().x, y = q.front().y, d = q.front().dist; q.pop();
if (x==n-1 && y==n-1){
cout << d << endl;
f=true; break;
}
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k){
if (!vis[x+dx[k]][y+dy[k]] && a[x+dx[k]][y+dy[k]]){
q.push({x+dx[k], y+dy[k], d+1});
vis[x+dx[k]][y+dy[k]] = 1;
}
}
}
if (!f) cout << "No solution!" << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 100005
using namespace std;
struct node{
int v, d, val;
};
int p, q, r, m, in[maxn], gate[maxn], out[maxn], cnt, st[maxn]; vector<int> v[maxn];
queue<node> qu;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> p >> q >> r >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=p; ++i){
cin >> in[i];
qu.push({i, 0, in[i]});
}
for (int i=1; i<=q; ++i){
cin >> gate[i];
st[i] = -1;
}
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
v[a].push_back(b);
}
while (!qu.empty()){
int x=qu.front().v, d=qu.front().d, val=qu.front().val; qu.pop();
for (int i:v[x]){
if (i>p && i<=p+q){ //gate
if (gate[i-p] == 1){
if (st[i-p] == -1) st[i-p] = val;
else qu.push({i, d+1, val&st[i-p]});
}else if (gate[i-p] == 2){
if (st[i-p] == -1) st[i-p] = val;
else qu.push({i, d+1, val|st[i-p]});
}else if (gate[i-p] == 3){
if (st[i-p] == -1) st[i-p] = val;
else qu.push({i, d+1, val^st[i-p]});
}else{
qu.push({i, d+1, !val});
}
}else if (i > p+q){ //output
out[i-p-q] = val;
cnt = max(cnt, d);
}
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
for (int i=1; i<=r; ++i){
if (i==r) cout << out[i] << endl;
else cout << out[i] << " ";
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 505
using namespace std;
struct coord{
char v;
bool n, s, e, w;
};
int n, m, cnt, maxcnt; coord a[maxn][maxn]; bool vis[maxn][maxn]; queue<pair<int, int>> q;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
cin >> a[i][j].v;
if (a[i][j].v == 'X'){a[i][j].n=1; a[i][j].s=1; a[i][j].w=1; a[i][j].e=1;}
else if (a[i][j].v == 'I'){a[i][j].n=1; a[i][j].s=1;}
else if (a[i][j].v == 'H'){a[i][j].e=1; a[i][j].w=1;}
else if (a[i][j].v == 'L'){a[i][j].n=1; a[i][j].e=1;}
else if (a[i][j].v == '7'){a[i][j].w=1; a[i][j].s=1;}
else if (a[i][j].v == 'F'){a[i][j].e=1; a[i][j].s=1;}
else if (a[i][j].v == 'J'){a[i][j].n=1; a[i][j].w=1;}
}
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
if (a[i][j].v != '0' && !vis[i][j]){
cnt = 0; vis[i][j] = 1;
q.push({i, j});
while (!q.empty()){
++cnt;
int x = q.front().first, y = q.front().second; q.pop();
if (x+1 <= n && a[x][y].s && a[x+1][y].n && !vis[x+1][y]){
vis[x+1][y] = 1;
q.push({x+1, y});
}
if (x-1 >= 1 && a[x][y].n && a[x-1][y].s && !vis[x-1][y]){
vis[x-1][y] = 1;
q.push({x-1, y});
}
if (y+1 <= m && a[x][y].e && a[x][y+1].w && !vis[x][y+1]){
vis[x][y+1] = 1;
q.push({x, y+1});
}
if (y-1 >= 1 && a[x][y].w && a[x][y-1].e && !vis[x][y-1]){
vis[x][y-1] = 1;
q.push({x, y-1});
}
}
maxcnt = max(maxcnt, cnt);
}
}
}
cout << maxcnt << endl;
}
深度優先搜尋 dfs
可以把它想像成一直走第一個可以走的,
比BFS好寫很多,只是會有遞迴層數的問題(如果你要用stack做DFS也可以)
舉例來說:
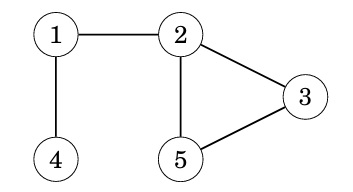
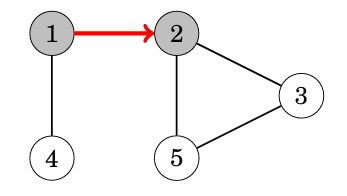
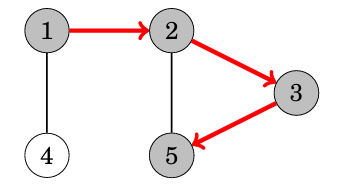
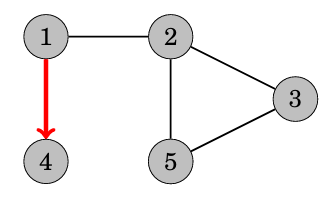
我們要使用遞迴來實作,每次就先遞迴下去可以走的
這樣就可以先走可以走的效果
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 515
#define inf 1e9
using namespace std;
int n, m, a[maxn][maxn], cnt, w, ns, s, e;
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void dfs(int x, int y){
++cnt; w=min(w, y); ns=min(ns, x); e=max(e, y); s=max(s, x);
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k){
if (a[x+dx[k]][y+dy[k]]){
a[x+dx[k]][y+dy[k]] = 0;
dfs(x+dx[k], y+dy[k]);
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j) cin >> a[i][j];
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
if (a[i][j] == 1){
cnt=0; w=inf; ns=inf; s=0; e=0; a[i][j] = 0;
dfs(i, j);
cout << w-1 << " " << ns-1 << " " << e-1 << " " << s-1 << " " << cnt << endl;
}
}
}
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 100005
#define inf 1e18
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, k, dv[maxn], root, counter; vector<int> v[maxn];
int dfs(int x, int depth){
if (v[x].size() == 0){
return depth;
}
int mdepth=0;
for (int i:v[x]){
mdepth = max(mdepth, dfs(i, depth+1));
}
counter += (mdepth-depth);
return mdepth;
}
signed main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> k;
for (int j=1; j<=k; ++j){
int a; cin >> a;
dv[a] = i;
v[i].push_back(a);
}
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if (dv[i] == 0) root = i;
}
cout << root << endl;
dfs(root, 0);
cout << counter << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 100005
#define inf 1e9
using namespace std;
int n, maxdepth, startnode;
vector<int> v[maxn];
void dfs(int x, int prenode, int depth){
if (depth > maxdepth){
maxdepth = depth;
startnode = x;
}
for(int i:v[x]){
if (i == prenode) continue;
dfs(i, x, depth+1);
}
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
v[a].push_back(b);
v[b].push_back(a);
}
dfs(0, 0, 0);
dfs(startnode, startnode, 0);
cout << maxdepth << endl;
}
動態規劃
dp
dp的精神就是把大問題拆成小問題,先解出比較小數字的答案,找出規律,並寫出我們的dp轉移式
舉例來說:
費式數列:
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 1;
for (int i=3; i<=n; ++i){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
}
我們先來講一些經典的dp問題,
再來寫一些APCS的題目:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 100005
#define inf 1e9
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int n; long long nums[maxn], dp[maxn], maxnum;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> nums[i];
dp[1] = nums[1]; maxnum = 0;
for (int i=2; i<=n; ++i){
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
maxnum = max(maxnum, dp[i]);
}
cout << maxnum << endl;
}
我們第一件事就是要定義dp:
我們開一個dp[n][m],dp[i][j]代表s1到第i項、s2到第j項 目前的LCS
第二件事就是要想轉移式:
我們先把s1[i]和s2[j]特別取出來,做比較
s1[i] == s2[j],我們就會是取這一項的數字,那dp[i][j]就會是:
s1[i] != s2[j],我們就會是s1[i]或s2[j]取一個,dp[i][j]就會是:
2. LCS
最後的程式:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 105
using namespace std;
int n, m, dp[maxn][maxn], n1[maxn], n2[maxn], counter;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
while (cin >> n >> m){
++counter;
if (n==0 && m==0) break;
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) cin >> n1[i];
for (int i=0; i<m; ++i) cin >> n2[i];
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
if (n1[i-1] == n2[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}else{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
cout << "Twin Towers #" << counter << endl;
cout << "Number of Tiles : " << dp[n][m] << endl;
}
}
2. LCS
dp會是一個vector,紀錄目前暫時的LIS
*記得我們這個dp裡的不是實際的LIS,只是拿來算的
3. LIS
並且在有一個position的陣列,
position[i] 紀錄我們剛剛把數字i 塞在哪個index裡。
我們在跑過每個數字時,我們會把這個數字放在最適合的位置,讓後面更有機會成為LIS,就會是第一個 >= 這個的數字的那一項 (用lower_bound找),並且用vector紀錄。
最後將position的陣列從尾找到頭,假設LIS長度是l
並且找到 第一個=l 的第i項,第一個=l-1 的第i項,...,第一個=1 的第i項
最後在把全部第i項的數字反過來輸出就是LIS了
最後的程式:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 500000
using namespace std;
int n, lis;
vector<int> nums, dp, position; stack<int> temp;
int main(){
while (cin >> n) nums.push_back(n);
dp.push_back(nums[0]);
position.push_back(1);
for (int i=1; i<nums.size(); ++i){
if (nums[i] <= dp.back()){
int idx = lower_bound(dp.begin(), dp.end(), nums[i]) - dp.begin();
dp[idx] = nums[i];
position.push_back(idx+1);
}else{
dp.push_back(nums[i]);
position.push_back(dp.size());
}
}
lis = dp.size();
cout << lis << endl << "-" << endl;
for (int i=position.size()-1; i>=0; --i){
if (position[i] == lis){
temp.push(nums[i]);
--lis;
}
if (lis == 0) break;
}
while (!temp.empty()){cout << temp.top() << endl; temp.pop();}
}
3. LIS
我們第一件事就是要定義dp:
我們開一個dp[n][w],dp[i][j]會是我們討論到第n個物品,重量為j時 價值最高是多少
第二件事就是要想轉移式:
我們討論dp[i][j]拿物品或不拿物品
拿物品:
不拿物品:
4. 0-1背包
最後取max:
最後的程式:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 105
#define maxw 100005
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll n, w, dp[maxn][maxw]; pair<ll, ll> v[maxn];
//v -> 存放<n, w>
//dp[第幾個物品][總共的重量] = 價值
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> w;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> v[i].first >> v[i].second;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=0; j<=w; ++j){
if (j-v[i].first < 0) dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
else dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-v[i].first] + v[i].second);
}
}
cout << dp[n][w] << endl;
}
4. 0-1背包
小補充:背包問題通常都可以壓空間,把 O(nw) 壓到 O(w)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 105
#define maxw 100005
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll n, w, dp[maxw]; pair<ll, ll> v[maxn];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> w;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> v[i].first >> v[i].second;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=w; j>=v[i].first; --j){
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-v[i].first] + v[i].second);
}
}
cout << dp[w] << endl;
}
4. 0-1背包
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 10005
#define maxm 55
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int n, m, a[maxm][maxn], dp[maxm][maxn], dpr[maxm][maxn], dpl[maxm][maxn], maxcnt;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=n; ++j){
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=n; ++j) dpr[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dpr[i][j-1]) + a[i][j];
for (int j=n; j>=1; --j) dpl[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dpl[i][j+1]) + a[i][j];
for (int j=1; j<=n; ++j){
dp[i][j] = max(dpr[i][j], dpl[i][j]);
if (i==m) maxcnt = max(maxcnt, dp[i][j]);
}
}
cout << maxcnt << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define maxn 100005
using namespace std;
int m, s, n, nums[maxn], dp[maxn], total;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> s >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin >> nums[i];
total += nums[i];
}
s = max(0, m-s);
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=s; j>=nums[i]; --j){
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-nums[i]]+nums[i]);
}
}
cout << total-dp[s] << endl;
}
# code yaaaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define inf 1e18
#define int long long
#define maxn 1005
using namespace std;
int n, m, a[maxn], b[maxn], dp[maxn][maxn];
int curnum=-inf, maxnum=-inf;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i) cin >> b[i];
for (int i=0; i<4; ++i){
if (i>=1) reverse(a+1, a+1+n);
if (i==2) reverse(b+1, b+1+m);
curnum = -inf;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j) dp[i][j] = -inf;
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
dp[i][j] = max(a[i]*b[j], dp[i-1][j-1] + a[i]*b[j]);
curnum = max(curnum, dp[i][j]);
}
}
maxnum = max(maxnum, curnum);
}
cout << maxnum << endl;
}
考試重點
快下課了ya
考前幾個重點:
1. 記得要一直刷題目!很重要!
2. 考前一天好好睡,不要熬夜!
考試幾個重點:
1. 小心作答,不要被edge case搞
(ex: 要開long long等)
2. 題目看完後先想好整個流程再開始打,這樣比較不容易錯。
3. 比較難的題目記得爭子題分數,很重要!
最後,助每個人都考到自己想要的分數!
(我想考 5 4 lol)
下課
ya ok bye
APCS 實作題複習
By MLGnotCOOL
APCS 實作題複習
- 206



