Ansible
An introduction to configuration and state management
How to Navigate Through this Presentation
- Space to progress incrementally
- Arrow keys to navigate
- Alt + Click to zoom in on a slide (Again to zoom out)
- Orange text is a link

Building Information
Important stuff like bathrooms/emergency exits and meeting points for anyone that hasn't visited before.
What we'll cover
- What is Ansible
- Foundation principals (building blocks)
- Making it work (Playbooks and Modules)
- Making it right (Refactoring)
- Troubleshooting and Validation
- Real World Examples (Time Allowing)
Questions!

What Is Ansible
Configuration Management
Stores the state of infrastructure as code.
- Reproducible
- Reduces Human Error
- Easier to find issues (peer review/automated testing/static analysis)
- Auditing (Who/What/When/Where)


Why not just use a script?
- Cross Platform
- Automation ready
- Templating and Variables
- Modular and Reusable
- Idempotence (State management)
- "Intuitive"

Why Ansible?
Ansible vs. other CM tools
Positives:
- Agentless
- SSH as connection protocol
- Playbooks can be run from anywhere, not just the "Master" server/s
- "Batteries Included"
Negatives:
- Performance on large scale
- Windows not supported as control.



Environment Setup
Topology
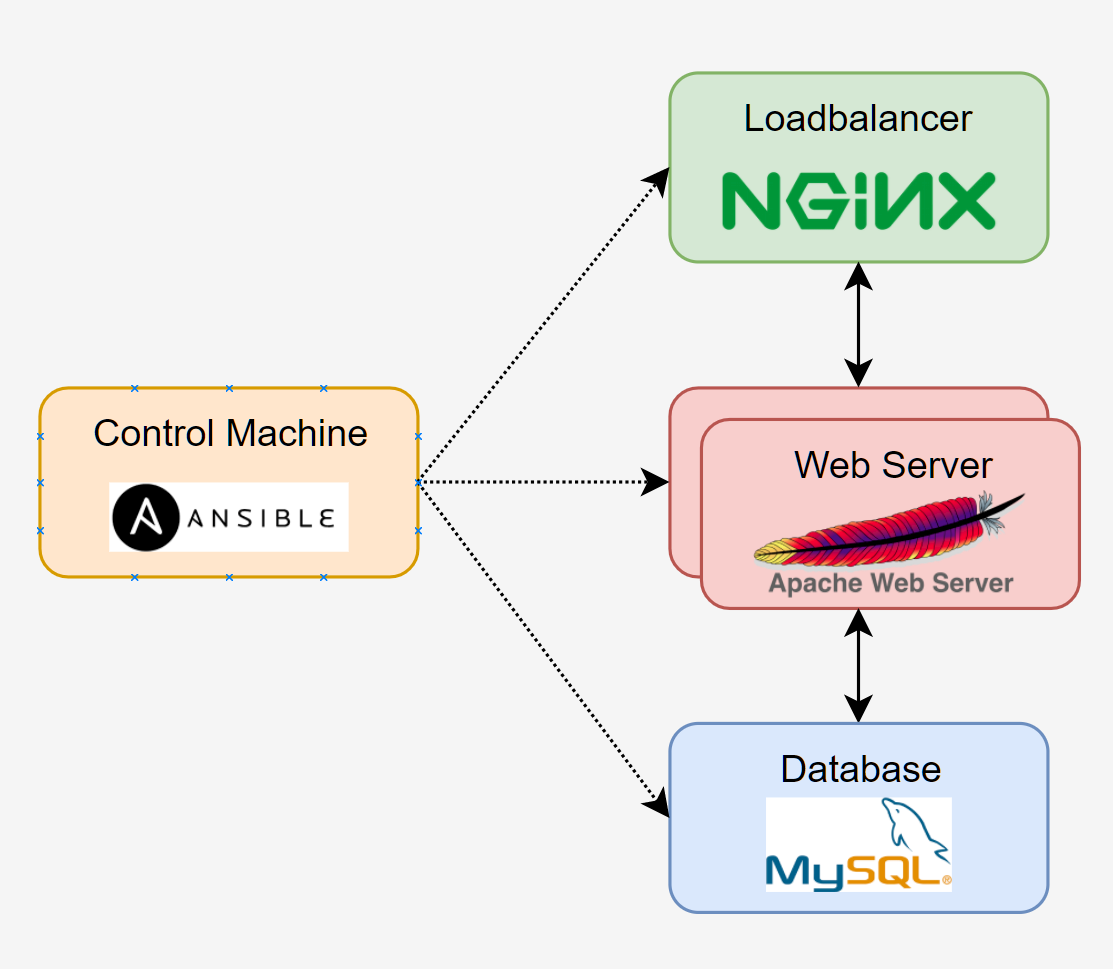
Control Machine Setup
- Installation via most package managers
- Also available via python-pip
- Windows as a control machine is not supported (except via Docker)
pip install ansible
Installation on Ubuntu
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
sudo apt-add-repository --yes --update ppa:ansible/ansible
sudo apt-get install ansible -y
ansible --version # Should be > 2.9Remote Host Setup
ssh-keygen -f $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa -t rsa -b 4096 -N ""
ssh-copy-id $REMOTE_HOST
ssh $REMOTE_HOST- Ansible requires SSH access to remote hosts
- Can be password/less
- Possible to run in pull-mode
- Requires "python-simplejson" package installed
ansible all -b -K -m raw -a "apt-get install -y python-simplejson"The Basics
Before we dive in
Ansible's configuration lives in "/etc/ansible".

sudo chown -R training:training /etc/ansibleIn order to change files in this directory, we need to have permissions to do so
Inventory
- /etc/ansible/hosts
- Where we define the hosts we want to work on
- Can be static or dynamic
- Comprised of groups of entries of hostnames
- Can be in INI or YAML format
- Can also include extra detail if needed
ansible --list-hosts allHosts File Layout
- One host per line
- Either hostname or IP
- Can be grouped with a header in square brackets
[loadbalancer]
john-proxy01
[webserver]
john-web01
john-web02
[database]
john-database01
[control]
john-control01More Hosts File Config
- Parent/Children Relationships
[demo_app:children]
loadbalancer
webserver
databaseVariables
[control]
john-control01 ansible_connection=local[loadbalancer]
johns-proxy01 # Is the same as
johns-proxy01.$DOMAIN # Is also the same as
192.168.0.10 # Is also the same as
some_stupid_hostname ansible_host=johns-proxy01Referencing groups
- Default groups (all/ungrouped)
- Globbing works too!
- Reference your groups
- Individual hosts
- Multiple groups
- Indexing
- Negation
ansible --list-hosts allansible --list-hosts "*"ansible --list-hosts controlansible --list-hosts john-proxy01ansible --list-hosts control,webserveransible --list-hosts webserver[0]ansible --list-hosts \!controlAd-hoc Commands
- Simple commands that complete a single action
- Great to learn how Ansible works
- Also for commands that don't need to run twice
- There is usually a better way (playbooks)
ansible all -m ping
ansible all -m command -a "hostname" # Is the same as
ansible all -a "hostname"
ansible all -a "/bin/false"ansible $HOSTS -m $MODULE -a $MODULE_ARGUMENTSMore on Ad-Hoc
- More options are available
ansible control -b -K -m copy -a \
"dest=/etc/sudoers.d/sudo_nopasswd mode=0660 \
content='%sudo ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL' validate='visudo -cf %s'"
ansible all -b -m pingansible control -m copy -a "dest=/tmp/foo content=''" -C
ansible control -m copy -a "dest=/tmp/foo content=''"
ansible control -m copy -a "dest=/tmp/foo content=''"
ansible control -m ping -b- Let's fix that

The Playbook
What are Playbooks?
- The meat of Ansible!
- Everything is either in or referenced by a playbook
- Usually live in /etc/ansible/playbooks
- A way to group and order tasks
- Written in YAML
- Consists of the target hosts and the tasks you would like to run against those hosts.

YAML?
- File optionally starts with "---" and ends with "..."
- Consists of (In Ansible) dictionaries and lists
Lists with '-'
- 2 spaces on each new line
Dictionaries are denoted with ':'
---
Fruits:
- Apple
- Banana
- Pear---
Key: Value---
foo: "{{ variable }}"Variables like '"{{ }}"'
My First Playbook
mkdir playbooks
vim playbooks/hostname.ymlansible-playbook playbooks/hostname.yml---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Print server hostname
command: hostnameansible all -a "hostname"

Static Checks
- "--syntax-check" checks a YAML file for compatibility with Ansible
- Doesn't run the playbook
- Great for use in CI testing
ansible-playbook playbooks/hostname.yml --syntax-checkMake It Work
But How?
As we write a playbook to provision each application, we'll approach it in 4 steps:
- Packages
- Service Management
- System Configuration
- Application Configuration
And at each step, we'll approach it in the same way:
- Pick a module
- Find what arguments it needs
- Try it!

Anatomy of a Module
Lets take a look at the 'apt' module as an example:
- Synopsis
- System Requirements
- Options
- Name
- Required?
- Default?
- Choices
- Comments
- Examples
Packages - apt
---
- hosts: loadbalancer
tasks:
- name: Install nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: presentplaybooks/loadbalancer.yml
---
- hosts: database
tasks:
- name: Install mysql-server
apt:
name: mysql-server
state: presentplaybooks/database.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/loadbalancer.ymlBecome
playbooks/loadbalancer.yml
playbooks/database.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/loadbalancer.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/database.yml---
- hosts: loadbalancer
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: present---
- hosts: database
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install mysql-server
apt:
name: mysql-server
state: present
loop
playbooks/webserver.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/webserver.yml---
- hosts: webserver
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install apache2
apt:
name: apache2
state: present---
- hosts: webserver
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install apache2
apt:
name: apache2
state: present
- name: Install libapache2-mod-wsgi
apt:
name: libapache2-mod-wsgi
state: present
- name: Install python-pip
apt:
name: python-pip
state: present
- name: Install python-virtualenv
apt:
name: python-virtualenv
state: present
- name: Install python-mysqldb
apt:
name: python-mysqldb
state: present---
- hosts: webserver
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install web server packages
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- apache2
- libapache2-mod-wsgi
- python-pip
- python-virtualenv
- python-mysqldb
- virtualenvServices
playbooks/loadbalancer.yml
---
- hosts: loadbalancer
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: present---
- hosts: loadbalancer
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Ensure nginx service is started
service:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yesansible-playbook playbooks/loadbalancer.ymlwget -qO- http://johns-proxy01curl Is Better
playbooks/control.yml
---
- hosts: control
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install curl
apt:
name: curl
state: presentansible-playbook playbooks/control.ymlcurl http://johns-proxy01Give this a go:
- Create a "control" playbook, which will apply to your ansible (local) machine.
- In this playbook, include a task to install the package "curl".
Finishing Services
playbooks/webserver.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/database.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/webserver.yml---
- hosts: webserver
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install web server packages
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- apache2
- libapache2-mod-wsgi
- python-pip
- python-virtualenv
- name: Ensure apache2 service is started
service:
name: apache2
state: started
enabled: yes---
- hosts: database
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install mysql-server
apt:
name: mysql-server
state: present
- name: Ensure mysql service is started
service:
name: mysql
state: started
enabled: yesplaybooks/database.yml
curl http://johns-web01
curl http://johns-web02Apache2 Module
playbooks/webserver.yml
---
- hosts: webserver
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install web server packages
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- apache2
- libapache2-mod-wsgi
- python-pip
- python-virtualenv
- name: Ensure apache2 service is started
service:
name: apache2
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Ensure mod-wsgi module is enabled
apache2_module:
name: wsgi
state: presentHandlers
playbooks/webserver.yml
tasks:
- name: Ensure mod-wsgi module is enabled
apache2_module:
name: wsgi
state: present
handlers:
- name: Restart apache2
service:
name: apache2
state: restarted tasks:
- name: Ensure mod-wsgi module is enabled
apache2_module:
name: wsgi
state: present
notify: Restart apache2
handlers:
- name: Restart apache2
service:
name: apache2
state: restartedansible-playbook playbooks/webserver.ymlPrepare Files
mkdir -p demo/appdemo/app/demo.wsgi
activate_this = '/var/www/demo/.venv/bin/activate_this.py'
execfile(activate_this, dict(__file__=activate_this))
import os
os.environ['DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql://demo:demo@$IP_ADDRESS/demo'
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, '/var/www/demo')
from demo import app as applicationdemo/demo.conf
<VirtualHost *>
WSGIDaemonProcess demo threads=5
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/demo/demo.wsgi
<Directory /var/www/demo>
WSGIProcessGroup demo
WSGIApplicationGroup %{GLOBAL}
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>demo/app/demo.py
from flask import Flask
from flask.ext.sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
import os, socket
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = os.environ['DATABASE_URI']
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
hostname = socket.gethostname()
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'Hello, from sunny %s!\n' % hostname
@app.route('/db')
def dbtest():
try:
db.create_all()
except Exception as e:
return e.message + '\n'
return 'Database Connected from %s!\n' % hostname
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()demo/app/requirements.txt
Flask==0.10.1
Flask-SQLAlchemy==2.0Change the $IP_ADDRESS
Copy
playbooks/webserver.yml
tasks:
- name: Copy demo application source
copy:
src: ../demo/app/
dest: /var/www/demo
mode: 0755
notify: Restart apache2ansible-playbook playbooks/webserver.ymltasks:
- name: Copy demo application source
copy:
src: ../demo/app/
dest: /var/www/demo
mode: 0755
notify: Restart apache2
- name: Copy apache2 virtualhost configuration
copy:
src: ../demo/demo.conf
dest: /etc/apache2/sites-available
mode: 0755
notify: Restart apache2
pip
playbooks/webserver.yml
tasks:
- name: Install python-pip dependencies
pip:
requirements: /var/www/demo/requirements.txt
virtualenv: /var/www/demo/.venv
notify: Restart apache2ansible-playbook playbooks/webserver.ymlFile
playbooks/webserver.yml
tasks:
- name: De-activate default apache site
file:
path: /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
state: absent
notify: Restart apache2
- name: Activate demo apache site
file:
src: /etc/apache2/sites-available/demo.conf
dest: /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/demo.conf
state: link
notify: Restart apache2ansible-playbook playbooks/webserver.ymlcurl http://johns-web01
curl http://johns-web02curl http://johns-proxy01Jinja2 Templates
templates/nginx.conf.j2
mkdir templates
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2upstream demo {
server johns-web01;
server johns-web02;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://demo;
}
}upstream demo {
{# Enter a server line for each host in the webservers group in Ansible #}
{% for server in groups.webserver %}
server {{ server }};
{% endfor %}
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://demo;
}
}
Template Module
playbooks/loadbalancer.yml
---
tasks:
- name: Configure nginx site
template:
src: ../templates/nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
mode: 0644
notify: Restart nginx
- name: De-activate default nginx site
file:
path: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
state: absent
notify: Restart nginx
- name: Activate demo nginx site
file:
src: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/demo
state: link
notify: Restart nginx
handlers:
- name: Restart nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restartedansible-playbook playbooks/loadbalancer.ymlcurl http://johns-proxy01
#Run it a couple times!---
tasks:
- name: Configure nginx site
template:
src: ../templates/nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
mode: 0644
notify: Restart nginx
- name: De-activate default nginx site
file:
path: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
state: absent
notify: Restart nginx
- name: Activate demo nginx site
file:
src: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/demo
state: link
notify: Restart nginx
handlers:
- name: Restart nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restartedlineinfile
playbooks/database.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/database.ymltasks:
- name: Ensure mysql is listening on all addresses
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
regexp: "^bind-address"
line: "bind-address = 0.0.0.0"
notify: Restart mysql
handlers:
- name: Restart mysql
service:
name: mysql
state: restartedssh -t johns-database01 "grep -R bind-address /etc/mysql"curl http://johns-app01/dbcurl http://johns-proxy01/dbmysql_db
playbooks/database.yml
ansible-playbook playbooks/database.yml---
- hosts: database
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install mysql-server
apt:
name: mysql-server
state: present
update_cache: yes---
- hosts: database
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install packages
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
update_cache: yes
loop:
- mysql-server
- python-mysqldbGive this a go:
- Modify the apt task in the database playbook to include the package "python-mysqldb" in the form of a loop.
- name: Create demo database
mysql_db:
name: demo
state: present
- name: Create demo user
mysql_user:
name: demo
password: demo
priv: demo.*:ALL
host: '%'
state: present
curl http://johns-proxy01/dbIt Lives!
Make It Right
What's Not Right?
- One playbook for each tier
- Playbooks specific to our site
- What if another team wants to use our code?
- How much code could they use for their site?
- What about different port numbers?
- How many teams do you have?
- What if a vulnerability needs fixing for all teams?
Roles
- A role is a folder structure where we function specific
- Tasks
- Handlers
- Files
- Templates
- /etc/ansible/roles/$ROLE
- Compose our infrastructure as a collection of roles
- Allows for easier code reuse
- Know where to look to make a change/fix an issue
Creating Roles - galaxy init
ansible-galaxy init roles/control
ansible-galaxy init roles/nginxGive this a go:
- Create skeleton roles for the rest of the infrastructure
ansible-galaxy init roles/control
ansible-galaxy init roles/nginx
ansible-galaxy init roles/apache2
ansible-galaxy init roles/mysql
ansible-galaxy init roles/demo_appImporting Roles - Tasks
roles/control/tasks/main.yml
---
- name: Install curl
apt:
name: curl
state: presentplaybooks/control.yml
---
- hosts: control
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install curl
apt:
name: curl
state: present---
- hosts: control
become: true
roles:
- controlImporting Roles - Handlers
roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml
playbooks/database.yml
---
- hosts: database
become: true
roles:
- mysql---
- hosts: database
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install packages
...
handlers:
- name: Restart mysql
service:
name: mysql
state: restartedroles/mysql/handlers/main.yml
---
- name: Restart mysql
service:
name: mysql
state: restarted---
- name: Install packages
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- mysql-server
- python-mysqldb
- name: Ensure mysql is listening on all addresses
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
regexp: "^bind-address"
line: "bind-address = 0.0.0.0"
notify: Restart mysql
- name: Ensure mysql service is started
service:
name: mysql
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Create demo database
mysql_db:
name: demo
state: present
- name: Create demo user
mysql_user:
name: demo
password: demo
priv: demo.*:ALL
host: '%'
state: presentnginx Role
roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
---
- name: Install nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Configure nginx site
template:
src: templates/nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
mode: 0644
notify: Restart nginx
- name: De-activate default nginx site
file:
path: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
state: absent
notify: Restart nginx
- name: Activate demo nginx site
file:
src: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/demo
state: link
notify: Restart nginx
- name: Ensure nginx service is started
service:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yesplaybooks/loadbalancer.yml
---
- hosts: loadbalancer
become: true
roles:
- nginxroles/nginx/handlers/main.yml
---
- name: Restart nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restartedGive this a go:
- Import the loadbalancer playbook into a role
- Modify the playbook file to include the new role
Importing Roles - Templates
roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: Configure nginx site
template:
src: ../templates/nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
mode: 0644
notify: Restart nginx- name: Configure nginx site
template:
src: nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
mode: 0644
notify: Restart nginxmv templates/nginx.conf.j2 roles/nginx/templatesapache2 Role
roles/apache2/tasks/main.yml
roles/demo_app/tasks/main.yml
- name: Install web server packages
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- libapache2-mod-wsgi
- python-pip
- python-virtualenv- name: Install web server packages
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- apache2- name: Ensure apache2 service is started
service:
name: apache2
state: started
enabled: yes- name: Ensure mod-wsgi module is enabled
apache2_module:
name: wsgi
state: present
notify: Restart apache2- name: Copy demo application source
copy:
src: demo/app/
dest: /var/www/demo
mode: 0755
notify: Restart apache2
- name: Copy apache2 virtualhost configuration
copy:
src: demo/demo.conf
dest: /etc/apache2/sites-available
mode: 0755
notify: Restart apache2
- name: Install python-pip dependencies
pip:
requirements: /var/www/demo/requirements.txt
virtualenv: /var/www/demo/.venv
notify: Restart apache2- name: Activate demo apache site
file:
src: /etc/apache2/sites-available/demo.conf
dest: /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/demo.conf
state: link
notify: Restart apache2- name: De-activate default apache site
file:
path: /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
state: absent
notify: Restart apache2apache2 Role Continued
playbooks/webserver.yml
---
- hosts: webserver
become: true
roles:
- apache2
- demo_approles/apache2/handlers/main.yml
---
- name: Restart apache2
service:
name: apache2
state: restartedroles/demo_app/handlers/main.yml
---
- name: Restart apache2
service:
name: apache2
state: restartedImporting Roles - Files
mv demo/* roles/demo_app/filesroles/demo_app/tasks/main.yml
- name: Copy demo application source
copy:
src: app/
dest: /var/www/demo
mode: 0755
notify: Restart apache2
- name: Copy apache2 virtualhost configuration
copy:
src: demo.conf
dest: /etc/apache2/sites-available
mode: 0755
notify: Restart apache2Site Playbook - Include
playbooks/site.yml
---
- hosts: control
become: true
roles:
- control
- hosts: database
become: true
roles:
- mysql
- hosts: loadbalancer
become: true
roles:
- nginx
- hosts: webserver
become: true
roles:
- apache2
- demo_appansible-playbook playbooks/site.yml---
- import_playbook: database.yml
- import_playbook: webserver.yml
- import_playbook: loadbalancer.ymlRefactoring with Variables
Facts
roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml
- name: Ensure mysql is listening on all addresses
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/mysql/my.cnf
regexp: "^bind-address"
line: "bind-address = 0.0.0.0"
notify: Restart mysqlansible -m setup john-database01ansible-playbook playbooks/database.yml- name: Ensure mysql is listening on all addresses
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/mysql/my.cnf
regexp: "^bind-address"
line: "bind-address = {{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}"
notify: Restart mysql
Role Defaults
roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml
- name: Create demo database
mysql_db:
name: demo
state: present
- name: Create demo user
mysql_user:
name: demo
password: demo
priv: demo.*:ALL host='%'
state: present- name: Create database
mysql_db:
name: demo
state: present
- name: Create user
mysql_user:
name: demo
password: demo
priv: demo.*:ALL host='%'
state: present- name: Create database
mysql_db:
name: "{{ db_name }}"
state: present
- name: Create user
mysql_user:
name: demo
password: demo
priv: "{{ db_name }}.*:ALL host='%'"
state: present- name: Create database
mysql_db:
name: "{{ db_name }}"
state: present
- name: Create user
mysql_user:
name: "{{ db_user }}"
password: "{{ db_password }}"
priv: "{{ db_name }}.*:ALL"
host: "{{ db_host }}"
state: presentroles/mysql/defaults/main.yml
---
db_name: mydb
db_user: mydbuser
db_password: mydbpass
db_host: mydbhostgroup_vars
ansible-playbook playbooks/database.ymlgroup_vars/all/vars.yml
---
db_name: demo
db_user: demo
db_password: demo
db_host: "%"mkdir -p group_vars/all
vim group_vars/all/vars.ymlgroup_vars - Continued
group_vars/all/vars.yml
---
db_name: demo
db_user: demo
db_password: demo
db_host: "%"
site_name: demoGive this a go:
- Replace the references to our site "demo" in the loadbalancer role with a variable:
- Three references in the tasks file
- Two references in the template
- You can call the variable whatever you want to!
- Remember to add definitions for this variable in group_vars
upstream {{ site_name }} {
{% for server in groups.webserver %}
server {{ server }};
{% endfor %}
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://{{ site_name }};
}
}- name: Configure demo nginx site
template:
src: nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
mode: 0644
notify: Restart nginx
- name: De-activate default nginx site
file:
path: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
state: absent
notify: Restart nginx
- name: Activate demo nginx site
file:
src: /etc/nginx/sites-available/demo
dest: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/demo
state: link
notify: Restart nginxroles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: Configure nginx site
template:
src: nginx.conf.j2
dest: "/etc/nginx/sites-available/{{ site_name }}"
mode: 0644
notify: Restart nginx
- name: De-activate default nginx site
file:
path: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
state: absent
notify: Restart nginx
- name: Activate nginx site
file:
src: "/etc/nginx/sites-available/{{ site_name }}"
dest: "/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/{{ site_name }}"
state: link
notify: Restart nginxroles/nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
upstream demo {
{% for server in groups.webserver %}
server {{ server }};
{% endfor %}
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://demo;
}
}ansible-vault
ansible-vault create group_vars/all/vault.ymlgroup_vars/all/vault.yml
...
vault_password_file = ~/.ansible/.vault_password_file
...~/.ansible_vault_password
really_super_secure_password_hereansible.cfg
---
vault_db_password: demogroup_vars/all/vars.yml
---
db_name: demo
db_user: demo
db_password: "{{ vault_db_password }}"
db_host: "%"
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
--check (-C)/--diff (-D)
- "--check" does a dry run of the playbook (doesn't change anything).
- Great for continuous integration checks before merging new code into master branch
- "--diff" shows the difference in the configuration
- Most effective when used with --check
--verbose (-v)
ansible-playbook playbooks/control.yml -vvvv- Simply shows more verbose output of the tasks as they are run.
- More verbose output can be requested by adding extra "v" characters:
- "-v" shows stdout and stderr
- "-vv" does the same as -v (?)
- "-vvv" shows the commands run by Ansible
- "-vvvv" shows connection debugging
We're all done!

We're all done!
Extra Topics
- Ansible Galaxy
- Real world examples
Time Allowing
Ansible
By mwadman
Ansible
An introduction to configuration and state management using Ansible.
- 1,159