Methods & Conditionals
What if...
Quick reminder
-
What is Java & Android Studio?
-
What is a variable? A variable has... ?
-
Variable data types in Java?
-
"4.0" + "4.0" = ? "4" + '4' ?
- int a = "4.0" + 4? String a = "4.0" + 4?

Weekly test time

Today's content
- Projects
- What are conditionals?
- The If operator
- Comparison & Boolean operators
- IF & Else & Else If
- The switch operator
- What are methods?
- Methods structure
- Summary
Projects for this week


Math Wars
Spaceship Commander
Lecture Project
Homework Project

Conditionals
IF operator
boolean isLectureDay = true;
if(isLectureDay == true) {
goToLecture();
writeSomeCode();
}if(CONDITION) {
STATEMENT1;
STATEMENT2;
...
STATEMENTN;
}Comparison operators
x > y: x is greater than y
x < y: x is less than y
int a = 10;
if(a = 10) {
// "=" Really !?
}if("Test" == "Test") { // !?
// "Test".equals("Test")
}
x >= y: x is greater than or equal to x
x <= y: x is less than or equal to y
x == y: x equals y
Boolean operators
&&: logical AND
||: logical OR
boolean isProgrammerAtHome = true;
int workingHours = 3;
if(isProgrammerAtHome) {
if(workingHours < 8) {
// You are fired :(
}
}boolean isProgrammerAtHome = true;
int workingHours = 3;
if(isProgrammerAtHome && workingHours < 8) {
// You are fired :(
}IF & ELSE
boolean isProgrammerHome = true,
shouldFireProgrammer = false;
if(!isProgrammerHome) {
System.out.println("WORK HARDER!");
} else {
shouldFireProgrammer = true;
}if(CONDITION) {
STATEMENT1;
} else {
STATEMENT2;
}IF & ELSE IF
if (CONDITION) {
STATEMENTS
} else if (CONDITION) {
STATEMENTS
} else if (CONDITION) {
STATEMENTS
} else {
STATEMENTS
}boolean isProgrammerAtHome = false;
int workingHours = 8;
if(isProgrammerAtHome) {
// Fire
} else if(workingHours < 8) {
// Fire
} else {
// WORK HARDER!
}
SWITCH
int workingHours = 8;
// Default value is ...?
boolean shouldReceiveBonus;
switch(workingHours) {
case 8:
shouldReceiveBonus = true;
break;
case 9:
shouldReceiveBonus = true;
break;
default:
shouldReceiveBonus = false;
}int workingHours = 8;
boolean shouldReceiveBonus;
switch(workingHours) {
case 8:
case 9:
shouldReceiveBonus = true;
break;
default:
shouldReceiveBonus = false;
}switch(CONDITION) {
case CONDITION1:
break;
case CONDITIONN:
break;
default:
}switch(1) {
case 1:
print("No break !?")
case 2:
print("I am leaving")
}
// Result:
// No break !?
// I am leavingTask time
Questions?

Break (10 mins)

Methods (Functions)
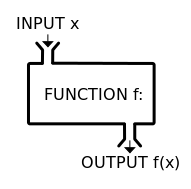
- A subprogram - a set of code
- Must have return type
- May or may not have input
- May or may not return result
- Can be called by name
When the method execution is finished the program returns to the area of the code from which it was called and continues on to the next line of code.
What is the function of a bread bakery?


Input?
Method signature
public static void NAME() {
STATEMENTS;
}
private static void makeBread() {
print("Your bread is ready, sir!");
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
// Call method
makeBread();
}Parameters
public static void method(TYPE NAME) {
STATEMENTS;
}
private static void makeBread(int flourAmount) {
print("Your bread with " + flourAmount +
"kg of flour is ready, sir!");
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
makeBread(5);
}Multiple Parameters
public static void NAME(TYPE NAME, TYPE NAME) {
STATEMENTS;
}
private static void makeBread(int flourAmount, int waterAmount) {
print("Your bread with " + flourAmount + "kg of flour and "
+ waterAmount + "L of water is ready, sir!");
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
makeBread(5, 2);
}Return Values
public static TYPE NAME() {
STATEMENTS
return EXPRESSION;
}void is the word for "no type"
void a = ""; // !?Methods example
public static int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
public static int pow(int number, int degree) {
int result = 0;
switch(degree) {
case 2:
result = multiply(number, number);
break;
case 3:
result = multiply(multiply(number, number),
number);
break;
}
return result;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
print(pow(2, 3));
}Methods Summary
-
They are a block of code
- Programs are built of small methods
- Methods can be reused and tested individually
- Keeping methods small will make your life better
- The caller of the method does not need to know how it works
- This is called "abstraction"
Math Wars 2
Questions?
Summary
- Conditional operators evaluate an expression to tell if it is true or false
- Use if-else-elseif when you don't have many conditions
- Use switch if you have more than 4 or 5 conditions
- Use comparison operators to skip or shorten conditional ones
- A method is a set of code
- Methods may have return type and input params
- Keep methods small and simple
- Methods create a reusable code abstraction
Daily reminder test
Thank you :)
Lecture 3 - Methods and Conditionals
By naughtyspirit
Lecture 3 - Methods and Conditionals
- 418



