Putting it all together
What we've done so far
Data Structures & Algorithms
- Problem solving steps
- Pseudo code
- Data structures overview
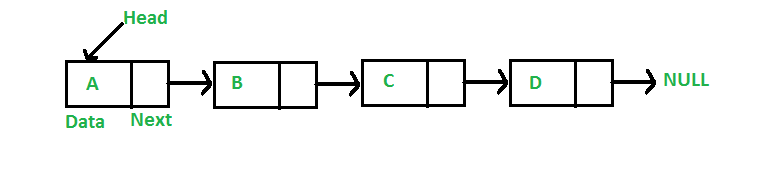
Linked Lists
Node: {
content: any,
next: Node
}
LinkedList: {
head: Node,
tail: Node
}
newLinkedList() -> LinkedList
newNode(content) -> Node
add(Node, LinkedList) -> null
delete(Node, LinkedList) -> nullJS programming Paradigms
Programming Paradigms
& design patterns
-
Imperative
- Procedural
- Object Oriented
-
Declarative
- Functional
- SQL
JavaScript is a multi-paradigm language
Supports OOP, procedural, and Functional
Read more on programming paradigms
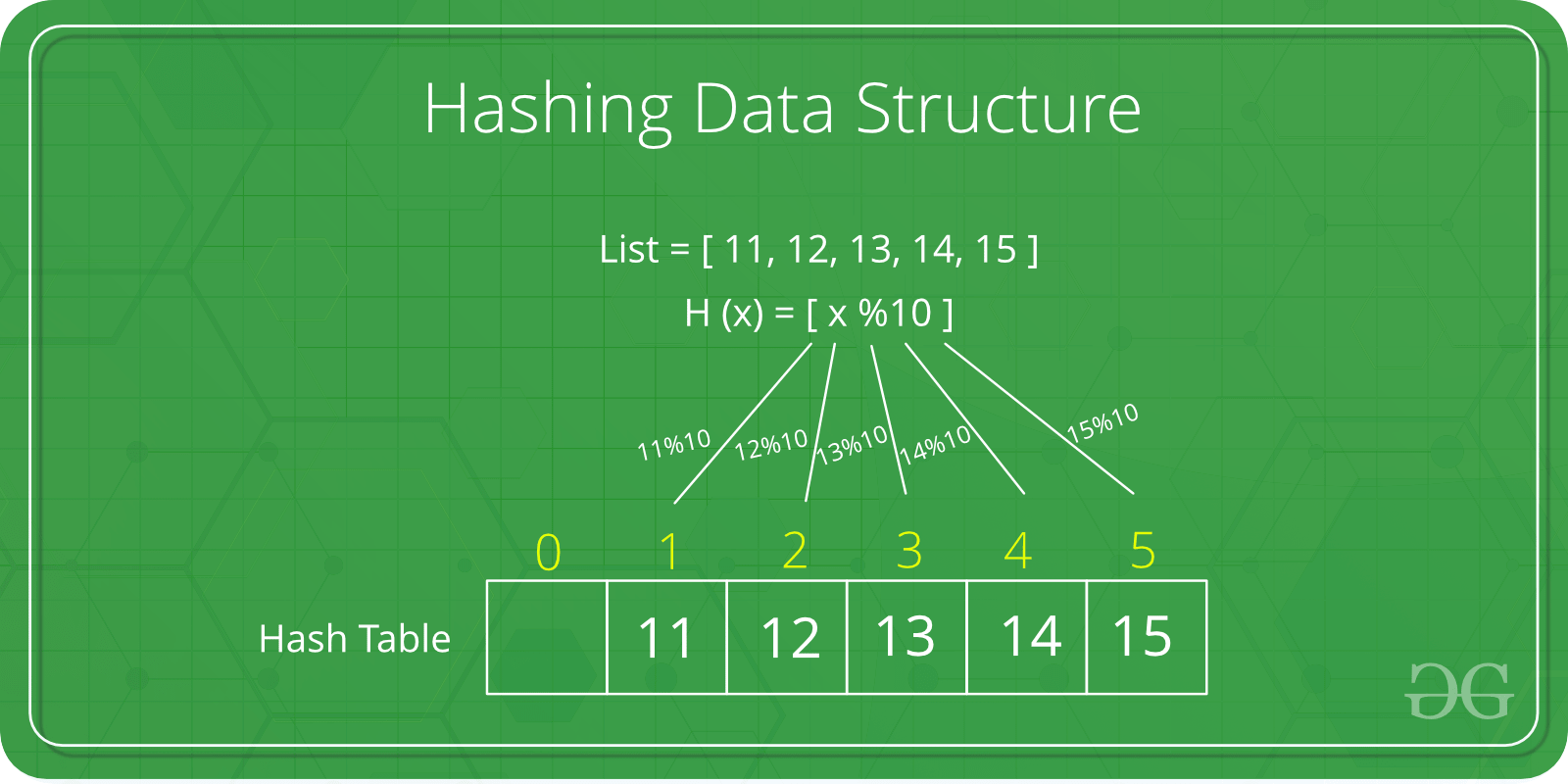
Hash Tables
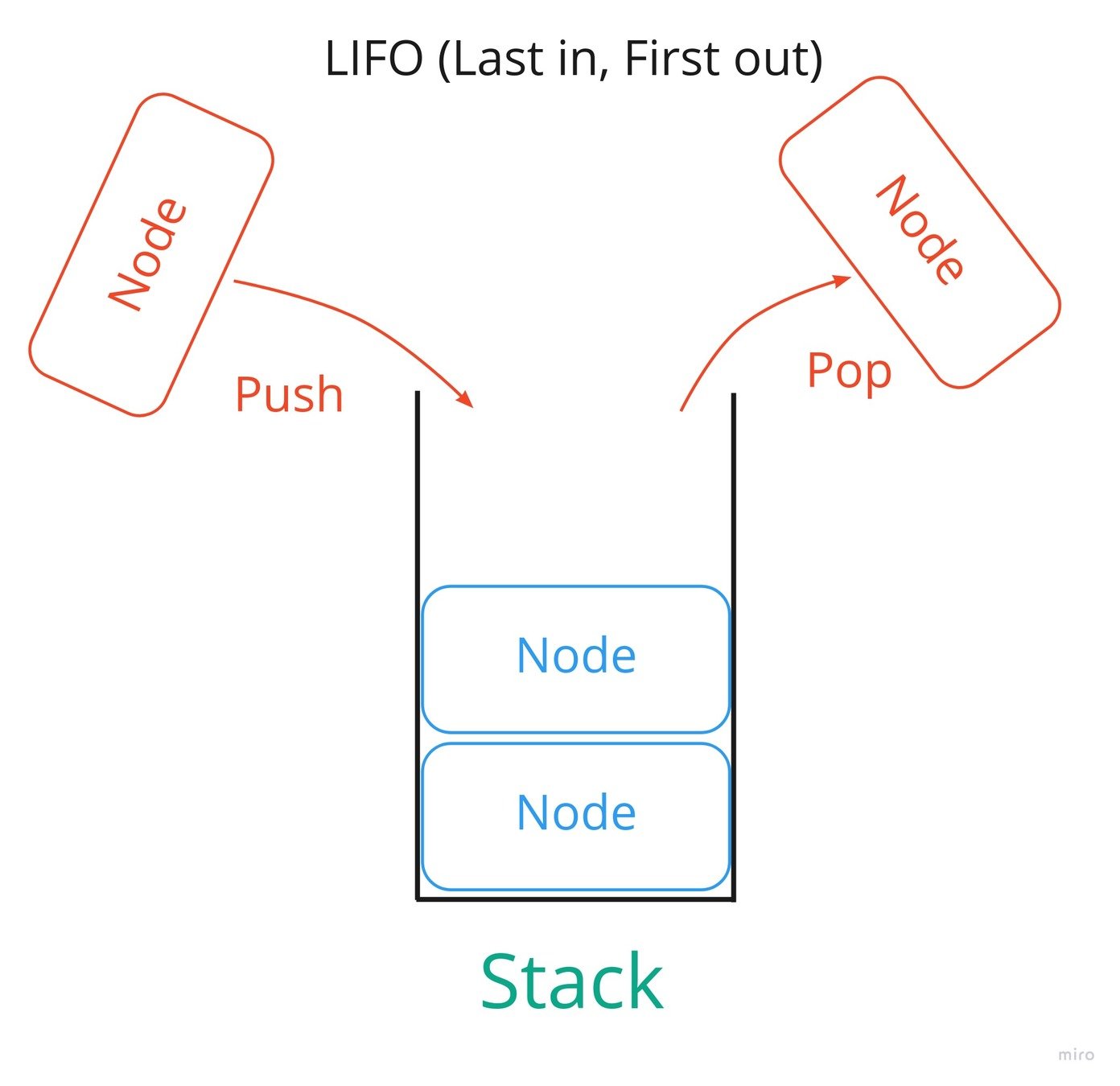
- Browser History
- Undo/Redo
- Code execution
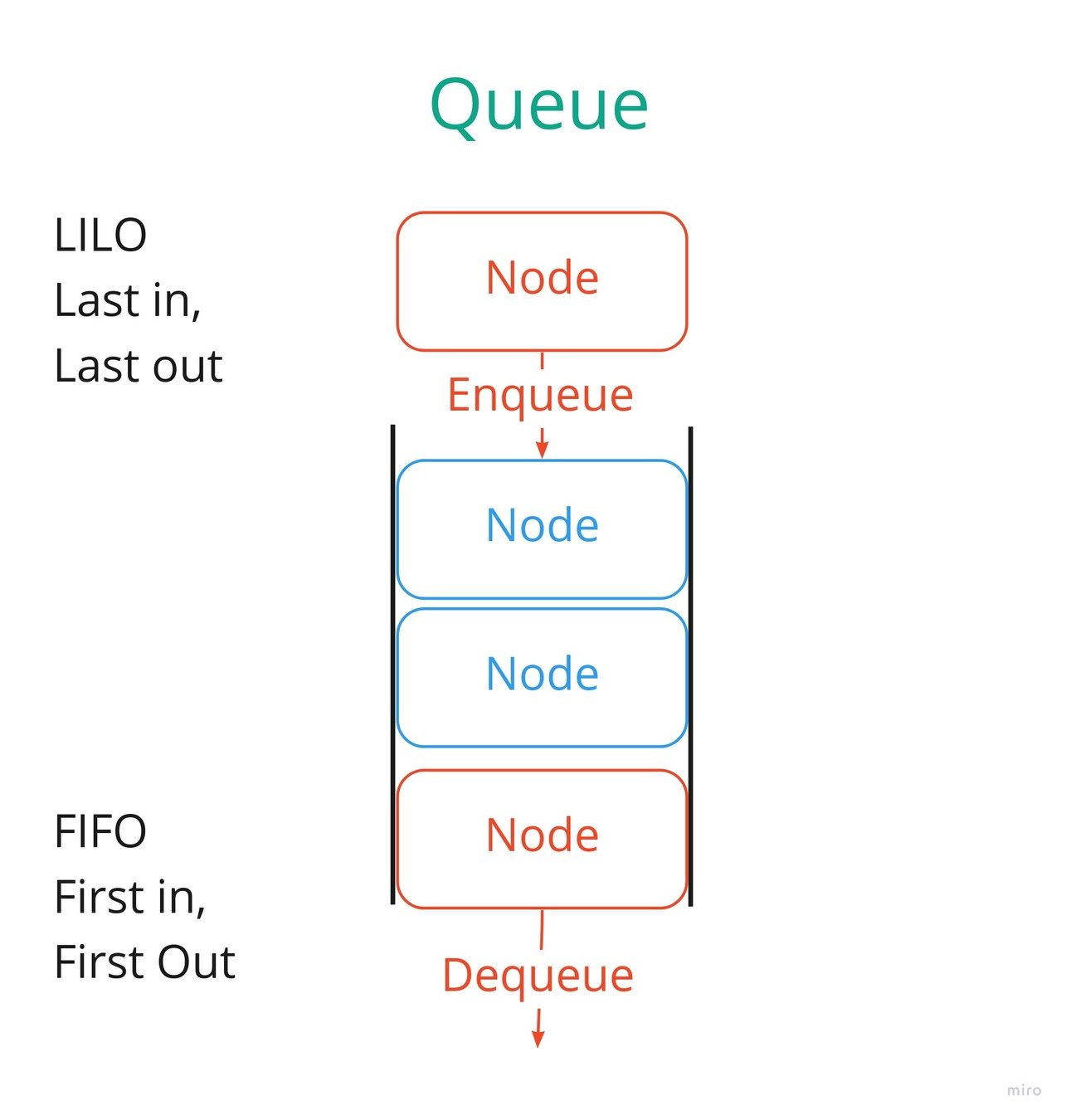
- Background jobs
- Requests to server
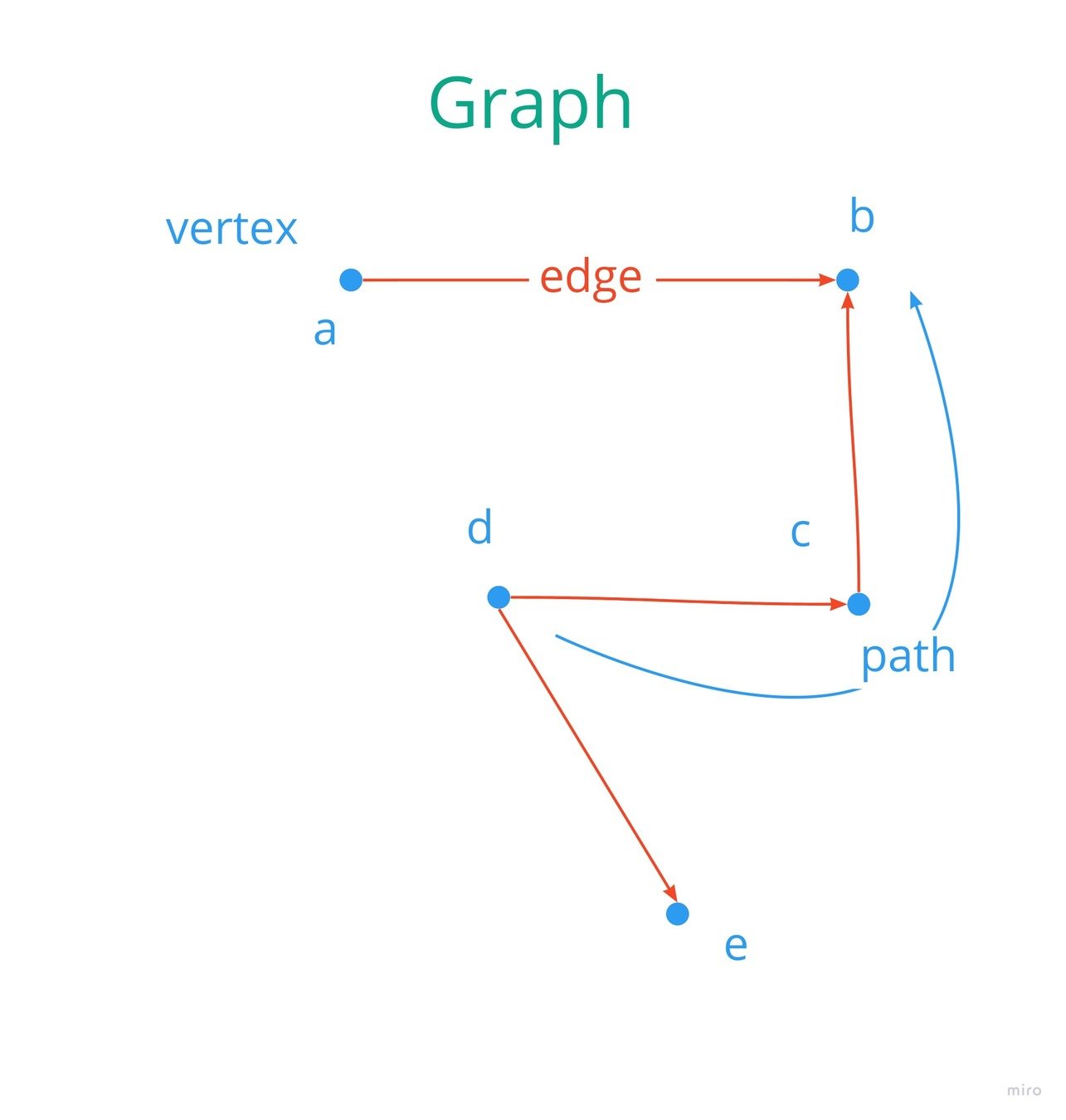
- The World Wide Web!
- Search algorithms
- Facebook Graph
- Find path from A to B
- Google maps
- Flight search
- Social Networks
- Connecting 2 people
What is JavaScript?
- Dynamic
- Interpreted
-
Object orientedmulti-paradigm - Can make computations
- Has 7 data types
- Has conditionals
- Has loops
JS Data Types
- Boolean
- Number
- String
- Object
- Function
- null
- Symbol
Variables
let x = 1;
const y = 2;Conditionals
if (condition) {
// do something
}Loops
while (condition) {
// do something
}for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// do something
}Functions
function test(arg1, arg2) {
// do something
}Arrays
const arr = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']
arr[0] // "foo"
arr[1] // "bar"
arr[2] // "baz"Objects
const car = {
color: 'red',
fuel: '50%',
topSpeed: 200
}
car.color // "red"
car.fuel // "50%"
car.topSpeed // 200Object Oriented
class Car {
velocity = 250
constructor(color, fuelType) {
this.color = color;
this.fuelType = fuelType;
}
paint(newColor) {
this.color = newColor;
}
static hasTheSameProperties(car1, car2) {
return car1.color === car2.color &&
car1.fuelType === car2.fuelType;
}
set fuelType(newFuelType) {
newFuelType = newFuelType.toLowerCase();
if (newFuelType !== 'electric' && newFuelType !== 'diesel') {
throw new Error('unsupported fuel type ' + newFuelType)
}
this._fuelType = newFuelType;
}
get fuelType() {
return this._fuelType;
}
}
class Prius extends Car {
constructor(color) {
super(color, 'Hybrid');
}
set fuelType(newFuelType) {
this._fuelType = 'Hybrid';
}
get fuelType() {
return this._fuelType;
}
}Async JS
Callbacks
// this code runs synchronously
doSomething();
doAnotherThing();
// this code runs asynchronously
doSomethingInTheBackground(callMeWhenDone);
doSomethingWithoutWaitingForPreviousLineToFinish();
function callMeWhenDone() {
console.log(
"doSomethingInTheBackground has finished");
}Callbacks
// this code runs synchronously
doSomething();
doAnotherThing();
// this code runs asynchronously
doSomethingInTheBackground(callMeWhenDone);
doSomethingWithoutWaitingForPreviousLineToFinish();
function callMeWhenDone() {
console.log(
"doSomethingInTheBackground has finished");
}
function doSomethingInTheBackground(callback) {
setTimeout(callback, 1000);
}Promises
// this code runs synchronously
doSomething();
doAnotherThing();
// this code runs asynchronously
doSomethingInTheBackground().then(callMeWhenDone);
doSomethingWithoutWaitingForPreviousLineToFinish();
function callMeWhenDone() {
console.log(
"doSomethingInTheBackground has finished");
}
function doSomethingInTheBackground(callback) {
return new Promise(function() {
// do stuff
})
}Async/Await
// this code runs synchronously
doSomething();
doAnotherThing();
// this code runs asynchronously
await doSomethingInTheBackground();
WaitForPreviousLineToFinishThenDoSomething();
async function doSomethingInTheBackground(callback){
// do stuff
}js-overview
By Mujtaba Al-Tameemi
js-overview
- 415



