by Oscar Ivarsson
MongoDB
Show-Off

What is it?
Type: Document Database
Designed as a scalable database (humongous)
Open Source
Released: 2009

Notation
Database
Collection
RDBMS
Schema
Instance
MongoDB
Instance
Table
Document
Row
Example
> printjson(db.towns.findOne({"_id":ObjectId("4d0b6da3bb30773266f39fea")}))
{
"_id":ObjectId("4d0b6da3bb30773266f39fea"),
"country": {
"$ref": "countries",
"$id": ObjectId("4d0e6074deb899526a8309e")
},
"famous_for": [
"beer",
"food"
],
"last_census": "Thu Sep 20 2007 00:00:00 GMT -0700 (PDT)",
"mayor": {
"name": "Sam Adams",
"party": "D"
},
"name": "Portland",
"population": 582000,
"state": "OR"
}Stored as BSON - Shown as JSON
Database: "db"
Collection: "towns"
Document: Between the brackets
Identifier: "_id"
0-3: Timestamp 4-6: Client Machine ID 7-8: Client Process ID 9-11: Incremented Counter
Notations
ObjectId (12 bytes)
Examples
> db.test.insert({color: "Red"})
> db.test.insert({shape: "Triangle"})Insert
> db.test.find()
{
"_id" : ObjectId("55ee924b34ec1a858b481962"),
"color" : "Red"
}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("55ee927f34ec1a858b481963"),
"shape" : "Triangle"
}Find
Examples
> db.test.find({ "_id" : ObjectId("55ee927f34ec1a858b481963") })
{
"_id" : ObjectId("55ee927f34ec1a858b481963"),
"shape" : "Triangle"
}Find by ID
> db.test.find( { "shape": "Triangle"} )
{
"_id" : ObjectId("55ee927f34ec1a858b481963"),
"shape" : "Triangle"
}Find by field (slower..)
> db.test.find( function() {
return this.shape == "Triangle";
})
{
"_id" : ObjectId("55ee927f34ec1a858b481963"),
"shape" : "Triangle"
}Find by function (slowest!)
Query Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| $regex | Match by regular expression |
| $lt | Less than |
| $in | Match any elements in an array |
| $exists | Check for existence of a field |
Examples for find
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| $set | Sets the given field with a given value |
| $push | Adds the value to an array |
| $pull | Removes matching value from array |
Examples for update
References
Mongo is not built for performing joins because of its distributed nature!
Documents can however reference eachother.
> db.towns.update(
{ _id : ObjectId("4d0ada87bb30773266f39fe5") },
{ $set : { country: { $ref: "countries", $id: "us" } } }
)
THEN
> var portland = db.towns.findOne({ _id : ObjectId("4d0ada87bb30773266f39fe5") })
> db.countries.findOne({ _id: portland.country.$id })
OR
>
db[ portland.country.$ref ].findOne({ _id: portland.country.$id })Performance
Query performance can be increased in MongoDB by using indexing.
Full collection scan
B-tree indexing
Scanned objects: 1 000 000
Scanned objects: 1
Execution Time 1st: 470 ms
Execution Time 2nd: 365 ms
Execution Time 1st: 5 ms
Execution Time 2nd: 0 ms
> populatePhones(800, 809, 5550000, 5650000)
> db.phones.find().limit(1)
{
"_id" : 18005550000,
"components" : {
"country" : 1,
"area" : 800,
"prefix" : 555,
"number" : 5550000 },
"display" : "+1 800-5550000"
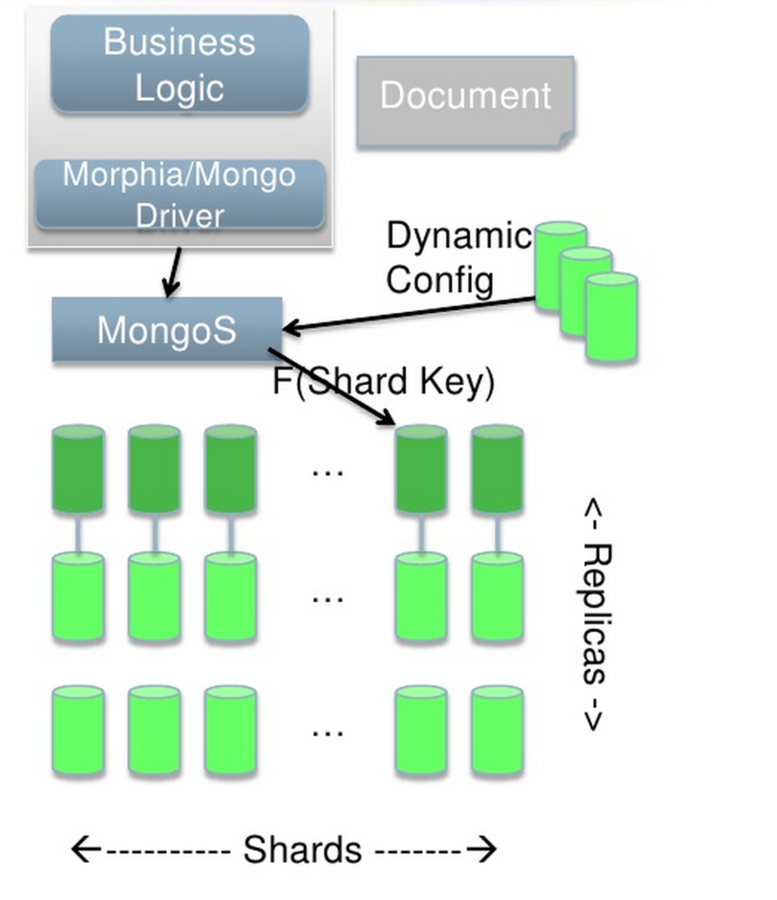
}Scaling Out!
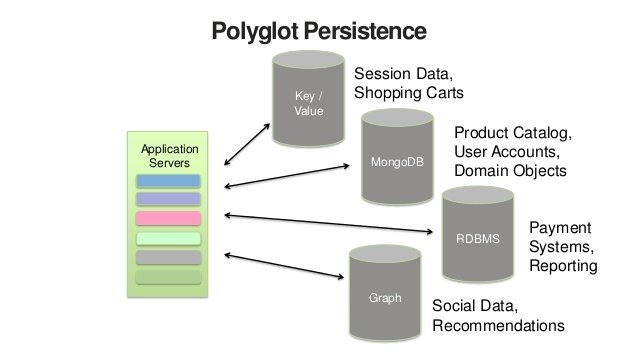
What makes document databases unique?
Their ability to efficiently handle arbitrary nested, schemaless data documents.
What makes MongoDB special?
The ability to scale across several servers by replicating or sharding collections.
MongoDB was built to scale out.
When to use it?
Strengths
Weaknesses
Replication and horizontal scaling
Flexible data model
The price for flexibility -> Error feedback
Development costs and speed
No joins of collections
Availability
Use Cases
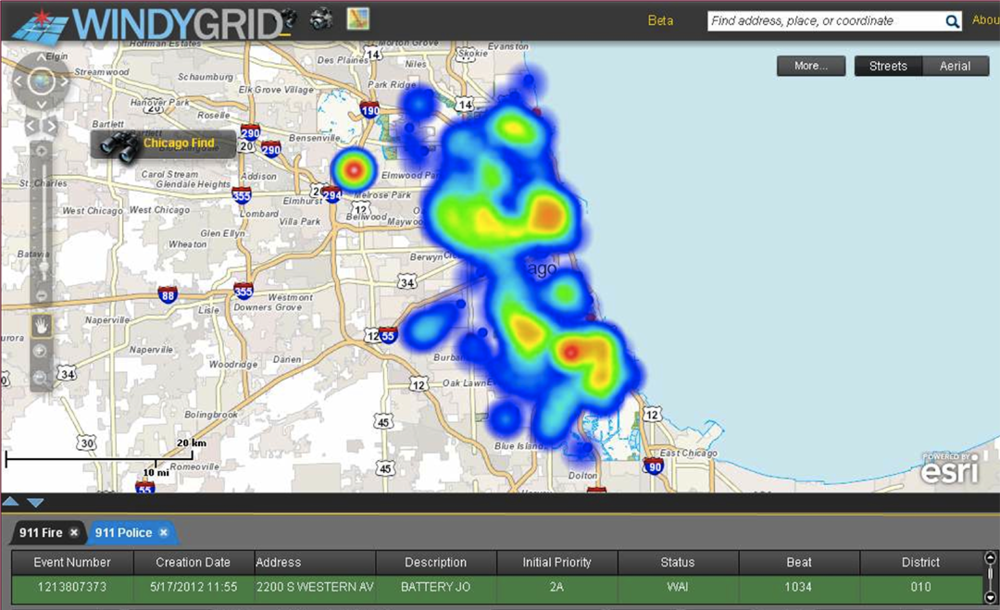
Real-Time Analytics
City of Chicago


McAfee

Crittercism
Use Cases
Product Data Management
Otto
Under Armour
Carfax



Use Cases
CMS
Forbes
Ebay
Pearson



MongoDB Show-off
By Oscar Ivarsson
MongoDB Show-off
- 257