Computer Networking
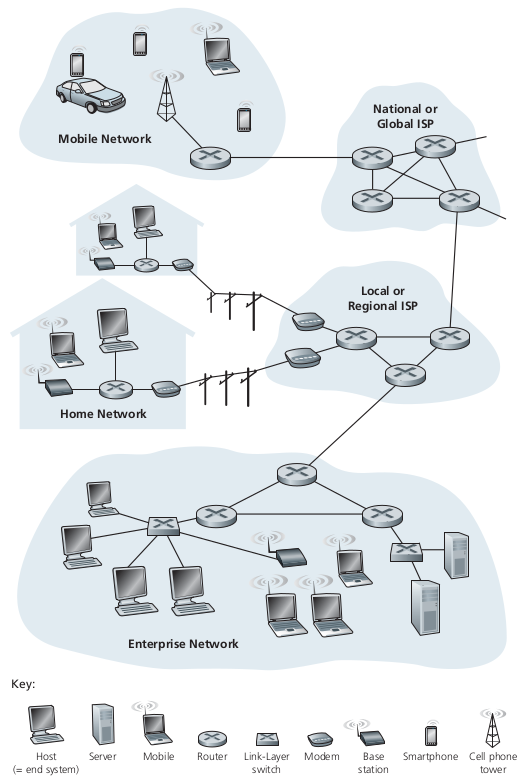
1990's - Internet limited to organisations (offices and workstations).
2K Boom - Mobiles and Laptops and PDAs and IOTs
Importance?
The evolution of IP Addressing scheme, i.e.
CIDR
\|/
NAT
\|/
IPv6
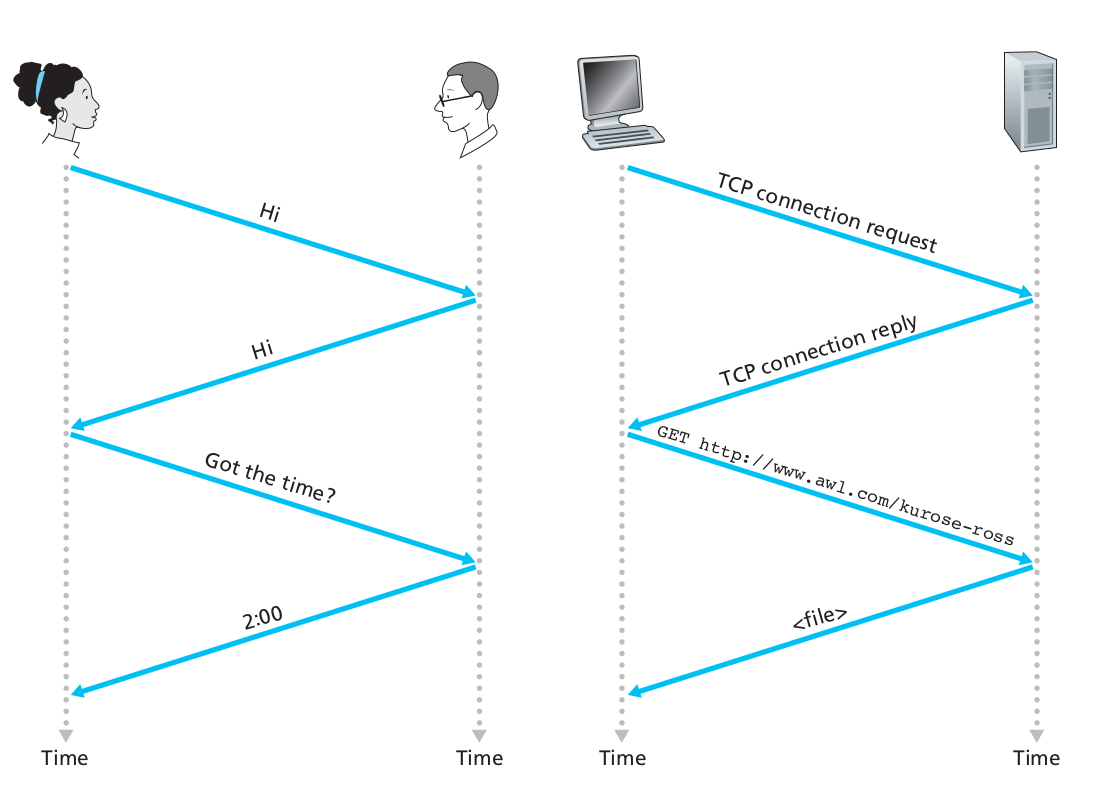
A protocol defines the format and order of messages exchanged between two communicating entities, as well as the actions taken on receipt/transmission of a message/event.
Text
A protocol
The Network
It's always 0's and 1's
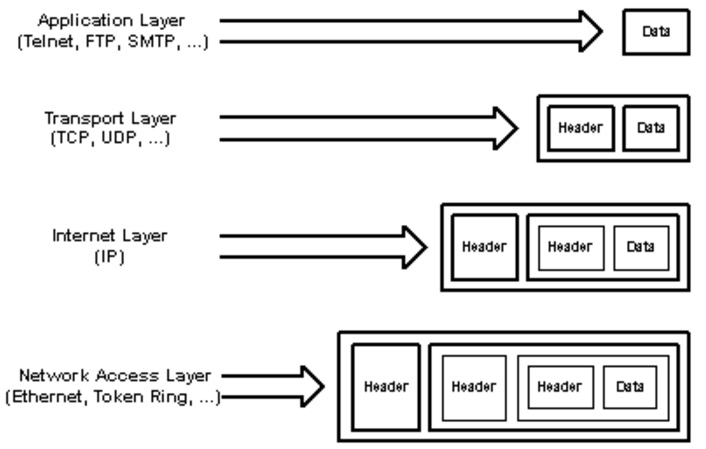
Provide services to upper layer
Agnostic to lower layer
IP over Ethernet, Token Ring, Frame relay(P.S.) and what not.
TCP over ABR/ATM(uncommon)
TCP/IP were designed together
Abstraction
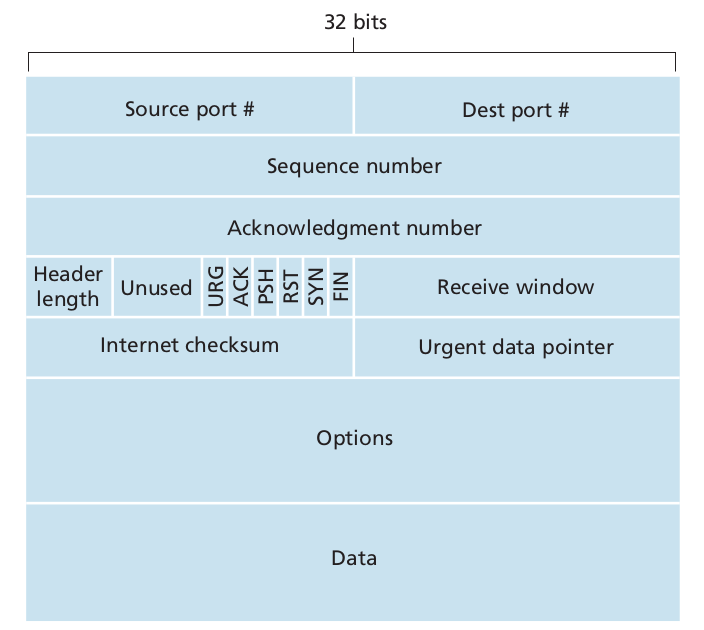
There is no segment size field in the TCP header (only the Data Offset, which gives the size of the TCP header). Therefore TCP will work only with a lower layer protocol that includes enough information to calculate the size of the TCP segment
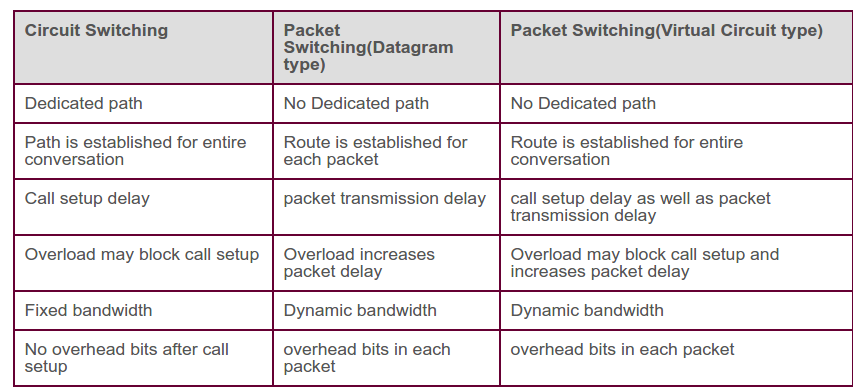
Connection Oriented services
Connectionless service
It is generally believed that the underlying network should do what it does best, which is deliver data bits as quickly as possible. Therefore, connection-oriented services are now primarily handled in the transport layer by end systems, not the network. This allows lower-layer networks to be optimized for speed.
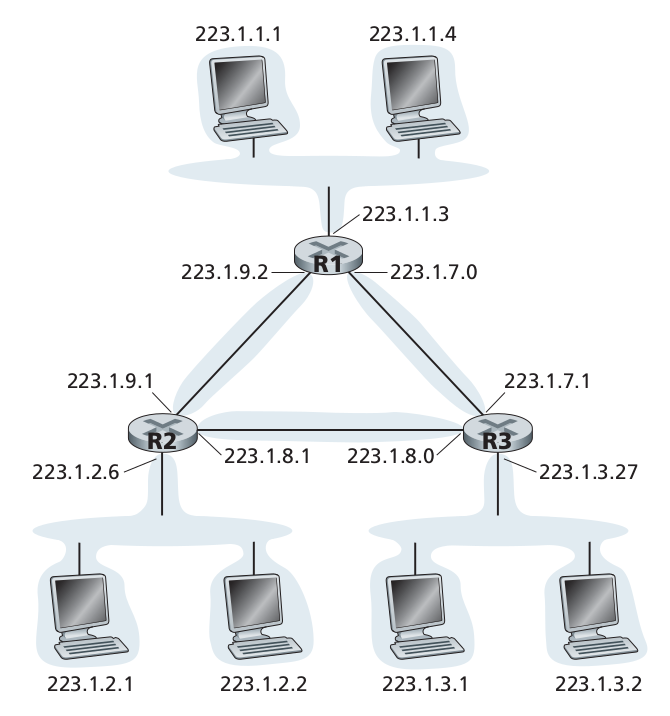
Routers and IP addressing

Longest prefix match
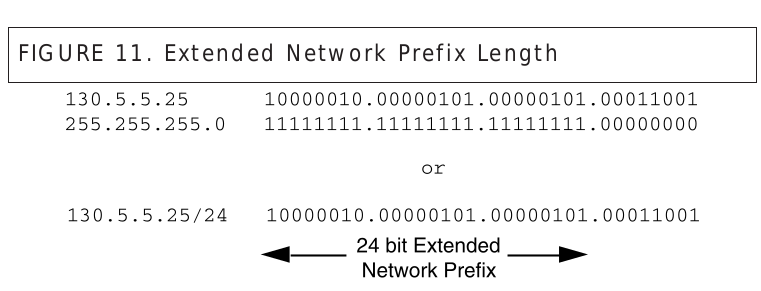
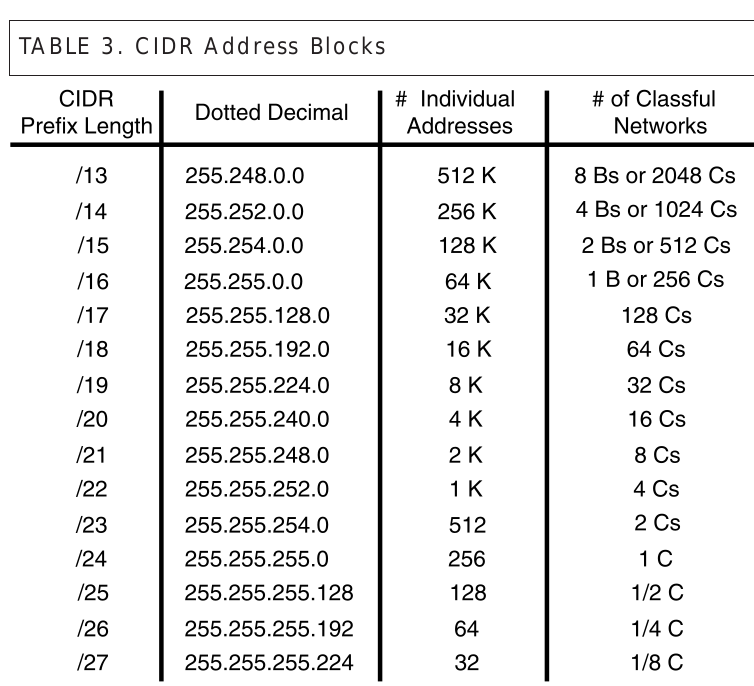
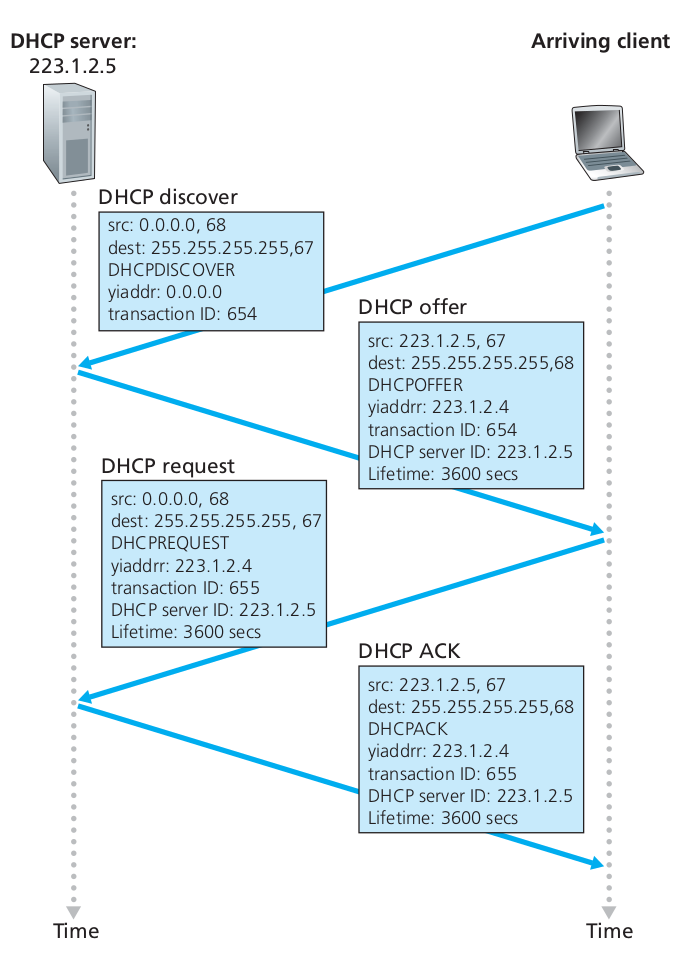
DHCP
The NAT-ted world
NAT RFC 1631

Why even use static NAT?
Eg. Getting rid of a ton of port forwarding (inbound traffic)
PAT/NAPT/IP masquerading/whatever

the only way the router knows which computer should receive the incoming packet is if one of the internal computers on the private LAN FIRST sent data packets out to the source of the returning packets.
NAT IS NOT FIREWALL!
Just get a 65536 * 65536 combination right to get in a traditional NAT
Doubly NAT-ted LANs
Computer Networking
By Mohan Agrawal
Computer Networking
- 396


