Data Structures

Data Structures
Data Structures

Data Structures
A data structure is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently and is generally based on the ability of a computer to fetch and store data at any place in its memory.
Data Structures

Data Structures
Data structures can implement one or more particular Abstract Data Types (ADT), which are the means of specifying the contract of operations and their complexity. A data structure is not an ADT, but is a concrete implementation of the contract provided by an ADT.
Data Structures

Data Structures
A list of common ADTs:
- Container
- Deque
- List
- Map
- Multimap
- Multiset
- Priority queue
- Queue
- Set
- Stack
- Tree
- Graph
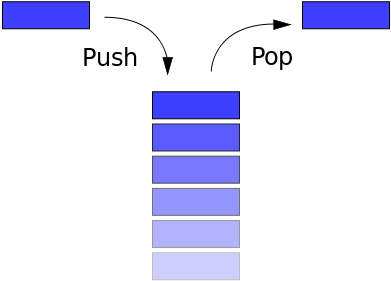
Stack
Last In First Out (LIFO)
Example: Undo button in a text editor

Data Structures
Stack

Data Structures
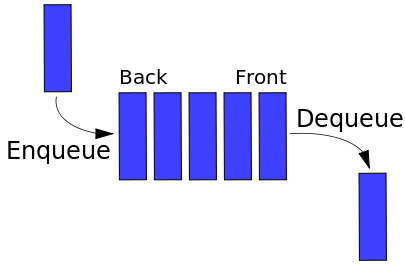
Queue
First In First Out (FIFO)
Example: A priority queue for customer orders

Data Structures
Queue

Data Structures
Linked Lists
A group of nodes which together represent a sequence.
Each node is composed of a data and a reference (link), to the next node in the sequence.

Data Structures
Linked Lists
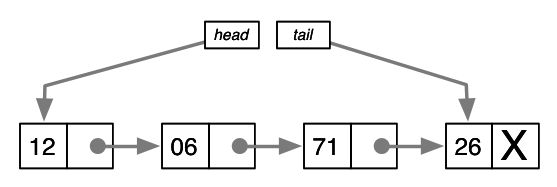
Head & Tail

Data Structures
Linked Lists
Advantages - Easily add / remove nodes without reorganization of the entire structure.
Disadvantage - No random access to the data (no indexing).

Data Structures
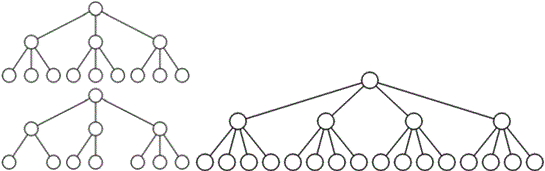
Trees
A tree is a collection of nodes where each node consists of a value as well as a list of references to its children
NOTE: In a normal tree, each node doesn't have a reference to its parent, just to their children.
What does this mean? Each of the children are also a tree!

Data Structures
Trees

Data Structures
Binary Search Trees
A BST is a data structure which allows for fast lookup, insertion and deletion.
Why? Because the BS tree is already sorted. When you are traversing the tree, the decision on where to go next is made by comparison.
How Fast? Ølog(n)

Data Structures
Binary Search Trees

Data Structures

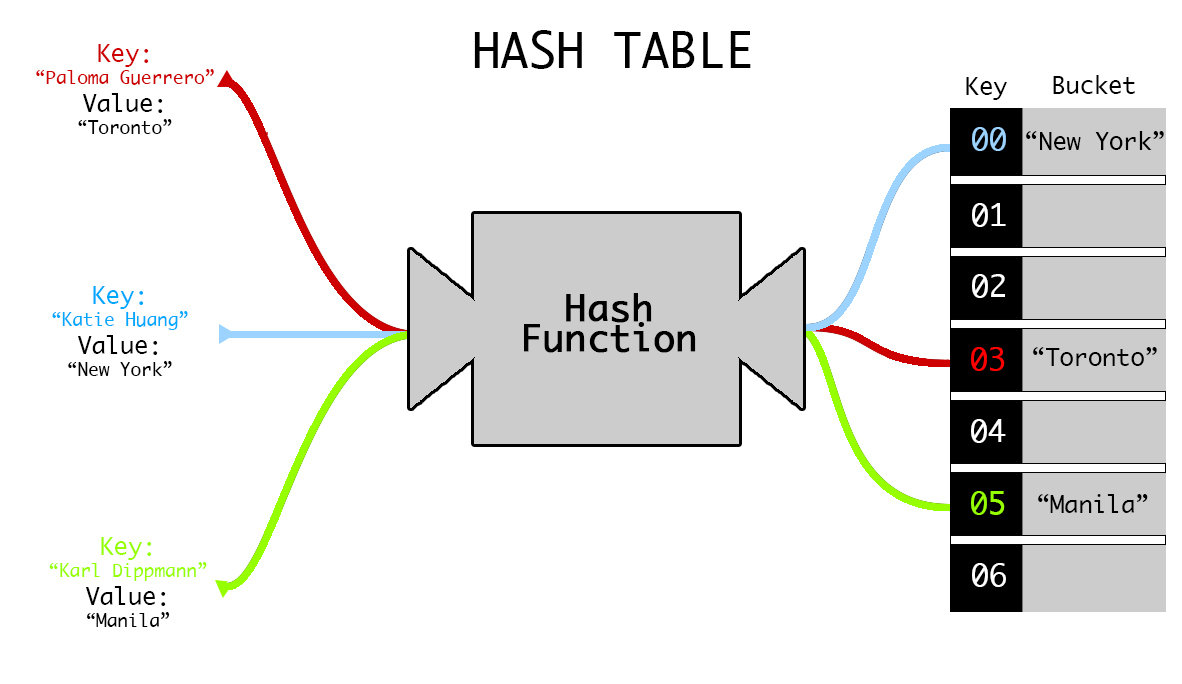
Hash Table/Map
A Hash table/map is a data structure that uses key-value pairs and allows for constant-time lookup.
How? On insertion of a value, a hashing function assigns a hash number to each key and uses that number to store the value in memory. On lookup/retrieval, the hashing function checks the requested key against the hash number and returns the corresponding value.
How Fast? Ølog(1)

Data Structures
Hash Table/Map

Data Structures
Data Structures
By moringaschool
Data Structures
- 721



