Waves and the Universe
the big questions

Waves
Waves
A wave is just the transfer of energy through space
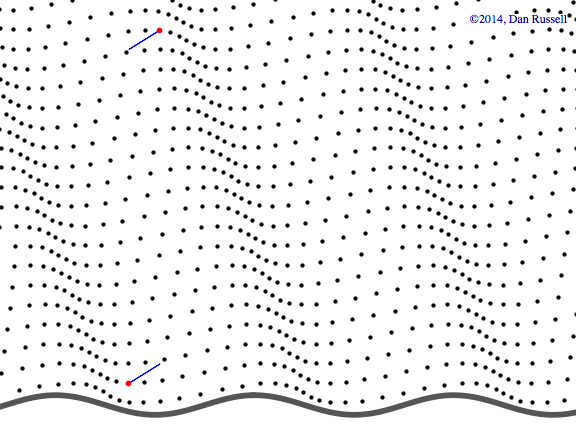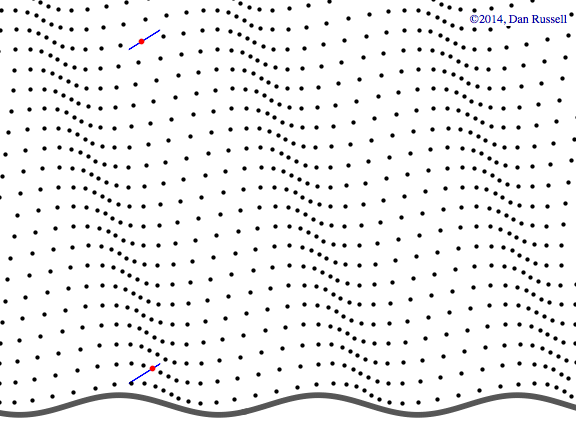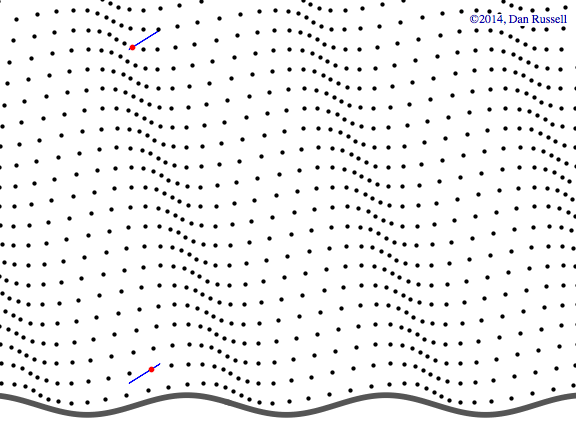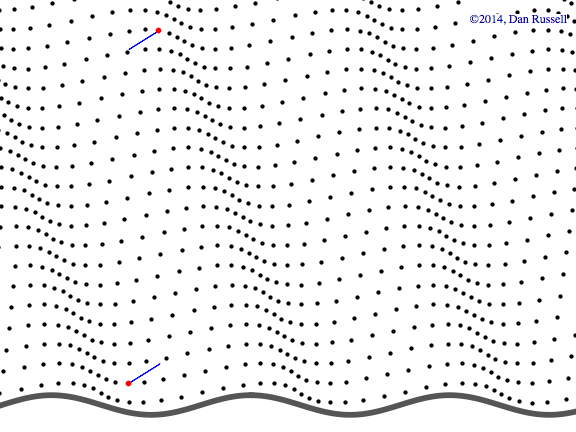
Watch the red dot.
It never will make it over to the right side
Even if it seems like it, waves just pass through things, jiggling them back and forth...
Characteristics of Waves
Amplitude: The distance from the midline to the top of a wave
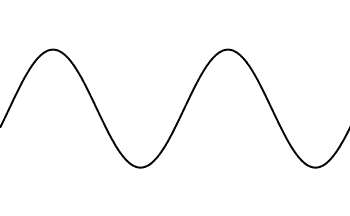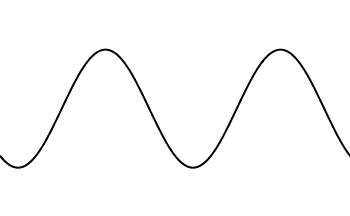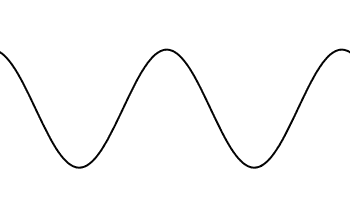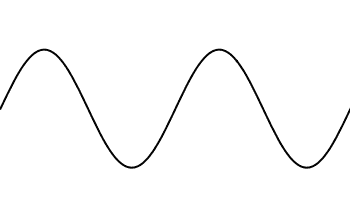
Frequency: How often a wave passes a point
Measured in meters
Measured in Hertz (waves per second)
Characteristics of Waves

Wavelength: the distance between each top of a wave
...or middle
...or bottom
Colors
Light is a wave.
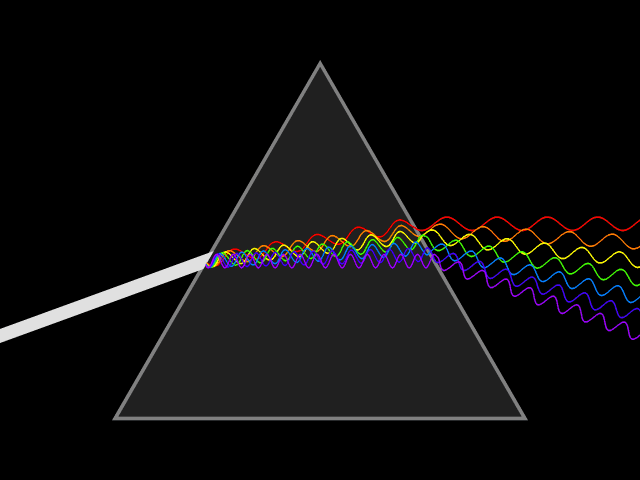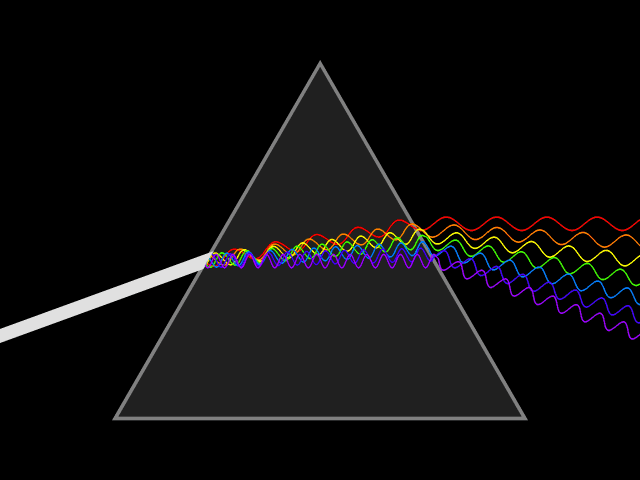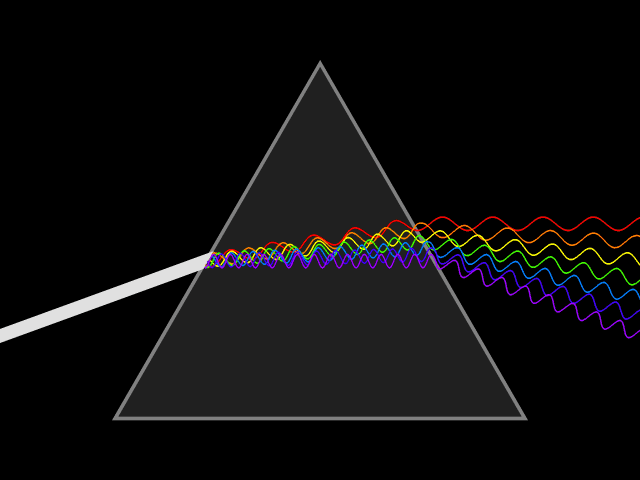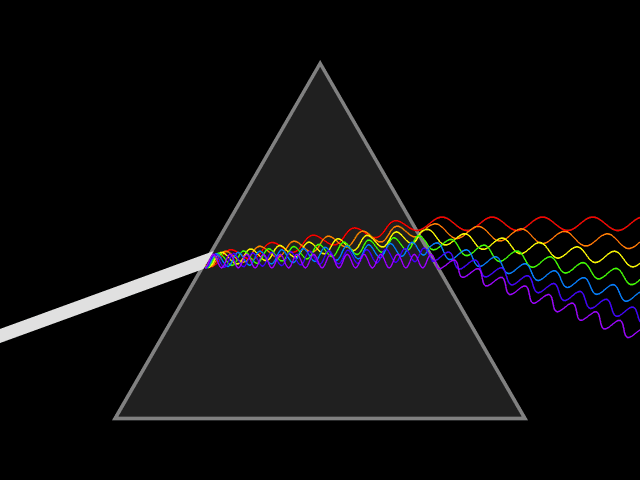
Notice the wavelength of each color
Notice the frequency is different too!
1. Which color has the longest wavelength?
2. Which color has the greatest frequency?
Colors
Are any of them getting closer to the edge?
All light travels at the same velocity
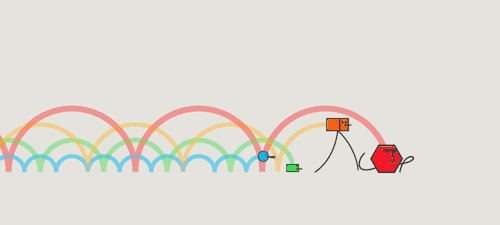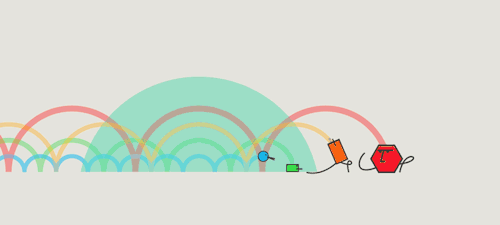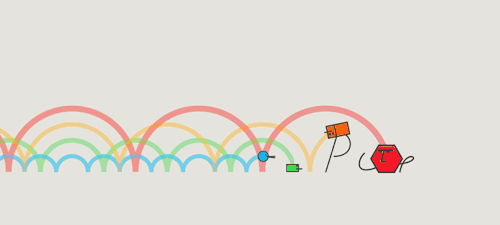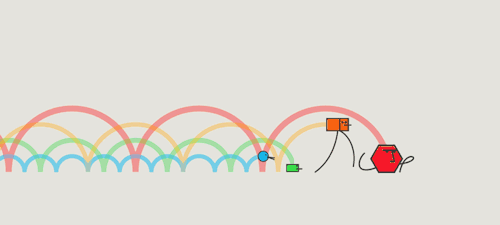
All light travels at the same velocity
All light travels at the same velocity!
3. Which color travels fastest?
Waves
All waves work in the same ways.
Wave Speed
We can describe a wave with only three characteristics:
Velocity (v)
Wavelength (λ)
Frequency (f)
Hooray!
That means we can use mAThs!
Wave Speed Equation
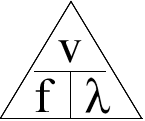


If we want to know the equation for wavelength, just cover up the wavelength symbol.
We are left with the equation:



Let's try to find the velocity of a wave!
We are left with the equation:


Easy!
What is the velocity of a wave that has a wavelength of 5 m and a frequency of 20 Hz?

Ooh! We're trying to find v, so we cover that up

Then just plug in your values.


Can we paaleeease do another?!
We are left with the equation:


...sure!
What is the frequency of a wave that has a wavelength of 5 m and travels at 200 m/s?

Ooh! We're trying to find f, so we cover that up

Then just plug in your values.
Star
Lives

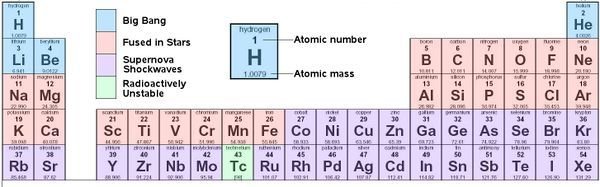
In the very early universe, only the smallest elements could form:
Hydrogen
Helium
and
*and maybe a tiny bit of Li and Be

This is a Nebula!
It is a clump of hydrogen dust in space, held together by gravity
Eventually, gravity will push all this hydrogen together hard enough to get fusion to happen
This explanation of where stars come from is called Nebular Theory

Bam!
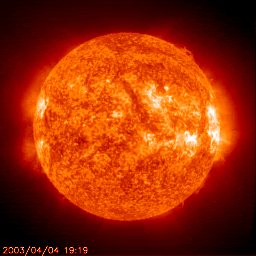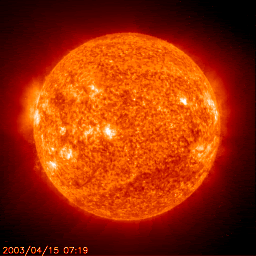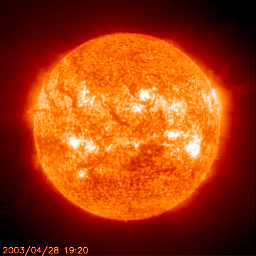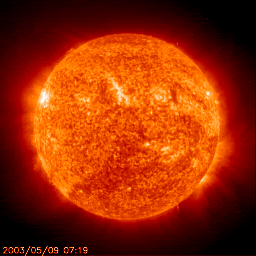
This is a new star!
It starts its life fusing the smallest element, hydrogen
Bam!

Our new star that's fusing hydrogen, can be found on the HR Diagram
As it fuses hydrogen, it will sit here, on the Main Sequence
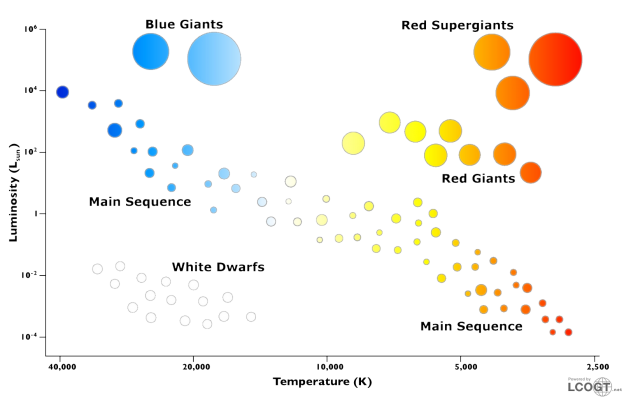
Bam!

Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence.
Main Sequence

Our sun is in the main sequence still (that's a good thing!)
Bam!

When our sun runs out of hydrogen, it will start fusing helium, and become a Red Giant

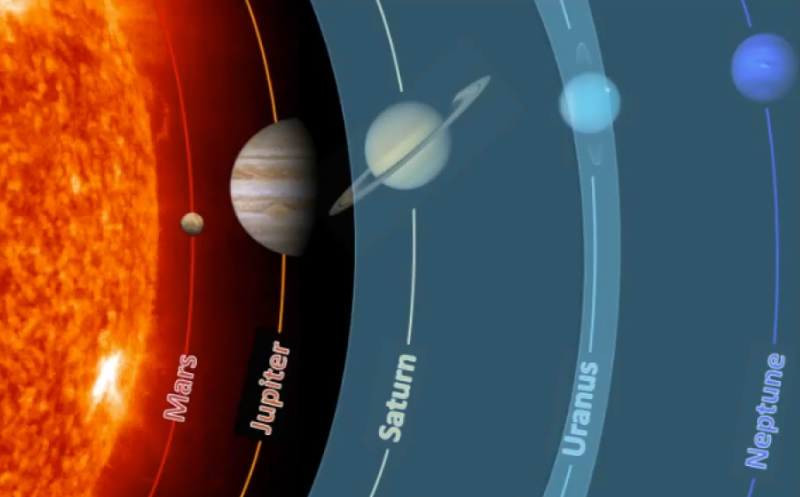
Bam!
Once our sun has fused all of its helium into carbon, it has reached the end of its life...

And it will become a White Dwarf
That was the end of a Low Mass star.
High Mass stars have a different end to their stories...
Bam!
A High Mass star will also begin its life by fusing hydrogen.
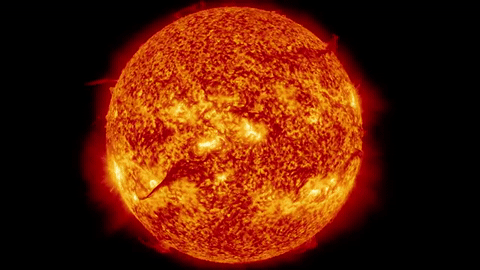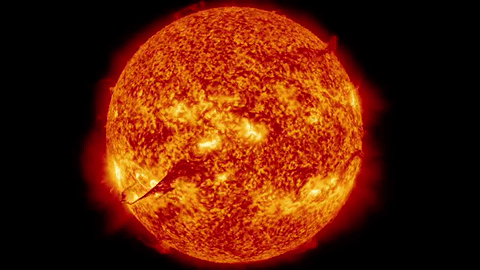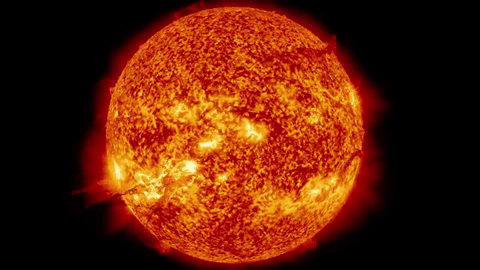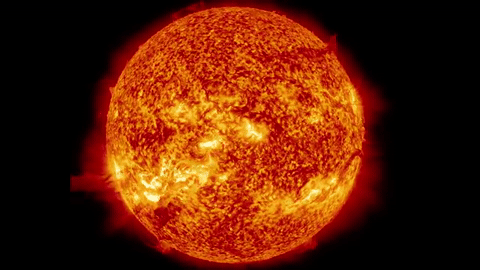
But because it is so massive, it can fuse even larger elements in its core.
High mass stars have enough gravity to fuse elements all the way up to Iron!

For stars, it's all about that mass...
Bam!
When our high mass star reaches Iron, it begins to collapse on itself, and one of the biggest events ever happens...


Supernova
Bam!
It is these crazy-huge explosions of high mass stars that creates all the elements larger than Iron.

Galaxy
Formation

Red
Shift
Title Text

Text
Astro-biology

Waves and Universe
By mrgliddon
Waves and Universe
- 1,010



