Unit Testing
I don't have time to write tests because I am too busy
Types of software testing
- Unit Testing (do the parts perform correctly alone?)
- Integration Testing (do the parts perform correctly together?)
- User Acceptance Testing (does the system meet the end user's expectations?)
Types of software testing
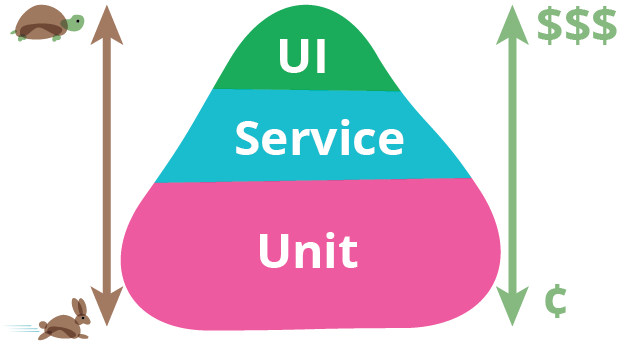
Unit Testing vs Integration Testing
- Unit Testing tests one layer
- Integration Testing tests across layers
Concept of Unit Testing
- A unit test is code that tests as small as possible a piece of functionality (the unit)
- One function may have multiple unit tests according to the usage and outputs of the function
- tests ensure
- the code meets expectations and specifications
- the code continues to meet expectations over time: avoiding regression
- tests are consider as code behavior documentation
Unit Test Best Practices
- Consistent
- Atomic
- Single Responsibility
- Self descriptive
- No conditional logic or loops
- No exception handling
- Informative Assertion messages
Consistent
Multiple runs of the test should consistently return true or consistently return false, provided no changes
Atomic
Only two possible results : PASS or FAIL
No partially successful tests
No side effects between tests
Isolation of tests
- Different execution order must yield same results
- Test B should not depend on outcome of Test A (use mocks instead)
Single Responsibility
One test should be responsible for one scenario only
Test behavior, not methods
- One method, multiple behaviors -> multiple tests
- One behavior, multiple methods -> one test
Self-descriptive
Unit test must be easy to read and understand
- variable, method and class names must be self descriptive
- no conditional logic
- no loops
Name tests to represent PASS conditions:
- canMakeReservation
- totalBillEqualsSumOfMenuItemPrices
<?php
namespace Riskio\SpecificationTest;
use Riskio\Specification\AndSpecification;
use Riskio\SpecificationTest\Fixtures\NotSatisfiedSpecification;
use Riskio\SpecificationTest\Fixtures\SatisfiedSpecification;
class AndSpecificationTest extends \PHPUnit_Framework_TestCase
{
/**
* @test
*/
public function isSatisfiedBy_GivenBothSpecificationsSatisfied_ShouldReturnTrue()
{
$spec = new AndSpecification(
new SatisfiedSpecification(),
new SatisfiedSpecification()
);
$isSatisfied = $spec->isSatisfiedBy('foo');
$this->assertThat($isSatisfied, $this->equalTo(true));
}
/**
* @test
*/
public function isSatisfiedBy_GivenOneSpecificationNotSatisfied_ShouldReturnFalse()
{
$spec = new AndSpecification(
new SatisfiedSpecification(),
new NotSatisfiedSpecification()
);
$isSatisfied = $spec->isSatisfiedBy('foo');
$this->assertThat($isSatisfied, $this->equalTo(false));
}
/**
* @test
*/
public function isSatisfiedBy_GivenBothSpecificationsNotSatisfied_ShouldReturnFalse()
{
$spec = new AndSpecification(
new NotSatisfiedSpecification(),
new NotSatisfiedSpecification()
);
$isSatisfied = $spec->isSatisfiedBy('foo');
$this->assertThat($isSatisfied, $this->equalTo(false));
}
}
No conditional logic or loops
Test should have no uncertainty:
- All inputs should be known
- Method behavior should be predictable
- Expected output should be strictly defined
- Split in to two tests rather than using "if" or "switch"
Test should not contain "while", "for" or "foreach" loops
- If test logic has to be repeated, it probably means the test is too complicated
- Call method multiple times rather than looping inside of method
No exception handling
Indicate expected exception
Catch only the expected type of exception
Fail test if expected exception is not caught
Let other exceptions go uncaught
<?php
use PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;
class MyTest extends TestCase
{
/**
* @expectedException MyException
* @expectedExceptionCode 20
*/
public function testExceptionHasErrorCode20()
{
throw new MyException('Foo', 20);
}
/**
* @expectedException MyException
* @expectedExceptionMessage Foo
*/
public function testExceptionHasErrorMessageFoo()
{
throw new MyException('foo', 20);
}
public function testExceptionHasErrorMessageBar()
{
$this->expectException(MyException::class);
throw new MyException('foo', 20);
}
}Informative Assertion messages
By reading the assertion message, one should know why the test failed and what to do
Include business logic information in the assertion message
Good assertion messages:
- Improve code documentation
- Inform developers about the problem if the test fails
Pattern Arrange/Act/Assert (aka AAA)
- Arrange initialize objects and prepare data needed for the test
- Act call the tested method with prepared data
- Assert uses assertion to determine if test passes or not
PHPUnit
Assertions
Assertions are the "checks" that you may perform to determine if a test passes or fails.
- assertEquals/assertSame
- assertTrue/assertFalse
- assertInstanceOf
- assertCount
- assertArrayHasKey
- assertInternalType
- assertEmpty
- assertRegExp
Assertions
As possible, you use only one assertion per test
Assertions
Use the more relevant assertion in each case.
assertEquals(true, $val)
assertTrue($val)
Assertions
Use the more relevant assertion in each case.
assertEquals(null, $val)
assertNull($val)
Assertions
Use the more relevant assertion in each case.
assertEquals(true, array_key_exists($items, $key))
assertArrayHasKey($key, $items)
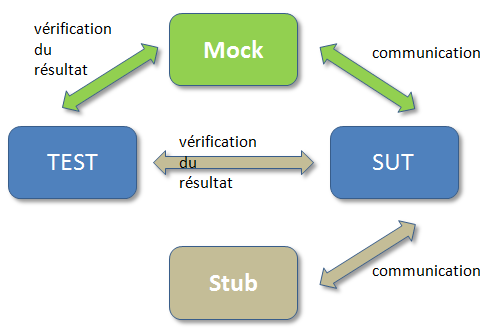
Mock/Stub
A mock allows a dependency to be imitated so the Unit test can be isolated
- Stub concern system under test (SUT). The Stub can never fail the test. We check the status of our SUT at the end of the test and not how this state was obtained. (state-based test)
- Mock concern test itself. We have expectations that are verified during the execution of the test. The mock decide that the test fails or succeeded. (Interactions Testing)
Mock/Stub
Code Coverage
you can't go into production with less than 87% coverage
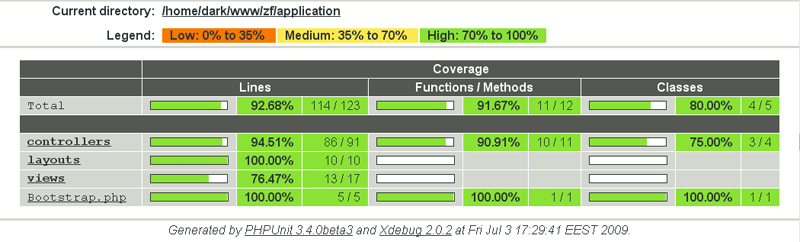
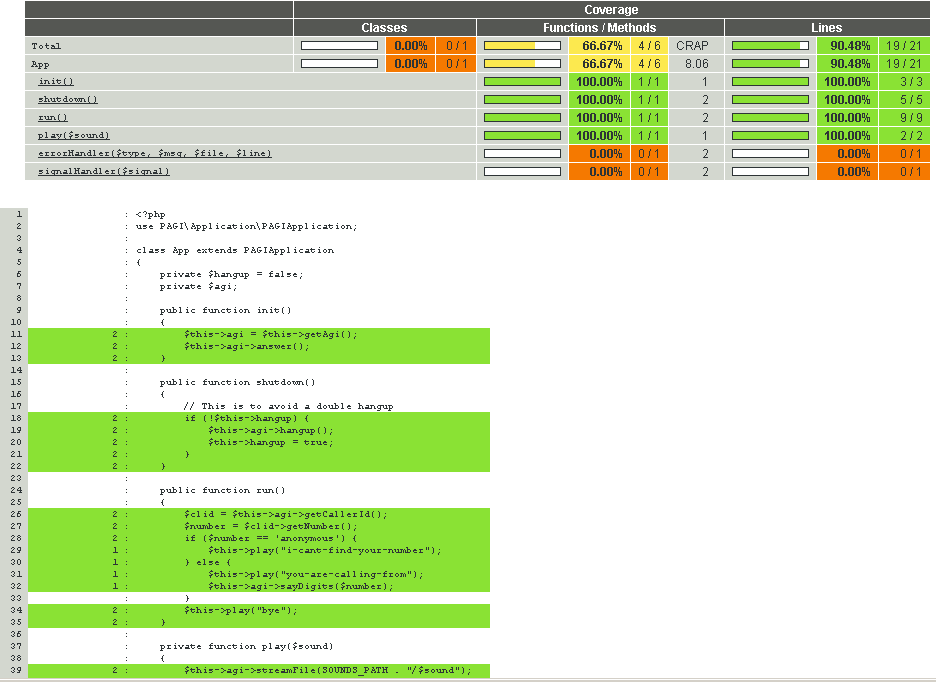
Code Coverage
Metric uses to determine code covered by unit tests
Useful to find untested code
Do not guarantee test quality and use cases coverage
We can have 100% code coverage without any assertions
Code Coverage
Code Coverage
PHPSpec
Behavioral Driven Development Oriented
Describing the software behavior
TDD focus on testing your application, BDD is more about describing its behavior
PHPSpec
Using a BDD approach will force you to constantly consider the actual requirements and desired behavior of the software you're building.
No code coverage
BDD
- Behat that describe the external behavior of your application, using the readable Gherkin language
- PHPSpec that describe the internal behavior of your application
Copy of Object Oriented Programming
By Nicolas Eeckeloo
Copy of Object Oriented Programming
- 1,004


