Data types And Variables
Data types in java
- Primitive type
- Class type
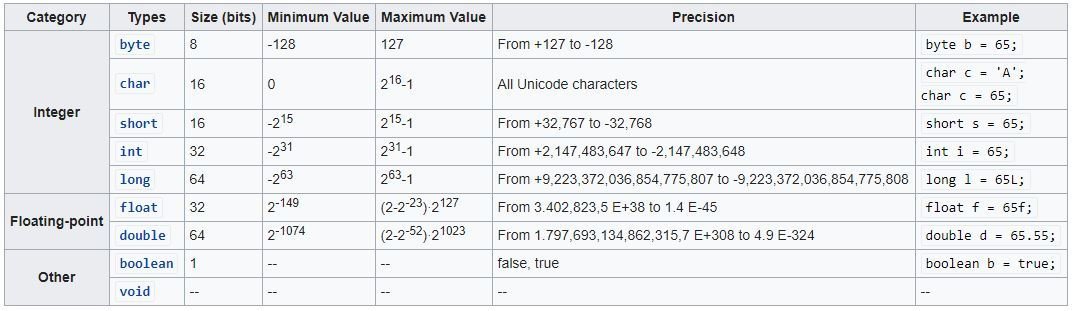
Primitive Data Types in Java
- Integer
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- char
- Floating-point
- float
- double
- Boolean
Class Data Types in Java
- String
- Array
- Scanner
- Applet
- etc
Variables in java
- Variabel adalah item yang digunakan data untuk menyimpan pernyataan objek
- Variabel memiliki tipe data, nama dan nilai
- Nama variable tidak dapat diubah, namun nilai dari suatu variable dapat berubah kecuali variabel bertipe final
// <tipe_data> <nama_variable> = <nilai>;
int exampleInt; // deklarasi variabel exampleInt
exampleInt = 10; // inisialisai variabel exampleInt
int anotherInt = 5; // deklarasi dan inisialisasi
anotherInt = anotherInt + exampleInt;
final int NUMBER = 7;
NUMBER = 10; // error: cannot assign a value to final variable NUMBERpublic class DataTypes {
public static void main (String[] args) {
byte myByte = 96;
byte highByte = Byte.MAX_VALUE; // highByte == 127
byte lowByte = Byte.MIN_VALUE; // lowByte == -128
short myShort = 987;
short highShort = Short.MAX_VALUE; // highShort == 32767
short lowShort = Short.MIN_VALUE; // lowShort == -32768
int myInt = 284;
int highInt = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // highInt == 2147483647
int lowInt = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // lowInt == -2147483648
long mylong = 549755813888L;
long highLong = Long.MAX_VALUE; // highLong == 9223372036854775807L
long lowLong = Long.MIN_VALUE; // lowLong == -9223372036854775808
char myChar = 'u';
char myChar2 = 65; // myChar2 == 'A'
char newline = '\n';
float myFloat = 92.7f; // with 'f' after digits = float
float positiveFloat = 89.3f; // it can be positive,
float negativeFloat = -89.3f; // or negative
double myDouble = 974.21; // without 'f' after digits = double
double anotherDouble = 658.7;
boolean foo = true;
boolean bar = false;
boolean notFoo = !foo; // notFoo == false
boolean fooAndBar = foo && bar; // fooAndBar == false
boolean fooOrBar = foo || bar; // fooOrBar == true
}
}Casting Data types
Casting adalah perubahan tipe data ke tipe data lainnya.
Di java terdapat 2 jenis casting, yaitu:
- Implicit casting
- Explicit casting
Implicit casting
implicit casting dapat mengkonversikan tipe data secara otomatis jika kedua tipe data memiliki kesamaan dan target tipe data yang diubah lebih besar dari tipe data sebelumnya
//Implicit casting
byte byteVar = 42;
short shortVar = byteVar;
int intVar = shortVar;
long longVar = intvar;
float floatVar = longVar;
double doubleVar = floatVar;
short shortVar2 = 45;
byte byteVar2 = shortVar2; // error: incompatible types: possible lossy conversion
// from short to bytebyte
short
int
long
float
double
Explicit casting
explicit casting dilakukan ketika target tipe data yang ingin diubah lebih kecil dari tipe data sebelumnya
//Explicit casting
double doubleVar = 42.0d;
float floatVar = (float) doubleVar;
long longVar = (long) floatVar;
int intVar = (int) longVar;
short shortVar = (short) intVar;
byte byteVar = (byte) shortVar;
byte byteVar2 = 42;
short shortVar2 = short (byteVar2);double
float
long
int
short
byte
Operators
Assignment Operator
public class AssignmentDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int cadence = 0;
int speed = 0;
int gear = 1;
}
}Arithmetic Operators
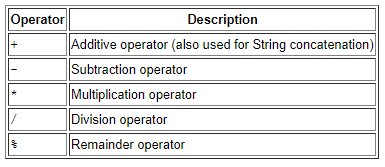
public class ArithmeticDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int result = 1 + 2;
System.out.println("1 + 2 = " + result);
int original_result = result;
result = result - 1;
System.out.println(original_result + " - 1 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result * 2;
System.out.println(original_result + " * 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result + 8;
System.out.println(original_result + " + 8 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result / 2;
System.out.println(original_result + " / 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result % 7;
System.out.println(original_result + " % 7 = " + result);
}
}
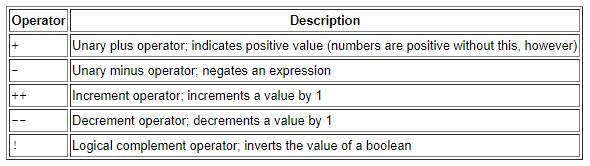
Unary Operators
class UnaryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = +1;
System.out.println(result);
result--;
System.out.println(result);
result++;
System.out.println(result);
result = -result;
System.out.println(result);
boolean success = false;
System.out.println(success);
System.out.println(!success);
}
}
Relational Operators
== equal to != not equal to > greater than >= greater than or equal to < less than <= less than or equal to
Conditional Operators
&& Conditional-AND
|| Conditional-OR
?: Ternary (shorthand for
if-then-else statement)
Exercise (1)
Hitunglah luas segita jika diketahui alas = 5 dan tinggi = 7
L = alas * tinggi / 2
Exercise (2)
Create a variable called bill and assign it the result of 10.25 + 3.99 + 7.15 (don't perform the calculation yourself, let Java do it!). Next, create a variable called tip and assign it the result of multiplying bill by a 15% tip rate. Finally, add the bill and tip together and store it into a variable called total
Exercise (3)
Use this equation and the variables fahrenheit and celcius to print the Fahrenheit equivalent of 12°C
F = C * 1.8 + 32
Exercise (4)
public class Exercise4 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int i = 10;
int n = i++ % 5;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
System.out.println("n = " + n);
}
}Solution
Exercise (1)
public class Exercise1 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int alas = 5;
int tinggi = 7;
float luas = (float) alas * tinggi / 2;
System.out.println("Luas segitiga adalah" + luas);
}
}Exercise (2)
public class Exercise2 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
float bill = 10.25 + 3.99 + 7.15;
float tip = bill * 15 / 100;
float total = bill + tip;
System.out.println("Total harga" + total);
}
}Exercise (3)
public class Exercise3 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
float celcius = 12;
float fahrenheit = celcius * 1.8 + 32;
System.out.println(celcius + " celcius = " + fahrenheit + " fahrenheit");
}
}Exercise (4)
public class Exercise4 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int i = 10;
int n = i++ % 5;
System.out.println("i = " + i); //i = 11
System.out.println("n = " + n); //n = 0
}
}Datatypes
By Nur Ratna Sari
Datatypes
- 146



