SENG3011
🌿 2.3 - Managing Dependencies
In this lecture
- What are software dependencies?
- Issues in managing dependencies
- Tradeoffs in reusability and platformisation
Software Libraries
- Avoid reinventing the wheel
- Leverage other APIs and abstractions
- Platform as a Service - platforms to help you build your software
- What are we depending on?
- The author doesn't remove the library
- The author doesn't break the library with an update
- The author isn't malicious
- The library's dependencies are available
Two types of dependencies
- Direct dependencies your application relies on
- Transitive dependencies - the libraries your dependencies rely on / dependencies of dependencies
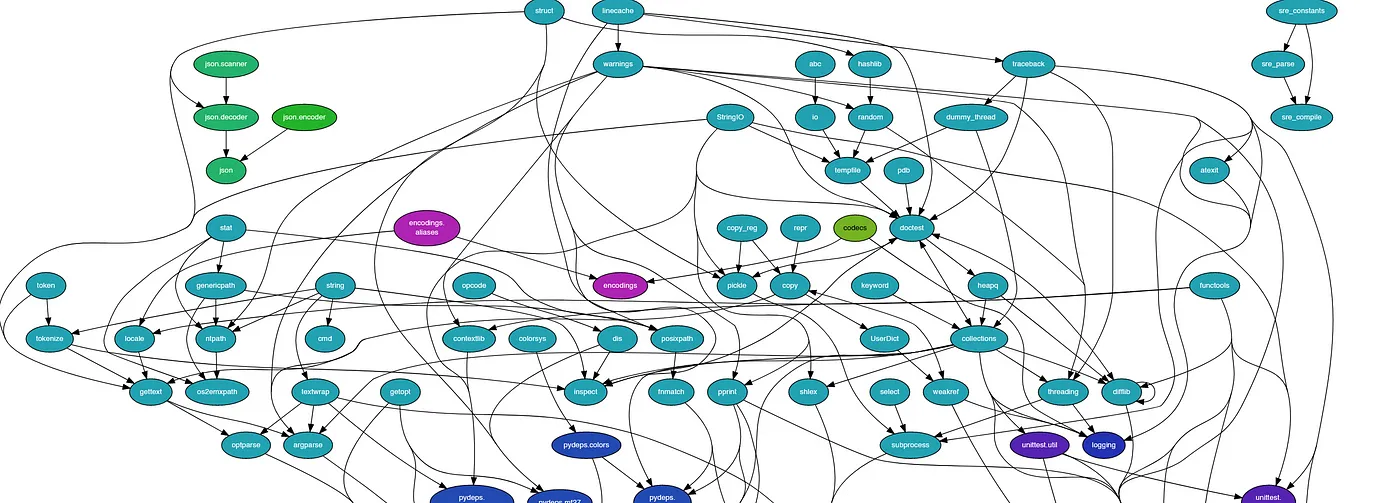
Diamond Dependencies
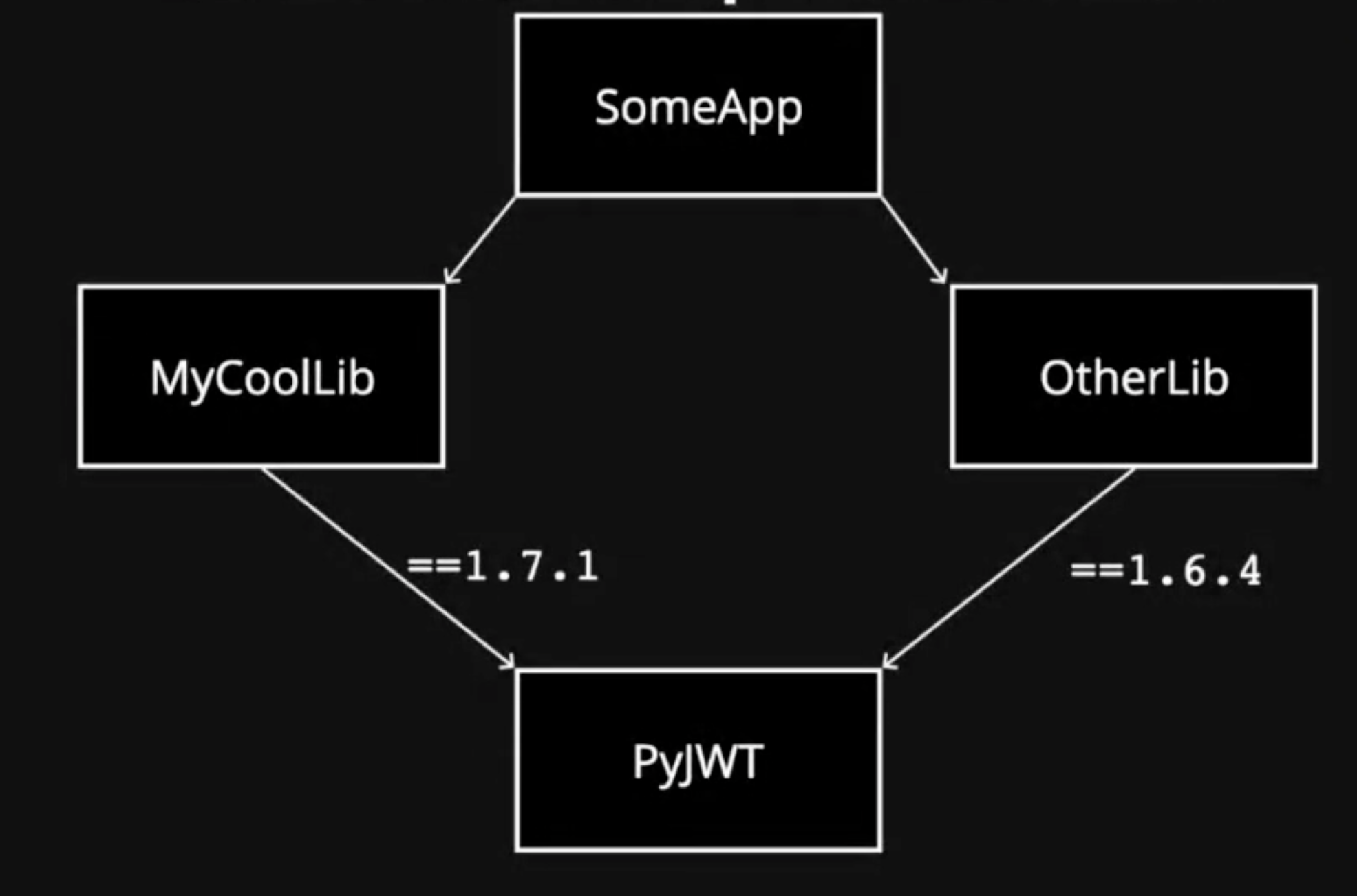
Cyclical Dependencies
Lockfiles
- Lockfile specifies an exact version of dependencies to be used
- Avoids the risk of automatically upgrading packages that depend on one another and breaking the dependency tree


Semantic Versioning
- Version number: major.minor.patch (e.g. 1.10.1)
- Major - when you make changes that break the API contract (break LSP)
- Minor - when you add functionality in a backwards compatible manner (maintain LSP)
- Patch - backwards compatible bug fix
A little copying is better than a little dependency.
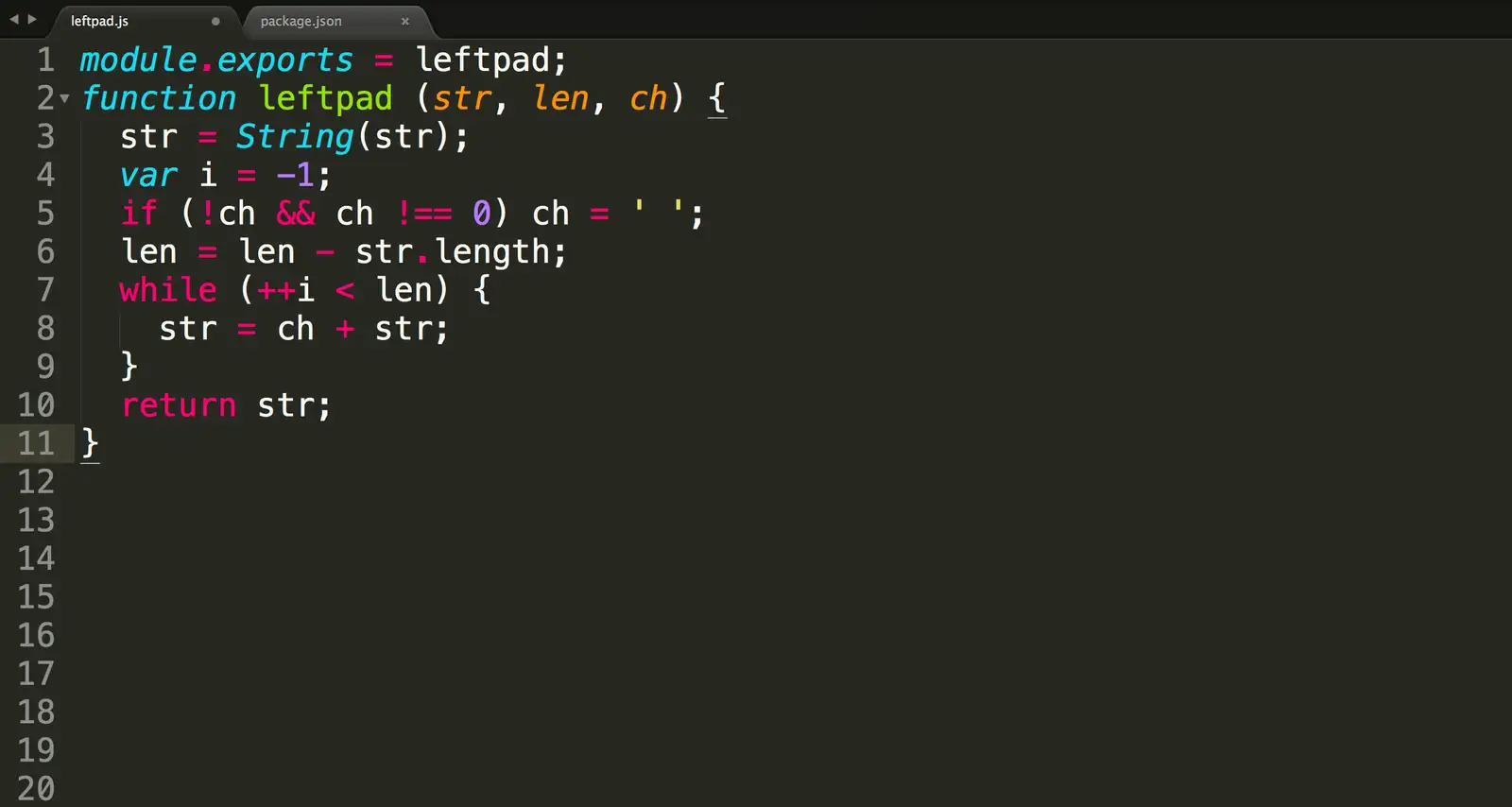
Case Study: Leftpad
Keeping supply chains secure
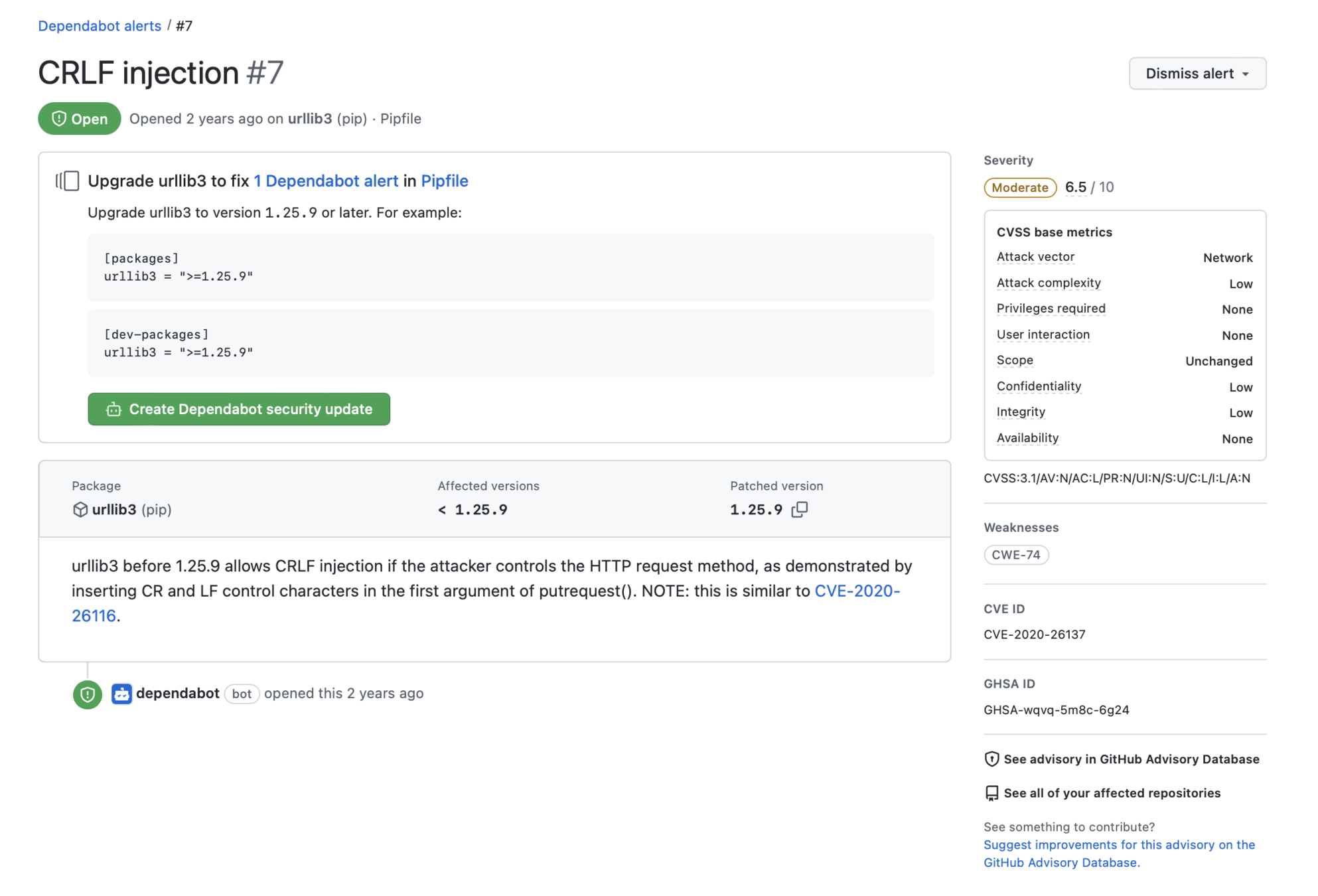
- Any software dependency creates a security risk
- Your code might be secure, but are your dependencies secure?
- SAST - Static Analysis Security Testing - tools to keep track of security upgrades to dependencies
SENG3011 23T1 - 2.3 - Managing Dependencies
By npatrikeos
SENG3011 23T1 - 2.3 - Managing Dependencies
- 807



