Bio
GSU
-IScAI
-LESIA/Obs Paris
photography/film
UNCC
-physics
-psych
-astro
Applied Physics
-biomedical optics
-medical physics
-astro
NASA/BAERI
-exoplanets
-speckle
CHARA
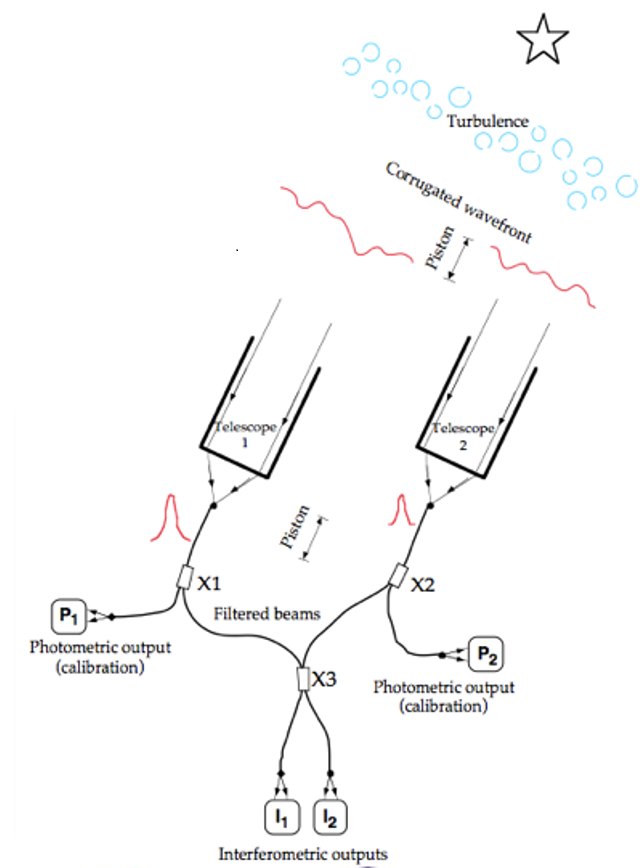
-long baseline optical interferometry

Early Research
- -RR Lyrae
- -PN


biomedical optics
-laser/tissue interactions
-pulsed Er:YAG laser scalpel
-ophthalmology/cataracts
-kidney/urinary stones
-other urology


Current position
Telescope Systems Scientist (CHARA)
Instrumentalist (NASA)
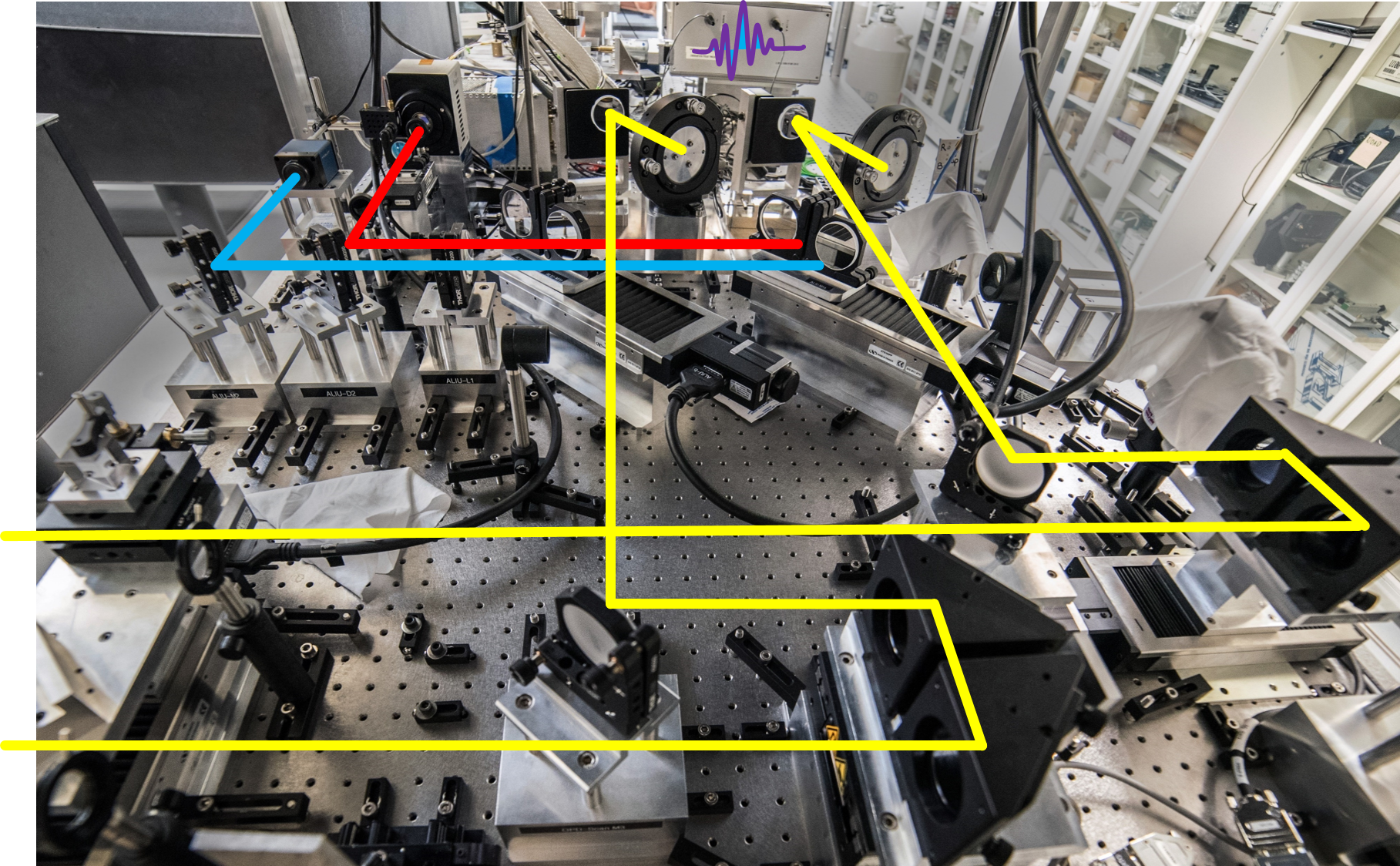
Instrumentation development and maintenance program
-telescopes, adaptive optics systems, enclosures, and the beam relay systems.
-laboratory electro-optical systems
-design and development of new instruments

"dedicated generalist"
Career Path
- Important steps along the career path
- transferring
- hearing about options
- after BS? (tuition waive, stipend)
- conferences (SPIE, AAS)
- Were there any setbacks? If yes - how did you deal with them?
- imposter syndrome
- Were there any “detours” or breaks?
- arguably astro was a detour from photo
- weird things -medical research (stones & rats)
- teaching at RCCC
-GSU
-LESIA
-NASA
-CHARA
Observing





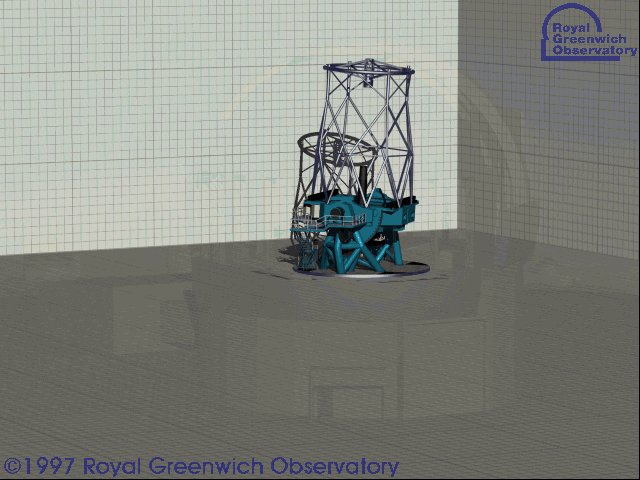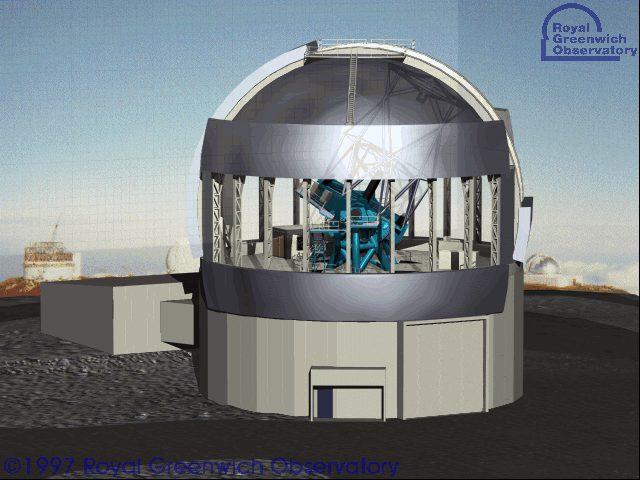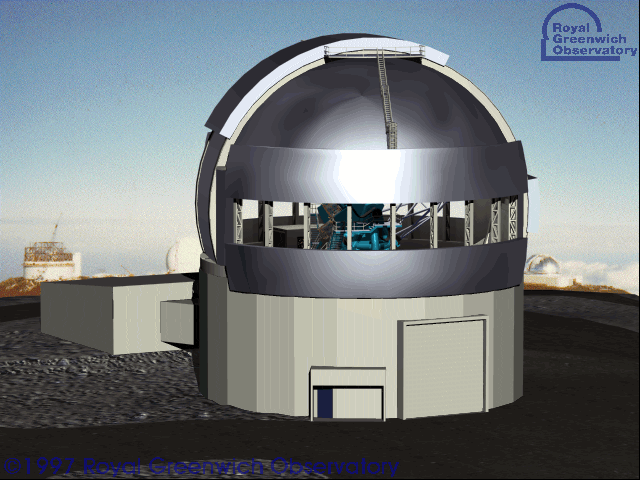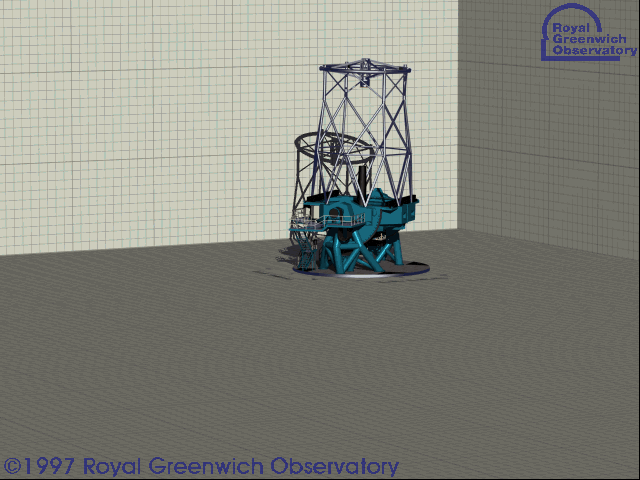








Kepler/K2
TESS
Instruments










Multiplicity of stars
40-50% of Kepler/K2/TESS objects of interest may have companions
- biases occurence rates & underestimates exoplanet radii by 50%
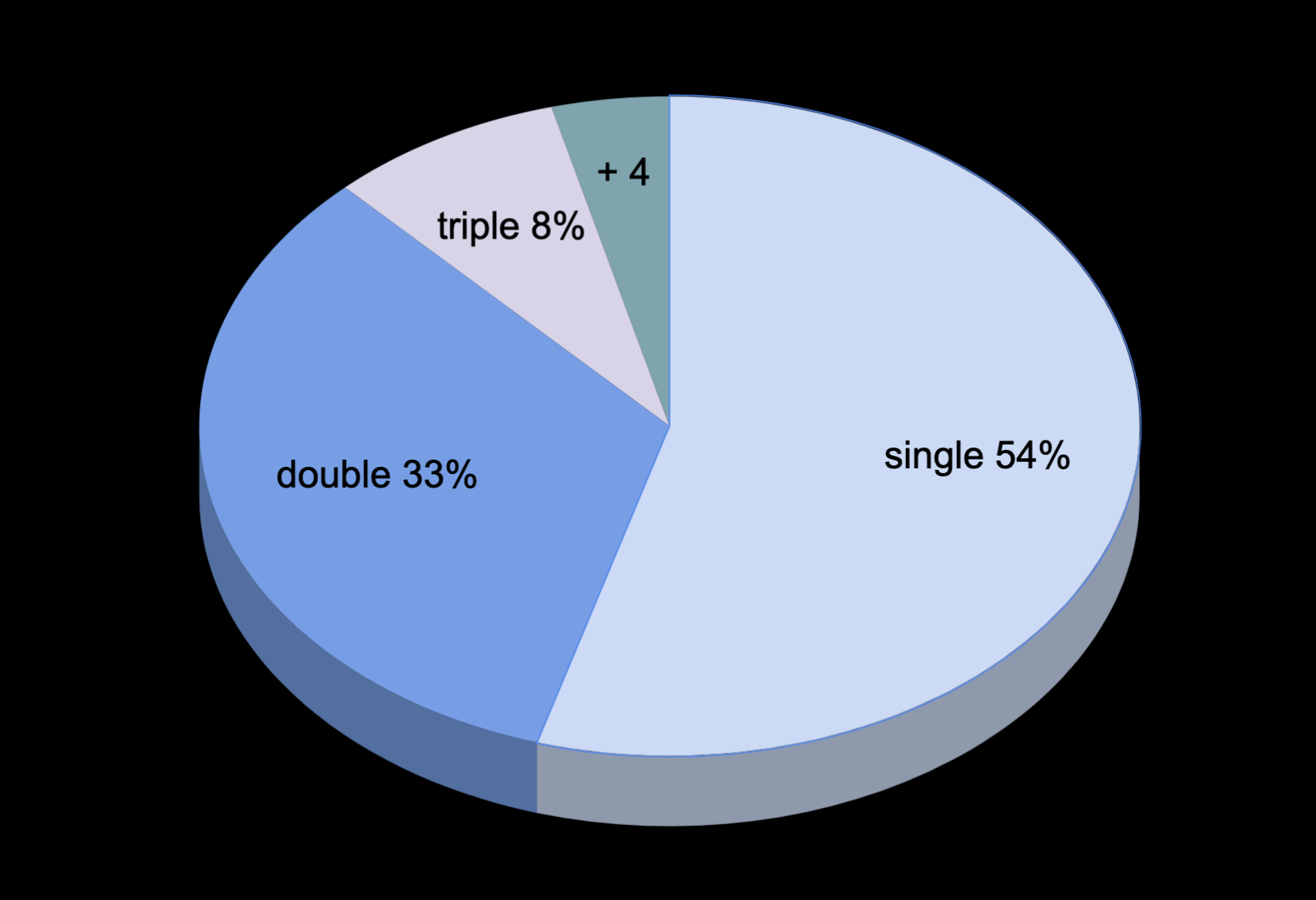
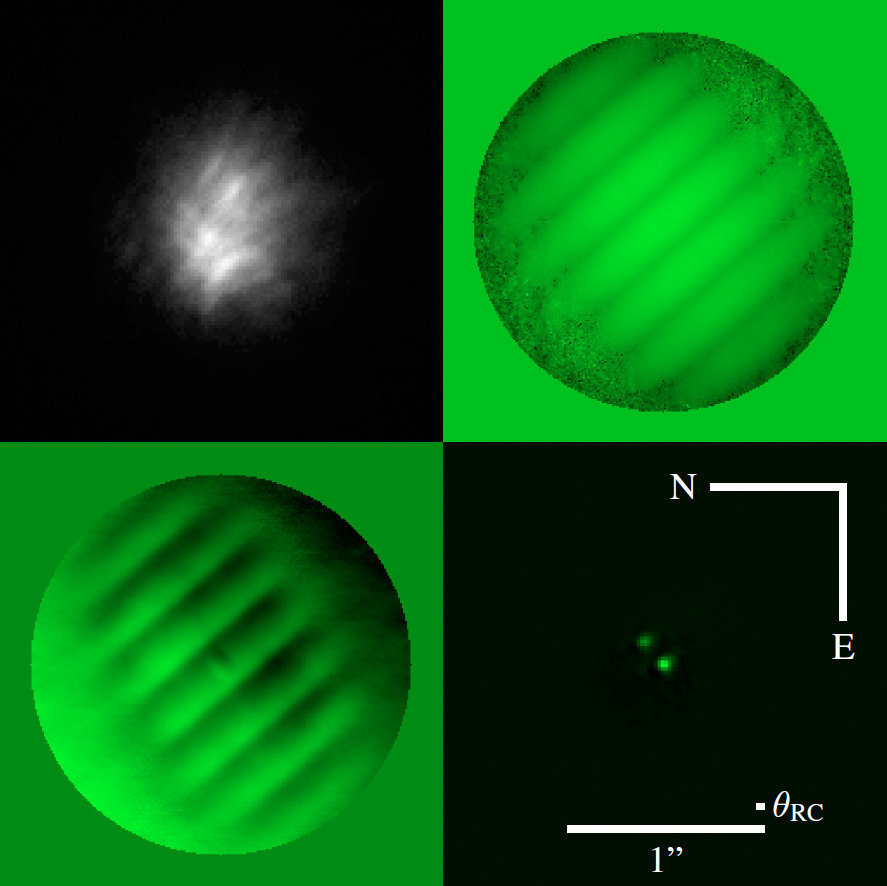
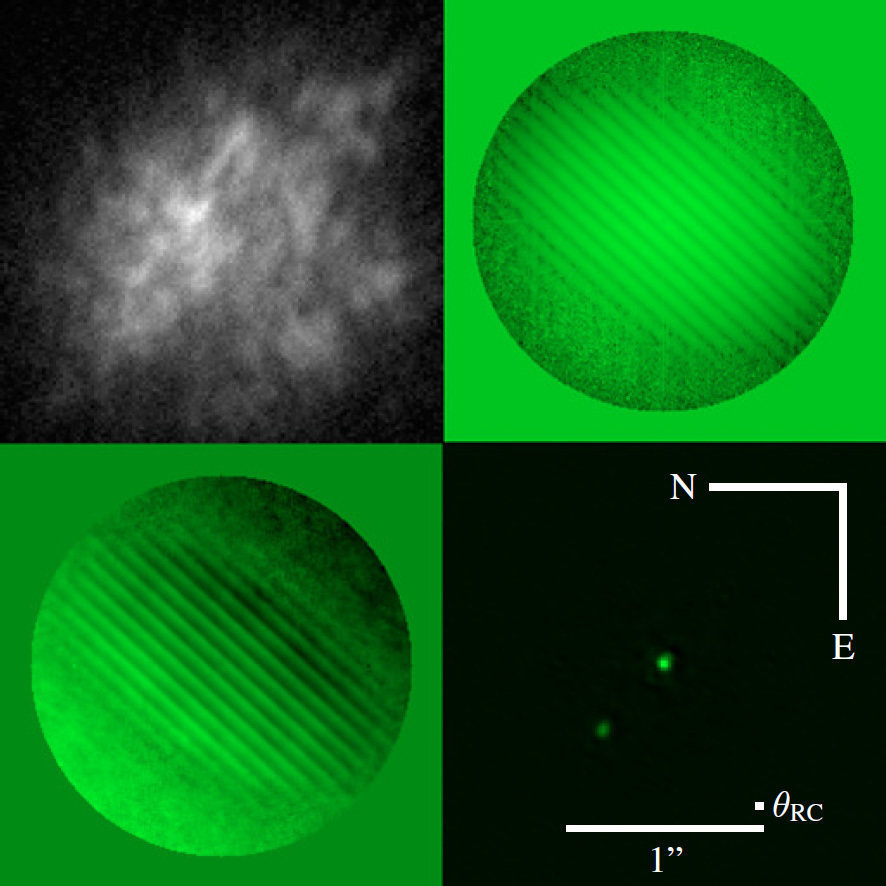
Fringe spacing
Fringe orientation
Fringe Depth
Binary separation
Binary position angle
Binary magnitude difference




1s
40s
20min
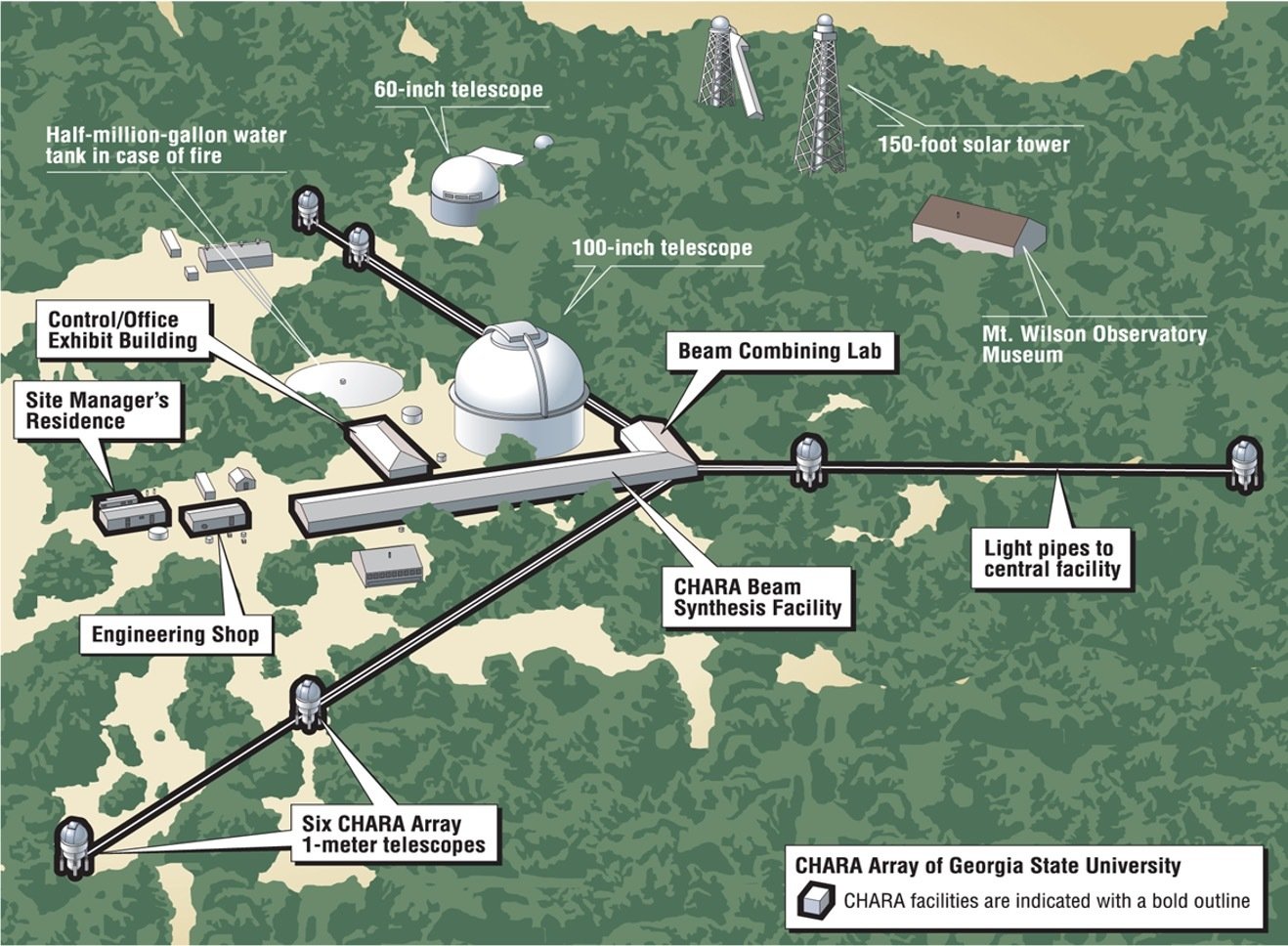
The CHARA Array
Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy



6 telescopes in Y configuration
15 baselines: 34-331m
Georgia State University
University of Michigan
University of Exeter
l'Observatoire de la Cote d'Azur
l'Observatoire de Paris
Sydney University
Australian National University
Université de Limoges
Kyoto Sangyo University
NOIR Lab
"The Array is capable of resolving details as small as 200 micro-arcseconds, equivalent to the angular size of a nickel seen from a distance of 10,000 miles. In terms of the number and size of its individual telescopes, its ability to operate at visible and near infrared wavelengths, and its longest baselines of 330 meters, the CHARA Array is arguably the most powerful instrument of its kind in the world."









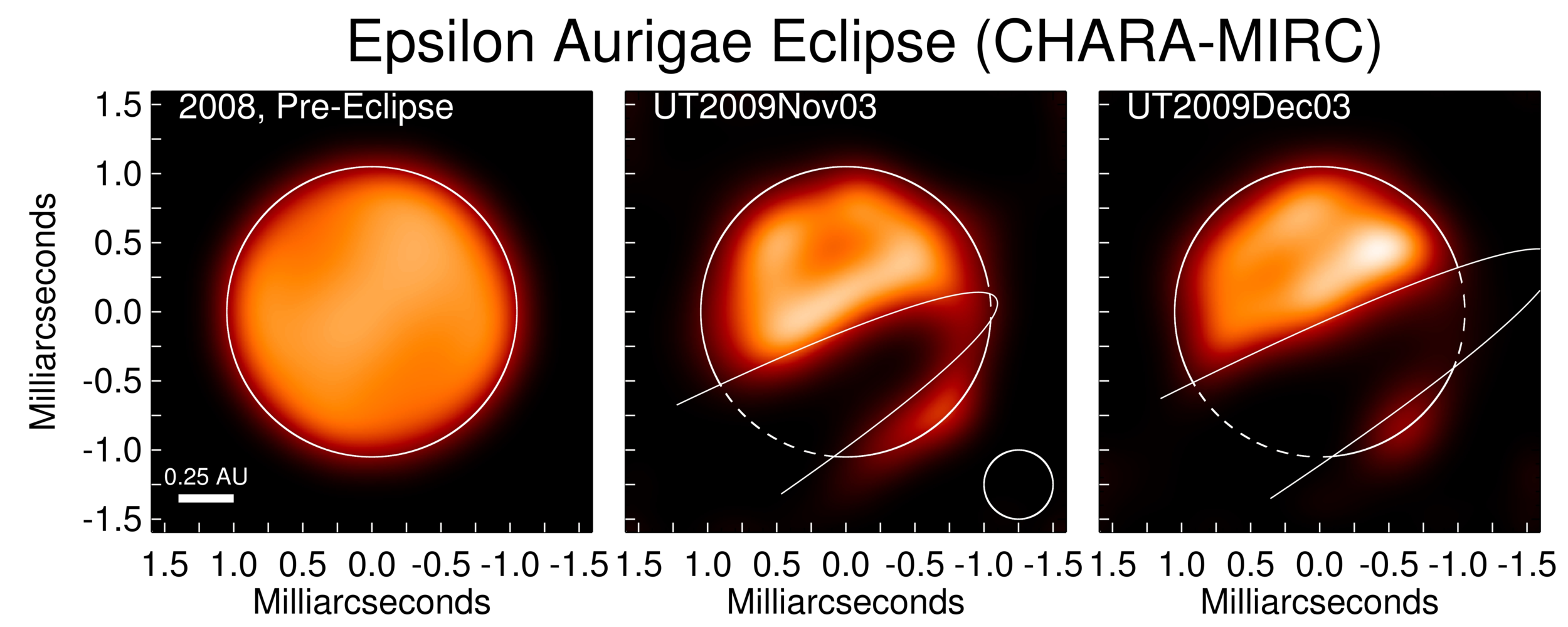
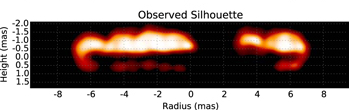

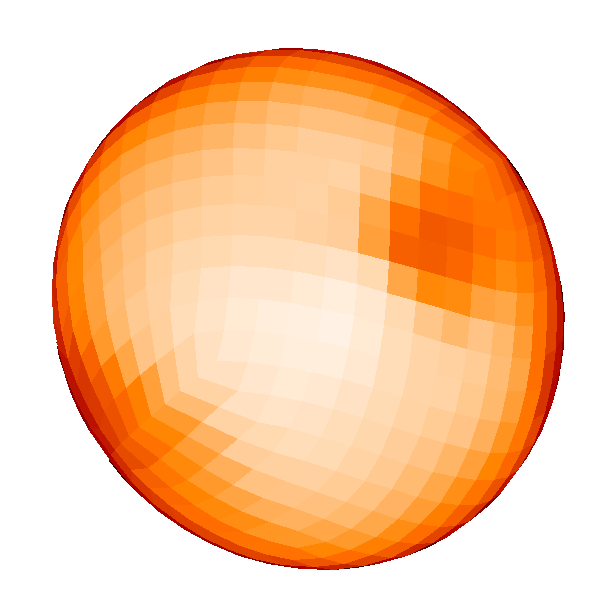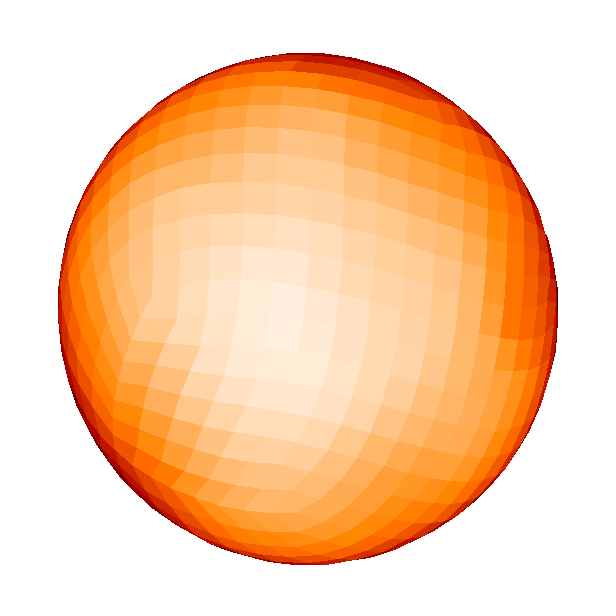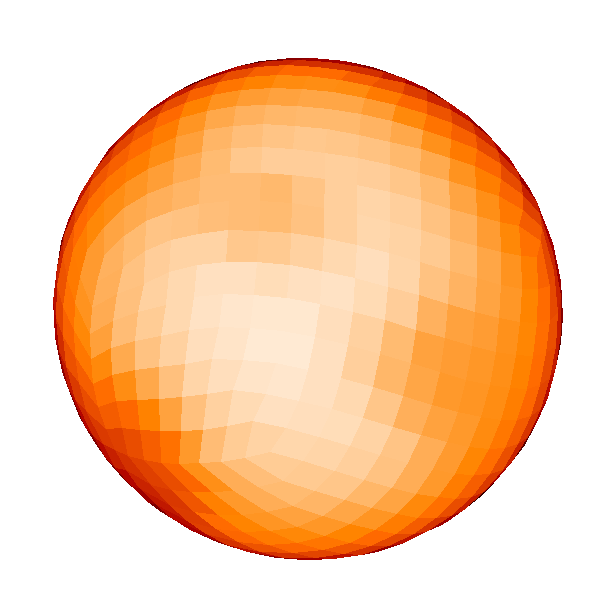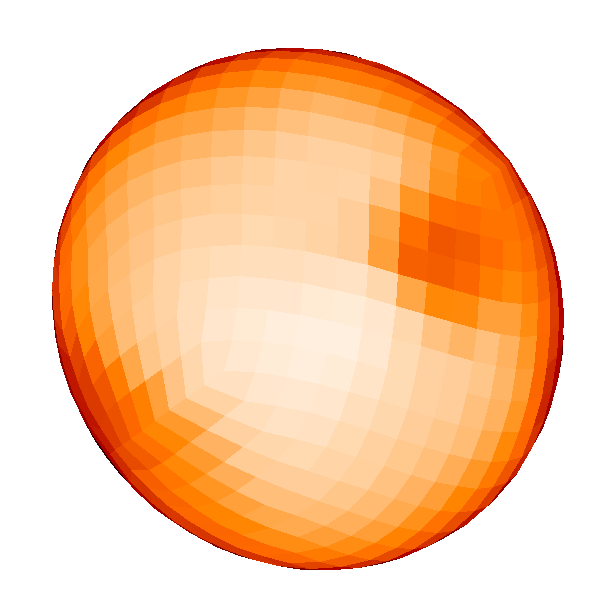
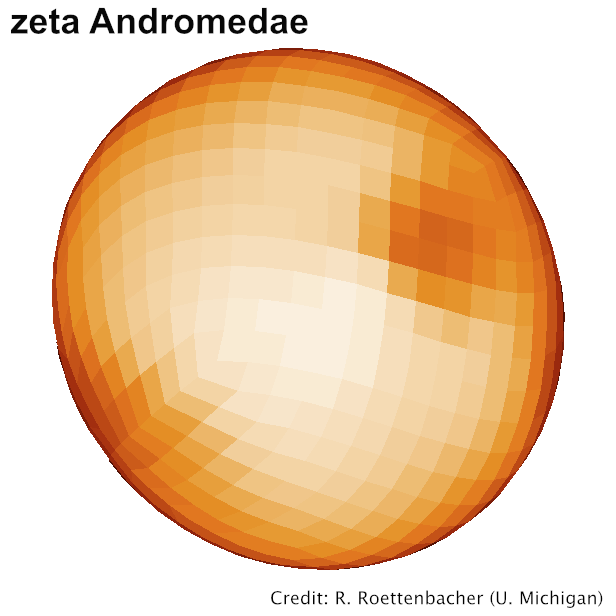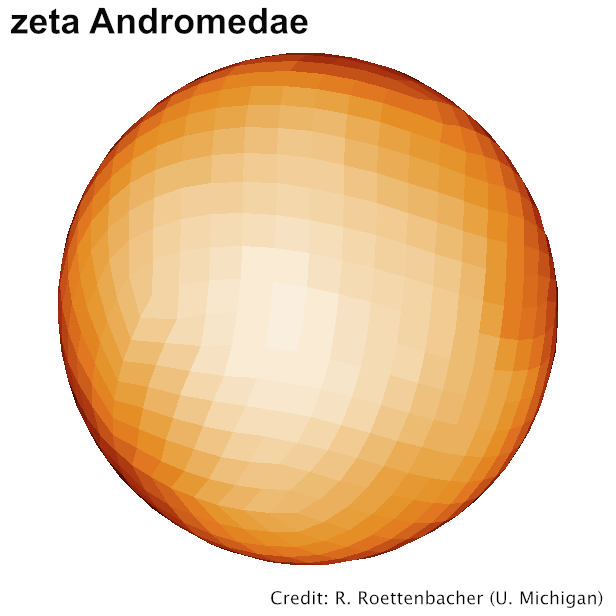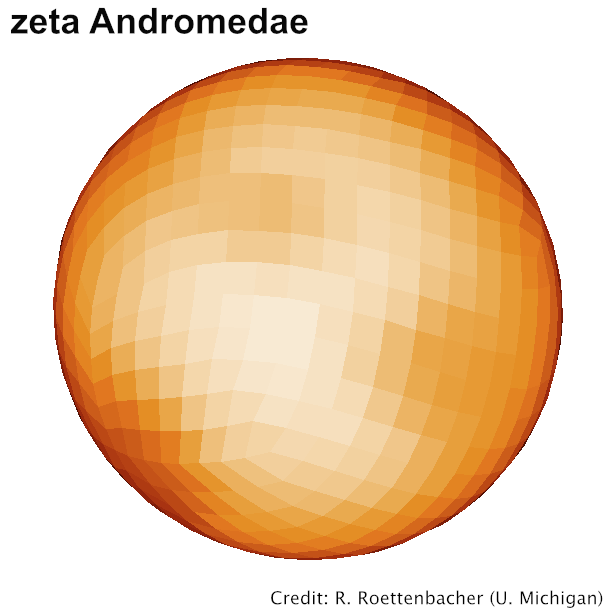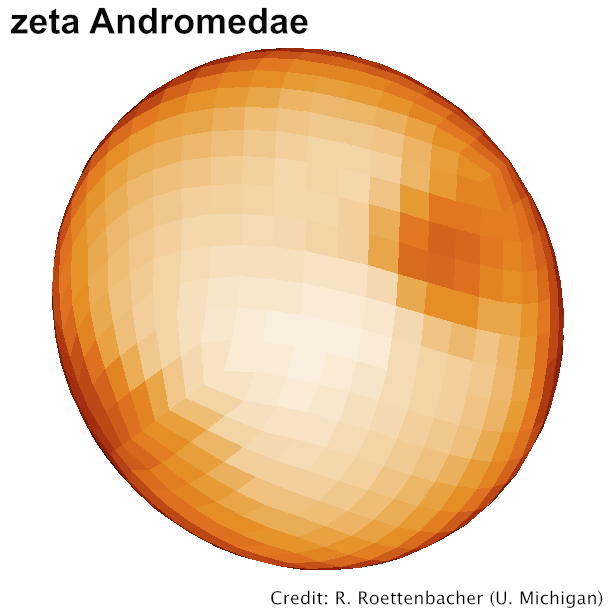
Spotted magnetic stars
Interacting binaries
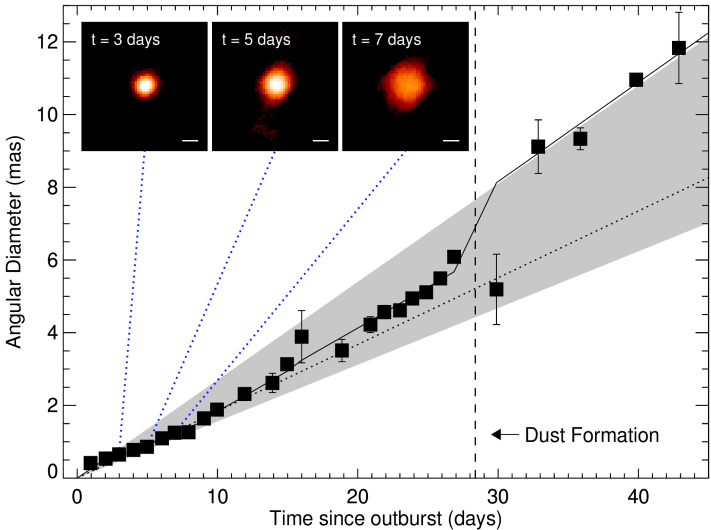
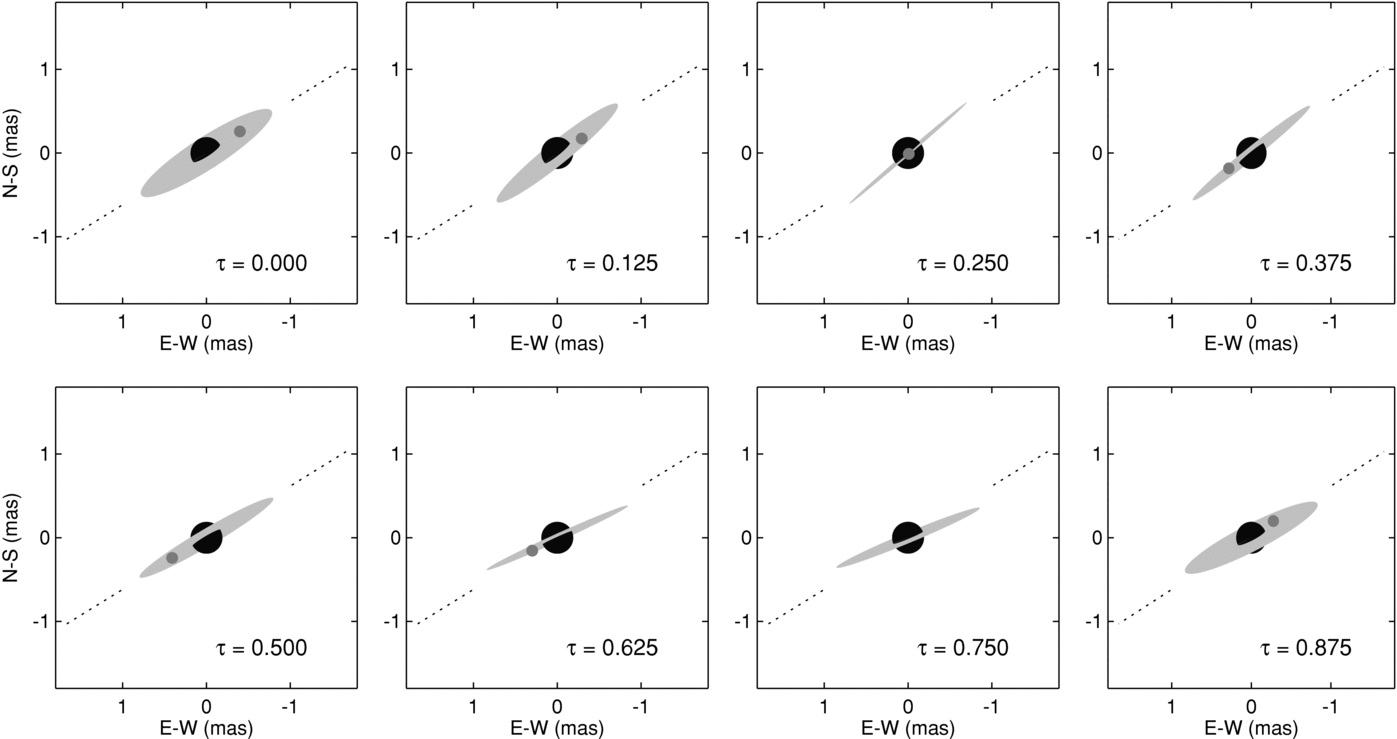
Expansion curve of Nova Del 2013.
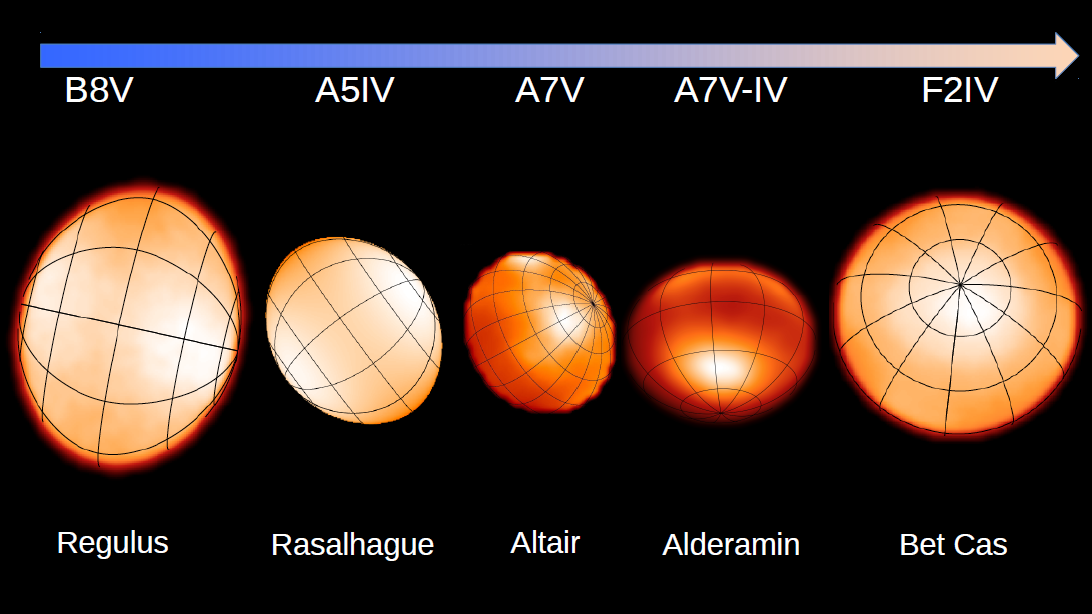
Regulus -- Che et al. 2011, ApJ, 732, 68
Rasalhague -- Zhao et al. 2009, ApJ, 701, 209
Altair -- Monnier et al. 2007, Science, 317, 324
Alderamin -- Zhao et al. 2009, ApJ, 701, 209
Beta Cas -- Che et al. 2011, ApJ, 732, 68

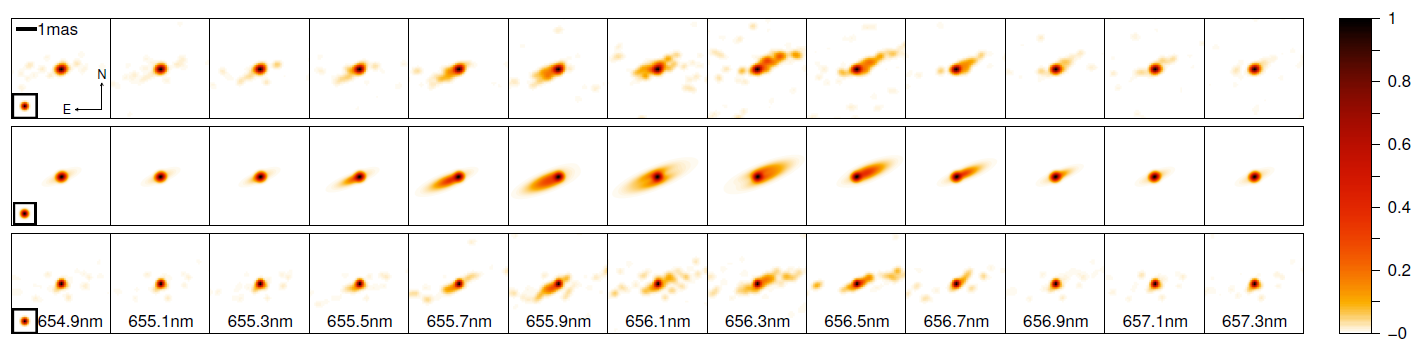
Be stars
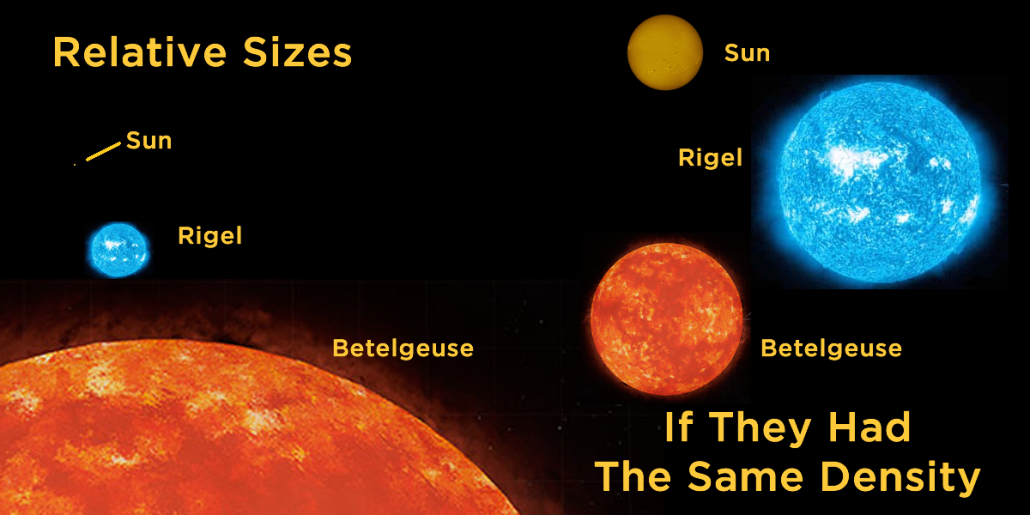
Stars
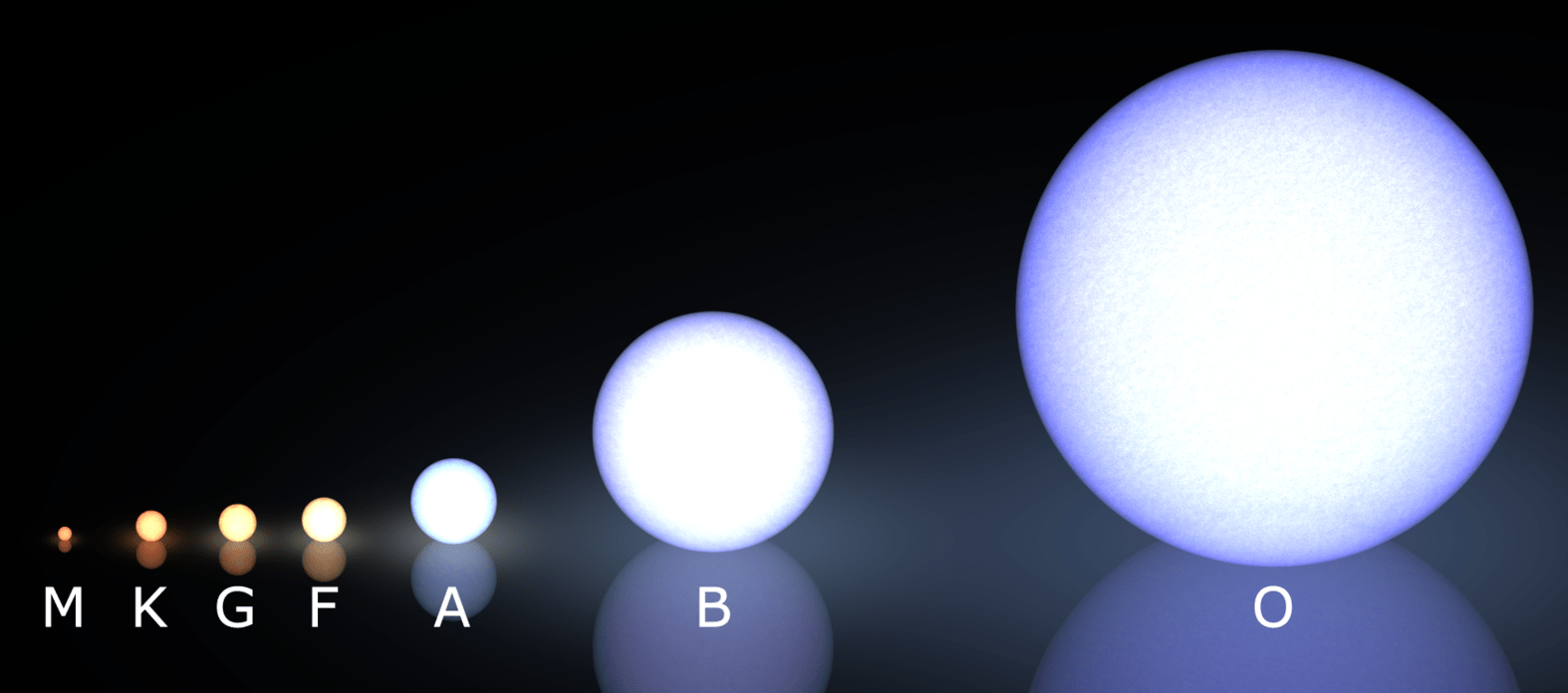
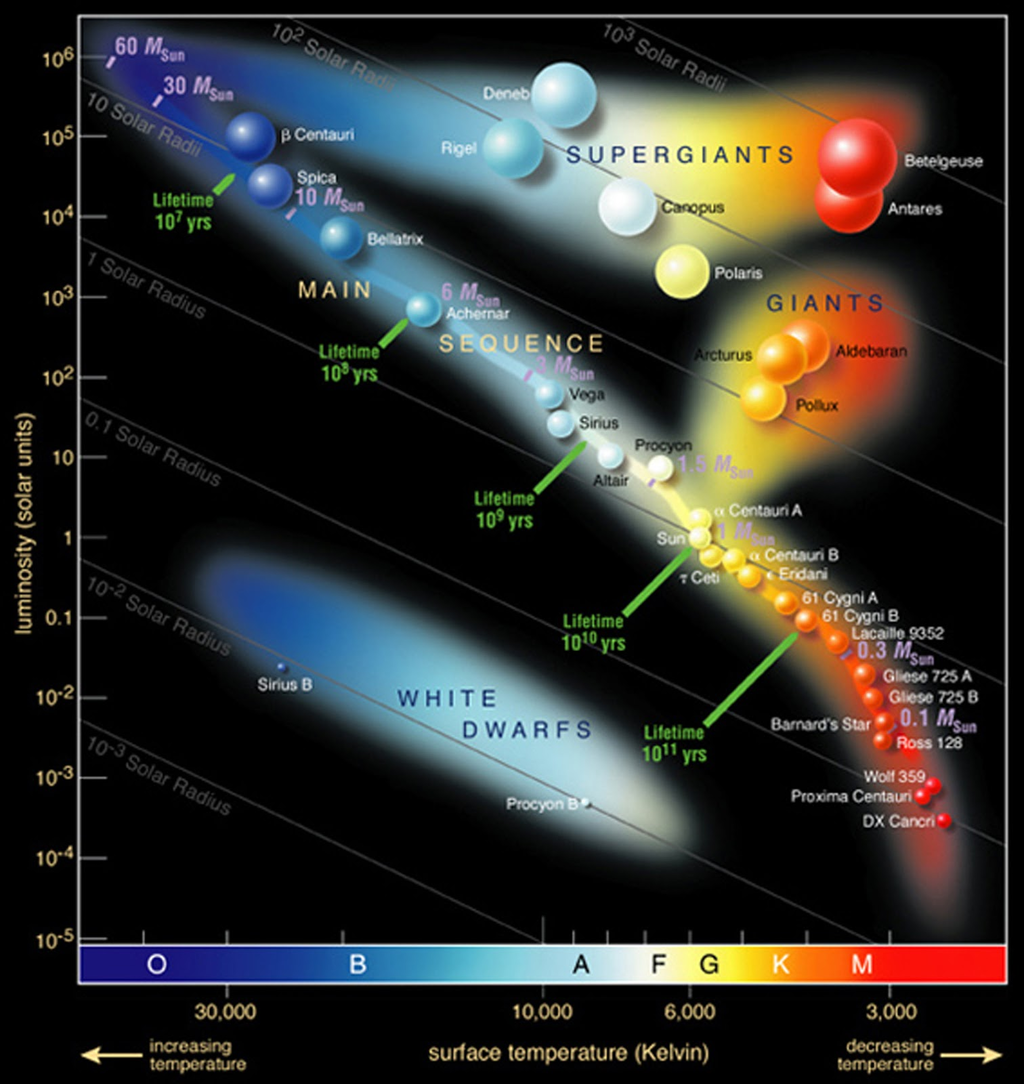
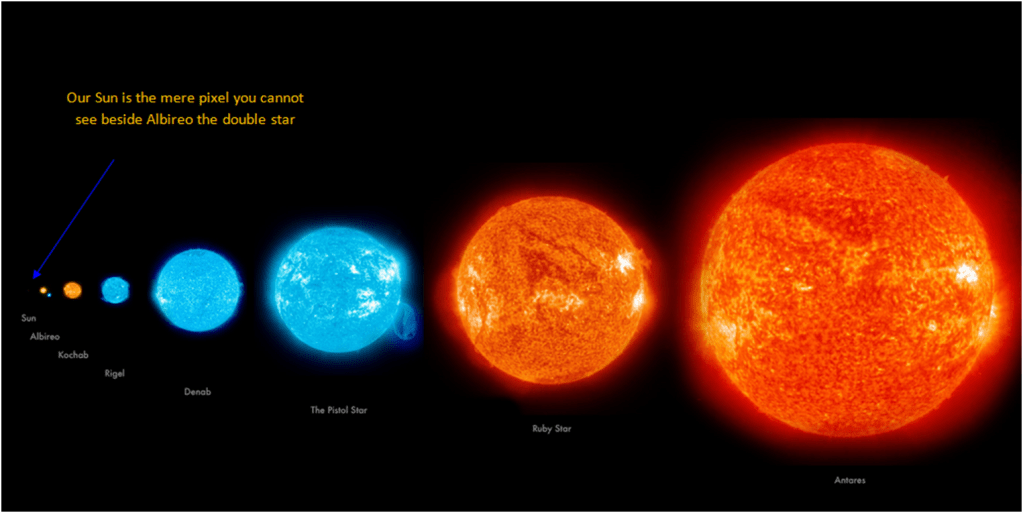




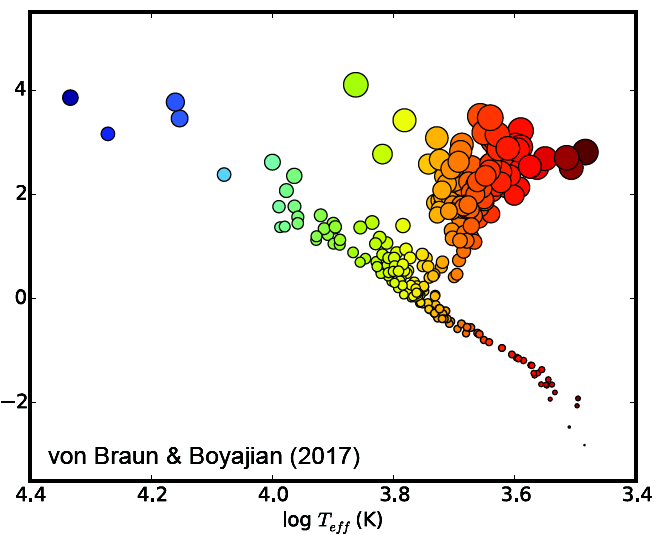
Stellar Evolution
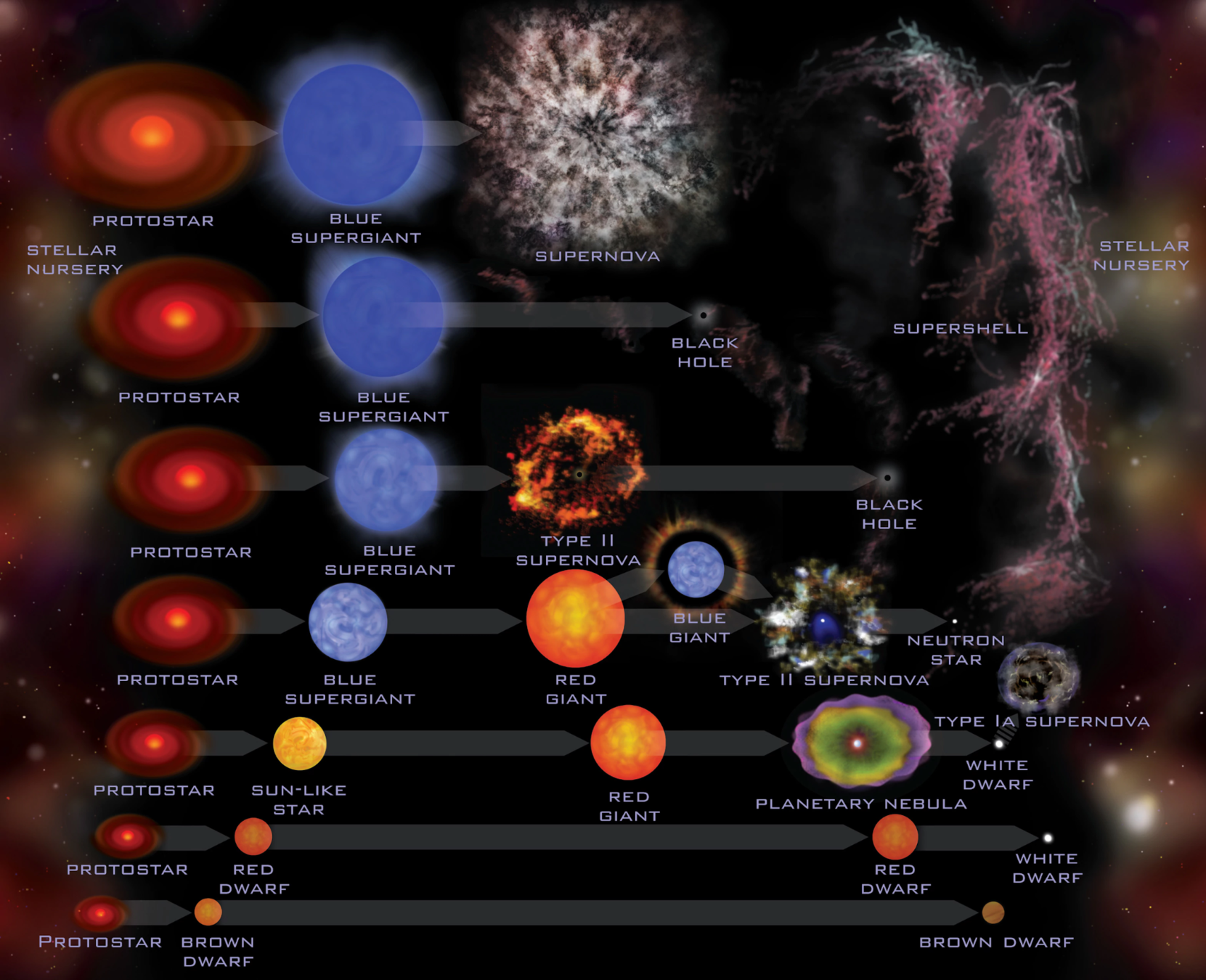
<0.08
0.08-0.4
0.4-8
>8
>20
>3
1.4-3
>1.4
Solar Masses
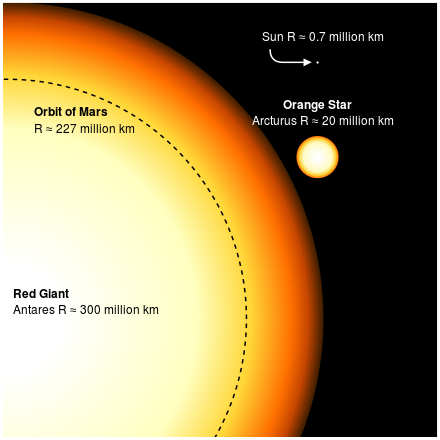




Scales and galaxies

A thousand seconds ago was ~ 17 mins ago
A million seconds ago was ~ 11.5 days ago
A billion seconds ago was ~ 32 years ago
A trillion seconds was 31,700 years ago
Light travels 1 foot in a nanosecond (1/billionth of a second)
Light would circumnavigate the equator 7.5 x in one second
Spending one million dollars in a year would require spending about ~ $2,700 per day.
Spending one billion dollars in a year would require spending about ~ $2,700,000 per day.
Radio and long wavelength infrared interferometry can record the timing and encode the timing of the occurrence. (intensity interferometry, heterodyne detection)
With shorter wavelengths the timing becomes so fast that the exposure time gets so short that you don't collect any light. (homodyne detection)



There's about 5077 stars visible by naked eye. Which works out to 404 stars per sterradian.
So if you hold an iphone out at arm's distance, there’re about 50 visible stars in that amount of sky
There’s estimated to be 200 billion galaxies. Which works out to about 15.9 billion per sterradian.
An iphone 12 screen pixel is ~0.3mm.
There’re about 1,400 galaxies in the area of that single pixel.
An estimate of the number of stars per galaxy is 100 billion.
So that puts around
140,000,000,000,000 stars in the area of that single pixel







Solar system










Moons that are other worlds:



















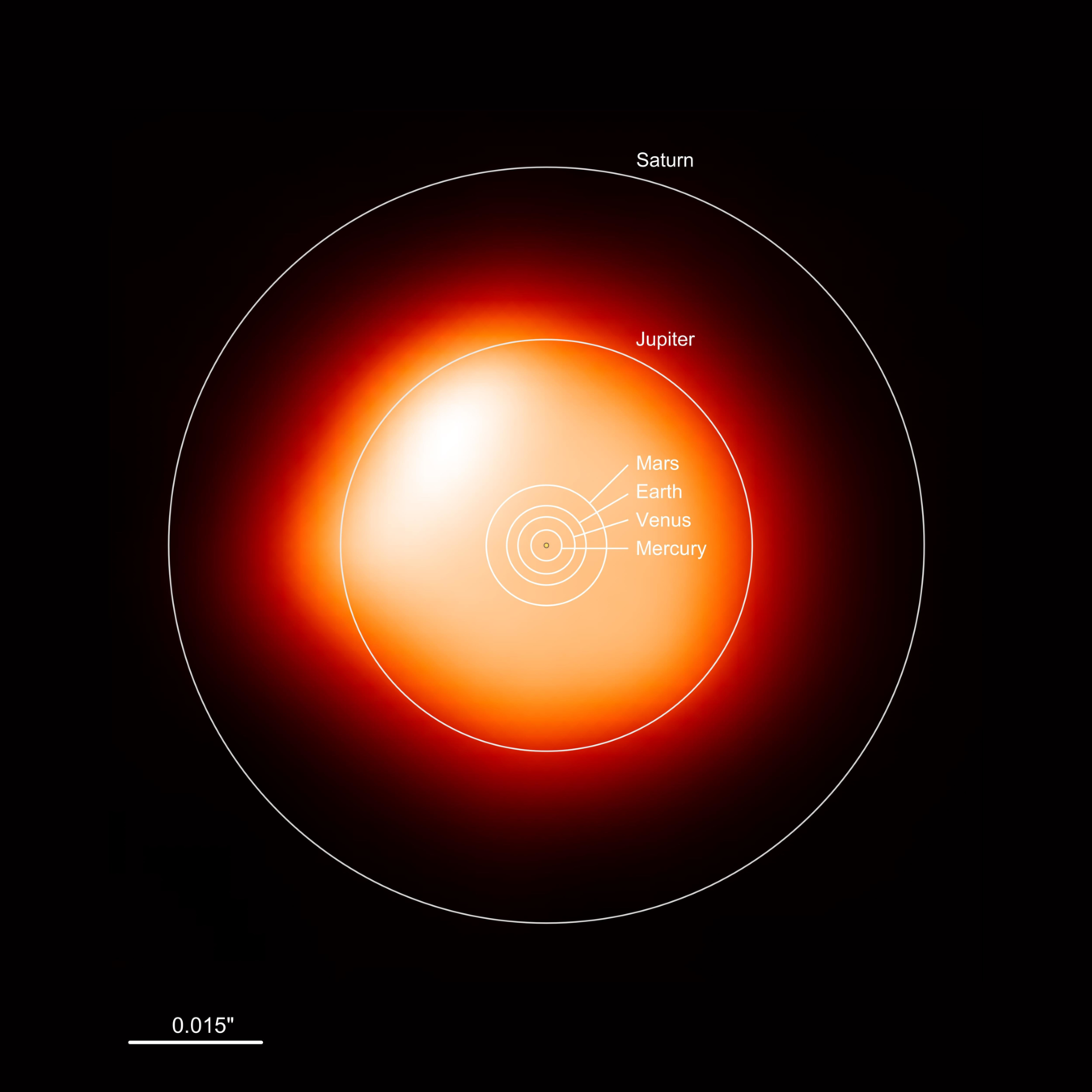
Finding exoplanets





TESS camera apertures
Kepler primary mirror



TESS



Types of
exoplanets






- Hot Jupiters
- lava planets
- rogue planets
- lethal rain
- devoured planets
- evaporating planets
- eccentric orbits
- ocean planets
- zombie planets





- tidally locked planets
- eyeball planets


- multiple-habitable worlds

- circumbinary planets

Super-Earth or mini-Neptune?



links:
The Sun:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6tmbeLTHC_0
black holes:
https://www.wikiwand.com/en/Black_hole
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4YzWosQYg6Q
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=if2opecmev8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wyuj7-XE8RE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TF8THY5spmo
exoplanets:
https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/interactable/11/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_exoplanet_extremes
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-farthest-exoplanet
https://www.space.com/29120-alien-planet-among-farthest-known.html
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/jpl/20-intriguing-exoplanets
http://seagerexoplanets.mit.edu/research.htm
known universe/scales:
https://neal.fun/size-of-space/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=17jymDn0W6U&list=PLrfcruGtplwHQB7fGpuohlVkRDhPaJfJt
Scale of the Solar system: http://joshworth.com/dev/pixelspace/pixelspace_solarsystem.html
https://www.space.com/30610-scale-of-solar-system-amazing-video.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GoW8Tf7hTGA
Scale of the universe: http://htwins.net/scale2/
Sizes of stars: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kBkNhMfrxuk&feature=youtu.be
How many exoplanets have been found?
https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/
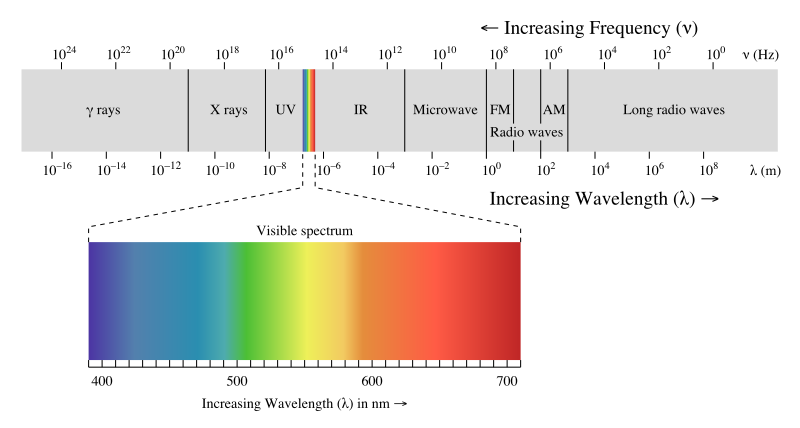
Light

Characteristics
- Intensity
- photometry
- magnitudes
- transits
- photometry
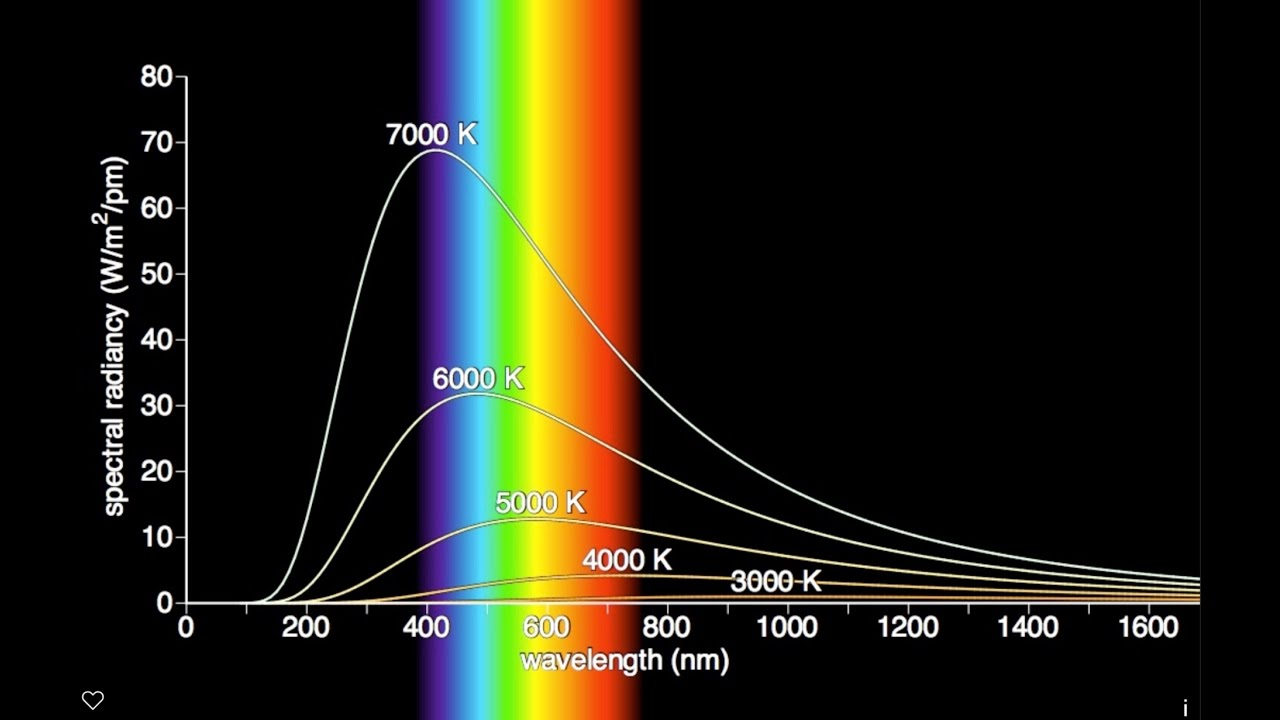
- Wavelength
- spectrum
- radial velocity
- composition
- incandescence
- emission
- absorption
- spectrum
- Interference
- Polarization
- linear
- circular


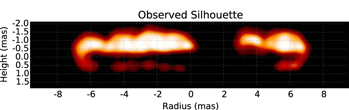
Oumuamua



Random














Your questions:
Fern
-
How was the asteroid belt made?
-
formation of solar system, disruption by Jupiter
-
-
Has any other life been found?
-
How many galaxies are there?
-
100s of billions: +100,000,000,000
- our galaxy has 250 billion stars: 250,000,000,000
-
-
Are there more spiral galaxies?
-
Are there planets outside our solar system?
-
How did the planets get in our solar system? Why not on a different star?
-
How do planets get moons?
-
Why are planets round?
-
Why does Saturn have rings? What are the rings?







-
How do planets get made?
-
Are there other planets with atmospheres like Earth’s
-
How do planets find their orbits?
-
How do we know what the Sun is made of?
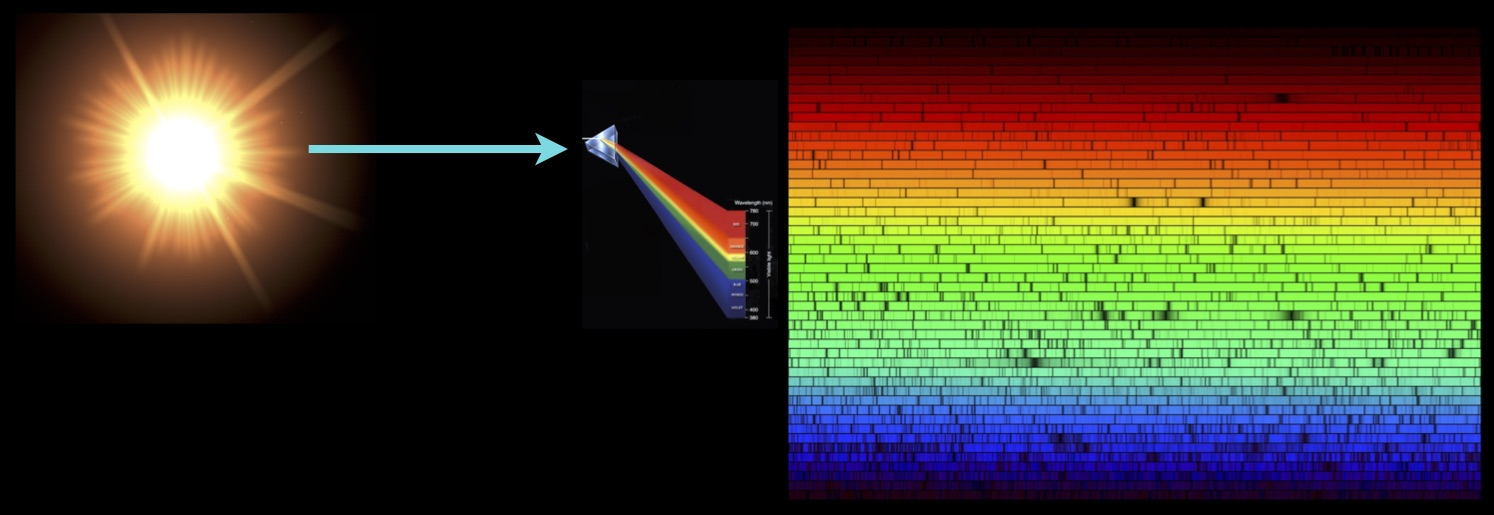
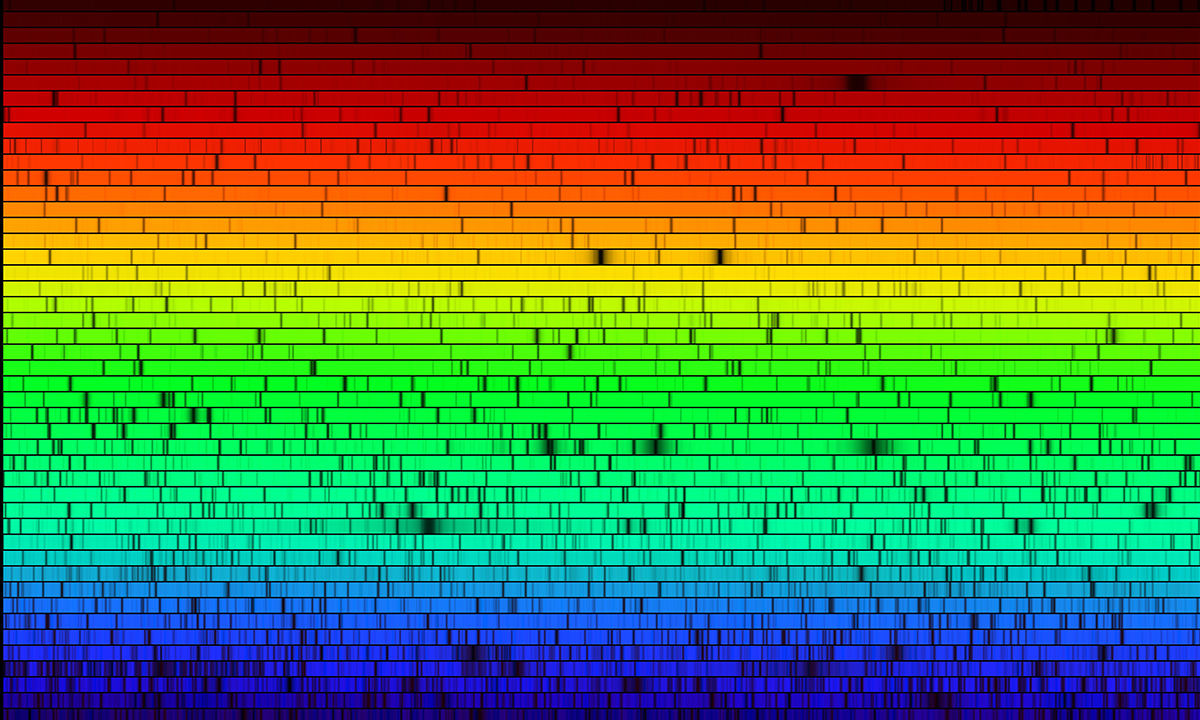
-
How many stars are in our galaxy?
-
What is the purpose of a star?
-
Why are stars different colors?
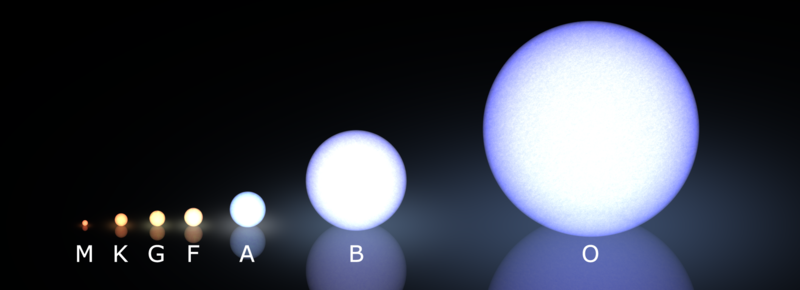
-
Why do stars twinkle?

-
What are stars made of?
-
What is a supernova?
-
Where’s our closest star after the Sun?
-
How long do stars live?
-
Was there another Sun here before ours?
-
How are stars formed?
-
Are there moons around the Sun?
-
How many people have been to the moon?
-
24 have been to the moon, 12 have walked on it
-
-
Why can’t we see the moon’s colors from Earth?
-
How many black holes are there in our galaxy?
-
10s of millions: +10,000,000
-
-
What is a black hole if it’s not a hole?
-
Can humans visit black holes?
-
Do black holes have names?
- Fornax A
- 1ES 2344+514.
- 3C 75.
- 3C 371.
- AP Lib.
- S5 0014+81
- APM 08279+5255
- Arp 220.
- GRS 1124-683/GU Mus
- GRS 1915+105/V1487 Aql
- GS 2000+25/QZ Vul
- GX 339-4/V821 Ara
- IGR J17091-3624
- Sagittarius A*
-
What makes black holes so powerful?
Your questions:
Heather
-
What advice would you have for a student looking for a career in Astro?
-
What is the most interesting thing you have studied?
-
delphinus nova 2013
-
-
How does the supplier of the telescope work? (who made it, etc)
-
When and how were you inspired to work with telescopes?
-
The most insane thing you have seen with a telescope?
-
oumuamua
-
-
Are mirrored/reflecting telescopes the best type?
-
What do you like about your job? What do you most dislike about your job?
-
If you weren’t working on telescopes, what would you be doing?
-
What is something NASA is working on right now?
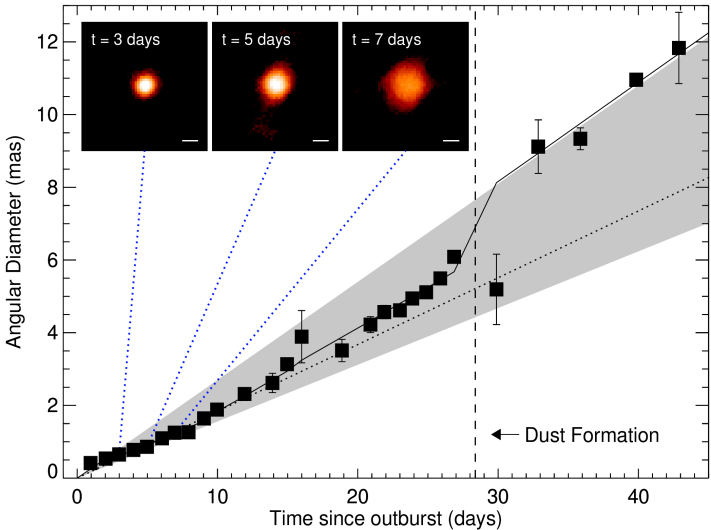
-
What can you say about other types of telescopes? (all kinds?)
-
Do you know when the luvoir telescope will launch?
-
What are your expectations for the future of humanity on other planets or finding life on other planets?
-
What climate change related projects is NASA working on?
-
If making money is your goal, what type of science should you study?
-
What is the most rewarding part of your job?
-
Are there any plans to send humans to space again soon?
-
humans are on the ISS right now
-
-
How does climate change affect NASA? (if the world is going to end, if climate change is such a big problem, wont that affect our study of other planets)


Why is the government underfunding NASA? Are there other ways for NASA to get money?

Your questions:
Taylor
- What are some of the other planets that are outside of our solar system?
- How many exoplanets are there?
-
What kind of things do you study, specifically?
-
What types of instruments do you build?
-
Do you use chemicals or gases, like helium, in your research?
-
spectral lamps, liquid nitrogen
-
-
Is there another planet that can support life?
-
Have you made any discoveries?
Have you ever tried space food? What was it like?
-
What is your theory on how the universe was created?
-
When you do research, how do you find things on other planets?
-
Why did you become a scientist?
-
Have you ever done any experiments? If so, what kind?
What is the closest exoplanet to our solar system?
Proxima Centauri b

Have you ever seen any planets through the telescope at NASA?

Was the moon landing fake?
- photos from LRO
- photos from the missions:
- equipment on the moon
- seismometers
- laser retroreflectors
- lunar samples
- broadcast tracking -inc Soviets

-
What is physics?
-
How long does it take to confirm an exoplanet? What steps do you have to take?
-
What did you have to do to become a successful scientist?
-
What is a day like for a scientist?
-
What is the experience of being a scientist? What is the reaction when you tell people you’re a scientist?
-
Do you have another job besides being a scientist? If you weren’t a scientist, what would you be?
-
Was it always your dream to be a scientist?
-
What is it like to use a telescope? How do you use one?
-
What are your thoughts on aliens?
-
What do you do for fun at work? For example, if you have some down time.
public talk
By Nic Scott
public talk
- 1,122



