Basic GUI programming. Listviews & Adapters.

Quick Review
-
What is Log and what are the available priorities?
-
What is a breakpoint? What can you do with it?
-
Some activity lifecycle methods are ... ?
-
What is an intent? What has an intent?
-
What is an intent-filter?
-
How is Android matching the intents?

Basic GUI programming
Components in Android
How can you create a component?
Programmatically
XML
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />new TextView(
new LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT,
MATCH_PARENT))Components attributes
Important
- layout_width - required
- layout_height - required
- layout_<something> - defines layout properties
- ID - referenced as int
- @ - to expand the rest of the string and identify it as a resource
- + means that it is a new resource and must be created
-
android has built-in ids-
@android:id/empty
- gravity vs. layout_gravity - inside vs. outside
Layout Params (layout_<something>)
wrap_content vs match_parent
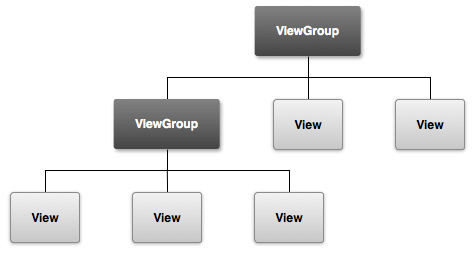
What is a View?
A view has a location (top and left coordinates) and dimensions (width and height).
View Dimensions
- dp - Density-independent Pixels - An abstract unit that is based on the physical density of the screen.
- sp - Scale-independent Pixels - This is like the dp unit, but it is also scaled by the user's font size preference.
- pt
- px
- mm
- in
Containers


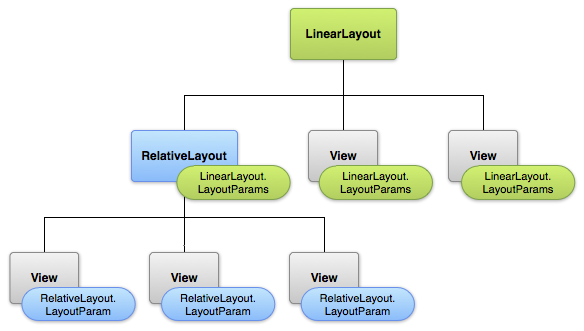
LinearLayout
RelativeLayout

WebView
FrameLayout
Linear vs Relative
+ layout_weight
+ vertical/horizontal
+ faster performance
- low flexibility
+ great flexibility
+ overlay with ease
+ support for different screens
- lots of ids declaration
- slow performance


Input controls
Buttons

EditText
Checkboxes
Toggle

Radio
Spinner
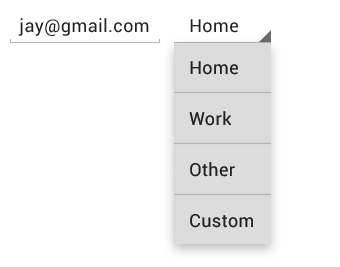
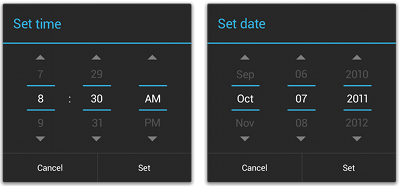
Pickers
Something more about controls
- inputType - phone
- bitwise operations
- imeOptions - actions to be done
- imeLabel
- hint
- AutoCompleteTextView
EditText
ToggleButton
- onCheckedChangeListener
- onToggleListener
Toast - another way for debugging
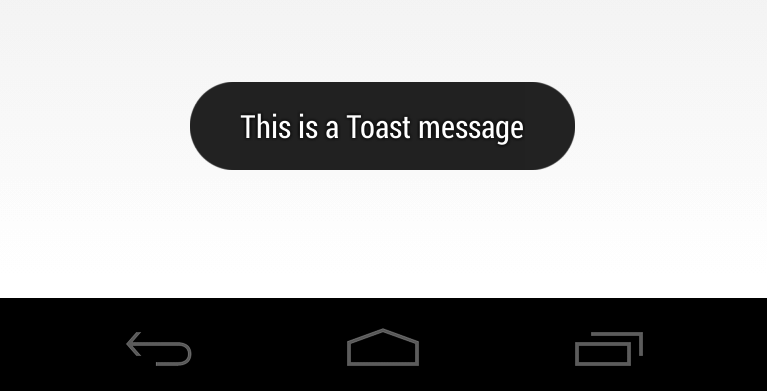
new Toast(context, "Test", Toast.LENGHT_SHORT)
.show()Let's code!

Break (10 mins)

ListViews & Adapters

What is a ListView?
-
Sublclass of AdapterView - populate the layout with views at runtime.
-
Needs an Adapter to populate the components
-
The adapter is a middleman between the data source and the AdapterView layout - it adapts the data and creates each listview entry
ArrayAdapter
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, myStringArray);- Context
- XML layout for a single row
- List of data
To create an adapter you need:
Let's try it!

Custom Adapters
- extend BaseAdapter - SOURCE
- override getView
- override getItem
- override getCount
- override getItemId
Reusing views to get a custom look
Let's try it!

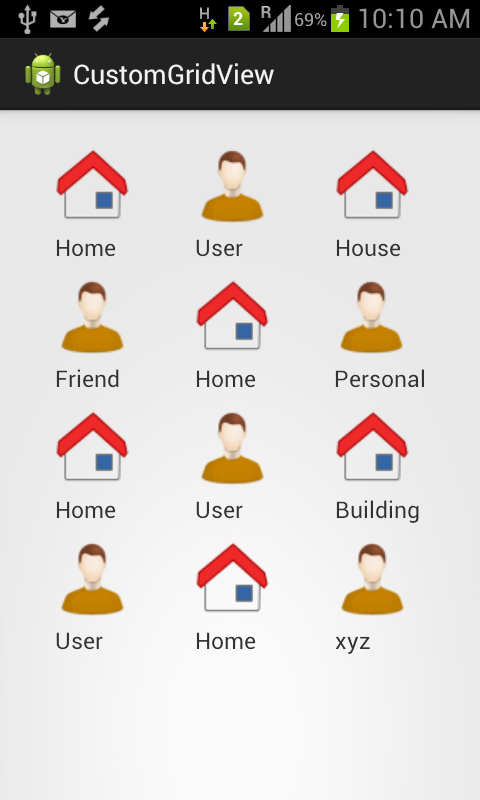
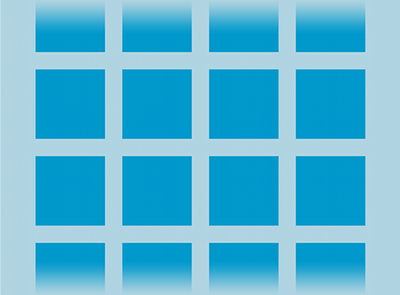
Just replace ListView with GridView
- Determine columns count
- Determine cell size
- More scalable than ListView
- Cells better than rows
- Takes more screen space
Let's try it!

Summary
-
What is a View and ViewGroup?
-
How can you create components?
-
Layout attributes
-
Containers and input controls
-
What are different dimensions (dp vs px vs pt ...)?
-
What is a ListView?
-
What is an adapter?
-
What is a GridView?


Lecture 11 - Basic GUI
By naughtyspirit
Lecture 11 - Basic GUI
- 461