Manuel Pichardo Marcano (UNAM-IA)
Anjali Yelikar (Vanderbilt University)
Karan Jani (Vanderbilt University)
Massive Double White Dwarf Binary Mergers from the Moon: Extending the Reach of Multi-messenger Astrophysics




See also recent work by Benetti et al. (2025)
Massive Double White Dwarf Binary Mergers from the Moon Recent Papers
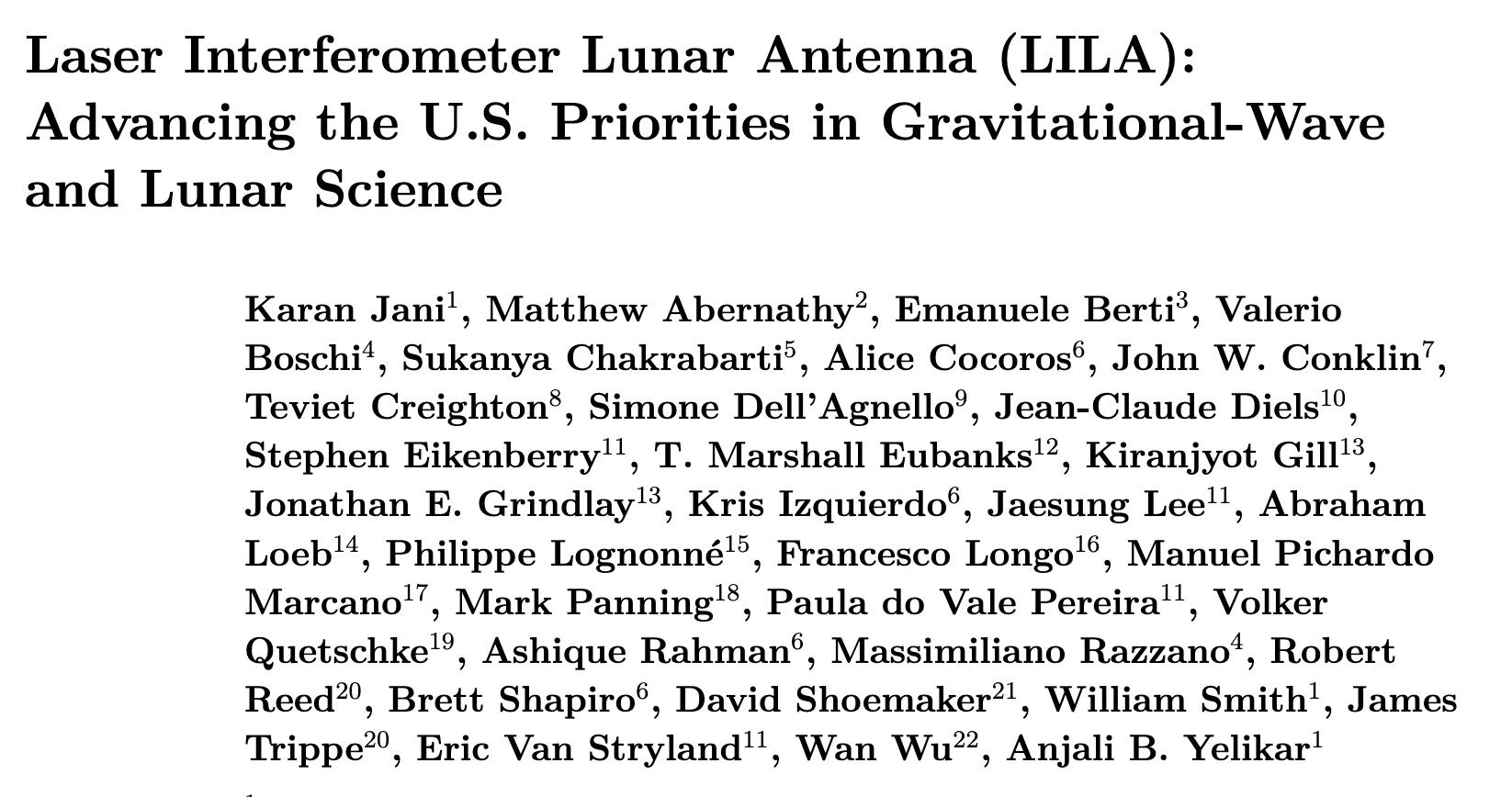
Remanentes Estelares
Estrellas Muertas
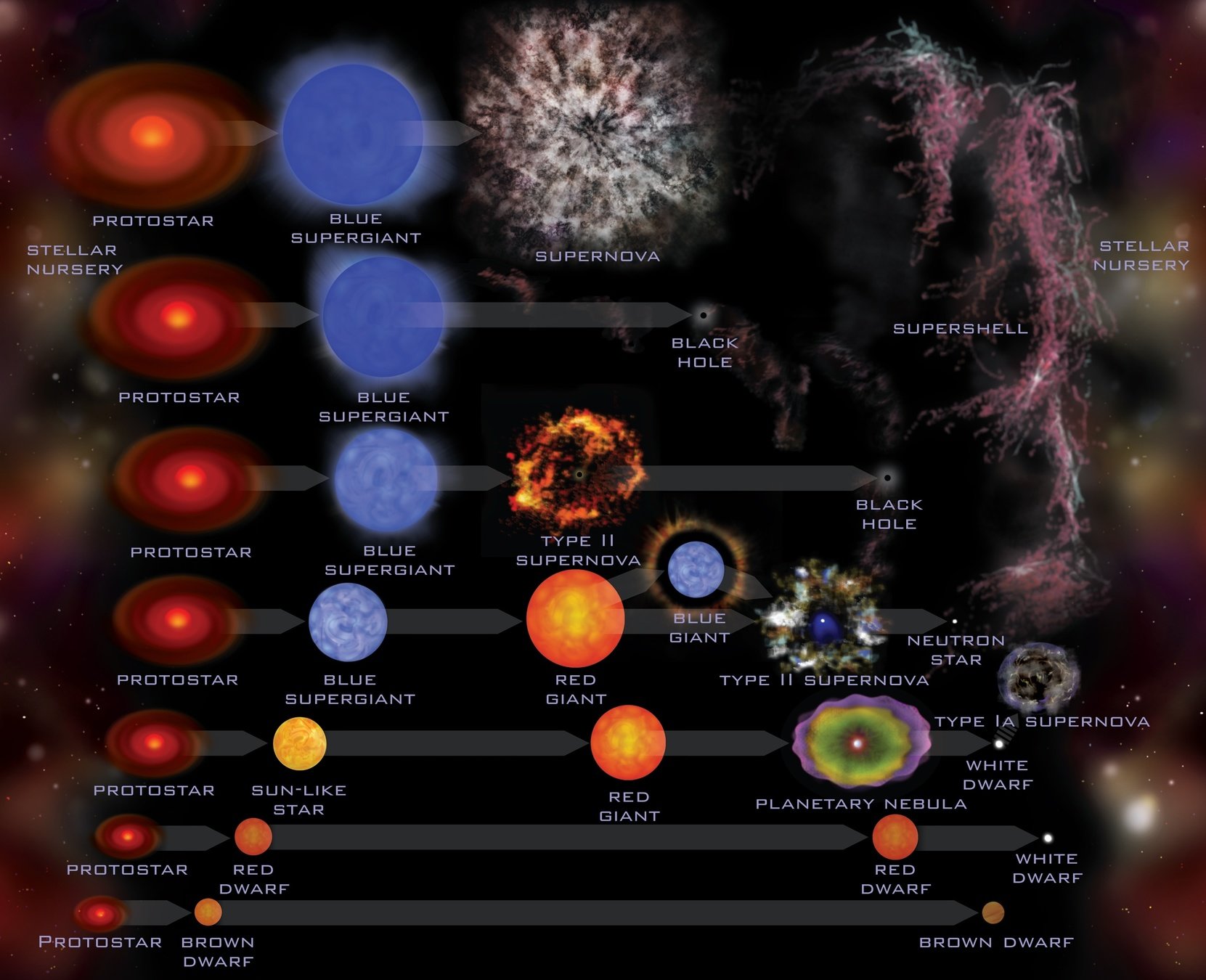
Enana Blanca
Enana Blanca
sol
sol
Tierra
Williamina Fleming:
Descubridora de las enanas blancas

Enanas Blancas

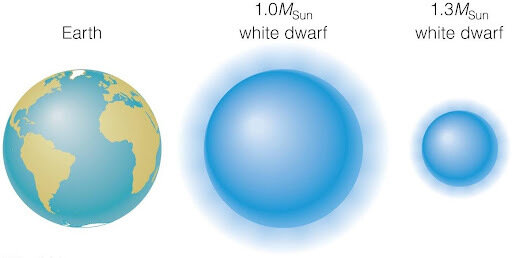
Sirius
Sirius A y Sirius B

NASA, ESA, H. Bond (STScI), and M. Barstow (University of Leicester).
Sirius A
Estrella "Normal"
Sirius B
Enana Blanca
- A 8.6 años luz
- Enana Blanca más cercana
Sirius A y Sirius B
- Período Orbital (Porb) de 50 años
-
Frequencia Orbital (1/Porb)
- 1/50 años = 10-9 Hz = 1 nHz
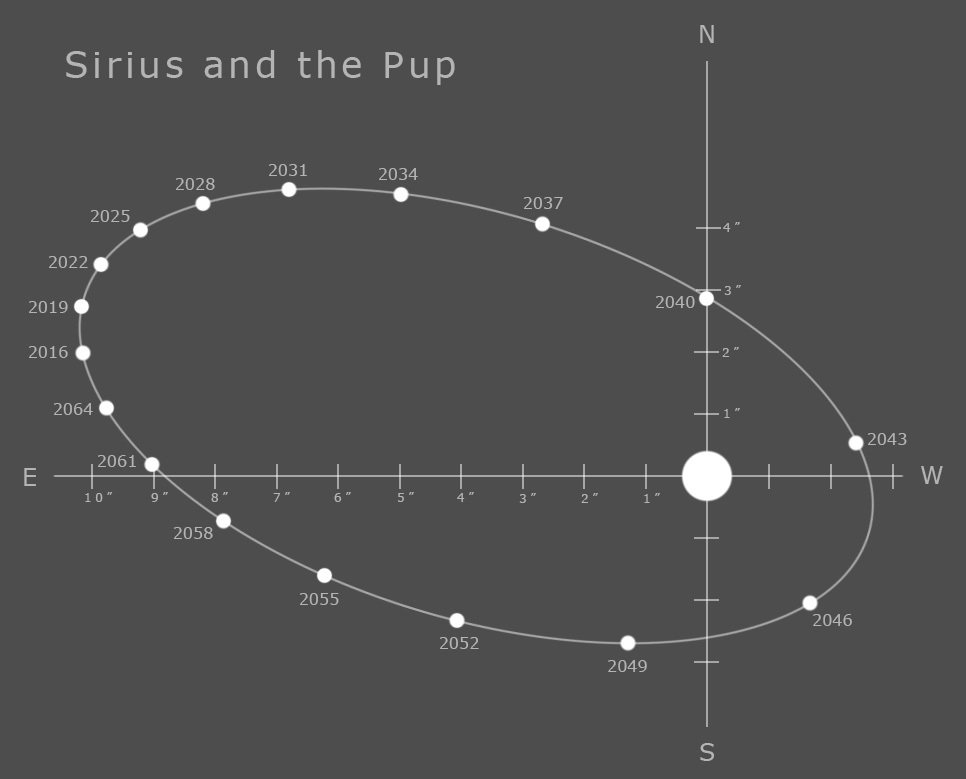
Separación 300 millones de km
El Sol a Urano (20 UA)
White Dwarfs
Caltech/NASA

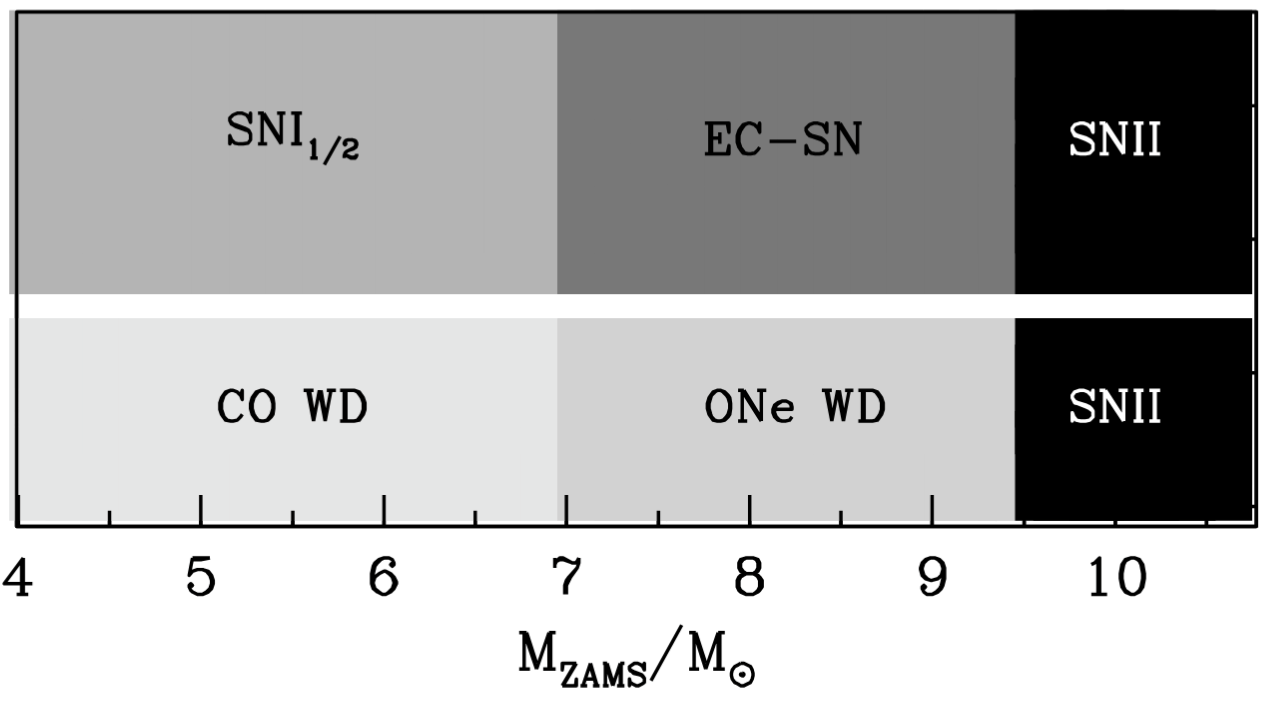
Gil-Pons+2013
Caiazzo+2021
0.3 to < 1.25 M⊙
< 1.08 to 1.4 M⊙
Type Ia SN
Accretion-induced collapse (AIC)
- Degenerate Objects:
- Maximum Mass = 1.4 M⊙
- Type Ia SN progenitors
- Neutron Stars Progenitors
~2000 km
1.33 M☉ - 1.37 M☉
Williamina Fleming:
Descubridora de las enanas blancas

Enanas Blancas

Sirius
Sirius A y Sirius B

NASA, ESA, H. Bond (STScI), and M. Barstow (University of Leicester).
Sirius A
Estrella "Normal"
Sirius B
Enana Blanca
- A 8.6 años luz
- Enana Blanca más cercana
Sirius A y Sirius B
- Período Orbital (Porb) de 50 años
-
Frequencia Orbital (1/Porb)
- 1/50 años = 10-9 Hz = 1 nHz

Separación 300 millones de km
El Sol a Urano (20 UA)
Binarias de enanas blancas

Variable Cataclísmica
Mark A. Garlick
Enana Blanca
Estrella 'normal'
- Período Orbital (Porb) de 10 horas
-
Freq. Orbital (1/Porb)
- 1/10 hr = 10-5Hz
Separación de 3 R☉
2 millones de km
Binarias de Enanas Blancas
NASA
Separación de Miles de Km
- Período Orbital (Porb) de Segundos
-
Freq. Orbital (1/Porb)
- 1/2 sec = 0.5 Hz
Ondas Gravitacionales
- Perturbaciones en el espacio-tiempo
-
Freq. Orbital (1/Porb)
- 1/2 sec = 0.5 Hz
- Freqondas grav = 2 x Freqondas grav = 1 Hz
Merging Double WD Binaries

Caltech/NASA
- Gravitational Wave Sources
- Multi-messenger sources
- Porb
- ~15 seconds to merge
- fgrav = 2 x forb
- ~0.1 Hz to 1 Hz
Type Ia Supernova
- Chandrasekhar Mass (Mch = 1.4M⊙)
- Double-degenerate vs Single degenerate channel
- Cosmological standard candles
- Hubble Tension
- Heavy-element factories


Caltech/NASA
Accretion-induced Collapse
- Formation of Neutron Stars (e.g. Nomoto et al. 1979)
- Important in GCs (Grindlay et al. 1988)
- Predicted EM:
- Gamma Rays (e.g. Dar et al. 1992)
- Radio (e.g. Piro et al. 2013)
- Optical (e.g. Sousa et al. 2023, Metzger et al. 2009)

NASA, ESA, and J. Anderson (STScI)
WD
NS
Lunar Gravitational Wave Observatories
- The Lunar Gravitational-wave Antenna (LGWA) (Parameswaran et al. 2024)
- Seismometer (Lunar-SEI)
- Laser Interferometer Lunar Antenna (LILA) (Jani et al. 2025):
- LIGO-like suspension system (Lunar-SUS)


Why go to the Moon?
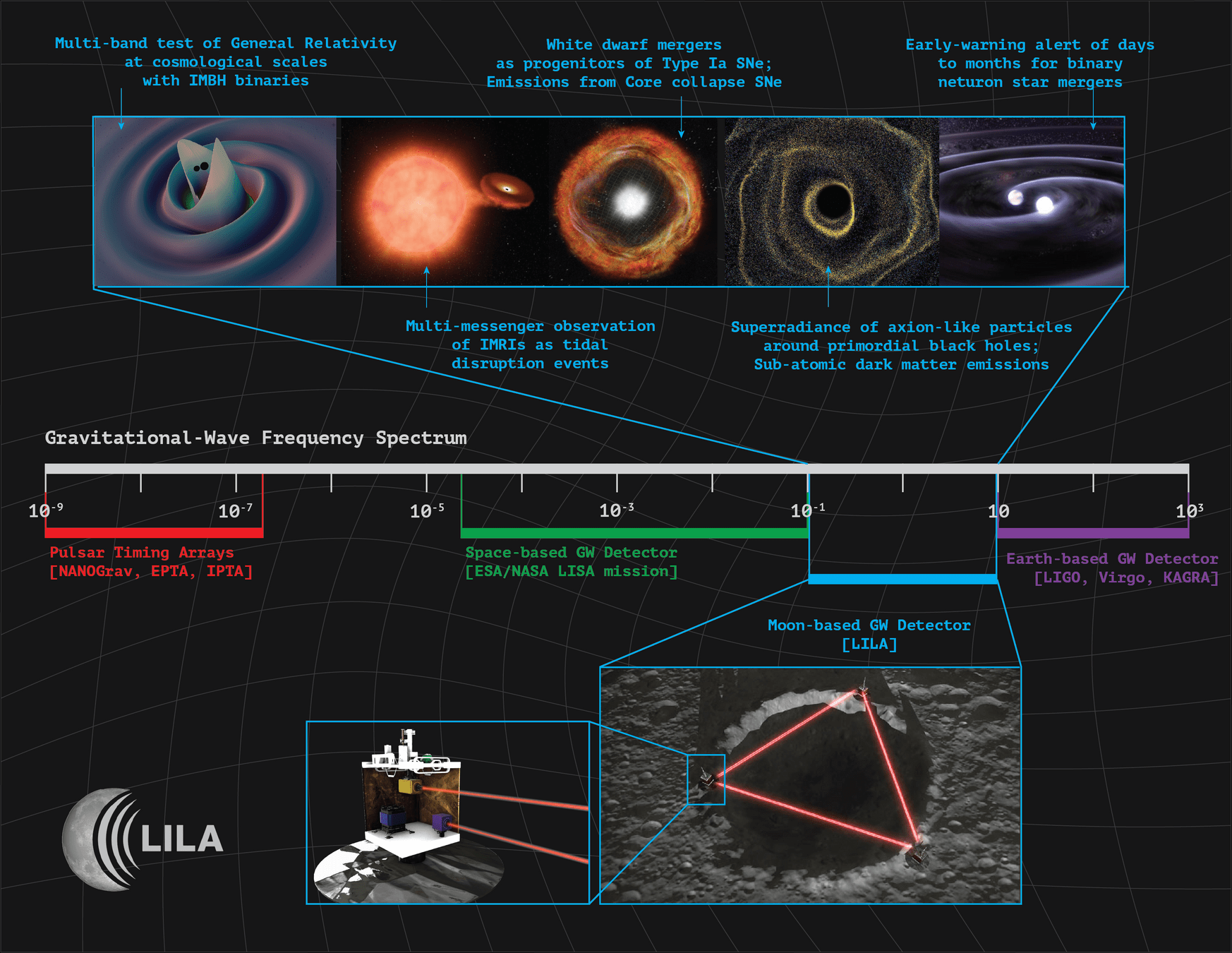
Methods

- Evolve WDs with masses 1. to 1.4 M⊙
- 1 years before merging:
- Roche-lobe: Lower Mass Fills Roche Lobe
- Contact: a = R1+R2
- Calculate SNR for LGWA and Gravitational-Wave Lunar Observatory for Cosmology (GLOC) as a LILA proxy

Wagg et al. (2022)
Dupletsa et al. (2023)
GW Strain
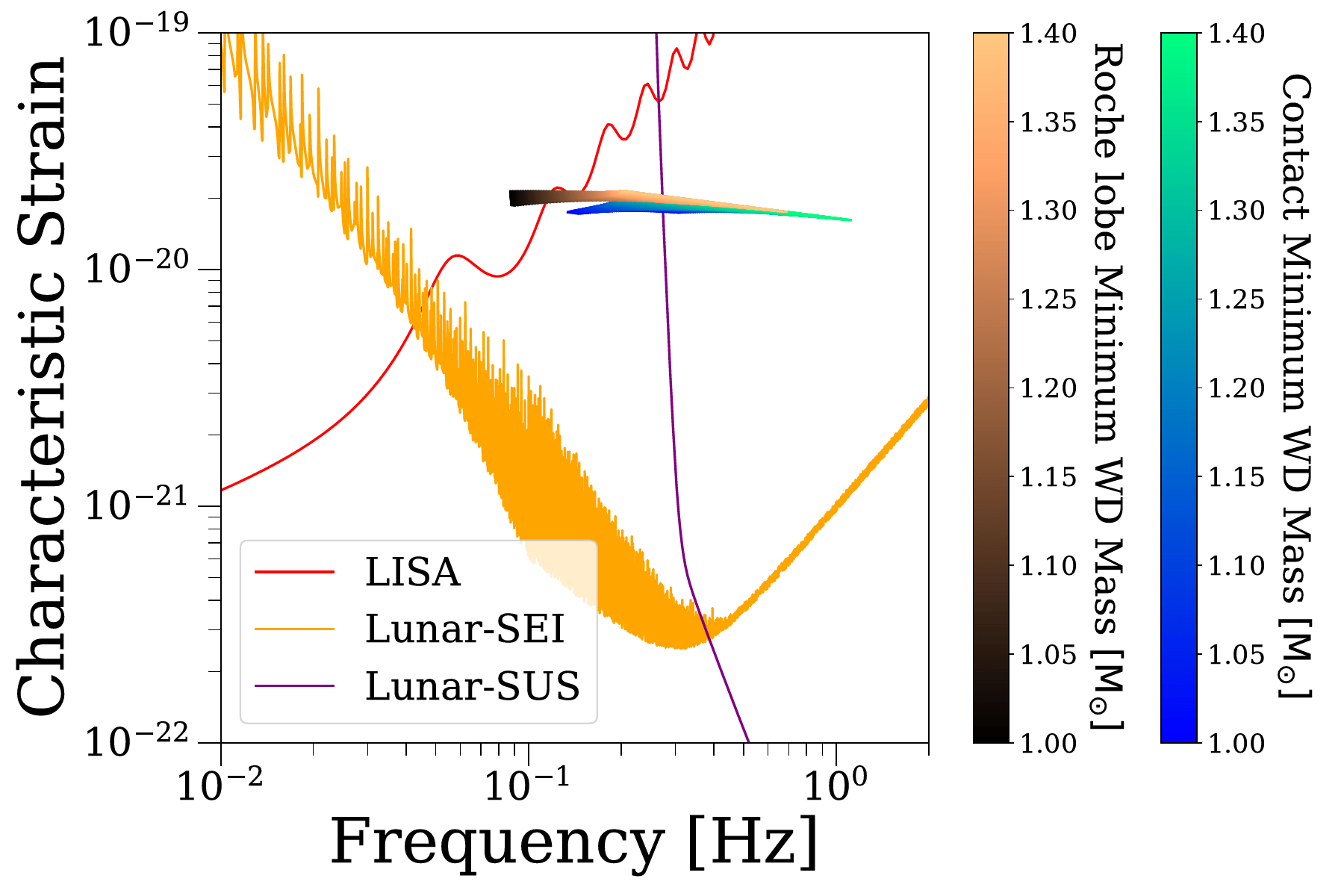
Pichardo Marcano et al. (2025)
GW
Detection Distance
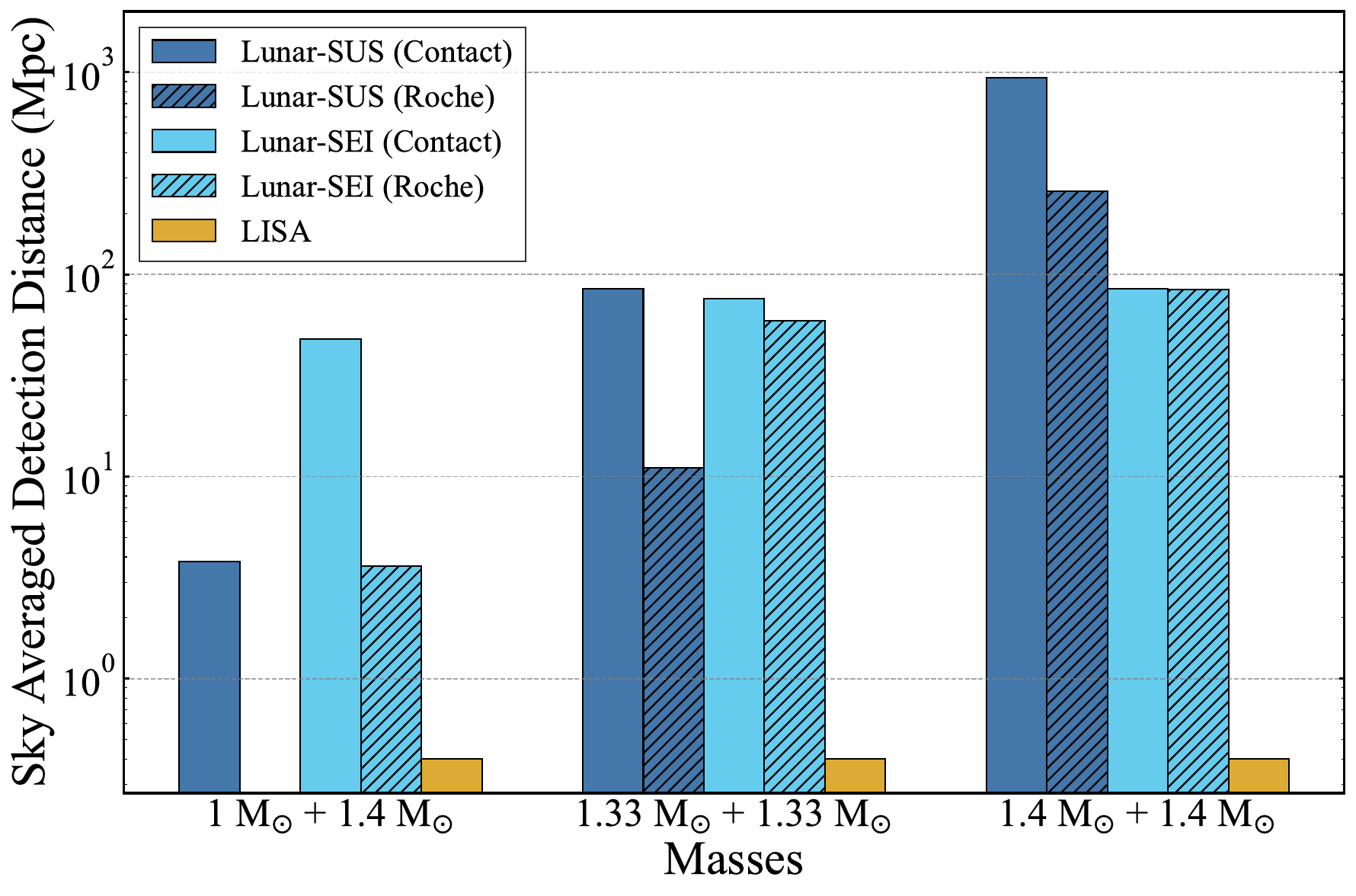
Pichardo Marcano et al. (2025)
Detection Distance
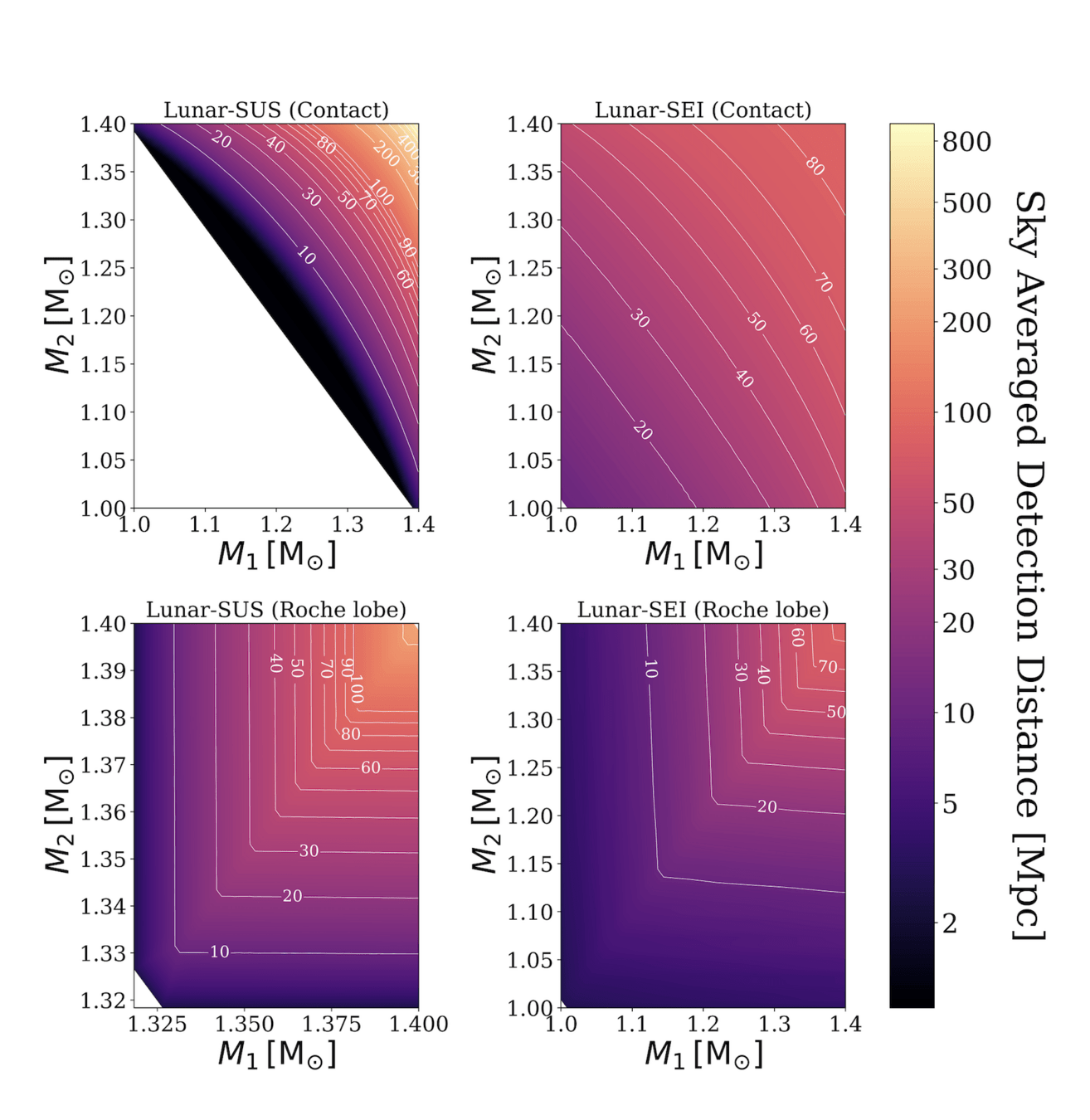
Pichardo Marcano et al. (2025)
Early Alert at 10 Mpc
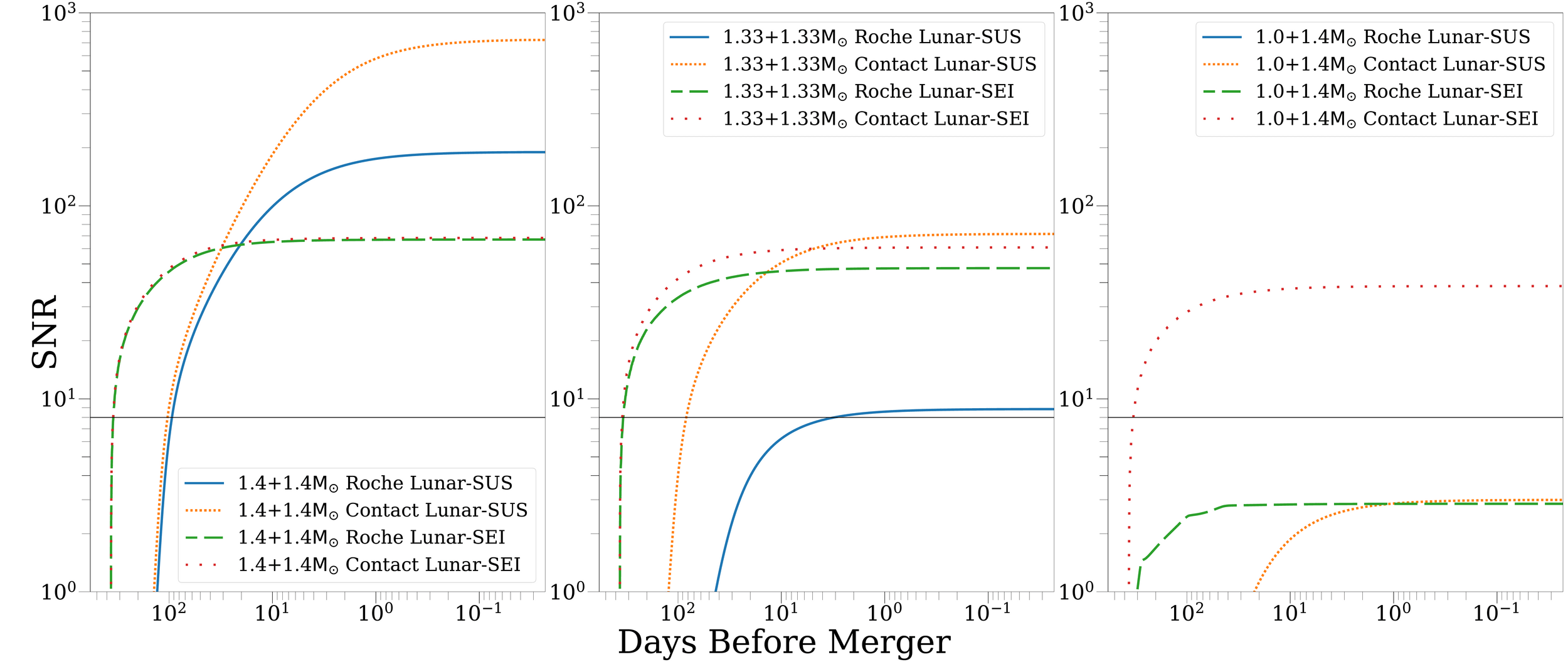
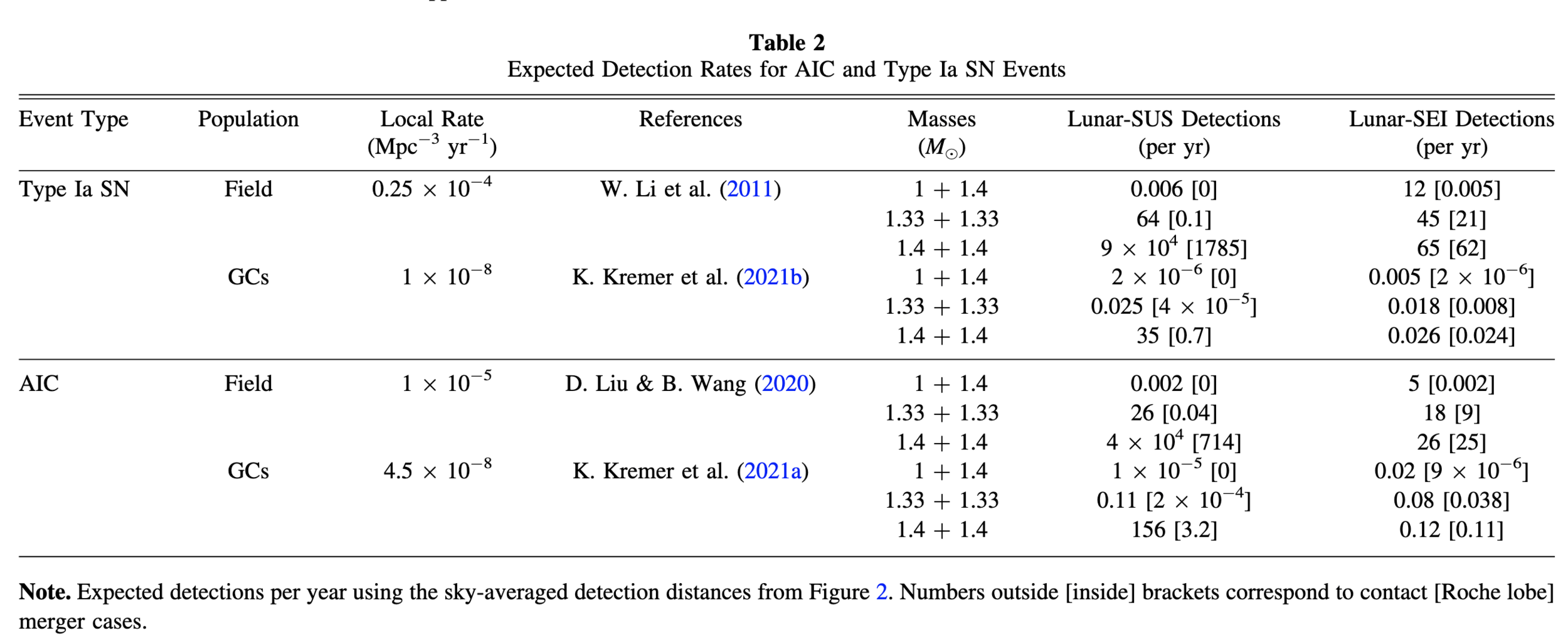
Pichardo Marcano et al. (2025)
Rates
- Type Ia SN
- 1 yr−1 in 10 Mpc (Kinugawa et al. 2022, Ajith et al. 2025)
- Massive pairs (ONe+ONe): 1 yr−1 for ∼100 Mpc
- AIC rates (Liu et al. 2020,Metzger et al. 2009):
- Best estimates: ~1 yr−1 at 30 Mpc
- Massive pairs (ONe+ONe): ~1 yr−1 events at 300 Mpc
- Type Ia and AIC rates in Globular Clusters (Kremer et al. (2021a,b):
- Type Ia: 10-5 yr−1
- AIC: 7 × 10−8 yr−1 per core-collapsed GCs
Constraint Common envelope Evolution
Multi-messenger and Multi-band Events

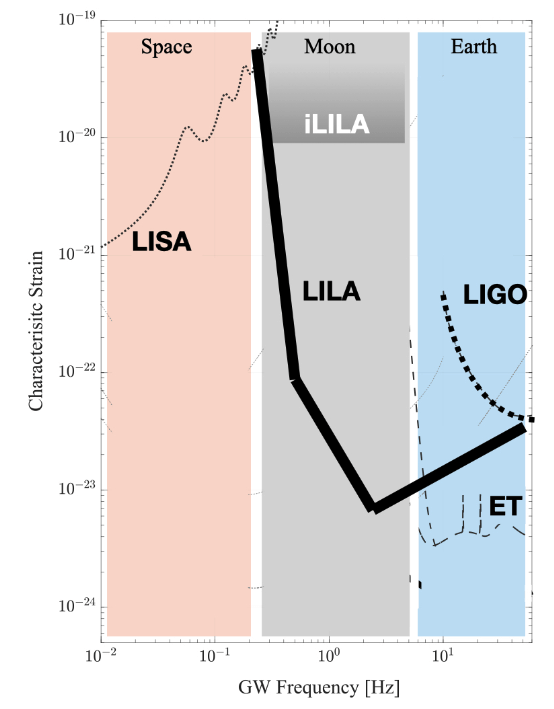
GWs from the Moon:
- WDs merger at Mpc distances
- Weeks of Early Alert
- LIGO source: Rapidly spinning NS
- WDs + PBHs (Yamamoto et al. 2024)
Extra
Detection Metrics
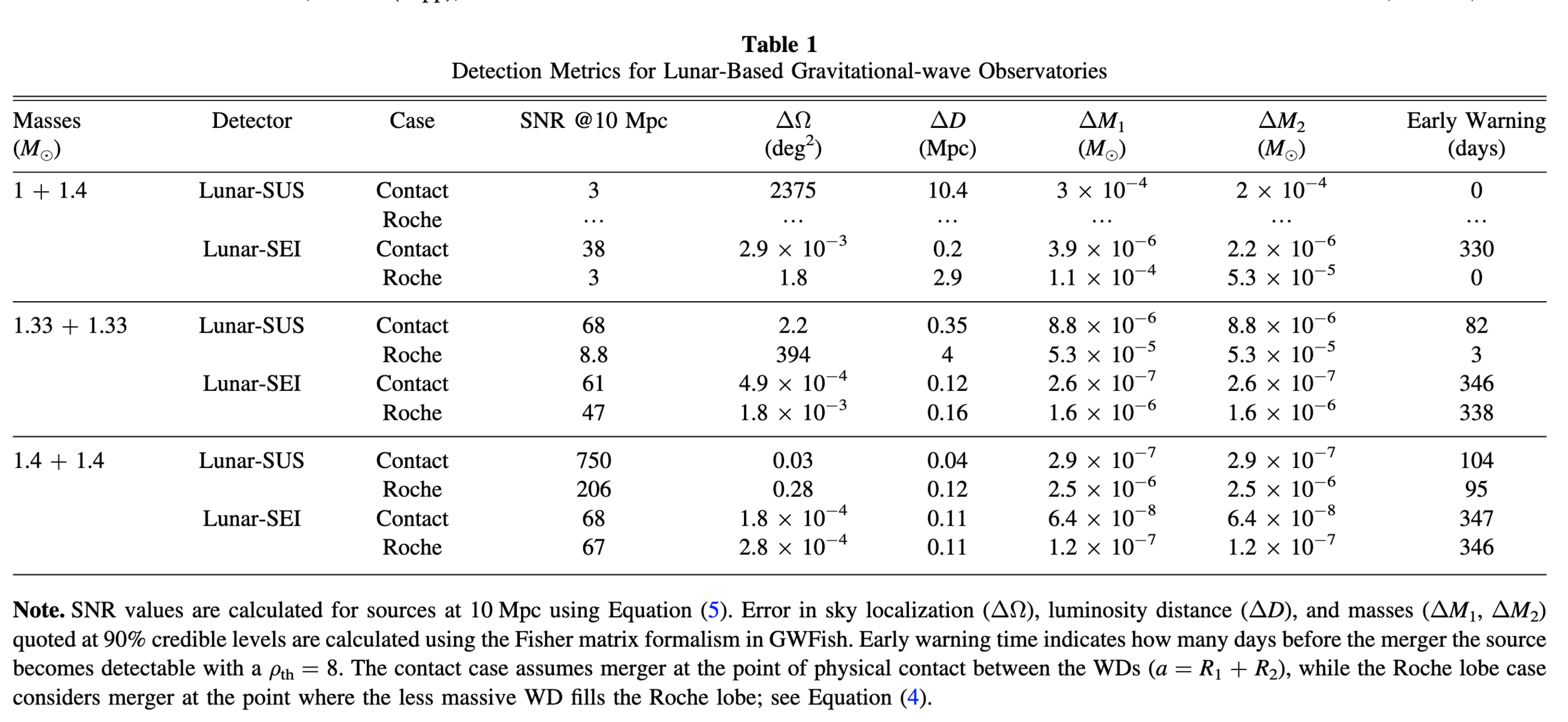
Rates
Old Slides
Multi-messenger and Multi-band Events

- LSST could see a few AIC events per year (Metzger et al. 2009)
- Possible FRBs
- Super-Chandrasekhar SN?
- LIGO source: Rapidly spinning NS
- WDs + BHs (Yamamoto et al. 2024)

GWs from the Moon:
GWs from the Moon
- GW freq. between LISA and LIGO
- Massive WDs merger at Mpc distances
- Weeks of Early Alert
- Multi-Messenger Astrophysics
- WDs + NS
- WDs + Primordial BHs

LSSTLATAM
By mmarcano22
LSSTLATAM
- 48



