Tieto React Advanced
🙋♂️
Frontend engineer
- 9 years FE experience
- AngularJS, Angular, Ember, React
- currently Staff engineer at Productboard
❤️ 📸
❤️ 🛞
Slides + code
Schedule
- 9-12 morning
- recap of the previous day
- breaks: 10:00, 11:00
- 12-13 lunch
- 13-17 afternoon
- breaks: 14:00, 15:00, 16:00
Course
- exercises build on top of each other!
- discussions welcomed
- on Wednesday if we have time let's do a project
- multipage
- tested
- optimized
- correct project structure
Your experience?
Setup IDE
Install
- Google Chrome
- nodejs
- Visual Studio Code
- React dev tools
🧠 React basics
- components, component tree
- props, events
- styling the app
- children props
- controlled input
- useState, useEffect
- making HTTP requests
- custom hooks
- React Context
➡️ Let's make http request
- open API request in browser to see structure of response
- display joke in the component
- create a button to load another joke
- disable button when loading the joke
GET https://api.chucknorris.io/jokes/random// create a new project
npx create-react-app react-playground --template typescript
// install axios
npm i axios
npm startLet's do more React! 💪
React hooks
- ✅ useState
- ✅ useEffect
- ✅ useContext
- useRef
- useImperativeHandle
- useCallback
- useMemo
- useReducer
Child to parent?
Parent
Child
do something
Control child component?
Parent
Child
do something
useRef
useRef
- manipulate with DOM elements
- object with mutable current property
import { useRef } from 'react';
function Component() {
const inputRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
function handleClick() {
inputRef.current?.focus();
}
return <div>
<input ref={inputRef} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>Focus the input</button>
</div>
}Expose element from
a component
- ref cannot be used as prop
- need to wrap component with forwardRef
function Parent() {
const inputRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
const handleClick = () => inputRef.current?.focus();
return <>
<Child ref={inputRef} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Focus
</button>
</>
}
const Child = forwardRef<HTMLInputElement>((props, ref) => {
return <div>
<input ref={ref} />
</div>
})Expose imperative API
- used to expose API of Child component to the Parent
function Parent() {
const childApiRef = useRef<{ focus: () => void }>(null);
const handleClick = () => childApiRef.current?.focus();
return <>
<Child ref={childApiRef} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Focus
</button>
</>
}
const Child = forwardRef<{ focus: () => void }>((props, ref) => {
const inputRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
focus: () => inputRef.current?.focus()
}), [inputRef])
return <div>
<input ref={inputRef} />
</div>
})React hooks
- ✅ useState
- ✅ useEffect
- ✅ useContext
- ✅ useRef
- ✅ useImperativeHandle
- useCallback
- useMemo
- useReducer
Performance
Problem
- lot of rerenders
- every render creates new function, object etc
- DOM operations are expensive
React Virtual DOM
- virtual representation of DOM = big object
- React updates the virtual DOM
- then creates a diff agains the real DOM
- and applies only necessary changes to the real DOM
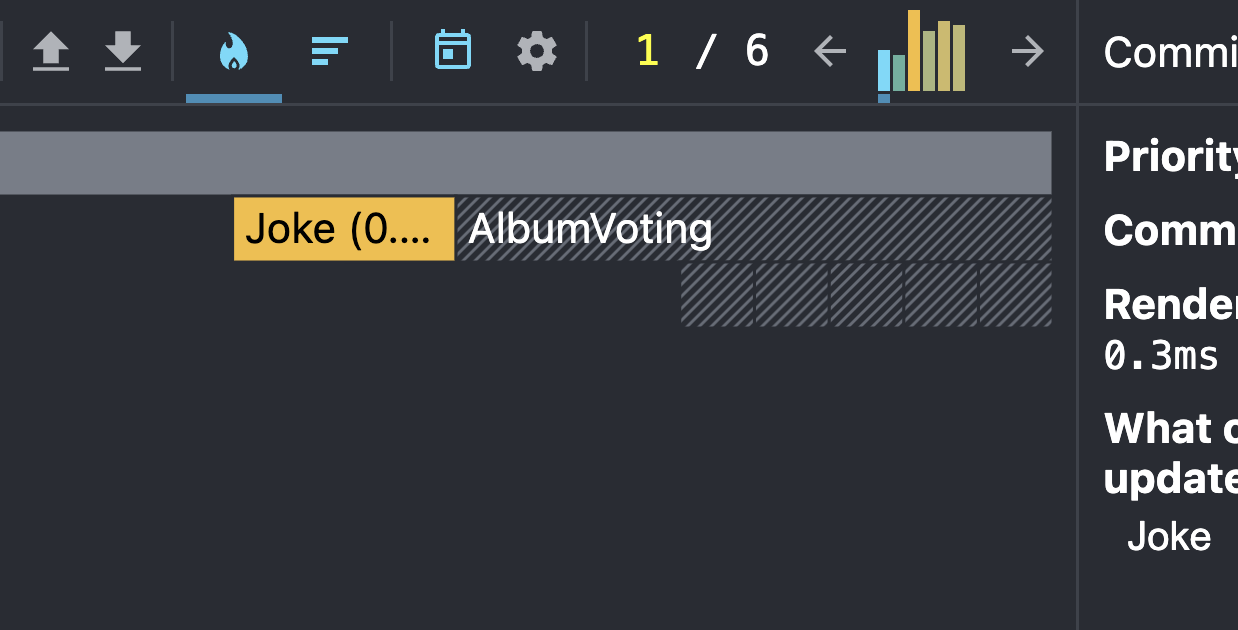
Profiler in dev tools
import { useState } from "react";
import { AlbumItem } from "./AlbumItem";
export type Album = {
id: number;
title: string;
rating: number;
}
export const AlbumVoting = () => {
const [albums, setAlbums] = useState(new Array(15).fill({
id: 0,
title: '',
rating: 0
}).map((album, index) => ({ ...album, id: index })));
function handleChange (updatedAlbum: Album) {
setAlbums(albums => albums.map(album => album.id === updatedAlbum.id ? updatedAlbum : album));
};
return <div>
{albums.map(album => <AlbumItem key={album.id} album={album} onChange={handleChange} />)}
</div>
}
import { Album } from "./AlbumVoting";
type Props = {
album: Album,
onChange: (updated: Album) => void
}
export const AlbumItem = ({ album, onChange }: Props) => {
function handleChange(change: Partial<Album>) {
onChange({
...album,
...change
});
}
return <p>
Title:
<input value={album.title}
onChange={(e) => handleChange({ title: e.target.value })}
/>
Rating
<input type='number'
value={album.rating}
onChange={(e) => handleChange({ rating: Number(e.target.value) })}
/>
</p>
}AlbumVoting.tsx
AlbumItem.tsx
- shows rerenders
- shows why
React.memo
- rerenders component only on prop change
const ExpensiveComponentMemoized = React.memo(function ExpensiveComponent() {
...
});
<ExpensiveComponentMemoized />useMemo
- precompute value
- for computation-expensive values
- avoids main thread lock
const useFibonacci = (n) => {
const result = useMemo(() => fibonacci(n), [n]);
return result;
}
function fibonacci(n) {
return n < 1 ? 0
: n <= 2 ? 1
: fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2)
}useCallback
- used to retain a single function reference
- avoids problem with recreating handler every render
type Props = {
me: string;
}
function Component({me}: Props) {
const handleClick = useCallback(
(name) => console.log(`Hello ${name} and ${me}`)
, [me]);
return <ExpensiveComponent onClick={handleClick} />;
}➡️ Optimize album voting
- only row which is updated should rerender
import { useState } from "react";
import { AlbumItem } from "./AlbumItem";
export type Album = {
id: number;
title: string;
rating: number;
}
export const AlbumVoting = () => {
const [albums, setAlbums] = useState(new Array(15).fill({
id: 0,
title: '',
rating: 0
}).map((album, index) => ({ ...album, id: index })));
function handleChange (updatedAlbum: Album) {
setAlbums(albums => albums.map(album => album.id === updatedAlbum.id ? updatedAlbum : album));
};
return <div>
{albums.map(album => <AlbumItem key={album.id} album={album} onChange={handleChange} />)}
</div>
}
import { Album } from "./AlbumVoting";
type Props = {
album: Album,
onChange: (updated: Album) => void
}
export const AlbumItem = ({ album, onChange }: Props) => {
function handleChange(change: Partial<Album>) {
onChange({
...album,
...change
});
}
return <p>
Title:
<input value={album.title}
onChange={(e) => handleChange({ title: e.target.value })}
/>
Rating
<input type='number'
value={album.rating}
onChange={(e) => handleChange({ rating: Number(e.target.value) })}
/>
</p>
}AlbumVoting.tsx
AlbumItem.tsx
React hooks
- ✅ useState
- ✅ useEffect
- ✅ useContext
- ✅ useRef
- ✅ useImperativeHandle
- ✅ useCallback
- ✅ useMemo
- useReducer
React Context
Context
- "global" state for subtree of components
- avoids passing props deep
- Provider + Consumer
type ContextValue = boolean;
const MyContext = React.createContext<ContextValue>(false);
function App() {
return <MyContext.Provider value={true}>
<Component />
</MyContext.Provider>;
}
function Component() {
const value = useContext(MyContext);
return <div>{value}</div>;
}Context
- pass object with value + setter
type ContextValue = {
value: number;
setValue: (value: ContextValue['value']) => void
};
const MyContext = React.createContext<ContextValue>({} as unknown as ContextValue);
function App() {
const [value, setValue) = useState(0);
return <MyContext.Provider value={{ value, setValue}}>
<Component />
</MyContext.Provider>;
}
function Component() {
const {value, setValue} = useContext(MyContext);
return <>
<div>{value}</div>
<button onClick={() => setValue(value + 1)}>Click</button>
</>;
}Encapsulate context
- Provider component instead of App component
type ContextValue = {
value: number;
setValue: (value: ContextValue['value']) => void
};
// not exported - private
const MyContext = React.createContext<ContextValue>({} as unknown as ContextValue);
export function MyContextProvider({children}: PropsWithChildren) {
const [value, setValue) = useState(0);
return <MyContext.Provider value={{ value, setValue}}>
{children}
</MyContext.Provider>;
}
// only way to read the value:
export const useMyContext = () => useContext(MyContext);
// in another file
import {useMyContext} from './my-context';
function Component() {
const { value, setValue } = useMyContext();
return <>
<div>{value}</div>
<button onClick={() => setValue(value + 1)}>Click</button>
</>;
}
<MyContextProvider>
<Component />
</MyContextProvider>Context initial state
- pass via props
type ContextValue = {
value: number;
changeValue: (newValue: ContextValue['value']) => void;
}
const MyContext = React.createContext<ContextValue>({} as unknown as ContextValue);
type Props = {
initialState: ContextValue['value'];
children: React.ReactNode
}
export function MyContextProvider({initialState, children}: Props) {
const [value, setValue] = useState(initialState);
return <MyContext.Provider value={{value, setValue}}>
{children}
</MyContext.Provider>;
}
<MyContextProvider initialState={5}>
...
</MyContextProvider>➡️ UserContext
- create a context for session with values:
- user
- username
- login = sets the user
- logout = sets user to null
- user
- create login component with login
- create component CurrentUserInfo showing currently logged user & logout button
export function UserInfoPane() {
const { user } = useUser();
return <div>
{user ? <CurrentUserInfo /> : <LoginForm />}
</div>
}export function LoginForm() {
const { login } = useUser();
const [username, setUsername] = useState('');
const [email, setEmail] = useState('');
return <div>
<input placeholder="username" value={username} onChange={(e) => setUsername(e.target.value)} />
<input placeholder="email" value={email} onChange={(e) => setEmail(e.target.value)} />
<button onClick={() => login({username, email})}>Login</button>
</div>
}
type UserContext = {
user: User | null,
login: (user: User) => void;
logout: () => void;
}const useUser = () => useContext(UserContext);➡️ UserContext
export function UserInfoPane() {
const { user } = useUser();
return <div>
{user ? <CurrentUserInfo /> : <LoginForm />}
</div>
}export function LoginForm() {
const { login } = useUser();
const [username, setUsername] = useState('');
const [email, setEmail] = useState('');
return <div>
<input placeholder="username" value={username} onChange={(e) => setUsername(e.target.value)} />
<input placeholder="email" value={email} onChange={(e) => setEmail(e.target.value)} />
<button onClick={() => login({username, email})}>Login</button>
</div>
}
type UserContext = {
user: User | null,
login: (user: User) => void;
logout: () => void;
}UserContextProvider
UserInfoPane
CurrentUserInfo
LoginForm
= missing
const useUser = () => useContext(UserContext);❗️Impact on performance
- Change of the context triggers rerender
Testing
Testing
- unit/component testing
- integration testing
- e2e testing
Jest
- testing framework
- https://jestjs.io
- provides assertions, mocks, test runner
import {add} from './add';
it('adds numbers', () => {
expect(add(1, 3)).toBe(4);
})import {add} from './add';
test('adding two numbers', () => {
expect(add(1, 3)).toBe(4);
})How to run tests?
- just execute jest
- to run them repeatedly: --watch
- looks for files named *.spec.js / *.test.js
- for Typescript it needs further configuration
- in create-react-app just run ➡️ npm test script
- looks for files named *.spec.ts / *.test.ts
Arrange / Act / Assert
import {add} from './add';
it('adds numbers', () => {
expect(add(1, 3)).toBe(4);
})import {add} from './add';
it('adds numbers', () => {
// Arrange
const a = 1;
const b = 3;
// Act
const result = add(a, b);
// Assert
expect(result).toBe(4);
})- arrange = prepare for tests (inputs, mocks...)
- act = run the tested unit
- assert = check the results (output, mocks)
Structuring tests
- describe
- beforeEach
- test
- test
- test
- describe
- beforeEach
- afterEach
- test
- describe
- test
- test
expect(add(1, 3)).toBe(4);subject
matcher
Matchers
Matchers
- .toBe() = exact match (like ===)
- .toEqual() = deep equal
- .toBeNull(), toBeUndefined()
- .toContain() = is the item in an array?
- .toContainEqual()
import {add} from './add';
it('adds numbers', () => {
expect(add(1, 3)).toBe(4);
})Negation
- .not.toBe()
- .not.toEqual()
- .not.toBeNull()
- ...
import {add} from './add';
it('adds numbers', () => {
expect(add(1, 3)).not.toBe(5);
})Match substring
- toEqual(expect.stringContaining(...))
expect('How are you?').toEqual(expect.stringContaining('How'));Match objects
- .toEqual({...})
- .toEqual(expect.objectContaining({ key: value }))
- .toHaveProperty(key, value)
expect({a: 1, b: 2}).toBe({a: 1, b: 2}); // ❌ DON'T
expect({a: 1, b: 2}).toEqual({a: 1, b: 2}); // ✅ DO
expect({a: 1, b: 2}).toEqual(expect.objectContaining({a: 1}));
expect({a: 1, b: 2}).toHaveProperty('a', 1);
expect({
one: 1,
two: {
nested: 2
}
}).toHaveProperty('two.nested', 2);Match arrays
- .toEqual([...])
- .toEqual(expect.arrayContaining([...]))
expect([1,2,3]).toBe([1,2,3]); // ❌
expect([1,2,3]).toEqual([1,2,3]); // ✅
expect([1,2,3]).toEqual(expect.arrayContaining([1,2]));Match exceptions
- expect( () => {...} ).toThrow()
- expect( () => {...} ).toThrow('Error message')
- expect( () => {...} ).toThrow(MyError)
expect(testedFn()).toThrow(); // ❌ DON'T
expect(() => testedFn()).toThrow(); // ✅ DOTotal number of asserts
- expect.assertions(2)
- used usually for async code
function doNTimes(fn, n) {
for(let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
fn();
}
}
// ❌ DON'T - better to use mocks (later)
it('calls the function n times', () => {
expect.assertions(3);
function fn() {
expect(true).toBe(true);
}
doNTimes(fn, 3)
})➡️ Update package.json
{
"name": "...",
"jest": {
"transformIgnorePatterns": [
"/node_modules/(?!(axios))"
]
},
...
}➡️ Update App.test.tsx
test.skip('renders learn react link', () => {
render(<App />);
const linkElement = screen.getByText(/learn react/i);
expect(linkElement).toBeInTheDocument();
});
➡️ Test the division
- each test should test only one thing
- test the happy path
- test edge cases
export function divideWithRemainder(a: number, b: number) {
if (b === 0) {
throw new Error('Cannot divide by zero.');
}
const result = Math.ceil(a / b);
const remainder = a % b;
return {
result,
remainder
};
}
Mocks
Mocks
- also called spies
- lets you spy on the behavior
- can also replace existing behavior
- you should mock the boundary of your system
Creating a mock
const fn = jest.fn(); // empty function
// pass implementation
const fn = jest.fn(() => {
return 5;
});
// override implementation
fn.mockImplementation(() => {
return 6;
});
fn.mockReturnValue(5);
fn.mockResolvedValue(5); // returns promise which resolves in 5
fn.mockReturnValueOnce(1);
fn.mockReturnValueOnce(2);
fn.mockReturnValue(3);
fn() // 1
fn() // 2
fn() // 3
fn() // 3- create mock
- define its behavior
Mock matchers
const fn = jest.fn(() => 42); // empty function
expect(fn).toHaveBeenCalled(); // fails
fn();
expect(fn).toHaveBeenCalled(); // passes
expect(fn).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(1);
fn(1,2,3)
expect(fn).toHaveBeenLastCalledWith(1,2,3);
expect(fn).toHaveReturnedWith(42); // test output- evaluates if mock has been called
➡️ Test doNTimes
- use mocks
function doNTimes(fn, n) {
for(let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
fn();
}
}Spy on existing
jest.spyOn(Math, 'random');
Math.random();
expect(Math.random).toHaveBeenCalled();
// change behavior
const randomMock = jest.spyOn(Math, 'random');
randomMock.mockReturnValue(1);
expect(Math.random()).toBe(1);- possible only on instances of classes or objects
- spyOn(object, methodName)
Mocking modules
- used to mock 3rd party library
- jest.mock hoists up before all imports
import { fetchUser } from './fetch-user';
import axios from 'axios';
jest.mock('axios');
const mockedAxios = axios as jest.Mocked<typeof axios>;
it('fetches user data', async () => {
const response = { data: { id: 1, name: 'Martin' } };
mockedAxios.get.mockResolvedValue(response);
expect(await fetchUser()).toEqual({ id: 1, name: 'Martin' });
});
import axios from 'axios';
function fetchUser() {
return axios.get('/url').then((response) => response.data);
}
React testing
Testing React
- testing components, hooks
-
test should be as close as possible to how user will use the component
- test what he sees
- test how he interacts (mouse, keyboard etc)
- mock boundary of the system
- mock HTTP, local storage etc.
- Jest uses JSDOM to emulate browser
🔨 React testing library
- provides API for:
- querying the DOM
- doing user actions
- matchers
- https://testing-library.com/docs/
1. Queries
Query DOM
- get = 1 match immediately
- query = 0 or 1 match immediately
- find = 1 match, waiting
| Type of Query | 0 Matches | 1 Match | >1 Matches | Retry (Async/Await) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Element | ||||
| getBy... | Throw error | Return element | Throw error | No |
| queryBy... | Return null | Return element | Throw error | No |
| findBy... | Throw error | Return element | Throw error | Yes |
| Multiple Elements | ||||
| getAllBy... | Throw error | Return array | Return array | No |
| queryAllBy... | Return [ ] | Return array | Return array | No |
| findAllBy... | Throw error | Return array | Return array | Yes |
Query By
- Accessibility
- getByRole - by ARIA role
- getByLabelText = good for forms
- getByPlaceholderText = good for forms without labels
- getByText = what user sees, good outside of forms
- getByDisplayValue = value of an input
- HTML semantic
- getByAltText
- getByTitle
- Test IDs
- getByTestId = for invisible elements or dynamic text
import { screen } from '@testing-library/react';
screen.getByRole('button', {name: /submit/i});Query by role
- check all ARIA roles
- default roles (W3 ARIA spec)
- button - "button"
- a - "link"
- h1...h6 - "heading"
-
accessible name
- usually what you want :-)
- label for form, alt for image...
getByRole('button', { name: 'Submit' });
// // checked input type checkbox
getByRole('checkbox', { checked: true });
// usually h2
getByRole('heading', { level: 2 });Query by text
screen.getByText('Hello World'); // full string match
screen.getByText('llo Worl', {exact: false}); // substring match
screen.getByText('hello world', {exact: false}); // ignore case
screen.getByText(/World/); // regexp
// custom function
screen.getByText((content, element) => content.startsWith('Hello'));- what user sees
Query by test-id
<div class="background red" data-testid="background">
...
</div>
const backgroundEl = screen.getByTestId('background');- test by HTML attribute data-testid
- used when the text is dynamic
- used when element has no content
Query within element
- useful when we want to scope query in specific area
import { render, fireEvent, screen, within } from '@testing-library/react';
const container = screen.getByTestId('container');
const helloMessage = within(container).getByText('hello');2. User actions
fireEvent
- fires DOM event on an element
- fires only a single event
- fireEvent.click doesn't trigger mouseDown, mouseUp
// click on an element
fireEvent.click(screen.getByText('Login'));
// change input value
fireEvent.change(getByLabelText(/username/i), {target: {value: 'martin'}});
3. Matchers
Matchers
- from jest-dom library
- makes tests easy to read
// check text content
const element = screen.getByTestId('title');
expect(element).toHaveTextContent('This is title');
// check if is in the document
const element = screen.queryByText('Submit');
expect(element).toBeInDocument();
// test focus
const input = screen.getByTestId('password');
expect(input).toHaveFocus();
// test checkbox state
const rememberPass = screen.getByRole('checkbox', {name: 'Remember password'});
expect(rememberPass).toBeChecked();Render component
import { render } from '@testing-library/react';
it('renders', () => {
render(<App />);
const element = screen.queryByText('Hello');
expect(element).toBeInDocument();
});
➡️ Test Joke component
- mock the server response
- test:
- loading state
- the fetched joke is displayed
- button to load the next joke
- button should be disabled when fetching
{
"name": "...",
"jest": {
"transformIgnorePatterns": [
"/node_modules/(?!(axios))"
]
},
...
}package.json
Testing hooks
renderHook
- simulates component lifecycle
- prefer testing hook when testing the component
- act() simulates work of React
- wrap when you expect something to change
import { act, renderHook } from "@testing-library/react";
import { useCounter } from "./use-counter";
it('increments', () => {
const {result} = renderHook(() => useCounter());
expect(result.current.count).toBe(0);
act(() => result.current.increment());
expect(result.current.count).toBe(1);
})export function useCounter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increment =() => setCount(count + 1);
return { count, increment };
}➡️ Test useCounter hook
export function useCounter(initialValue: number) {
const [count, setCount] = useState(initialValue);
const increment = () => setCount(count + 1);
const randomize = () => setCount(Math.random());
return { count, increment, randomize };
}
Render props
Render props
Children
<WrapperComponent>
</WrapperComponent>
Render props
- wrapping component encapsulates the functionality
- composition pattern
function Component() {
return <MousePosition render={
(x, y) => <p>Position is x={x}, y={y}</p>
} />
}
type Props = {
render: (x: number, y: number) => React.ReactNode;
}
function MousePosition({ render }: Props) {
...
return <>{render(position.x, position.y)}</>;
}Render props using children
function Component() {
return <div>
<Counter>
{({counter, increment}) => <>
<div>Counter value: {counter}</div>
<button onClick={increment}>INC</button>
</>}
</Counter>
</div>
}
type CounterApi = {
counter: number,
increment: () => void
};
type Props = {
children: (api: CounterApi) => React.ReactNode;
}
function Counter({children}: Props) {
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
function increment() {
setCounter(counter + 1);
}
return <>{children({counter, increment})}</>
}➡️ Create <JokeFetcher>
- create a component that fetches the joke
- it passes joke via render props
<JokeFetcher>
{({joke, isLoading}) => <p>{isLoading ? 'Loading...' : joke}</p>}
</JokeFetcher>Routing
React router
- used to create multiple pages
- install react-router-dom + type definitions
- npm i react-router-dom @types/react-router-dom
- docs
Building blocks
- Layout page
- App.tsx
- router
Routable pages
Navbar
Layout.tsx
import { Outlet } from "react-router";
export function Layout() {
return <div>
<NavBar />
<Outlet />
</div>
}- template for the root component
Here other routes render
Routable pages
<Outlet />
<Navbar />
App.tsx
import { RouterProvider, createBrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
const router = createBrowserRouter([
... // (later)
]);
function App() {
return (
<RouterProvider router={router} />
);
}Router
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: <Layout />,
children: [
{
index: true,
element: <Home />
},
{
path: 'about',
element: <About />
},
{
path: 'articles',
element: <ArticlesContainer />,
children: [
{
path: ':articleId',
element: <Article />
}
{
path: ':articleId/comments',
element: <ArticleComments />
}
]
}
]
}
]);Must have <Outlet /> inside
Layout component
Nested routes
- components can define subroutes
Routable pages
Navbar
<Outlet>
Routable pages
Navigation using links
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
<Link to="/about">About</Link>
<Link to="/articles">Articles</Link>
<Link to="/articles/{articleId}">Specific article</Link>Imperative navigation
const navigate = useNavigate();
navigate('/articles');- using useNavigate() hook
Reading url parameters
import { useParams } from "react-router-dom";
function Joke() {
const params = useParams();
return (
{params.category}
);
}/path-segment/:pathParam/something?query1=one&query2=twouseSearchParams
useParams
➡️ Create multiple pages
- UserInfoPane should be always visible
- NavBar should be always visible
- Create routes
- /votes -> album voting
- /categories -> categories list
- /categories/:category -> joke from category
- load joke based on category
GET https://api.chucknorris.io/jokes/random?category={category}Error Boundary
Error boundary
- catches errors from render/component life cycle
- catches errors in Error Boundary children
- create-able only using the class component
- wrap any part of the app with error boundary
<JokeErrorBoundary>
<Joke />
</JokeErrorBoundary>Error Boundary
import React, { PropsWithChildren } from "react";
type Props = PropsWithChildren;
type State = {
hasError: boolean;
error?: unknown;
}
export class JokeErrorBoundary extends React.Component<Props, State> {
constructor(props: Props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error: unknown) {
return { hasError: true, error };
}
// optional
componentDidCatch(error: unknown, errorInfo: ErrorInfo) {
console.error(error, errorInfo);
}
render() {
const {error, hasError} = this.state;
if (hasError) {
// fallback
return <div>{String(error)}</div>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}➡️ Test ErrorBoundary
- create "error" route for ThrowPage (code below)
- create a global error boundary
- when something bad happens it shows
- "Upss, our fault"
export function ThrowPage() {
throw 'Something went wrong.'
return <></>
}Suspense
Suspense
- used to wait for something to finish
- usually, we wait for the data to be loaded
- or for JS chunk to load
- Suspense wraps component which gets suspended
function Parent() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<ComponentWithLoading />
</Suspense>
)
}How does it work?
- suspendable component must be wrapped with <Suspense>
- suspendable component throws an exception with a Promise in the render
- until the promise is resolved, Suspense shows fallback
- when the promise resolves, Suspense tries to render the component again
Split app into chunks
Chunks
- by default we have only main chunk
- contains the whole app
- better to usually split the app by routes
- user doesn't have to load code he doesn't need
- vendor chunk = for 3rd party libraries
How to create chunk
- combine React.lazy & import()
// default export
const ComponentLazy = React.lazy(
() => import('./Component')
);
// rename named export as default
const ComponentLazy = React.lazy(() =>
import('./Component').then(({Component}) => ({default: Component}))
);
function Parent() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<ComponentLazy prop="value" />
</Suspense>
);
}Support in React Router
- chunk per route
- expects key Component
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: <Layout />,
children: [ {
path: 'about',
// key must be "Component"
lazy: () =>
import("./about").then(({ About }) => ({Component: About}))
},
]
}
]);Must be under Component key
React Portal
Portal
- used to render JSX anywhere in the DOM
- everything works as if the JSX was rendered as normal
- useful for modal dialog (z-index, positioning)
createPortal
- first argument - JSX
- second argument - DOM element
import {createPortal} from 'react-dom';
function Component() {
return <div>
{createPortal(<div>Hello</div>, document.body)}
</div>
}➡️ Create a modal dialog
- create a component that renders children in a modal window
- in the middle of the screen
<Modal>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<p>I am modal</p>
</Modal>React hooks
- ✅ useState
- ✅ useEffect
- ✅ useContext
- ✅ useRef
- ✅ useImperativeHandle
- ✅ useCallback
- ✅ useMemo
- useReducer
useReducer
- alternative to useState
- better for complex logic
- good when there is several useState depending on each
- "simple" redux built-in React
Example: counter
type State = number;
type Increment = { type: 'increment'; payload: number };
type Randomize = { type: 'randomize' };
type Action = Increment | Randomize;
function reducer(state: State, action: Action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "increment":
return state + 1;
case "randomize":
return Math.random();
default:
return state;
}
}
export function Counter() {
const [ state, dispatch ] = useReducer(reducer, 0);
return <div>
Counter: {state}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'increment', payload: 1 })}>Increment</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'randomize' })}>Randomize</button>
</div>
}Initial state
➡️ useReducer in Joke
- write reducer with the following actions
- fetching joke
- joke fetched
- Joke fetching error
Redux
Redux
- state management library
- one global store
- big object
- actions to modify the state
- browser extension: Redux Devtools
- npm install @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux
Store
Actions
Reducers
Store example
{
jokeSlice: {
currentJoke: "Chuck Norris can speak Braille.",
isLoading: false
},
counterSlice: {
count: 5
},
uiSlice: {
dropdownVisible: false
}
}View
Reducer
Store
dispatch an action
update the store
view reads data from the store
increment = (state) => {
state.count += 1;
}1. Create slices
// /src/store/counterSlice.ts
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import type { PayloadAction } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
export type CounterState = {
count: number;
};
const initialState: CounterState = {
count: 0,
};
export const counterSlice = createSlice({
name: 'counter',
initialState,
reducers: {
increment: (state, action) => {
state.count += 1;
}
},
});
export const { increment } = counterSlice.actions;
export const counterReducer = counterSlice.reducer;
2. Create a store
// src/store/store.ts
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import { jokeReducer } from './jokeSlice';
import { counterReducer } from './counterSlice';
import { uiReducer } from './uiSlice';
export const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
jokeSlice: jokeReducer,
counterSlice: counterReducer,
uiSlice: uiReducer
},
});
export type RootState = ReturnType<typeof store.getState>;
export type AppDispatch = typeof store.dispatch;
3. Provide the store
// index.tsx
import { store } from './store/store'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>
);
4. Created typed hooks
// src/store/hooks.ts
import { TypedUseSelectorHook, useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
import type { RootState, AppDispatch } from './store';
export const useAppDispatch: () => AppDispatch = useDispatch;
export const useAppSelector: TypedUseSelectorHook<RootState> = useSelector;
- avoid using useDispatch & useSelector
- create copies typed by your store
5. Read the state in a component
import { useAppSelector } from '../store/hooks';
function Counter() {
const count = useAppSelector(state => state.counterSlice.count);
return <div>Current count: {count}</div>
}- a selector should transform data into a shape for the component
5. Dispatch actions
import { useAppDispatch } from '../store/hooks';
import { increment } from "../store/counterSlice";
function IncrementButton() {
const dispatch = useAppDispatch();
return (
<button onClick={() => dispatch(increment())}>
Increment
</button>
);
}When to use Redux state?
- global state
- Is it used by multiple components?
- Do you need the state after a component unmounts?
- Do you want it to work with timetravel?
- Do you want to cache it?
➡️ Move state to Redux
- move Joke state from the local state into Redux
React eco system
How to choose a library?
- measurable metrics
- number of downloads, github stars, github issues, repository activity (opened PRs, merged PRs...)
- stackoverflow questions
- documentation
- migration guide
- how often does it have breaking changes
- Proof of concept
- does it work for us? How easy is to use? How easy is it to learn?
A typical project
- router (react-router)
- state management (redux, MobX, xstate...)
- CSS library, design system framework
- data fetching (axios, React Query)
- form library (Formik,React Hook Form )
- run & build (webpack, vite)
- test (react-testing-library, jest)
- check awesome-react for libraries
Webpack
Webpack
- module bundler
- anything you import
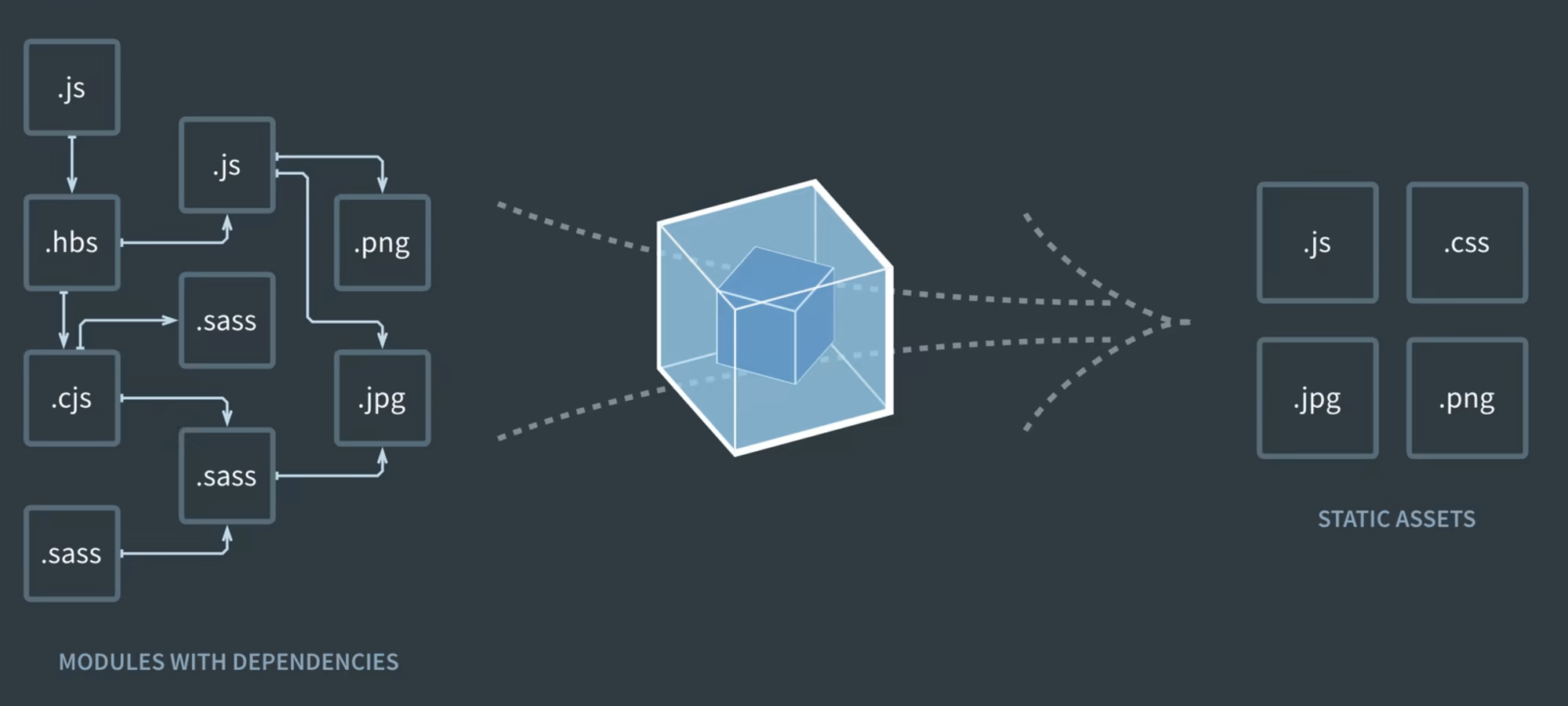
New project
npm init -y
npm i react react-dom
npm i -D typescript \
webpack webpack-cli webpack-dev-server \
ts-loader @types/react @types/react-dom \
html-webpack-plugin
npx tsc --init
// Update tsconfig:
"jsx": "react"
"outDir": "./dist",
webpack.config.js
npx webpack serve // dev server
npx webpack // buildwebpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.tsx',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.tsx?$/,
use: 'ts-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
},
],
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.tsx', '.ts', '.js', '.jsx'],
},
output: {
filename: 'main.bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({template: './public/index.html'}),
],
};
Chunks example
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const webpack = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.tsx',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.tsx?$/,
use: 'ts-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
},
],
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.tsx', '.ts', '.js'],
},
output: {
filename: '[name].bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
},
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.SplitChunksPlugin({minSize: 1}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({template: './public/index.html'}),
]
};
NX
- tooling for monorepo
- apps + libraries
- define tasks for each app/library
- collection of commands
- nx affected - runs task only for changed parts
- plugins for adding storybook, generating e2e tests...
Dependency graph
- npx nx graph
- you can define boundaries of packages
- what can import what
🎉
Tieto React Advanced
By Martin Nuc
Tieto React Advanced
- 265



