Data Structures and Algorithms
muigai unaka
Week 6
Tree
Tree
Node
Node
Node
Root Node
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
Level 0
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Root Node
Height: 5
Root: A
Leaves: C, E, I, J
Preorder: ABCDEFGHIJ
Inorder: CBEDAFIHJG
Postorder: CEDBIJHGFA Breadth: ABFCDGEHIJ
// To create a Tree you will need "Nodes"
// Nodes will have data
// (this can be a string, an integer, an object, etc)
// and a reference to the left child Nodes and right child Nodes
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
// initiate a root node and assign the left and right
let root = new Node("A");
root.left = new Node("B");
root.right = new Node("F");
root.left.left = new Node("C");
root.left.right = new Node("D");
root.left.right.left = new Node("E");
root.right = new Node("F");
root.right.right = new Node("G");
root.right.right.left = new Node("H");
root.right.right.left.left = new Node("I");
root.right.right.left.right = new Node("J");// To create a Tree you will need "Nodes"
// Nodes will have data
// (this can be a string,
// an integer, an object, etc)
// and a reference to the left child
// Nodes and right child Nodes
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
// initiate a root node
// and assign the left and right
let root = new Node("A");
root.left = new Node("B");
root.right = new Node("F");
root.left.left = new Node("C");
root.left.right = new Node("D");
root.left.right.left = new Node("E");
root.right = new Node("F");
root.right.right = new Node("G");
root.right.right.left = new Node("H");
root.right.right.left.left = new Node("I");
root.right.right.left.right = new Node("J");A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
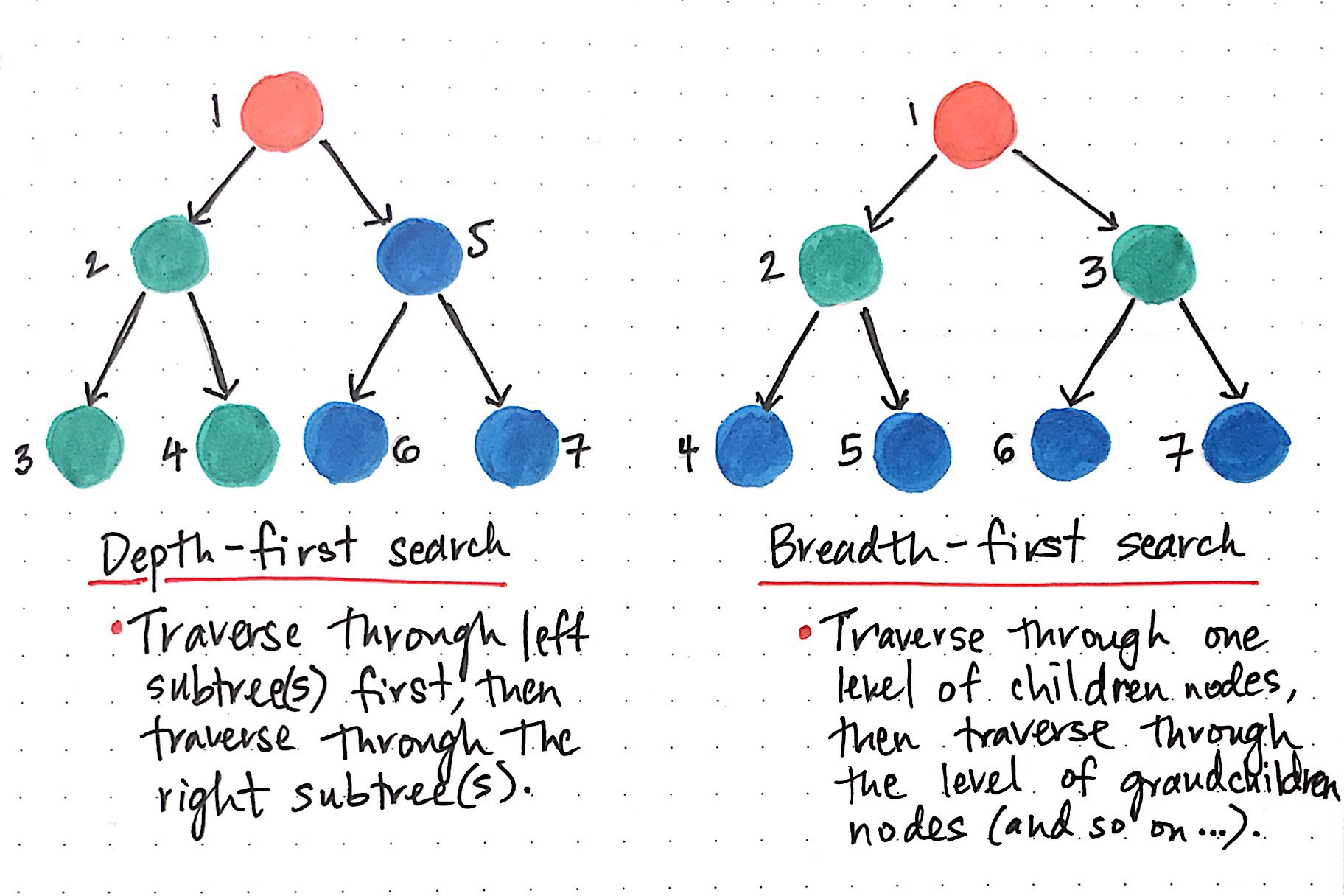
Depth First Search
/**
* Preorder traversal is used to create a copy of the tree.
* Preorder traversal is also used to get prefix expression
* on of an expression tree.
* <root> <left> <right>
* @param {Node} root
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
*/
const preorderTraverse = (root) => {
try {
if (root == null) return;
if (!(root instanceof Node)) {
throw new Error("TypeError: Cannot traverse non node");
}
console.log(root.data);
preorderTraverse(root.left);
preorderTraverse(root.right);
} catch (e) {
throw e;
}
}/**
* In case of binary search trees (BST), Inorder traversal gives nodes
* in non-decreasing order. To get nodes of BST in non-increasing order,
* a variation of Inorder traversal where Inorder traversal is reversed
* can be used.
* <left> <root> <right>
* @param {Node} root
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
*/
const inorderTraverse = (root) => {
try {
if (root == null) return;
if (!(root instanceof Node)) {
throw new Error("TypeError: Cannot traverse non node");
}
inorderTraverse(root.left);
console.log(root.data);
inorderTraverse(root.right);
} catch (e) {
throw e;
}
}/**
*
* <left> <right> <root>
* @param {Node} root
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
*/
const postorderTraverse = (root) => {
try {
if (root == null) return;
if (!(root instanceof Node)) {
throw new Error("TypeError: Cannot traverse non node");
}
postorderTraverse(root.left);
postorderTraverse(root.right);
console.log(root.data);
} catch (e) {
throw e;
}
}Breadth First Search
Breadth-first search involves search through a tree, level by level, one level at a time
// BFT uses a queue, better to do it iteratively
// Level order traversal
const bft = (node) => {
let q = [node]
let output = []
while (q.length) {
let current = q.shift()
output.push(current.data)
console.log(current.data)
// check the left node
if (current.left) {
q.push(current.left)
}
// check the right node
if (current.right) {
q.push(current.right)
}
}
return output
}
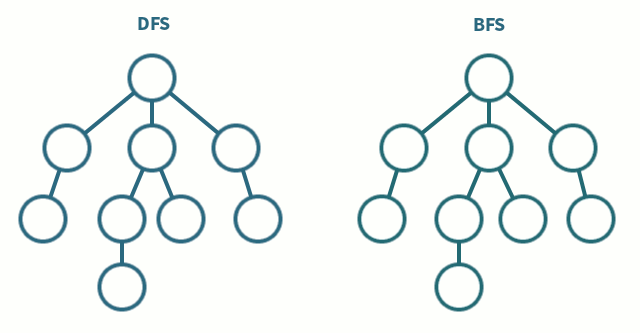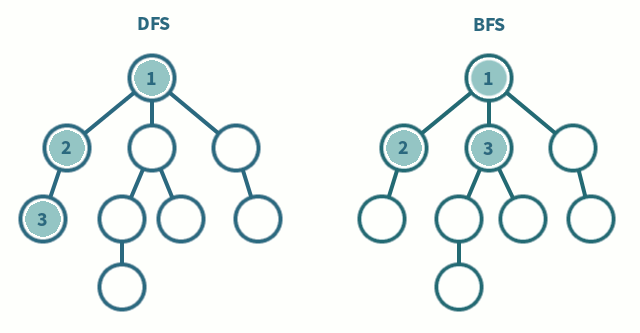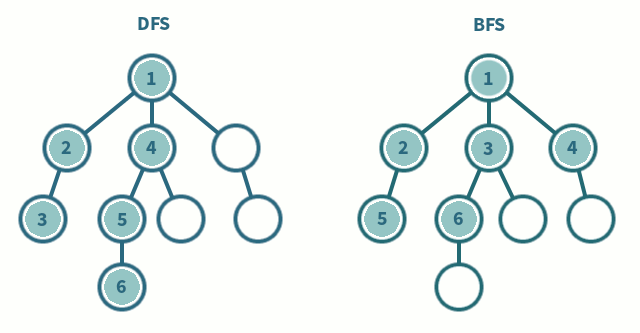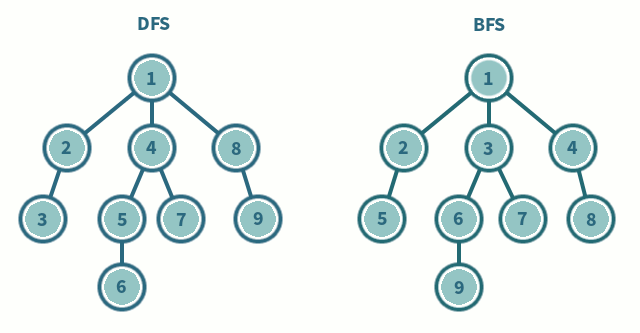
For all of these traversals - whether done recursively or iteratively - you’ll have to visit every node in the tree. That means that you’ll get a runtime complexity of 𝑂 (𝑛) - where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
Tree Traversal Runtime
For all of these traversals - whether done recursively or iteratively - if we don’t consider size of stack for function calls then 𝑂 (1) otherwise 𝑂 (𝑛)
Tree Traversal Space Complexity
Tree Terms
Root: the node at the top of a tree. There can only be one root node
Node: data struct that hold references to other nodes
Leaf: a node without children
Edge: a one to one connection between nodes
Path: the sequence of nodes along the edges of a tree
Visiting: accessing a node in a tree
Traversal: the act of passing through nodes in a specific way
Level: the current specific depth of a node
Depth: the number of edges from the root to the node
Height: the number of edges from the node to the deepest leaf
credit: shinyashanka
Binary Tree is a special kind of tree where each Node can have at most 2 children.
Binary Tree
- All the keys (data inside the node) are distinct.
- In every parent node, the left child key value is smaller than the parent node key value.
- In every parent node, the right child key value is larger than the parent node key value.
Binary Search Tree
(binary tree but with a few conditions)
Leetcode Problems
Tree & Binary Tree
Depth First Search
257. Binary Tree Paths
105. BT from preorder and inorder
111. Minimum Depth of a Binary Tree
Breadth First Search
160. Intersection of
pitanjas?
Data Structures and Algorithms Week 6
By Muigai Unaka
Data Structures and Algorithms Week 6
Data Structures and Algorithms week 6 at Resilient Coders. Data Structures II: Trees
- 484



