Javascript
Javascript
- first appeared in Netscape Navigator browser
- scripting language
<script>
var name = prompt("Please enter your name");
console.log(name)
</script>Load JS from a file
<script src="my-script.js"></script>- we usually store Javascript source outside of HTML
Create html page with JS
- index.html
- load Javascript from a file
- open in the browser
Two best friends
- console.log()
- debugger
Variables
var- let, const
let name = 'Martin';
name = 'Lucas';
const surname = 'Nuc';
Basic types
- number
- string
- boolean
- null, undefined
- objects
Numbers
- integers and floating point numbers
- beware of calculations!
- try 0.2*0.4
- special numbers
- Infinity, -Infinity, NaN
let one = 1;
one = one + 5;Strings
// 1) double quotes
let name = "Martin";
// 2) single quotes
let name = 'Martin';
// 3) backticks
let name = `Martin`;
let fullName = `${name} Nuc`;Strings
let name = 'Martin';
console.log(name.toUpperCase());
let characters = name.split('');
console.log(characters); // ['M', 'a', 'r'...]- have methods
null, undefined
- undefined = value was not set
-
null = "nothing"
- like null pointer in C
Objects
later...
Loops
- for
- while
Conditions
let a = 5;
if (a === 5) {
console.log('is five');
}for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// ...
}
let i = 0;
while(i < 10) {
// ...
i++;
}Functions
- sequence of commands
- inputs
- output
- no return = undefined
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}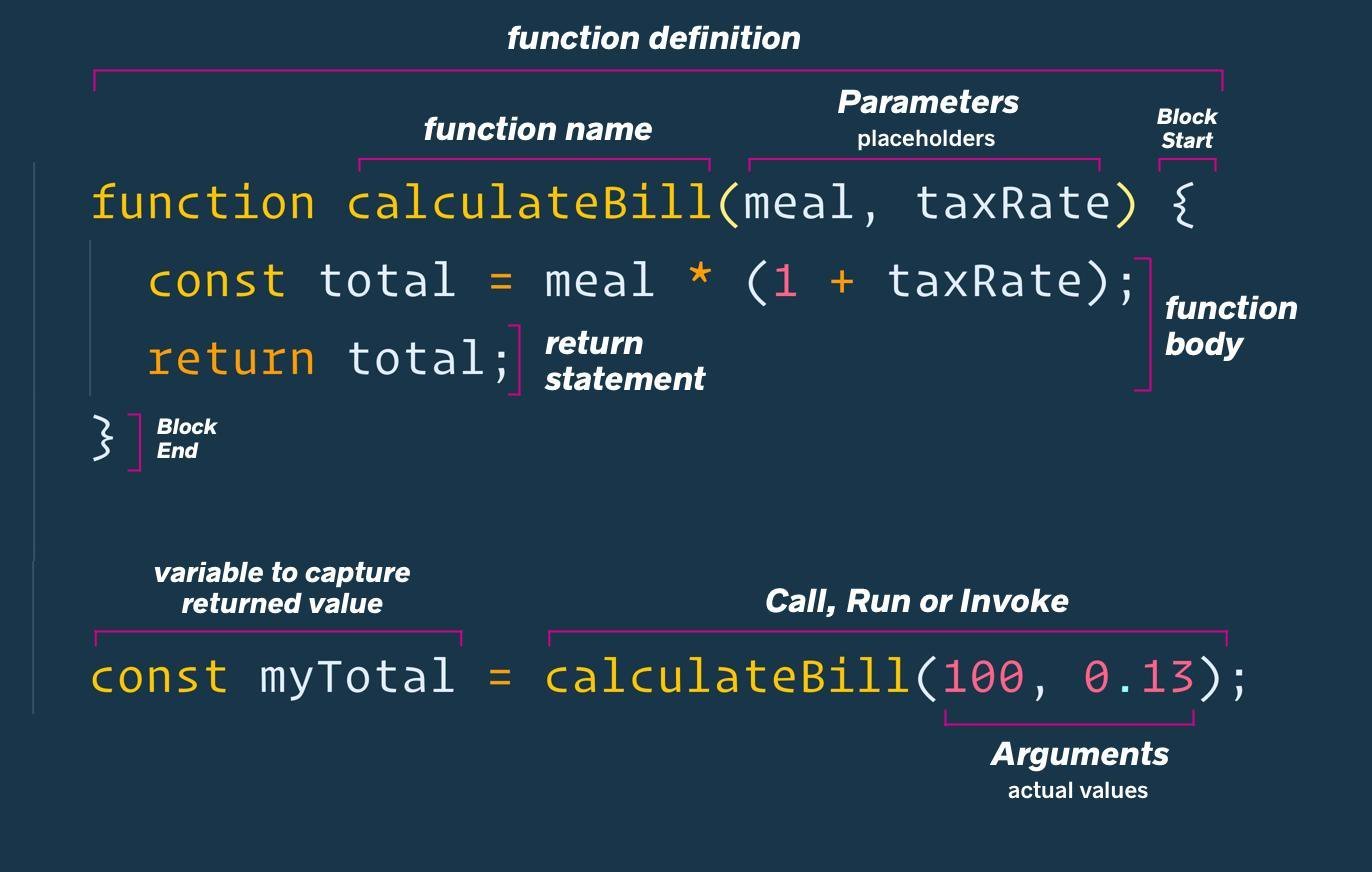
source: Wes Bos
How to create a function?
// 1) named function
function hello() {
console.log('hello');
}
// 2) anonymous function
const hello = function() {
console.log('hello');
}
// 3) using arrow function (also anonymous)
const hello = () => console.log('hello');named
anonymous
Arrow function
// with body
const one = () => {
return 1;
};
// single returned statement
const two = () => 2;Variable scope
Variable scope
- global scope
- module scope
- function scope
- block scope (let, const)
- lexical scope
Global scope
- available anywhere
- declared outside of functions
- or on the window object
let thisIsGlobal = 1;
window.something = 2;
console.log(something);Function scope
- variables in function are not visible outside
function hello() {
let something = 5;
console.log(something);
}
console.log(something); // errorBlock scope
- applies to let and const
- variable exists only in a block { ... }
let name = 'Martin';
if (true) {
let name = 'Lucas';
console.log(name);
}
console.log(name);Lexical scope
- access to the outer scope
let name = 'Martin';
function sayHello() {
console.log(`Hi, ${name}`);
}Question
- Will this work?
- What scope name has?
function one() {
let name = 'Martin';
function two() {
function three() {
console.log(`Hi, ${name}`);
}
}
}IIFE
function() {
// isolated code
console.log('one');
}();
function() {
// isolated code
console.log('two');
}();Immediately Invoked Function Expression
Create a counter
// ... your code ...
increment();
increment();
increment();
decrement();
print(); // 2- start with 0
- create functions
- increment
- decrement
Objects
Objects
- not a primitive type
- used for structured data
- key: value
- key = property
let teacher = {
firstName: 'Martin',
surname: 'Nuc',
age: 32
}Modify object
let teacher = {
firstName: 'Martin',
surname: 'Nuc',
age: 32
}
// using dot notation
teacher.age = 33;
// using key name
teacher['age'] = 33;
let keyName = 'age';
teacher[keyName] = 33;Remove property
let teacher = {
firstName: 'Martin',
surname: 'Nuc',
age: 32
}
delete teacher.age;
console.log(teacher);Create object shorthand
let firstName = 'Martin';
let age = 32;
// create object
let teacher = {
firstName: firstName,
age: age
}
// shorthand:
let teacher = {
firstName,
age
}Does the key exist?
let teacher = {
firstName: 'Martin',
age: 32
}
console.log('age' in teacher);Stored as a reference
let teacher = {
firstName: 'Martin',
age: 32
}
let teacherTwo = teacher;
teacherTwo.age = 55;
console.log(teacher.age); // ????- not like primitive types
- use Object.assign() to create a copy (not in IE11)
Calculate a distance
- create object to store coordinates (x, y)
- create a function which given two coordinates it returns a distance between these two
Safe setter
- create a function set(obj, key, value)
- it will set property key with value only if there is no value under such key
const obj = {};
set(obj, 'name', 'Martin');
console.log(obj); // { name: 'Martin' }
set(obj, 'name', 'Lucas');
console.log(obj); // { name: 'Lucas' }
set(obj, 'name', 'George');
console.log(obj); // { name: 'Lucas' }Methods in objects
const obj = {
one: function() { return 1; },
two: () => 2
three() {
return 3;
}
};
obj.four = () => 4;
obj.one();
obj.two();
obj.three();
obj.four();Destructuring object
let obj = {
firstName: 'Martin',
surname: 'Nuc',
age: 32
};
let { name, surname } = obj;
console.log(name, surname);
function printAge({age}) {
console.log(age);
}
printAge({
name: 'Martin',
age: 32
});
typeof
typeof 5 // 'number'
typeof 'hi' // 'string'
typeof {} // 'object'
typeof undefined // 'undefined'
typeof null // 'object' !!
Arrays
Arrays
- store multiple items
- in order
- .length = number of items
- push to add
let items = [1, 2, 3];
items.push(4);
console.log(items); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(items.length) // 4Access the index
- index starts with 0
let arr = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
console.log(arr[0]); // 'one'
console.log(arr[1]); // 'two'
console.log(arr[5]); // undefinedPalindrome
- create a script which determines if user's input is palindrome (use prompt())
- palindrome = word that reads the same backwards as forwards
Array methods
.join()
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
let output = arr.join('-');
console.log(output); // '1-2-3-4'- creates string by joining items in the array
.reverse()
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
arr.reverse();
console.log(arr); // [4, 3, 2, 1].forEach()
- loops over the array
[1, 2, 3, 4].forEach(item =>
console.log(item)
);.every(), .some()
- checks condition for every item
let result = [1, 2, 3, 4].every(item =>
item > 0
);
console.log(result); // true.map()
- creates a new array
- every item modified by a function
let result = [1, 2, 3, 4].map(item =>
item + 1;
);
console.log(result); // [2, 3, 4, 5].filter()
- creates a new array
- includes only items that pass the condition
let result = [1, 2, 3, 4].filter(x => x > 2);
console.log(result); // [3,4].reduce()
- accumulates intermediate result
[1,2,3,4].reduce((accumulator, current) =>
accumulator + current
, 0); // 10
| accumulator | current | result |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 3 | 6 |
| 6 | 4 | 10 |
Sum of positives
- you have an array of numbers
-
(1) count how many positive numbers are there
- example: [1,-4,7,12] => 3
-
(2) you would like to calculate sum of positive values only
- example: [1,-4,7,12] => 1 + 7 + 12 = 20
String methods
.split()
- creates an array
- split by character
'Good morning'.split(' '); // ['Good', 'morning']
.replace()
- replaces only first match and returns a new string
let result = 'Good morning'
.replace('morning', 'afternoon');.match()
- search using RegEx
let result = 'aaa,aab,aac,abc,acc'.match(/aa.?/g);
console.log(result) // [ 'aaa', 'aab', 'aac' ] Shortest word
- given a string of words, return the length of the shortest word(s)
- example: "Hi my name is Martin" => 2
Classes
What is a class?
- template for future objects
- needs to be instantiated using new keyword
- like a "recipe" for a chocolate cake. Using recipe you make a cake (instance of a cake)
class Dog {
bark() {
console.log('woof-woof');
}
}let rex = new Dog();
rex.bark();Might have properties
class Dog {
setName(newName) {
this.name = newName;
}
bark() {
console.log('woof-woof, I am ' + this.name);
}
}
let rex = new Dog();
rex.setName('Rex');
let lassie = new Dog();
lassie.setName('Lassie');
rex.bark(); // woof-woof, I am Rex
lassie.bark(); // woof-woof, I am Lassie- use this keyword to access properties
Constructor
class Dog {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
bark() {
console.log('woof-woof, I am ' + this.name);
}
}
let rex = new Dog('Rex');
rex.bark(); // woof-woof, I am Rex- method which is executed when the class is instantiated (when used with new)
Inheritance
class Animal {
eat() {
console.log('yum yum');
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
bark() {
console.log('woof-woof, I am ' + this.name);
}
}
let rex = new Dog('Rex');
rex.bark(); // woof-woof, I am Rex
rex.eat(); // yum yum- class can extend another class
- parent class should be more generic
Examples in JS
- new Date()
- new Set()
- new RegExp()
Bank account example
class BankAccount
constructor(iban) {
this.iban = iban;
this.balance = 0;
}
deposit(amount) {
this.balance = this.balance + amount;
}
withdraw(amount) {
this.balance = this.balance - amount;
}
}Elevator
- open doors, close doors
- move to different floor
- anytime you should be able to tell:
- which floor the elevator is in
- whether doors are closed or opened
setTimeout
setTimeout()
- do something later
- asynchronous
console.log(1);
setTimeout(() => console.log(2), 1000);
setTimeout(() => console.log(3), 2000);Context
this
What is context?
- the value of this keyword
- related not only to classes, it's everywhere
- typically it's set to object which the function belongs to BUT you never know
class Dog {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
bark() {
console.log('woof-woof, I am ' + this.name);
}
}
let rex = new Dog('Rex');
rex.bark();
Context
- depends on how the function is called
let obj = {
name: 'Martin',
sayHi() {
console.log(this.name);
}
}
obj.sayHi();
let fn = obj.sayHi;
fn();Enforce context
- using call+apply, bind
function fn(num) {
console.log(this, num);
}
// classic invocation
fn(1);
// call + apply
fn.call('test', 2);
fn.apply('test', [3]);
// bind
let bound = fn.bind('test');
bound(4);
Example
- jQuery uses context:
$('a').each(function() {
console.log(this.href);
});Problem
- What context does a callback function have?
let obj = {
name: 'Martin',
hi() {
console.log(this.name);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(this.name);
}, 1000);
}
}
obj.hi();
Arrow functions
- always pass the current context
let obj = {
name: 'Martin',
hi() {
console.log(this.name);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this.name);
}, 1000);
}
}
obj.hi();
Improve your JS
- Write a function for calculating a Fibonacci number
Fx = Fx-1 + Fx-2 ; F0 = 0; F1 = 1
- Write a function to get the number of occurrences of each letter in specified string.
- Write a function to find the first not repeated character.
obj = {a: 2, b: 3};
for(key in obj) {
console.log(key)
}
Feedback form
DOM
What is it?
- document object model
- big javascript object with all information about HTML page
- before working with DOM you must wait for the page be loaded
Waiting for page to load
<body onload="ready()">
<script>
function ready() {
console.log('page is ready');
}
</script>
</body><body>
<script>
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
console.log('page is ready')
});
</script>
</body>Finding element
- document.querySelector(<selector>)
var element = document.querySelector('.my-class');
element.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
element.innerHTML = '<h1>Hello</h1>';
element.style.opacity = 1;Finding element inside of the element
- element.querySelector(<selector>)
var element = document.querySelector('.outer');
var inner = element.querySelector('.inner');<div class="outer">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>Finding multiple children
- document.querySelectorAll(...)
- returns an array
let items = document.querySelectorAll('.item');
console.log(items[0]);Listening for clicks
- execute Javascript function on click
<button type="button" onclick="myScript()">click me</button>
<button id="work" type="button">work</button>
<script>
function myScript() {
console.log('clicked');
}
var element = document.querySelector('#work');
element.addEventListener('click', function() {
console.log('clicked');
});
</script>Is it palindrome?
- display prompt after clicking on the button
- ask for a word
- display green when the word is palindrome
- display red when it's not
Math
- Math.PI
- Math.round(5.5) -> 6
- Math.sqrt(9) -> 3
- sin, cos
- Math.random()
setTimeout(callback, time)
- executes after <time> ms
- uses callback function
var timeoutReference = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('after 3s');
}, 3000);cancelling timeout
clearTimeout(timeoutReference);Flip the coin
- download image for coin heads and coin tails
- show / hide coin n times
- n should be random number between 4-10
- ADVANCED:
- make animation of coin flipping
Modifying DOM
- create element
var el = document.createElement('div'); - set content
el.innerHTML = '<p>Hello World!</p>'; - insert it into the page
document.body.appendChild(el);
Fetch data from server
fetch() and GET
fetch('http://stapi.co/api/v1/rest/season/search?pretty')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));- connects to the server and download data
- fetch on MDN
HTTP methods
- GET - reading data
- POST - saving new data
- might have body
- PUT - updating existing data
- might have body
- DELETE - removing data
- OPTIONS, HEAD ...
HTTP status code
- 2xx - success (200 OK, 204 No Content)
- 3xx - redirects
- 4xx - client error
- 401 Unauthorized
- 404 Not Found
- 5xx - server error
- 500 - Internal server error
- 503 - Service unavailable
- 504 - Timeout
fetch() and POST
- sends payload (body)
let payload = new URLSearchParams();
payload.set('name', 'Picard');
let fetchOptions = {
method: 'POST',
body: payload,
};
fetch('http://stapi.co/api/v1/rest/character/search', fetchOptions)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));Promises
- fetch() returns a Promise
- way how to write asynchronous code in flat way
- callback in .then(callback) is called after operation is finished
Search in StarTrack database
- create a button which downloads info about seasons from http://stapi.co/api-browser
- create a list in the page
- display names of series
Promises
What are they for
- to avoid "callback hell"
- flat and readable code
- mostly used for asynchronous operations
- any asynchronous operation can be wrapped to a Promise
Promise state
- pending
- fulfilled
- rejected
pending
rejected
fullfilled
.then(...)
.catch(...)
How to create a promise
- Promise.resolve()
- Promise.reject()
- instantiate a Promise object
function wait5seconds() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(), 5000);
});
};
wait5seconds().then(() => console.log('after 5s'));Promise chaining
- what you return in then you get in the next then
- when it returns a Promise it will wait for that promise to resolve before going to next then
Promise.resolve('hey')
.then(data => console.log(data)) // hey
.then(() => anotherPromise())
.then(() => {
return 'hello';
})
.then(param => console.log(param)); // helloWaiting for multiple promises
- Promise.all([promise1, promise 2])
- returns a single promise
Wrap setTimeout in Promise
- create function wait
- parameter: how long it should wait
- use promise chain (.then) to count down:
- console.log: 3,2,1, go!
async / await
async/await
- syntactic sugar around promises
- works only in async function
async function countDown() {
console.log(3);
await wait(1000);
console.log(2);
await wait(1000);
console.log(1);
await wait(1000);
console.log('go!');
}
countDown().then(() => console.log('done'));async/await
async function countDown() {
console.log(3);
await wait(1000);
console.log(2);
await wait(1000);
console.log(1);
await wait(1000);
console.log('go!');
}
countDown().then(() =>
console.log('done'));function countDown() {
console.log(3);
return wait(1000)
.then(() => console.log(2))
.then(() => wait(1000))
.then(() => console.log(1)
.then(() => wait(1000))
.then(() => console.log('go!'))
}
countDown().then(() =>
console.log('done'));Elevator
- modify elevator class to be asynchronous
- moving through every floor should take 500ms
- opening doors should take 250ms
Exceptions
Exceptions
throw 'message';
// better:
throw new Error('message');
try { ... }
catch (err) { ... }Catch in async functions
async function() {
try {
await Promise.reject('this is reason');
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
}Event loop
Event loop
- queue for async operations
- setTimeout()
What happens?
console.log(1);
setTimeout(() => console.log(2), 0);
console.log(3);Improve your Javascript
-
Finders Keepers
- find first item in array which passes provided function
- training for callback
-
Mutations
- are both strings from same letters?
-
Caesars cipher
- ROT13
- every letter is shifted by 13 letters
- take a look on String.charCodeAt() and String.fromCharCode()
Alpiq Javascript
By Martin Nuc
Alpiq Javascript
- 367



