discussion week 6
Define:
- Performative Speech Act (+1example)
- Non-performative Speech Act (+1 example)
- What are the main utterance functions?
- What are the main utterance forms?
Let's review direct Speech Act
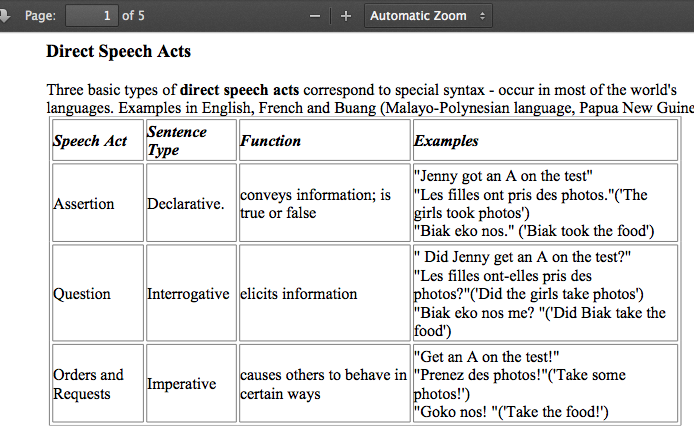
Combination of form and function
Give one example and identify which Speech Act (direct or indirect):
- declarative+requesting info.
- imperative+trying to get someone to do something
- imperative+providing info.
- interrogative+trying to get someone to do something
Principles of conversation
1. Quality
2.Relevance
3. Quantity
4. Manner
Examples

Relevance
The person reading this letter assumes that all the relevant information will be included; so the principle of quantity and relevance lead one to suspect that this is the best that the professor can say!
Example
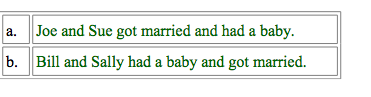
Manner
The "be orderly" aspect of the principle
of manner is what causes us to interpret the following sentences differently,
even though,in a literal sense, they convey the same information
Monty Python
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-8bqQ-C1PSEhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KbtVaTWs6II
Violations
Choose 2 violations of principles and prepare a dialogue.
Let the others guess which principles were violated.
Definition
- Performative speech-acts are cases in which the very act of speaking, if performed by an authorized person under the proper conditions, makes a change in the social world (as in the christening of a ship) — and often also changes the physical world (as when a judge performs an act of sentencing that impacts someone’s freedom or even life).
- Non-performative speech-acts do not, by themselves, change the social or the physical world; thus, all speech acts that are not clearly performative can be classified as non-performative: e.g., if someone says Leave this building immediately! but the addressee stays put, the utterance in question has had no (appreciable) effect on its own
Definition
Forms: declarative, imperative, interrogative, nominal
Functions:
- Providing information, as in telling someone what one’s name is.
- Requesting information, as in asking what time it is.
- Trying to get someone to do something, as in trying to get someone to stop talking.
discussion week 6
By obscrivn
discussion week 6
- 686