ReactJS

A JAVASCRIPT LIBRARY FOR BUILDING USER INTERFACES
MVC
ReactJS is the View in MVC
Virtual DOM for high performance
Data flow is one-way
*Typically paired with JSX compiler*
React Components
The simplest component need only include a render() method
/** @jsx React.DOM */ var WelcomeBanner = React.createClass({ render: function() { return(<div>Welcome to our webapp!</div>);} }); React.render(<WelcomeBanner />, document.body);
Without the JSX compilation
var WelcomeBanner = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return React.DOM.div(null, "Welcome to our webapp!");
}
});
React.render(WelcomeBanner({}), document.body);
Less-Static Components
Components have properties
/** @jsx React.DOM */ var WelcomeBanner = React.createClass({ render: function() { return(<div>Welcome to our webapp { this.props.name }!</div>);} }); React.render(<WelcomeBanner name="Nick" />, document.body);
Smarter Components
Components have state
/** @jsx React.DOM */ var WelcomeBanner = React.createClass({ getInitialState: function() { return { times: 0 }; }, handleClick: function() { this.setState({ times: this.state.times + 1 }); }, render: function() { return( <section> <div>Welcome to our webapp { this.props.name }!</div> <div>Times clicked: { this.state.times }</div> <button onClick={ this.handleClick }>Add One</button> </section> ); } });React.render(<WelcomeBanner name="Nick" />, document.body);
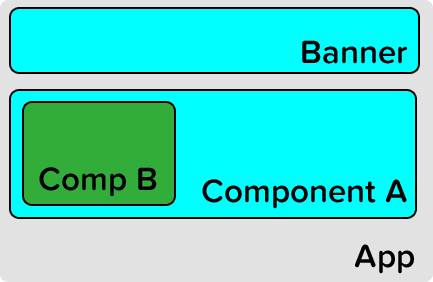
Component Hierarchies
-
ReactJS supports complex component hierarchies.
-
Applications can be built from a single app component down.
-
Or you can place components wherever they are needed.
Use Components Like HTML
/** @jsx React.DOM */ var WelcomeBanner = React.createClass({ render: function() { return(<section> <div>Welcome to our webapp { this.props.name }!</div> <Adder /> </section>); } }); var Adder = React.createClass({ // getInitialState, addOne methods render: function() { return( <article> <div>Current click count: { this.state.count }</div> <button onClick={this.addOne}>Add One</button> </article> ); } });React.render(<WelcomeBanner />, document.body);
Virtual DOM = Speed
-
ReactJS uses a virtual DOM for fast updates.
-
Components are re-rendered top-down from point of change
-
Updates are triggered by:
-
State update
- Properties update
- Forced update
Data Flow
-
Data can flow 2-ways.
- From parent components to children through props
- From child components to parent through callbacks
Component Properties
-
JavaScript is Duck Typed
-
Component properties tend to be of
one
data type
- ReactJS supports property validation
var Adder = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
attr1: React.PropTypes.string,
attr2: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired
},
// Rest of React code (render())
});Default Property Values
For optional properties, we can assign default values.
var MyComp = React.createClass({
getDefaultProps: function() {
return {
attr1: 5,
attr2: true
};
},
// Rest of React code
});Transfer Properties
-
ReactJS components are HTML components
-
Some properties may be HTML properties
-
To pass properties set on a React component, use transferProps()
var MyComp = React.createClass({
render: function() {
this.transferPropsTo(<div>DIV gets the properties set on MyComp</div>);
}
});Children Elements
In HTML elements are not always single components.
Some components provide purely layout & style functionality
Nested components can be accessed from this.props.children
<MyGrid cols="4"> <Gravatar email={ this.userEmail } /> <Gravatar email={ this.theirEmail } /> <Gravatar email={ this.thatEmail } /> </MyGrid>
// MyGrid render function
render: function() {
var computedChildren = myCustomProcess(this.props.children);
return (
<div class="row">
{ computedChildren }
</div>
);
}
Component Lifecycle
- ReactJS components have life
- We can tap into these by creating the methods
There are three stages to a component's lifecycle
- Mounting
- Updating
- Unmounting
Component Mounting
getInitialState()
componentWillMount() - before mounting occurs
componentDidMount() - after mounting occurs (DOM available)
var MyComp = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function() {
// return initial state object
},
componentWillMount: function() {
// any setup logic we have
},
componentDidMount: function() {
// post mount logic, manipulating dom, etc..
}
});Component Updating
componentWillReceiveProps(object nextProps)
shouldComponentUpdate(object nextProps, object nextState) : boolean
componentWillUpdate(object nextProps, object nextState)
componentDidUpdate(object prevProps, object prevState)
Cannot call setState from componentWillUpdate
Component Unmounting
componentWillUnmount()
There is no componentDidUnmount because it will have been destroyed
Mixins
-
ReactJS uses Mixins to share common functionality
-
Mixins' code does not overwrite component's code
var LoggerMixin = {
componentWillMount: function() { console.log("Component mounting"); },
componentWillUnmount: function() { console.log("Component unmounting"); }
};
var MyComp = React.createClass({
mixins: [LoggerMixin],
componentWillMount: function() {
// Both lifecycle methods will be called
},
render: function() {
return(<div>Render something</div>);
}
});LinkValue
Markdown?
Other Neat Features
- React provides a refs property to refer actual DOM elements
- Supports animations with an addon using the .enter .leave paradigm
- Supports testing, simulated events, and mock components
ReactJS
By Nick Ferraro
ReactJS
An introduction to ReactJS
- 877
