Tieto React
🙋♂️
Frontend engineer
- 9 years FE experience
- AngularJS, Angular, Ember, React
- currently Staff engineer at Productboard
❤️ 📸
❤️ 🛞
Slides
Schedule
- 9-12 morning
- recap of the previous day
- a break: 10:15 - 10:30
- lunch?
- 13-17 afternoon
- a break: 14:30 - 14:45
Course
- exercises build on top of each other!
- discussions welcomed
Setup IDE
Install
- Google Chrome
- nodejs
- Visual Studio Code
- Quokka plugin
- VS Code ➡ extensions ➡ search for quokka
Javascript & Typescript
Let's talk about React! 💪
React
- library for managing view
- component based
- helps split the app into small pieces
- used to create SPA
Client
Server
Database
HTTP
browser
request
html page
Client
Server
Database
HTTP
React in browser, mobile app...
API
request
data
Single page application
Web server
html, js
Create React app
CRA
- tool for scaffolding react app
npx create-react-app my-app --template typescriptImportant parts
package.json
- describes the package
- dependecies list
- npm scripts
tsconfig.json
- settings for typescript compiler
- "target" = build for version of JS
/public folder
- contains assets
- index.html
index.tsx
- renders React into HTML element
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(
document.getElementById('root') as HTMLElement
);
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
App.tsx
- the main component
➡️ Start the React app
JSX
Elements
const label = React.createElement('a', {
href: 'https://google.com'
}, 'Go to Google.com');<a href="https://google.com">Go to Google.com</a>children
props
type
What is JSX?
- syntactic sugar around createElement
- almost like HTML
- transpiled to Javascript
- example in App.tsx:
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
Hello
</div>
);
}function App() {
return React.createElement('div', { className: 'App' }, 'Hello');
}Q: Why className?
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
Hello
</div>
);
}function App() {
return React.createElement('div', { className: 'App'}, 'Hello');
}Q: What happens now?
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<div>
Yes
</div>
<div>
No
</div>
);
}function App() {
return ????????
}Solution: React Fragment
- like empty element
- when you want to return multiple elements - wrap them in fragment
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<>
<div>
Yes
</div>
<div>
No
</div>
</>
);
}➡️ Before we continue
- remove everything in the body of App.tsx component
- notice the browser reloads
function App() {
return <h1>Hello</h1>;
}
Print a variable
function App() {
let something = 'hello';
return <div>{something}</div>;
}Print an array
function Array() {
let array = [1,2,3];
return <div>
{array.map((item, index) => <span key={index}>{item}</span>)}
</div>;
}
Components
Component
- reusable unit
- just a function
-
input
- ="props"
-
output
- React element
type Props = {
name: string;
};
function NameComponent(props: Props) {
return <h1>Hi, my name is {props.name}!</h1>;
}
ReactDOM.render(
<NameComponent name="Martin" />,
document.getElementById('root')
);Component tree
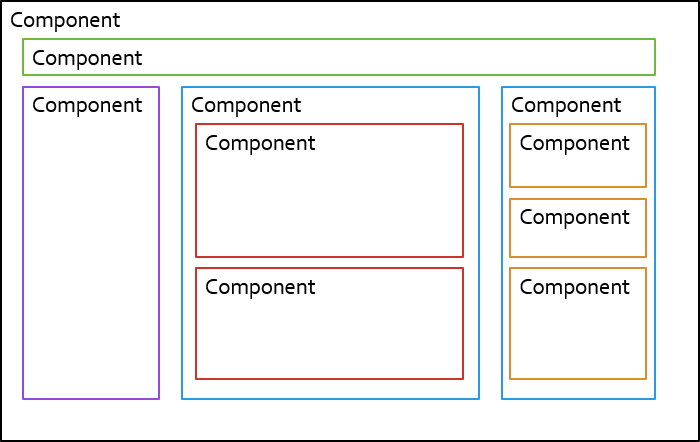
- split big problems to smaller ones
Component tree
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component tree
- Stateful components (smart)
- used to fetch data
- data manipulation
- Stateless components (dumb)
- only display data
- pass data down, emit events up
Component tree
Component
User info
ArticleList
Article
Today Weather
Article
I am smart 💡
Stateless component
- everything to display is received via props
- just a function
- input: props (=properties)
- output: React element
- easy to test
function NameComponent(props) {
return <h1>{props.name}</h1>;
}How to use a component?
- pass data down via props
function App() {
return <NameComponent name="Martin" />
}➡️ Dynamic table
- create a component which displays a table using JSX
- receives number of columns and rows as parameter
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
<Table columns={4} rows={3} />Children props
Children props
- you might pass HTML as body of element:
<Table columns={5} rows={2}>
<h1>Hello</h1>
</Table>- Table component receives react element via children prop:
function Table(props) {
return (
<table>
<tr>
<td>
{props.children}
</td>
</tr>
</table>
)
}Event handling
- React unifies API of events (link)
<button type="button" onClick={() => console.log('Hello')}>
Hello world
</button>State
useState
- hook for storing data
- instead of declaring variable
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [name, setName] = useState('nobody');
function handleGiveName(name: string) {
setName(name);
}
return <div>
My name is {name}.
<button onClick={() => handleGiveName('Martin')}>
Give me name
</button>
</div>
}initial value
➡️ Create counter
- create button with counter as text
- start from 0
- everytime you click the button the counter is increased
Class components
- rarely used nowadays
- uses a class instead of a function
- this.props
- this.setState() to change state
- life cycle hooks
- componentDidMount
- componentWillUnmount
Counter example
import React from 'react';
type State = {
counter: number;
}
export class MyComponent extends React.Component<{}, State> {
state = {
counter: 0
};
increment() {
this.setState({ counter: this.state.counter + 1 });
}
render() {
const { counter } = this.state;
return <div>
Counter: {counter}
<button type="button" onClick={() => this.increment()}>Increment</button>
</div>
}
}➡️ Rewrite class component as a functional component
type Props = {
pregeneratedCount: number
}
type State = {
generatedNumbers: number[];
}
export class NumberGeneratorClass extends React.Component<Props, State> {
constructor(props: Props) {
super(props);
for (let i = 0; i < props.pregeneratedCount; i++) {
this.state = {
generatedNumbers: [...this.state?.generatedNumbers || [], Math.random()]
};
}
}
generateNew() {
this.setState({ generatedNumbers: [...this.state.generatedNumbers, Math.random()] });
}
render() {
const { generatedNumbers } = this.state;
return <div>
{generatedNumbers.map((num, index) => <div key={index}>{num}</div>)}
<button type="button" onClick={() => this.generateNew()}>Generate new</button>
</div>
}
}Important things to notice
- setter needs a new reference
- the initial set is generated on every render
Conditions
- use if statement
- use ternary operator
function MyComponent() {
const random = Math.random();
if (random < 0.5) {
return <span>lower</span>
} else {
return <span>higher</span>
}
}function MyComponent() {
const random = Math.random();
return <span>
{random < 0.5 ? 'lower' : 'higher'}
</span>
}function MyComponent() {
const condition = true;
return <>{condition && <span>It's true</span></>
}Styling app
Import CSS
- global CSS
- can use preprocessors (SCSS, SASS)
import './App.css';
function Component() {
return <div className="red">Hello</div>
}.red {
color: red;
}App.css
App.tsx
CSS modules
- scoped CSS
- can use preprocessors (SCSS, SASS)
- css file must be named .module
import styles from './App.module.css';
function Component() {
return <div className={styles.red}>Hello</div>
}.red {
color: red;
}App.module.css
App.tsx
Conditional styling without CSS modules
- classnames library
- npm i classnames @types/classnames
- key = class to be applied
- value = condition
import cn from 'classnames';
function ValidationState() {
const [invalid, setInvalid] = useState(false);
return <div className={cn({ red: invalid })}>
Status
</div>
}Conditional styling with CSS modules
- dynamic keys
import cn from 'classnames';
import styles from './App.module.css';
function ValidationState() {
const [invalid, setInvalid] = useState(false);
return <div className={cn({ [styles.invalid]: invalid })}>
Status
</div>
}useEffect
- hook for side effects
- second argument say when it runs
- empty - on every render
- [ ] - only at the begining (=on mount)
- [ variable ] - when a variable changes
- should return cleanup function
useEffect example
- tracks mouse position
export const MyMouse = () => {
const [mousePosition, setMousePosition] = useState({x: 0, y: 0});
useEffect(() => {
const onMouseMove = event => {
setMousePosition({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
});
};
window.addEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
};
}, []);
const {x, y} = mousePosition;
return (
<div>My mouse x position is {x} and y position is {y}</div>
);
};
Try useEffect
- show text with mouse position
- show text with last mouse click coordinates
- when the mouse position is
- on the left to the last click - change text to green color
- on the right to the last click - change text to red color
Create automatic counter
- create component which increases counter every second
- in parent component create button which shows/hides this component
Creating own event
- component emits event up
type Props = {
onTrigger: () => void;
};
function ChildComponent(props: Props) {
return <button onClick={props.onTrigger}>emit event</button>;
}<ChildComponent onTrigger={() => console.log('triggered')} />parent component:
child component:
➡️ Create a dropdown
- What is dropdown?
- button which opens a menu when clicked
- 3 components
- smart + button + dropdown
www.google.com
www.instagram.com
www.facebook.com
Toggle button
emit click
DropdownComponent
shows
Controlled input
- use component state as the only source of truth
function Component() {
const [name, setName] = useState('nobody');
const [inputName, setInputName] = useState(name);
function handleGiveName() {
setName(inputName);
}
return <>
My name is {name}.
<input
value={inputName}
onChange={(e) => setInputName(e.target.value)} />
<button onClick={() => handleGiveName()}>Save</button>
</>
}Create input
- input of type number
- how much the counter will increment
API request
Axios library
- used to make HTTP requests
- supports promises
- docs: https://axios-http.com/docs/example
- install: npm install axios
Axios POST usage
import axios from 'axios';
const payload = { name: 'Martin' };
const response = await axios.post('/api/users', payload);
console.log(response);
➡️ Let's make http request
- open API request in browser to see structure of response
- display joke in the component
- create a button to load another joke
GET https://api.chucknorris.io/jokes/randomComponent tree
Component
User info
JokeFetcher
Joke
I am smart 💡
data down
Custom hooks
Custom hooks
- separate logic from view
- no render
- named use*
- hooks to component lifecycle
- clear API
useMouseMove
const useMouseMove = () => {
const [mousePosition, setMousePosition] = useState({ x: 0, y: 0 });
useEffect(() => {
const onMouseMove = (event: MouseEvent) => {
setMousePosition({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY,
});
};
window.addEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
};
}, []);
return { x: mousePosition.x, y: mousePosition.y };
};- mouse position example
- no input
- outputs x, y of mouse
Fetch joke hook
- encapsulate fetching joke logic into a custom hook
- think about API first
Debugging
Main tools
- console.log
- React dev tools
- Chrome debugger
debugger;Chrome dev tools
- Network
- Source
- Performance
- Application
- React dev tools
- Components
- Profiler
Logging
- Sentry.io
- TrackJS
React Context
Context
- "global" state for subtree of components
- avoids passing props deep
- Provider + Consumer
type ContextValue = boolean;
const MyContext = React.createContext<ContextValue>(false);
function App() {
return <MyContext.Provider value={true}>
<Component />
</MyContext.Provider>;
}
function Component() {
const value = useContext(MyContext);
return <div>{value}</div>;
}Encapsulate context
- Provider component
type ContextValue = {
value: boolean;
changeValue: (newValue: boolean) => void;
}
// avoid the need to specify initial value
const MyContext = React.createContext<ContextValue>({} as unknown as ContextValue);
type Props = {
initialState: boolean;
children: React.ReactNode
}
export function MyContextProvider({initialState, children}: Props) {
const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
const contextValue = {
value: state,
changeValue: (newValue: boolean) => setState(newValue)
};
return <MyContext.Provider value={contextValue}>
{children}
</MyContext.Provider>;
}
// used to read value from comopnent
export const useMyContext = () => useContext(MyContext);
const { value, changeValue } = useMyContext();➡️ Dark & Light theme 🌗
- style your components to support dark & light theme
- background + text color
- create a button to switch the theme
Redux
Redux
- state management library
- one global store
- big object
- actions to modify the state
- browser extension: Redux Devtools
- npm install @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux
Store
Actions
Reducers
State example
{
jokeSlice: {
currentJoke: "Chuck Norris can speak Braille.",
isLoading: false
},
counterSlice: {
count: 5
},
uiSlice: {
dropdownVisible: false
}
}View
Reducer
Store
dispatch an action
update the store
view reads data from the store
increment = (state) => {
state.count += 1;
}1. Create slices
// /src/store/counterSlice.ts
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import type { PayloadAction } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
export type CounterState = {
count: number;
};
const initialState: CounterState = {
count: 0,
};
export const counterSlice = createSlice({
name: 'counter',
initialState,
reducers: {
increment: (state, action) => {
state.count += 1;
}
},
});
export const { increment } = counterSlice.actions;
export const counterReducer = counterSlice.reducer;
2. Create a store
// src/store/store.ts
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import { jokeReducer } from './jokeSlice';
import { counterReducer } from './counterSlice';
import { uiReducer } from './uiSlice';
export const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
jokeSlice: jokeReducer,
counterSlice: counterReducer,
uiSlice: uiReducer
},
});
export type RootState = ReturnType<typeof store.getState>;
export type AppDispatch = typeof store.dispatch;
3. Provide the store
// index.tsx
import { store } from './store/store'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>
);
4. Created typed hooks
// src/store/hooks.ts
import { TypedUseSelectorHook, useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
import type { RootState, AppDispatch } from './store';
export const useAppDispatch: () => AppDispatch = useDispatch;
export const useAppSelector: TypedUseSelectorHook<RootState> = useSelector;
- avoid using useDispatch & useSelector
- create copies typed by your store
5. Read the state in a component
import { useAppSelector } from '../store/hooks';
function Counter() {
const count = useAppSelector(state => state.counterSlice.count);
return <div>Current count: {count}</div>
}- a selector should transform data into a shape for the component
5. Dispatch actions
import { useAppDispatch } from '../store/hooks';
import { increment } from "../store/counterSlice";
function IncrementButton() {
const dispatch = useAppDispatch();
return (
<button onClick={() => dispatch(increment())}>
Increment
</button>
);
}When to use Redux state?
- global state
- Is it used by multiple components?
- Do you need the state after a component unmounts?
- Do you want it to work with timetravel?
- Do you want to cache it?
➡️ Move state to Redux
- move ButtonCounter state from the local state into Redux
Asynchronnous in Redux
- Where?
- reducers are pure
- must be separated from redux
- usually, we place it in actions
1. Define reducers
const jokeSlice = createSlice({
name: 'joke',
initialState,
reducers: {
jokeFetchingStarted: (state) => {
state.isLoading = true;
},
jokeLoaded: (state, action: PayloadAction<string>) => {
state.joke = action.payload;
state.isLoading = false;
},
},
});
export const { jokeLoaded, jokeFetchingStarted } = jokeSlice.actions;
export const jokeReducer = jokeSlice.reducer;2. Action creator
// src/actions/fetch-joke.ts
import axios from 'axios';
import { jokeFetchingStarted, jokeLoaded } from '../store/jokeSlice';
import { AppDispatch } from '../store/store';
type ResponseType = {
value: string;
};
export const fetchJoke = () => async (dispatch: AppDispatch) => {
dispatch(jokeFetchingStarted());
const response = await axios.get<ResponseType>(
'https://api.chucknorris.io/jokes/random'
);
dispatch(jokeLoaded(response.data.value));
};
3. Dispatch from a component
import { fetchJoke } from '../actions/fetch-joke';
import { useAppDispatch } from '../store/hooks';
export const NextJokeButton = () => {
const dispatch = useAppDispatch();
return (
<button type="button" onClick={() => dispatch(fetchJoke())}>
Fetch next joke
</button>
);
}➡️ Move state to Redux
- move Chuck Norris Joke state from the local state into Redux
Render props
Render props
- pass function as children
- composition pattern
function Counter({children}) {
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
function increment() {
setCounter(counter + 1);
}
return <>{children({counter, increment})}</>
}
function MyComponent() {
return <div>
<Counter>
{({counter, increment}) => <>
<div>Counter value: {counter}</div>
<button onClick={increment}>INC</button>
</>}
</Counter>
</div>
}
useRef
useRef
- manipulate with DOM elements
- object with mutable current property
function Component() {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
function handleClick() {
inputRef.current.focus();
}
return <div>
<input ref={inputRef} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>Focus the input</button>
</div>
}Routing
React router
- used to create multiple pages
- install react-router-dom + type definitions
- docs
Define pages and links
import { BrowserRouter, Routes, Route, Link } from "react-router-dom";
function App() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
<Link to="/categories">About</Link>
<Link to="/categories/animals">Joke about animals</Link>
<Link to="/categories/history">Joke about history</Link>
<Routes>
<Route index path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path="/categories" element={<JokeCategories />} />
<Route path="/categories/:category" element={<Joke />} />
</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}- everything must be inside of <BrowserRouter>
Navigate
const navigate = useNavigate();
navigate('/categories');- either using <Link>
- or using useNavigate() hook
Reading url parameters
import { useParams } from "react-router-dom";
function Joke() {
const params = useParams();
return (
{params.category}
);
}Try routing
- Create routes
- / -> categories list
- /categories/:category -> joke from category
- load joke based on category
Performance optimizations
Problem
- lot of rerenders
- every render creates new function, object etc
- DOM operations are expensive
React.memo
- rerenders component only on prop change
const JokeMemoized = React.memo(function Joke() {
...
});
<JokeMemoized />useMemo
- precompute value
- for computation-expensive values
- avoids main thread lock
const useFibonacci = (n) => {
const result = useMemo(() => fibonacci(n), [n]);
return result;
}
function fibonacci(n) {
return n < 1 ? 0
: n <= 2 ? 1
: fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2)
}useCallback
- used to retain a single function reference
- avoids problem with recreating handler every render
type Props = {
me: string;
}
function Component({me}: Props) {
const handleClick = useCallback(
(name) => console.log(`Hello ${name} and ${me}`)
, [me]);
return <ExpensiveComponent onClick={handleClick} />;
}➡️ Optimize Joke
- it should not rerendered on theme change (=on context change)
- useCallback for handlers to prevent child components rerenders
Formik
Formik
const schema = yup.object().shape({
email: yup.string().required().email(),
age: yup.number().required().positive().integer()
})
const initialValues = {
email: '',
age: 0
}
export function MyForm() {
return (
<Formik
initialValues={initialValues}
validationSchema={schema}
onSubmit={values => console.log(values)}
>
{({ handleSubmit }) => (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<Field type="email" name="email" />
<ErrorMessage name="email" component="div" />
<Field type="number" className="error" name="age" />
<ErrorMessage name="age" className="error" component="div"/>
<button type="submit">
Submit
</button>
</form>
)}
</Formik>
);
}➡️ Create a form
- create registration form using formik
- include validations
- fields
- password (at least 8 chars)
🎉
Tieto React
By Martin Nuc
Tieto React
- 267


