MVC
Model-View-Controller
An architectural pattern that splits applications into sections each of which have a unique purpose.
Overview
Model
Models determine how data is structured in a database.
View
Views are what the user sees and can interact with
Controller
Controllers listen for requests, interact with the models, request appropriate views and respond with those views to the client.
In web apps, we add some extra pieces.
Router
Routers listen for user requests and send them to the appropriate controller.
Database
The database stores data our models define. They interact with the models.
What does it all look like?
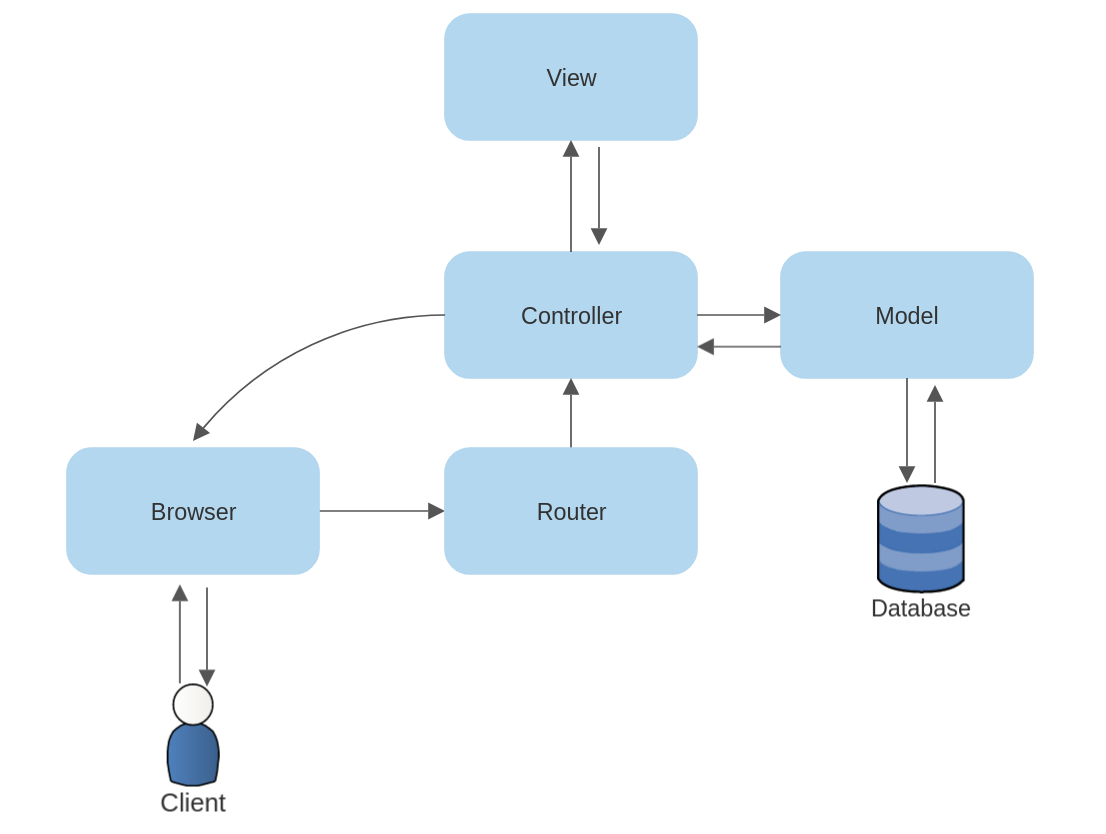
- The user interacts with their browser to send a request to the server
- The router examines the request and directs it to the appropriate controller
- The controller handles the request. Often this involves handing it off to a model. Suppose it's a PUT request, the controller waits for a promise to complete...
- The controller calls the model with the data in order to update the information
- The model may validate the information against a Schema to ensure correctness
- The model creates a request to the database to update the information
- The database responds to the model
- The model responds to the controller with any information or in the case of javascript a completed promise
...Then
- The controller continues its process, and assuming the request was successful to redirect the browser to the appropriate page, which will cause a new GET request (see diagram). The GET is made, and the controller receives the data from the model for the GET, it selects a view to render for the GET request.
- The view is rendered
- The page the view generates is returned to the controller, which passes it back to the browser
- The user see the newly rendered page
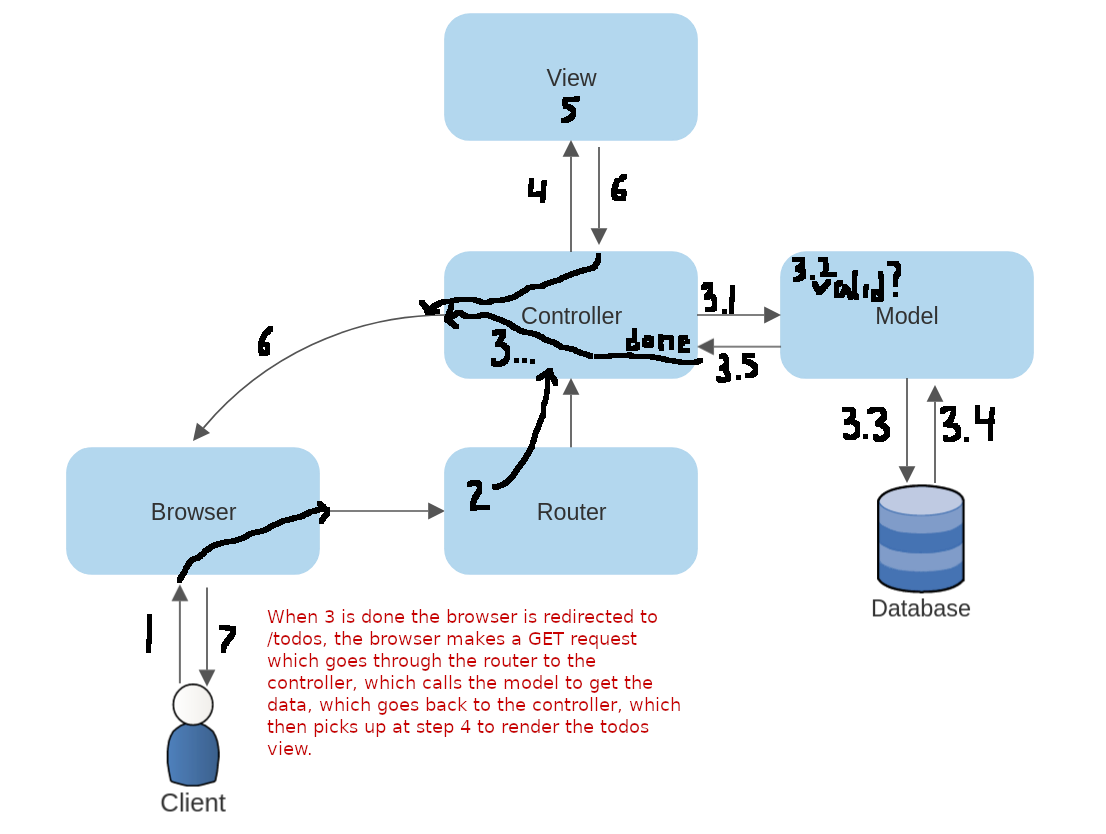
Taking the previous slides and combining them into the image before, we see
const TodoSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
todo: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
completed: {
type: Boolean,
required: true,
},
date: {
type: Date,
required: false,
min: new Date(),
}
})
Mongoose is an Object Data Modeling library which acts as a wrapper over MongoClient that makes working with mongoDB more straightforward by provide schema-based models and validation for programs to work with. It transforms data objects in code into a suitable form for storage as documents in MongoDB.
It provides the model component of the MVC in our MERN app.
What does an MVC implementation in MERN look like?
Inside the project Root
- config
- .env
- database.js
- controllers
- home.js
- todos.js
- models
- Todo.js
- public
- js -> main.js
- css -> style.css
- routes
- home.js
- todos.js
- views
- index.ejs
- todos.ejs
- package-lock.json
- package.json
- server.js
The MVC architecture allows developers to quickly locate pertinent sections of code, swap out different implementations of components with minimal impact on other parts of the code.
For example, suppose you want to use a relational database instead of a non-relational one. Just change the implementation of the model to use the new relational database and everything else still works.
MVC is scalable, speeds up development through coherent organization, and supports multiple methods of displaying or interacting with the app.
MVC slides
By Ned Park
MVC slides
- 203