Service Worker

Properties
- Separate isolated worker script
- Run in a separate thread
- Lifecycle is independent from web pages
- It can intercept requests and create responses
- Has a flexible storage API for caching requests
- No DOM access
- Communicates through postMessage
- Needs HTTPS (except for localhost)
- Uses Promises extensively

Why not AppCache?
- Simple to create but hard to debug
- Limiting API
- http://alistapart.com/article/application-cache-is-a-douchebag

Example Use CAses
- Offline support
- Background sync*
- Push notifications*
- Scheduled events*
- Manipulate responses
- Stub servers for testing
* Not available yet

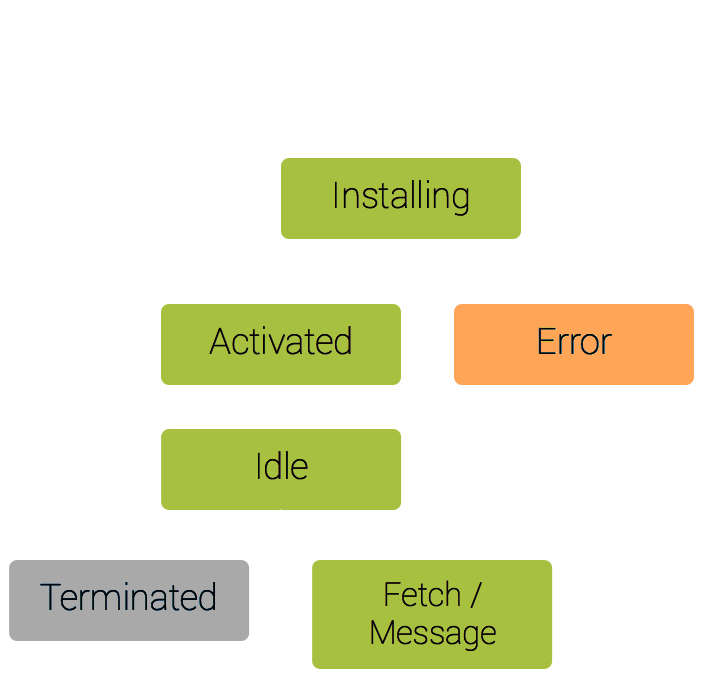
Lifecycle
- Download
- Install
- Activate
- Terminate



if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/service-worker.js', {
scope: '/api/'
}).then(function (sw) {
// registration worked
}).catch(function () {
// registration failed
});
}Register worker for /api/.* URLS
Idempotency
register() is idempotent - it can be called multiple times without spawning multiple identical workers.

Register fails when...
- URLs have different origin
- Service Worker script fails to download or parse
- Origin is not served with HTTPS
- Service Worker script is not at the root of the scope, or higher

Register might fail Silently

Worker vs Document Lifetime
- The lifetime of a Service Worker is not coupled to the registering document
- register() and unregister() only affects subsequent requests
- A document loaded without a Service Worker will not get one during its lifetime

INstall
- Runs after registration (even if prior registration failed)
- Typically caches static assets directly


var urlsToCache = [
'/',
'/assets/bundle.css',
'/assets/bundle.js'
];
self.addEventListener('install', function (event) {
event.waitUntil(
caches.open('the-cool-app-1.0.0')
.then(function (cache) {
return cache.addAll(urlsToCache);
})
);
});Install - UpFront caching
Activate
- Runs after install
- Typically deletes old caches (you want to do this)


self.addEventListener('activate', function(event) {
var usedCaches = ['static-1.3.0', 'api-1.0.0'];
event.waitUntil(
caches.keys().then(function (cacheNames) {
return Promise.all(
cacheNames.map(function (cacheName) {
if (usedCaches.indexOf(cacheName) === -1) {
return caches.delete(cacheName);
}
})
);
})
);
});Activate - Delete old caches
Let's cache stuff

self.addEventListener('fetch', function(event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request)
.then(function(response) {
// Cache hit
if (response) {
return response;
}
return fetch(event.request);
}
)
);
});Return cached response
Cloning
Both Request and Response objects are streams and can only be consumed once.
Use clone() to consume them more than once!


self.addEventListener('fetch', function(event) {
var response = caches.match(event.request).then(function(cached) {
// Check cache hit
if (cached) {
return cached;
}
// Clone request, will be consumed by cache.put(...).
return fetch(event.request.clone()).then(function (fetched) {
// (Check for HTTP status code omitted for brevity)
caches.open('my-cache-1.0.0').then(function (cache) {
// Clone fetched response, will be consumed by browser.
cache.put(event.request, fetched.clone());
});
return fetched;
});
});
event.respondWith(response);
});Cloning
Do not go global!
- Service Workers might be terminated at any time
- You can't rely on global state
- Use IndexedDB if shared state is needed

Some gotchas
- Cache API is not complete, needs a polyfill
- Chrome tends to crash when debugging the Service Worker (at the time of writing)
- Don't forget to change your cache names and delete old ones

Debugging

Useful Links

LAB

Slides
Service Worker
By oskarwickstrom
Service Worker
- 972


